Introduction to Counters
- 1. Counter
- 2. Introduction to Counter • The filp-flops are essential component in clocked sequential circuits. • Circuits that include filp-flops are usually classified by the function they perform. Two such circuits are registers and counters. • As the name suggests, it counts. The main purpose of counter is to count the number of occurrence of input . • Counter is frequently used in digital computers and digital systems to record the number of events occurring in a specified interval of time. • The combination of flip-flops that perform the counting operation are known as Counters. • N-nit counter will have N flipflops and 2^N states.
- 3. • A digital circuit which is used for a counting pulses is known counter. • Counters are classified into two categories according to the way they are clocked : • Asynchronous/Ripple/Serial Counter • Synchronous/Parallel Counter • In asynchronous counter we don’t use universal clock, only first flip flop is driven by main clock and the clock input of rest of the following counters is driven by output of previous flip flops. • An asynchronous counter is one in which the flip-flops (FF) within the counter do not change states at exactly the same time because they do not have a common clock pulse.
- 4. • We can understand it by following diagram
- 5. • If the "clock" pulses are applied to all the flip-flops in a counter simultaneously, then such a counter is called as synchronous counter. • Unlike the asynchronous counter, synchronous counter has one global clock which drives each flip flop so output changes in parallel. • The one advantage of synchronous counter over asynchronous counter is, it can operate on higher frequency than asynchronous counter as it does not have cumulative delay because of same clock is given to each flip flop.
- 6. • We can understand it by following diagram
- 7. Assignment • Difference between synchronous counter and asynchronous counter.
- 8. • Depending on the way in which the counting progresses, the synchronous or asynchronous counters are classified as follows − • Up counters • Down counters • Up/Down counters
- 9. Synchronous Counter • A synchronous counter is one in which all the flip-flops in the counter are clocked at the same time by a common clock pulse. • J-K flip-flops are used to illustrate most synchronous counters. • D flip-flops can also be used but generally require more logic because of having no direct toggle or no-change states
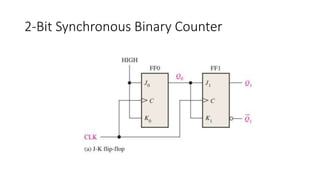
- 10. 2-Bit Synchronous Binary Counter
- 11. Operation • The operation of a J-K flip-flop synchronous counter is as follows: First, assume that the counter is initially in the binary 0 state; that is, both flip-flops are RESET. When the positive edge of the first clock pulse is applied, FF0 will toggle and Q0 will therefore go HIGH. What happens to FF1 at the positive-going edge of CLK1? To find out, let’s look at the input conditions of FF1. Inputs J1 and K1 are both LOW because Q0, to which they are connected, has not yet gone HIGH. Remember, there is a propagation delay from the triggering edge of the clock pulse until the Q output actually makes a transition. So, J = 0 and K = 0 when the leading edge of the first clock pulse is applied. This is a no-change condition, and therefore FF1 does not change state
- 14. 3-Bit Synchronous Binary Counter
- 15. Timing Diagram
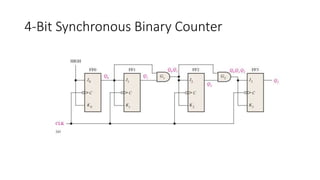
- 16. 4-Bit Synchronous Binary Counter
- 17. 4-Bit Synchronous Decade Counter
- 22. Summary
- 23. Summary