Garbage collection
- 1. GARBAGE COLLECTOR Automatic garbage collection is the process of looking at heap memory, identifying which objects are in use and which are not, and deleting the unused objects. An in use object, or a referenced object, means that some part of your program still maintains a pointer to that object. An unused object, or unreferenced object, is no longer referenced by any part of your program. So the memory used by an unreferenced object can be reclaimed. In a programming language like C, allocating and deallocating memory is a manual process. In Java, process of deallocating memory is handled automatically by the garbage collector.
- 2. The basic process can be described as follows: ● Step 1: Marking The first step in the process is called marking. This is where the garbage collector identifies which pieces of memory are in use and which are not. Referenced objects are shown in blue. Unreferenced objects are shown in gold. All objects are scanned in the marking phase to make this determination. This can be a very time consuming process if all objects in a system must be scanned.
- 3. Step 2: Normal Deletion Normal deletion removes unreferenced objects leaving referenced objects and pointers to free space. The memory allocator holds references to blocks of free space where new object can be allocated.
- 4. Step 2a: Deletion with Compacting To further improve performance, in addition to deleting unreferenced objects, you can also compact the remaining referenced objects. By moving referenced object together, this makes new memory allocation much easier and faster.
- 5. Why Generational Garbage Collection? ● As stated earlier, having to mark and compact all the objects in a JVM is inefficient. As more and more objects are allocated, the list of objects grows and grows leading to longer and longer garbage collection time. However, empirical analysis of applications has shown that most objects are short lived. JVM Generations ● The information learned from the object allocation behavior can be used to enhance the performance of the JVM. Therefore, the heap is broken up into smaller parts or generations. The heap parts are: Young Generation, Old or Tenured Generation Permanent Generation ● The Young Generation is where all new objects are allocated and aged. When the young generation fills up, this causes a minor garbage collection. Minor collections can be optimized assuming a high object mortality rate. A young generation full of dead objects is collected very quickly. Some surviving objects are aged and eventually move to the old generation.
- 6. ● Stop the World Event - All minor garbage collections are "Stop the World" events. This means that all application threads are stopped until the operation completes. Minor garbage collections are always Stop the World events. ● The Old Generation is used to store long surviving objects. Typically, a threshold is set for young generation object and when that age is met, the object gets moved to the old generation. Eventually the old generation needs to be collected. This event is called a major garbage collection. ● Major garbage collection are also Stop the World events. Often a major collection is much slower because it involves all live objects. So for Responsive applications, major garbage collections should be minimized. Also note, that the length of the Stop the World event for a major garbage collection is affected by the kind of garbage collector that is used for the old generation space. ● The Permanent generation contains metadata required by the JVM to describe the classes and methods used in the application. The permanent generation is populated by the JVM at runtime based on classes in use by the application. In addition, Java SE library classes and methods may be stored here. ● Classes may get collected (unloaded) if the JVM finds they are no longer needed and space may be needed for other classes. The permanent generation is included in a full garbage collection.
- 7. The pictures that follow walks through the object allocation and aging process in the JVM: First, any new objects are allocated to the eden space. Both survivor spaces start out empty.
- 8. When the eden space fills up, a minor garbage collection is triggered.
- 9. ● Referenced objects are moved to the first survivor space. Unreferenced objects are deleted when the eden space is cleared.
- 10. ● At the next minor GC, the same thing happens for the eden space. Unreferenced objects are deleted and referenced objects are moved to a survivor space. However, in this case, they are moved to the second survivor space (S1). In addition, objects from the last minor GC on the first survivor space (S0) have their age incremented and get moved to S1. Once all surviving objects have been moved to S1, both S0 and eden are cleared. Notice we now have differently aged object in the survivor space.
- 11. ● At the next minor GC, the same process repeats. However this time the survivor spaces switch. Referenced objects are moved to S0. Surviving objects are aged. Eden and S1 are cleared.
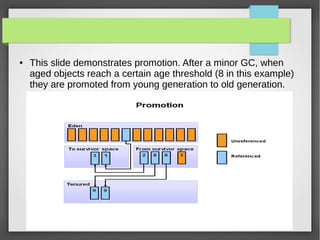
- 12. ● This slide demonstrates promotion. After a minor GC, when aged objects reach a certain age threshold (8 in this example) they are promoted from young generation to old generation.
- 13. ● As minor GCs continue to occure objects will continue to be promoted to the old generation space.
- 14. ● So that pretty much covers the entire process with the young generation. Eventually, a major GC will be performed on the old generation which cleans up and compacts that space.
- 16. Common Heap Related Switches There are many different command line switches that can be used with Java. Switch Description -Xms Sets the initial heap size for when the JVM starts. -Xmx Sets the maximum heap size. -Xmn Sets the size of the Young Generation. -XX:PermSize Sets the starting size of the Permanent Generation. -XX:MaxPermSize Sets the maximum size of the Permanent Generation The Serial GC The serial collector is the default for client style machines in Java SE 5 and 6. With the serial collector, both minor and major garbage collections are done serially (using a single virtual CPU). In addition, it uses a mark-compact collection method. This method moves older memory to the beginning of the heap so that new memory allocations are made into a single continuous chunk of memory at the end of the heap. This compacting of memory makes it faster to allocate new chunks of memory to the heap.
- 17. The Parallel GC The parallel garbage collector uses multiple threads to perform the young genertion garbage collection. By default on a host with N CPUs, the parallel garbage collector uses N garbage collector threads in the collection. The number of garbage collector threads can be controlled with command-line options: -XX:ParallelGCThreads=<desired number> On a host with a single CPU the default garbage collector is used even if the parallel garbage collector has been requested. On a host with two CPUs the parallel garbage collector generally performs as well as the default garbage collector and a reduction in the young generation garbage collector pause times can be expected on hosts with more than two CPUs. The Parallel GC comes in two flavors. The Parallel collector is also called a throughput collector. Since it can use multilple CPUs to speed up application throughput. This collector should be used when a lot of work need to be done and long pauses are acceptable. For example, batch processing like printing reports or bills or performing a large number of database queries.
- 18. Parallel Old GC(-XX:+UseParallelOldGC) ● Parallel Old GC was supported since JDK 5 update. Compared to the parallel GC, the only difference is the GC algorithm for the old generation. It goes through three steps: mark – summary – compaction. The summary step identifies the surviving objects separately for the areas that the GC have previously performed, and thus different from the sweep step of the mark-sweep-compact algorithm. It goes through a little more complicated steps.
- 19. The Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) Collector (-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC) The Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) collector (also referred to as the concurrent low pause collector) collects the tenured generation. It attempts to minimize the pauses due to garbage collection by doing most of the garbage collection work concurrently with the application threads. Normally the concurrent low pause collector does not copy or compact the live objects. A garbage collection is done without moving the live objects. If fragmentation becomes a problem, allocate a larger heap.
- 20. The G1 Garbage Collector The Garbage First or G1 garbage collector is available in Java 7 and is designed to be the long term replacement for the CMS collector. The G1 collector is a parallel, concurrent, and incrementally compacting low-pause garbage collector that has quite a different layout from the other garbage collectors described previously. In G1 garbage collector, one object is allocated to each grid, and then a GC is executed. Then, once one area is full, the objects are allocated to another area, and then a GC is executed. The steps where the data moves from the three spaces of the young generation to the old generation cannot be found in this GC type. This type was created to replace the CMS GC, which has causes a lot of issues and complaints in the long term. The biggest advantage of the G1 GC is its performance. It is faster than any other GC types that we have discussed so far. But in JDK 6, this is called an early access and can be used only for a test. It is officially included in JDK 7.