Dependency Injection(DI) Design Pattern
Last Updated :
04 Apr, 2025
Effective dependency management is essential to building scalable and maintainable systems. The Dependency Injection (DI) design pattern is one strategy that has become very popular. Fundamentally, dependency injection is a method that addresses how components or objects are constructed and how they acquire the dependencies required for proper operation.
 Dependency Injection(DI) Design Pattern
Dependency Injection(DI) Design PatternWhat is the Dependency Injection Design Pattern?
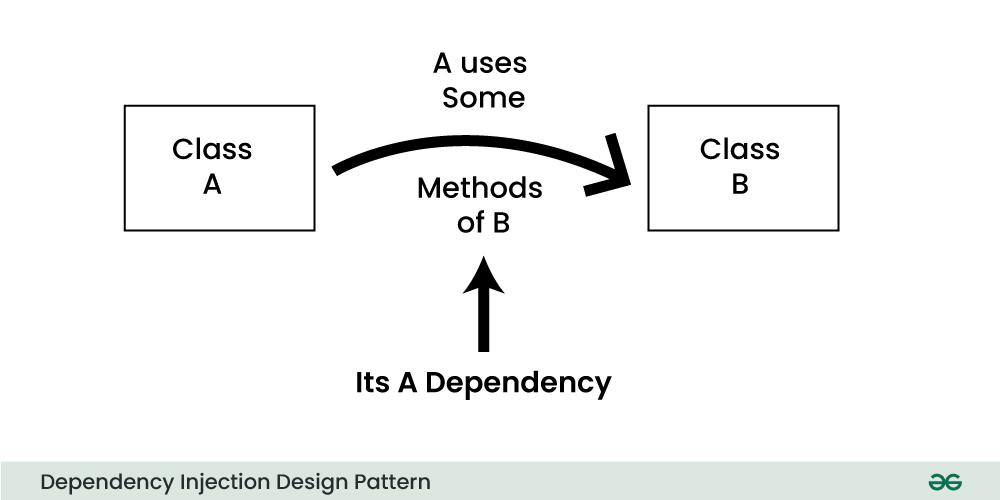
In object-oriented programming, the Dependency Injection (DI) design pattern is a technique that reduces the connection between system components, making the code more modular, testable, and maintainable. Classes frequently rely on other classes to carry out their tasks in a typical software program.
For Example:Car class might depend on a Engine class to run. Without DI, the Car class would directly create or manage the Engine instance within its code, which makes the two classes tightly coupled. This approach can create problems, particularly when you need to test, extend, or modify the classes in the future.
- Dependency Injection solves this problem by injecting the dependencies (like the
Engine ones in the Car example) into the class from an external source, rather than having the class create them. - In simpler terms, DI allows you to "inject" the things a class needs (its dependencies) from the outside, instead of letting the class create or manage them itself.
Four Roles of Dependency Injection
In Dependency Injection, the dependencies of a class are injected from the outside, rather than the class creating or managing its dependencies internally. This pattern has four main roles:
 Four Roles of Dependency Injection
Four Roles of Dependency Injection- Client:
- The client is the component or class that depends on the services provided by another class or module.
- The Client does not provide dependencies, it only receives them from the Injector. (The Injector is responsible for providing dependencies, not the Client).
- Service:
- The service is the component or class that provides a particular functionality or service that the client depends on.
- It focuses on offering particular functionality and is made to be independent of the clients.
- Injector:
- Instances of services must be created and injected into the client by the injector.
- It is aware of the dependencies of the client and provides the necessary services during runtime.
- Interface:
- The interface defines the contract or set of methods that a service must implement.
- Clients rely on these interfaces rather than specific implementations, promoting flexibility and the ability to swap implementations.
When to use Dependency Injection Design Pattern?
Below are the key scenarios where dependency injection is a valuable approach:
- Loose Coupling and Reusability:Objects don't create their own dependencies, breaking tight connections and making them more independent.
- Testability: Inject mock or test doubles for dependencies, allowing you to test individual objects in isolation without relying on external systems or services.
- Maintainability and Flexibility: Dependency injection frameworks often manage dependencies, making it easier to track and configure them.
- Scalability and Extensibility: In large-scale applications, DI helps manage complex dependency graphs and enables easier scaling and extension.
- Cross-Cutting Concerns: Inject services for logging, security, caching, or other cross-cutting concerns that are used across multiple components, avoiding code duplication and promoting a consistent approach.
When not to use Dependency Injection Design Pattern?
Dependency Injection (DI) should be avoided in the following situations:
- Simple Applications: For small or straightforward projects, using DI can add unnecessary complexity.
- Performance Concerns: DI frameworks can introduce overhead, which may impact performance, especially in real-time or high-performance applications.
- Few Dependencies: If a class has only a few simple dependencies, manually injecting them might be easier than using DI.
- Legacy Systems: Refactoring a tightly coupled legacy system to use DI can be time-consuming and risky.
- Lack of Flexibility Needed: If dependencies won’t change frequently, DI may be overkill.
Example for Dependency Injection Design Pattern
Below is the problem statement to understand dependency injection design pattern:
Imagine you're building an application that sends notifications to users. You want to make the notification system flexible so you can change the notification provider (email, SMS, push notifications, etc.) without modifying the core application logic.
1. Code Without Dependency Injection:
Java
public class NotificationService {
private EmailProvider emailProvider = new EmailProvider(); // Tightly coupled to email
public void sendNotification(String message, String recipient) {
emailProvider.sendEmail(message, recipient);
}
}
Issues:
- Tight Coupling: The
NotificationService is tightly coupled to the EmailProvider, making it difficult to switch to a different provider without code changes. - Testability: Testing
NotificationService in isolation is challenging as it directly uses EmailProvider.
2. Code With Dependency Injection:
Java
// Interface for different notification providers
public interface NotificationProvider {
void sendNotification(String message, String recipient);
}
// Concrete implementations
public class EmailProvider implements NotificationProvider {
@Override
public void sendNotification(String message, String recipient) {
// Send email logic
}
}
public class SMSProvider implements NotificationProvider {
@Override
public void sendNotification(String message, String recipient) {
// Send SMS logic
}
}
// Refactored NotificationService with dependency injection
public class NotificationService {
private NotificationProvider notificationProvider;
public NotificationService(NotificationProvider notificationProvider) { // Inject dependency
this.notificationProvider = notificationProvider;
}
public void sendNotification(String message, String recipient) {
notificationProvider.sendNotification(message, recipient);
}
}
Benefits of using Dependency Injection Design Pattern in this solution above:
- Loose Coupling:
NotificationService no longer depends on a specific implementation, making it adaptable to different providers. - Testability: You can easily inject mock providers for testing
NotificationService in isolation. - Flexibility: You can change the notification provider at runtime by configuring the injection mechanism.
- Maintainability: Code becomes more modular and easier to manage as dependencies are explicit.
Types of Dependency Injection
There are mainly three types of dependency injection, that are Constructor Injection, Setter Injection and Interface Injection. Let's understand these three approaches to dependency injection using an example with the implementation.
You are building a Vehicle Management System for a car rental service. The system needs to manage cars and their engines. Each car should have an engine type and the system should ensure that the car has all necessary components when it's instantiated.
1. Constructor Injection
With Constructor Injection, dependencies are provided to a class through its constructor when the object is created. This is the most common form of DI because it makes dependencies clear, mandatory, and immutable after the object is constructed.
Java
class Engine {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Engine started");
}
}
class Car {
private Engine engine; // Declaring a dependency on Engine
// Constructor Injection: Dependency is provided through the constructor
public Car(Engine engine) {
this.engine = engine; // Engine dependency is injected via constructor
}
public void drive() {
engine.start(); // Using the injected Engine dependency
System.out.println("Car is driving");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Engine engine = new Engine(); // Create Engine object (dependency)
// Injecting Engine dependency when creating Car
Car car = new Car(engine); // Pass the Engine instance to the constructor
car.drive(); // Call the drive method to use the Engine
}
}
Engine started
Car is driving
- Engine Class: Defines a simple class with a
start() method to simulate starting an engine. - Car Class:
- It has a dependency on
Engine (i.e., Car needs an Engine to drive). - The
Car class's constructor takes an Engine object as a parameter. This is where the constructor injection happens—Engine is passed in when Car is created. - Inside the
drive() method, the Car uses the engine to call engine.start().
- Main Method:
- A new
Engine is created and passed to the Car constructor. This injects the dependency into Car. - Then, the
drive() method of Car is called, which uses the injected Engine to start the car and print the output.
2. Setter Injection
Setter Injection involves providing the dependency via a setter method after the object is created. This approach is more flexible than constructor injection because it allows dependencies to be set or changed after object creation.
Java
class Engine {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Engine started");
}
}
class Car {
private Engine engine; // Declaring a dependency on Engine
// No constructor injection here. Using setter to inject dependency
public void setEngine(Engine engine) {
this.engine = engine; // Injecting dependency via setter method
}
public void drive() {
engine.start(); // Using the injected Engine dependency
System.out.println("Car is driving");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Engine engine = new Engine(); // Create Engine object (dependency)
// Create a Car object without providing the Engine immediately
Car car = new Car();
// Inject the Engine dependency using the setter method
car.setEngine(engine); // Set the dependency via the setter method
car.drive(); // Call the drive method to use the Engine
}
}
Engine started
Car is driving
- Engine Class: This is the same as in Constructor Injection. It has a
start() method to simulate engine behavior. - Car Class:
- Instead of passing the
Engine dependency via the constructor, it has a setter method setEngine() to allow the Engine to be injected after the object is created. - In the
drive() method, the Car uses the engine dependency to call start().
- Main Method:
- The
Engine is created first, then a Car object is created. - The
setEngine() method is called to inject the Engine dependency into the Car. - After the dependency is injected,
car.drive() is called to use the engine.
3. Interface Injection
Interface Injection requires the class to implement an interface that provides a method for receiving the dependency. This is less commonly used in Java, but it allows for more flexibility and decoupling.
Java
class Engine {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Engine started");
}
}
// Define an interface for injecting dependencies
interface EngineInjector {
void injectEngine(Engine engine); // Method to inject the Engine dependency
}
class Car implements EngineInjector {
private Engine engine; // Declaring a dependency on Engine
// Implement the injectEngine method to set the Engine dependency
@Override
public void injectEngine(Engine engine) {
this.engine = engine; // Dependency injected through the interface method
}
public void drive() {
engine.start(); // Using the injected Engine dependency
System.out.println("Car is driving");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Engine engine = new Engine(); // Create Engine object (dependency)
Car car = new Car(); // Create Car object
car.injectEngine(engine); // Inject dependency via the injectEngine() method
car.drive(); // Call the drive method to use the Engine
}
}
Engine started
Car is driving
- Engine Class: This class has a
start() method to simulate starting the engine. - EngineInjector Interface: This interface defines a method
injectEngine(Engine engine) which must be implemented by any class that wants to receive an Engine dependency. - Car Class:
- The
Car class implements the EngineInjector interface, meaning it must provide an implementation for the injectEngine() method. - In the
injectEngine() method, the Car accepts the Engine and sets it. - The
drive() method uses the injected Engine to call start().
- Main Method:
- A new
Engine object is created. - A
Car object is created, and the injectEngine() method is used to inject the Engine dependency. - Finally, the
drive() method is called on Car, which uses the injected Engine.
Benefits of using Dependency Injection Design Pattern
Dependency injection offers a lot of benefits for your software development.
- Increased Modularity and Maintainability: Code becomes cleaner and more modular by decoupling components from their dependencies.
- Improved Testability: Mocks and stub dependencies can be easily injected for unit testing, facilitating isolated testing of components.
- Reduced Coupling and Improved Loose Coupling: Components depend on abstractions, not specific implementations, promoting loose coupling.
- Easier Collaboration and Reusability: Developers can focus on implementing core functionalities without worrying about dependencies.
Challenges of using Dependency Injection Design Pattern
While there are many benefits that come with dependency injection (DI), it's essential to acknowledge potential downsides and consider them in your software development decisions. Below are some key challenges to be aware of:
- Increased Complexity: Introducing DI frameworks or managing manual injection can add complexity to smaller projects or simple codebases.
- Runtime Errors: Improper configuration or injection of incompatible dependencies can lead to runtime errors that are harder to debug than compile-time errors in tightly coupled code.
- Overhead and Performance: DI frameworks can introduce additional overhead in terms of memory usage and runtime performance, especially compared to tightly coupled architectures.
- Testing Dependency Injection Itself: Testing your DI configuration and its interactions with injected dependencies can be more challenging than testing directly coupled components.
Also read:Java Dependency Injection (DI) Design Pattern
Similar Reads
What is Advanced Java?
In the realm of coding, creativity, and state-of-the-art technology have a pivotal role in the domain of software creation. Java is known for its platform independence, robustness, and extensive libraries. Advanced Java concepts let you make really complicated programs, it encompasses an array of te
13 min read
Dependency Injection(DI) Design Pattern
Effective dependency management is essential to building scalable and maintainable systems. The Dependency Injection (DI) design pattern is one strategy that has become very popular. Fundamentally, dependency injection is a method that addresses how components or objects are constructed and how they
10 min read
Spring
Introduction to Spring Framework
The Spring Framework is a powerful, lightweight, and widely used Java framework for building enterprise applications. It provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for Java-based applications, making development faster, scalable, and maintainable.Before Enterprise Java Beans (EJB),
9 min read
Spring Framework Architecture
The Spring framework is a widely used open-source Java framework that provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for building enterprise applications. Its architecture is designed around two core principles: Dependency Injection (DI) Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)The Spring fram
7 min read
Spring Initializr
Spring Initializr is a popular tool for quickly generating Spring Boot projects with essential dependencies. It helps developers set up a new application with minimal effort, supporting Maven and Gradle builds. With its user-friendly interface, it simplifies project configuration, making it an essen
4 min read
Spring - BeanFactory
The first and foremost thing when we talk about Spring is dependency injection which is possible because Spring is a container and behaves as a factory of Beans. Just like the BeanFactory interface is the simplest container providing an advanced configuration mechanism to instantiate, configure, and
4 min read
Spring - ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext belongs to the Spring framework. Spring IoC container is responsible for instantiating, wiring, configuring, and managing the entire life cycle of beans or objects. BeanFactory and ApplicationContext represent the Spring IoC Containers. ApplicationContext is the sub-interface of B
5 min read
Spring Dependency Injection with Example
Dependency Injection is the main functionality provided by Spring IOC(Inversion of Control). The Spring-Core module is responsible for injecting dependencies through either Constructor or Setter methods. The design principle of Inversion of Control emphasizes keeping the Java classes independent of
7 min read
Spring - IoC Container
The Spring framework is a powerful framework for building Java applications. It can be considered a collection of sub-frameworks, also referred to as layers, such as Spring AOP, Spring ORM, Spring Web Flow, and Spring Web MVC. We can use any of these modules separately while constructing a Web appli
2 min read
Spring - Autowiring
Autowiring in the Spring framework can inject dependencies automatically. The Spring container detects those dependencies specified in the configuration file and the relationship between the beans. This is referred to as Autowiring in Spring. To enable Autowiring in the Spring application we should
4 min read
Spring Framework Annotations
Spring framework is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. Spring framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business obje
6 min read
SpringBoot
Introduction to Spring Boot
Spring is widely used for creating scalable applications. For web applications, Spring provides Spring MVC, a commonly used module for building robust web applications. The major drawback of traditional Spring projects is that configuration can be time-consuming and overwhelming for new developers.
5 min read
Difference between Spring and Spring Boot
Spring Spring is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made the development of Web applications much easier
4 min read
Spring Boot - Architecture
Spring Boot is built on top of the core Spring framework. It simplifies and automates Spring-based application development by reducing the need for manual configuration. Spring Boot follows a layered architecture, where each layer interacts with other layers in a hierarchical order. The official Spr
3 min read
Spring Boot - Annotations
Spring Boot Annotations are a form of metadata that provides data about a spring application. Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the
7 min read
Spring Boot Actuator
Developing and managing an application are the two most important aspects of the application’s life cycle. It is very important to know what is going on beneath the application. Also, when we push the application into production, managing it gradually becomes critically important. Therefore, it is a
5 min read
Spring Boot - Code Structure
There is no specific layout or code structure for Spring Boot Projects. However, there are some best practices followed by developers that will help us too. You can divide your project into layers like service layer, entity layer, repository layer,, etc. You can also divide the project into modules.
3 min read
Spring - RestTemplate
Due to high traffic and quick access to services, REST APIs are getting more popular and have become the backbone of modern web development. It provides quick access to services and also provides fast data exchange between applications. REST is not a protocol or a standard, rather, it is a set of ar
7 min read
How to Change the Default Port in Spring Boot?
Spring Boot framework provides a default embedded server i.e. the Tomcat server for many configuration properties to run the Spring Boot application. The application runs on the default port which is 8080. As per the application need, we can also change this default port for the embedded server. In
4 min read
Spring Boot - Scheduling
Spring Boot provides the ability to schedule tasks for execution at a given time period with the help of @Scheduled annotation. This article provides a step by step guideline on how we can schedule tasks to run in a spring boot application Implementation:It is depicted below stepwise as follows:Â St
4 min read
Spring Boot - Sending Email via SMTP
Spring Boot provides the ability to send emails via SMTP using the JavaMail Library. Here we will be illustrating step-by-step guidelines to develop Restful web services that can be used to send emails with or without attachments. In order to begin with the steps, let us first create a Spring Boot p
5 min read
Spring Boot - REST Example
In modern web development, most applications follow the Client-Server Architecture. The Client (frontend) interacts with the server (backend) to fetch or save data. This communication happens using the HTTP protocol. On the server, we expose a bunch of services that are accessible via the HTTP proto
4 min read
Introduction to the Spring Data Framework
Spring Data is a powerful data access framework in the Spring ecosystem that simplifies database interactions for relational (SQL) and non-relational (NoSQL) databases. It eliminates boilerplate code and provides an easy-to-use abstraction layer for developers working with JPA, MongoDB, Redis, Cassa
3 min read
Spring MVC
Spring - MVC Framework
The Spring MVC Framework follows the Model-View-Controller architectural design pattern, which works around the Front Controller, i.e., the Dispatcher Servlet. The Dispatcher Servlet handles and dispatches all incoming HTTP requests to the appropriate controller. It uses @Controller and @RequestMapp
4 min read
Spring - Multi Action Controller with Example
Spring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made
4 min read
Spring MVC using Java Based Configuration
Spring MVC framework enables the separation of modules, namely Model, View, and Controller, and seamlessly handles application integration. This enables the developer to create complex applications using plain Java classes. The model object can be passed between the view and the controller using map
3 min read
ViewResolver in Spring MVC
Spring MVC is a powerful Web MVC Framework for building web applications. It provides a structured way to develop web applications by separating concerns into Model, View, and Controller. One of the key features of Spring MVC is the ViewResolver, which enables you to render models in the browser wit
7 min read
Spring MVC - Exception Handling
Prerequisites: Spring MVC When something goes wrong with your application, the server displays an exception page defining the type of exception, the server-generated exception page is not user-friendly. Spring MVC provides exception handling for your web application to make sure you are sending your
6 min read
Spring - MVC Form Handling
Prerequisites: Spring MVC, Introduction to Spring Spring MVC is a Model-View-Controller framework, it enables the separation of modules into Model, View, and Controller and uniformly handles the application integration. In this article, we will create a student login form and see how Spring MVC hand
6 min read
How to Make Post Request in Java Spring?
Java language is one of the most popular languages among all programming languages. There are several advantages of using the java programming language, whether for security purposes or building large distribution projects. One of the advantages of using JAVA is that Java tries to connect every conc
4 min read
Spring MVC CRUD with Example
In this article, we will explore how to build a Spring MVC CRUD application from scratch. CRUD stands for Create, Read/Retrieve, Update, and Delete. These are the four basic operations to create any type of project. Spring MVC is a popular framework for building web applications. Spring MVC follows
7 min read
What are Microservices?
Microservices are an architectural approach to developing software applications as a collection of small, independent services that communicate with each other over a network. Instead of building a monolithic application where all the functionality is tightly integrated into a single codebase, micro
12 min read