Artificial Neural Network (draft)
- 1. Artificial Neural Networks An Introduction
- 2. Why study ANNs? • To understand how the brain actually works • To understand a type of parallel computation • IBM’s “The Brain Chip” (1 million neurons and 256 synapses) • To solve practical problems • Artificial Neural Networks should be good for things brains are good at and bad at things brains are bad at (Vision, speech recognition) (eg: 32 * 71 = ???)
- 4. What neurons look like Our model will be simplified: Synapses -> Weighted Inputs Soma -> An activation function Axon -> Outputs Neuron – an electrically excitable cell that transmits information Dendrites receive signals from many other neurons These signals can be either excitatory or inhibitory Soma (cell body) processes this information Above a certain threshold, an electrical signal is fired down the axon.
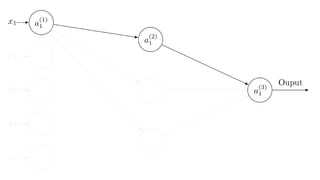
- 5. A Feed Forward Neural Net Weighted connections
- 6. What can NNs do? • Image recognition MNIST handwritten digits Read reCAPTCHA better than humans do • Speech recognition and NLP • Answer the meaning of life
- 7. Using recurrent neural net to predict the next character • In 2011, Ilya Sutskever used 5 millions strings of 100 characters, taken from Wikipedia. • Training took one month on a GPU • Once trained, the neural net will predict the next character in a sequence of characters • He fed it the phrase “The meaning of life is” _______________
- 9. A Brief History of ANNs • 1943 – McCulluogh and Pitts NN models can represent any Boolean • 1949 – Donald Webb describes how learning might take place: “cells that fire together, wire together.” • 1959 – Rosenblatt’s perceptron can learn linearly separable data • 1969 – Minsky & Papert criticize the perceptron • 1970-1986 – The dark ages of neural networks (No funding) • 1986 – Hinton, LeCun et al. describe the backpropagation algorithm for training neural networks of arbitrary depth ( Paul Werbos, 1974) • 1997 – A.K. Dewdney – "Although neural nets do solve a few toy problems, their powers of computation are so limited that I am surprised anyone takes them seriously as a general problem- solving tool.“ • Other techniques (Random Forests[1995] and Support Vector Machines[1995]) are considered state of the art ML for classification problems • 2006 – Second Renaissance of neural networks with new methods for training deep and recurrent NNs.
- 10. 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 Ln(#ofPublications) ANN Scholarly Publications Per Year (Ln Normalized) 1986 1969
- 13. “the embryo of an electronic computer that [the Navy] expects will be able to walk, talk, see, write, reproduce itself and be conscious of its existence." 1958 Frank Rosenblatt’s Perceptron
- 14. The Perceptron
- 15. Weight space Consider all the different sets of weights that will output the correct value for a 2-D input vector. Here, threshold = 0 Input vector with output value = 1 Good weight Bad weight
- 16. NAND example Input Data 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 One of many possible solutions:
- 17. NAND Decision Boundary One possible solution:
- 18. NAND Decision Boundary 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 One possible solution:
- 19. Training Data 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 A single perceptron can only solve linearly separable problems XOR Problem
- 20. Training Data 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 Multiple layers of perceptrons solve the XOR problem, but Rosenblatt did not have an learning algorithm to set the weights XOR Problem
- 21. Training Data 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 Multiple layers of perceptrons solve the XOR problem, but Rosenblatt did not have an learning algorithm to set the weights XOR Problem
- 22. Training Data 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 XOR Problem 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 2 weight planes
- 23. Training Data 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 XOR Problem 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 weight plane
- 24. Sigmoid (Logistic Function) • The sigmoid function is similar to the binary threshold function, but it is continuous “Squashes” – outputs a value between 0 and 1 • It’s derivative has a nice property – it is computationally inexpensive
- 26. Sigmoid Neurons
- 27. Sigmoid Neurons • We can “bake in” the bias by augmenting with an element, , that we set to a constant value (say, 1) for every sample. • now represents the bias value. • With the bias “baked in,” the model has a simpler notation and will be more computationally efficient
- 33. } Matrix notation is easier to read, and used in production code
- 34. How to train a feed forward net? • There are several cost functions (cross entropy, classification error, squared error). • To measure the error in this sample we will use the squared error • Major Difficulty We know what the output target is, but nobody is telling us directly what the hidden units should be
- 35. How to train a feed forward net? • Try: randomly perturb one weight and see if it improves performance • But this is very, very slow
- 36. Backpropagation, 1986* • The “backward propagation of errors” after forward propagation • Here is the cost for a single training sample • If we calculate the error derivatives w.r.t. each weight, we can update the weights with gradient descent.
- 37. Backpropagating errors Step 0. Feed Forward Network
- 38. Backpropagating errors Step 1. Backpropagate the error derivative to each node
- 39. Backpropagating errors Step 1. Backpropagate the error derivative to each node Step 2. Use the node deltas to compute the incoming weight derivatives
- 40. Backpropagation error derivatives Feed Forward Back Propagate Linear Output Neuron
- 44. Back Propagation can be used to train a neural net with which of the following activation functions? Logistic (sigmoid) Linear Binary threshold neurons (Perceptron) Hyperbolic Tangent ( )
- 47. Selecting Hyper-Parameters Generally, we use trial and error (with cross-validation) to select hyperparameters What learning rate? Momentum? How many layers? How many nodes / layer? Regularization coefficient? Activation function(s)?
- 48. Regularization • Without some form of regularization, large ANNs are prone to over fitting • ANNs can approximate any function; they can fit the noise in the training data set • One traditional solution is L2 regularization. We modify our error function by including for every weight in the matrix. • L2 regularization drives the weights towards 0 • As the weights approach zero, the sigmoid function becomes more linear • Recently, new forms of regularization have improved ANNs learning
- 49. New regularizers • Force neurons to share weights
- 50. Learning Curves – Overfitting - regularization
- 51. NN libraries • Theano (python) • PyLearn2 (python) • Torch (Lua) • Deep Learning Toolbox (MATLAB) • Numenta (python) • Nnet (R)
- 52. Do walk through with ConvnetJS
- 53. Google Trends “Neural Network” searches
- 54. Google Trends “Random Forests” searches
- 55. Google Trends “Deep Learning” searches
- 56. Addressing ANN’s weaknesses: Averaging many models • Unlike random forests (which average many decision trees), creating many neural network models has not been feasible • Averaging models is important because it prevents over fitting • NN Dropout (2012) provides a way to average many models, without having to train them separately
- 57. Provide motivation for Deep Learning








![A Brief History of ANNs
• 1943 – McCulluogh and Pitts NN models can represent any Boolean
• 1949 – Donald Webb describes how learning might take place: “cells that
fire together, wire together.”
• 1959 – Rosenblatt’s perceptron can learn linearly separable data
• 1969 – Minsky & Papert criticize the perceptron
• 1970-1986 – The dark ages of neural networks (No funding)
• 1986 – Hinton, LeCun et al. describe the backpropagation algorithm for training
neural networks of arbitrary depth ( Paul Werbos, 1974)
• 1997 – A.K. Dewdney – "Although neural nets do solve a few toy problems, their powers of
computation are so limited that I am surprised anyone takes them seriously as a general problem-
solving tool.“
• Other techniques (Random Forests[1995] and Support Vector Machines[1995]) are considered
state of the art ML for classification problems
• 2006 – Second Renaissance of neural networks with new methods for training deep and recurrent
NNs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annpresodraft-140818224650-phpapp02/85/Artificial-Neural-Network-draft-9-320.jpg)



![“the embryo of an electronic computer that [the
Navy] expects will be able to walk, talk, see, write,
reproduce itself and be conscious of its existence."
1958
Frank Rosenblatt’s Perceptron](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annpresodraft-140818224650-phpapp02/85/Artificial-Neural-Network-draft-13-320.jpg)