(ATS4-PLAT01) Core Architecture Changes in AEP 9.0 and their Impact on Administrators
- 1. (ATS4-PLAT01) Core Architecture Changes in AEP 9.0 and Their Impact on Administrators Steven Bush R&D, AEP Core Infrastructure [email protected]
- 2. Platforms • Except where noted, the information within this presentation applies to both Windows and Linux installations. • Starting in 9.0, AEP server installations are now 64-bit only
- 3. Services • 8.5 and earlier – 32 and 64 bit – Apache • 9.0 – 64 bit only – Apache • Manages running jobs • Other services including access to protocol database and files – Tomcat • Back end service provider – Security filter – Internal configuration and system database – Periodic cleanup tasks – Other scheduled tasks – AEPManager (Windows) • Responsible for managing the other services
- 4. Tomcat Cleanup tasks • Remove stale job directories – Expired and invalid jobs • Queue processing – When max running jobs is reached • Remove stale lck files – <InstallDir>/temp/lck • Each running job creates a file with basic information • Running jobs reports, when to queue based on lck file count • If the job process crashes, the lck file remains • Clean up /var/tmp files (Linux) – Used for OS synchronization files (mutexes, conditions, pipes)
- 5. Managing the services (Windows) • AEPManager service – Starts and shuts down Tomcat and Apache – Monitors status of each service to restart when necessary – Right click “My Computer”, choose “Manage”, Navigate to Services. Start/Stop AEPManager. • Modified ApacheMonitor.exe – Based on Apache Foundation apachemonitor.exe – Shows all installed Apache services – Combines all services within same AEP install directory – 8.5 and earlier: use apachemonitor.exe that ships in apache folder
- 6. Managing the services (Windows) • Services Administration Panel • Processes and Memory – Task Manager – Process Explorer • Improved Task Manager • http://technet.microsoft.com/en-US/sysinternals
- 7. Managing the services (Linux) • startserver, stopserver scripts still used – Starts and stops both Apache and Tomcat – /etc/rc.d used for autostart services • Installed by root installation script (scirootinstall) • ps and top • “free –m” to check memory (-m = Megabytes) – read “-/+ buffers/cache” line for real results
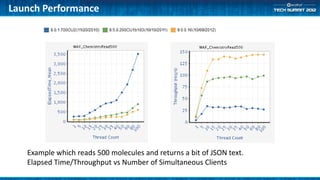
- 8. Launch Performance Example which reads 500 molecules and returns a bit of JSON text. Elapsed Time/Throughput vs Number of Simultaneous Clients
- 9. Exporting/Importing Configurations • Export configuration from administration portal – Clone server configurations – Set up new nodes for load balancing configuration
- 10. Maintenance Mode • Disable launching jobs without shutting down the server – Professional UI can still be used to build protocols – Admin portal is still accessible
- 11. New Deployment Options 8.5 9.0 Single Server Yes Yes Windows 32/64 bit 64 bit Linux 32/64 bit 64 bit Private Cluster Linux Linux Public Cluster Linux Linux Grid Engine Linux Linux SSL Only/HTTP Only No Yes Port Forwarded No Yes Load Balanced Web Farm No Yes
- 12. New Globals/URL creation • Should no longer build URLs from server name and port – Will not work with reverse proxies and single port setups – Had problems on clusters and grids • Use @ServerRoot and @ServerSSLRoot instead – Reflects configuration of server • SSL/HTTP only • Reverse proxy/port forwarded • Load balanced • Clusters and grids • Old globals will continue to work for basic configurations
- 13. New Globals/URL Creation 8.5 9.0 HTTP URLs http://$(ServerName):$(ServerPort)/myFile $(ServerRoot)/myfile HTTPS URLs https://$(ServerName):$(ServerSSLPort)/myFile $(ServerSSLRoot)/myfile Internal HTTP URLs Same as client @/pilot_settings/ROOT Internal HTTPS URLs Same as client @/pilot_settings/SSLROOT Internal Server Name Same as client @/pilot_settings/InternalServerName Shared Data Directory @ScitegicRoot @SharedPublicDir
- 14. Protocol Links • http://<server>:<port>/auth/launchjob – Faster launch times – Improved features • streaming results • Integrated authentication – runjob.pl links map to launchjob with _compat=1 flag
- 15. SSL and HTTP Only Modes • Setting found in Admin Portal – Server ConfigurationServer Port Usage • Changes all outgoing URLs to point to correct endpoint – In SSL only mode, @ServerRoot becomes https://.... – In HTTP only mode, @ServerSSLRoot becomes http://.... • Does not turn off second port by default – To disable listening on the unused port, contact support
- 16. Reverse Proxy
- 17. Reverse Proxy • Deploy behind a port forwarding server – Deployment into DMZs – Multiple subnet deployments • Some clients outside firewall, others inside • “SSL termination” option – Connection to reverse proxy is via SSL – From proxy to AEP server is HTTP only
- 18. Reverse Proxy: Configuration • Configure in Admin portal – SetupReverse Proxy and Load Balancing – Set the default server name for your reverse proxy (e.g. firewall.mydomain.net) • Add aliases that might be used as well (e.g. 10.1.2.3,firewall,othername.mydomain.net) – Set the port numbers that are available for your reverse proxy • Leave HTTP or SSL blank if not used
- 20. Load Balanced
- 21. Load Balanced vs. Cluster vs. Grid • Load Balanced (Windows or Linux) – Large numbers of simultaneous users – Individual web requests are distributed – Parallel subprotocols are not distributed – Ideal for short running web based applications that require simultaneous user scalability or failover – Cannot be used for ad-hoc use • Cluster (Linux) – Large numbers of long running jobs – Running jobs are distributed – Parallel subprotocols are distributed – Ideal for long running jobs with large parallelization needs – Useful for ad-hoc use • Grid (Linux) – Similar to cluster – Load is controlled by third party grid software (eg. OGE, LSF, PBS) – Slowest launch times – Ideal for large numbers of very long running jobs and taking advantage of existing grid systems – Possibly slow for ad-hoc use
- 22. Load Balancer Requirements • Install behind any off the shelf load balancer – The AEP server itself does not require affinity, but some applications may choose to impose this limitation – One requirement for the load balancer: Must preserve the HTTP “Host” header.
- 23. Load Balanced: Benefits • Throughput – Huge improvement under high usage • Performance – No difference under low usage versus single servers – Moderate improvement under high usage • High Availability – If a node goes down, other nodes continue functioning
- 24. Load Balanced: Performance Example which reads 500 molecules and returns a bit of JSON text tested against 1-3 nodes. Elapsed Time/Throughput vs Number of Simultaneous Clients
- 25. Load Balanced: Restrictions • Protocol Database is read only – Deploy protocols and components using packages – Can not build models – Intended for applications that rarely change • Parallel subprotocols do not distribute across nodes – Set “Server” to the name of the load balancer instead of “localhost” • Admin Portal connected through the load balancer can only show running jobs – Connect to individual nodes for full portal access – Use “Export/Import” to update each node
- 26. Load Balanced: Shared Data • “Folder Locations” in Admin portal • Jobs directory • Users directory • Shared Public directory – Use @SharedPublicDir instead of @ScitegicRoot • On a single server system, both are equal
- 27. Load Balanced: Configuration • SetupReverse Proxy and Load Balancing – Follow same setup as for reverse proxy – Check box for “Load Balanced” • SetupFolder Locations – Jobs directory – Users directory – Shared Public directory • Use @SharedPublicDir instead of @ScitegicRoot
- 28. The information on the roadmap and future software development efforts are intended to outline general product direction and should not be relied on in making a purchasing decision.