Instruction Set Architecture – II
- 1. Instruction Set Architecture – II CS2052 Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering University of Moratuwa Dilum Bandara [email protected]
- 2. Outline Types of memory Von Neumann vs. Harvard architecture Addressing modes RISC & CISC 2
- 3. Blocks of a Microprocessor 3 Literal Address Operation Program Memory Instruction Register STACK Program Counter Instruction Decoder Timing, Control and Register selection Accumulator RAM & Data Registers ALU IO IO FLAG & Special Function Registers Clock Reset Interrupts Program Execution Section Register Processing Section Set up Set up Modify Address Internal data bus Source: Makis Malliris & Sabir Ghauri, UWE
- 4. Memory Instruction memory Store program instructions Data memory Store data for instructions Stack e.g., stack of plates For temporary storage of state Initially stored in ROM Or Flash Read/Write while in RAM 4
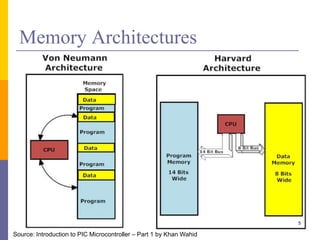
- 5. Memory Architectures 5 Source: Introduction to PIC Microcontroller – Part 1 by Khan Wahid
- 6. Von Neumann vs. Harvard Architecture 6
- 7. Memory Addressing Place an address on address bus Read or write operation Data placed on data bus 7 Source: www.alf.sd83.bc.ca/courses/It12/using_it/processor_speed.htm
- 8. Memory Addressing (Cont.) 8 Address Data Word No of words 0 9
- 9. Memory Addressing (Cont.) Memory Capacity = Word Size × No of Words Example PIC 16F877A can store up to 8K instructions Each instruction is 14-bit This is the size of Instruction Register What is the size of instruction memory in KB? 8 × 1024 x 14 /(8 x 1024) = 14 KB 9
- 10. Example – Memory Addressing PIC 16F877A can store up to 8K instructions What is the length of an instruction address? No of bits required to uniquely address each word log2 8 × 1024 = log2 213 = 13 bits This is the size of Program Counter How many bits are required to address 348 instructions? 10 0 8K -1
- 11. Example – Instruction Memory How many bits we need to address 4Kbit memory? It depends on smallest unit (word length) that we need to address Suppose 8-bit addressable 4Kb/8b = 512 locations Requires log2 512 = 9 bits 11
- 12. Addressing Modes Way the microprocessor Identifies location of data Access data Absolute address Actual physical address Direct addressing Relative address Address relative to a known reference Indirect addressing 12
- 13. Segments Special areas in memory that is used to hold code, data, & stack 13 Programmers View of Memory 0 100 50 100 50 150 SS – Stack Segment DS – Data Segment CS – Code Segment
- 14. 14 Segment + Offset Addressing Indicate address using segment boundary & offset Example 1 What is the actual memory location if DS register is 03E0h & offset is 32h? DS 03E0 Offset 32 + Address 412
- 15. 15 Pointer Registers Are used to hold offset values Example 2 What is the actual memory location if CS register is 39B0h & Instruction Pointer (IP) register is 514h? CS 39B0 Offset 514 + Address 3EC4
- 16. Addressing Modes 1. Immediate addressing Data/operand specified in instruction e.g., MOVLW k 2. Direct/Register addressing Register address is specified in instruction e.g., MOVF f, d 16
- 17. Addressing Modes (Cont.) 3. Indexed addressing Index Register store index Value in index register is added to address specified in instruction e.g., while accessing an element in an array MOV R1, Table[2] 17 ….. 1st Element 2nd Element 12th Element 3rd Element 215 Index Register
- 18. Addressing Modes (Cont.) 4. Base Register addressing Same idea as Index Register addressing Used with segments Enable relocation of code e.g., MOV R1, [21] 18 21st value 1st value 2nd value ….. ….. 215 Base Register
- 19. Addressing Modes (Cont.) 5. Register indirect addressing Address is stored in some other register Instruction specify which register to look at Address field of instruction can be smaller than actual physical address 19 Source: http://cnx.org/content/m29425/latest/
- 20. Example – 8086 Addressing Modes 20 Source: www.electronics.dit.ie
- 21. Swapping Data Swap contents of W with register R5 Use only PIC instructions No register-register operations Routine requires 2 temporary locations W tempA tempB R5 movwf tempA movf R5, 0 movwf tempB movf tempA, 0 movwf R5 movf tempB, 0 21
- 22. Stack For temporary storage of state Last in first out e.g., stack of plates Example 100 CALL Delay 101 ..... 214 Delay: ..... ..... 218 Return 22 Source: http://sir.unl.edu/portal/bios/Stack.php
- 23. Stack Example 105 a { … 112 b() … } 231 b { … 236 f() … } 175 f { … 179 g() … } 23 113 180 237
- 24. CISC vs. RISC Complex Instruction Set Computer Many instructions e.g., 75-100 Many instructions are macro-like Simplifies programming Most microcontrollers are based on CISC concept e.g., PDP-11, VAX, Motorola 68k PIC is an exception Reduced Instruction Set Computers Few instructions e.g., 30-40 Smaller chip, smaller pin count, & very low-power consumption Simple but fast instructions Harvard architecture, instruction pipelining Industry trend for microprocessor design e.g., Intel Pentium, PIC 24
















![Addressing Modes (Cont.)
3. Indexed addressing
Index Register store index
Value in index register is
added to address specified
in instruction
e.g., while accessing an
element in an array
MOV R1, Table[2]
17
…..
1st
Element
2nd
Element
12th
Element
3rd
Element
215
Index Register](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06-instructionsetarchitectureii-150216185310-conversion-gate02/85/Instruction-Set-Architecture-II-17-320.jpg)
![Addressing Modes (Cont.)
4. Base Register
addressing
Same idea as Index
Register addressing
Used with segments
Enable relocation of
code
e.g., MOV R1, [21]
18
21st
value
1st
value
2nd
value
…..
…..
215
Base Register](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06-instructionsetarchitectureii-150216185310-conversion-gate02/85/Instruction-Set-Architecture-II-18-320.jpg)





