Top 7 types of Statistics Graphs for Data Representation
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes456 views
Are you struggling with choosing the right type of graph to represent your data set? if yes then have a look at this presentation to choose the best statistics graph to represent your data set.
1 of 11
Download to read offline










Ad
Recommended
Displaying data using charts and graphs



Displaying data using charts and graphsCharles Flynt Bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and histograms are commonly used types of charts. Each type of chart has distinct characteristics that make it suitable for visualizing certain types of data relationships. Bar charts are useful for comparing discrete categories, line graphs show trends over time, pie charts show proportions, scatter plots reveal correlations between two variables, and histograms display frequency distributions. Proper chart selection and design ensure data is presented clearly and accurately.
Interpret data for use in charts and graphs



Interpret data for use in charts and graphsCharles Flynt The document discusses various concepts for interpreting and dealing with data for use in charts and graphs, including describing the Cartesian coordinate system in 2D and 3D, explaining direct and inverse relationships between variables, and defining terms like mean, median, mode, independent and dependent variables, control, and empirically and computationally derived data.
Types of charts in Excel and How to use them



Types of charts in Excel and How to use themVijay Perepa There are different Chart types and some times we face difficulty to find which chart is suitable for a specific Data set. In this series of Videos, we have discussed about each chart type and when to use etc.
Types of graphs and charts and their uses with examples and pics



Types of graphs and charts and their uses with examples and picsMakati Science High School This document discusses different types of graphs and charts, their uses, and provides examples. It summarizes 6 common types: line graphs show trends over time; bar charts compare categorical data with bars; pie charts illustrate proportional data with slices; histograms show distributions of continuous data with columns; scatter plots show relationships between two variables with x-y axes; and Venn charts visualize logical relationships between groups with overlapping circles. The document provides examples and descriptions of when each type would be useful.
Analysing charts and graphics



Analysing charts and graphicsŠkola Futura Analysing charts and graphics workshop, Information literacy, Erasmus+ project New Literacy Set, 2015-2017
Graphs and chars



Graphs and charssalemhusin This document discusses different types of graphs and charts, their purposes and guidelines for use. It defines the key difference between graphs and charts, with graphs representing relationships between objects and charts representing data through symbols. Common chart types are described like line charts to show changes over time, bar charts to compare categories, and pie charts to show proportions of a whole. The document provides examples and guidelines for effective graph and chart creation.
Drawings, Tables, Graphs



Drawings, Tables, GraphsDwayne Squires Scientific illustrations like drawings, photographs, tables, and graphs can clearly show relationships and details that may be difficult to explain through text alone. Drawings can depict object details and hidden features. Photographs capture objects at a single moment. Tables organize data in rows and columns. Common graphs are line graphs showing relationships between two variables, bar graphs comparing variables, and circle graphs displaying parts of a whole. Careful analysis of scales is important when interpreting graphs.
Different types of charts



Different types of chartsZakaria Salim The document discusses different types of charts including column charts, bar charts, pie charts, line charts, area charts, stock charts, radar charts, bubble charts, scatter charts, and combo charts. For each chart type, the document outlines typical uses, advantages, and disadvantages. It provides an example of each chart type to illustrate how the chart can be constructed and interpreted.
Presenting information presentation.



Presenting information presentation.danielle93 This document discusses different ways to present information visually, including tally charts, key points, bar charts, line graphs, and percentages. Tally charts can record responses to questions, using lines to show answers. Key points from sources should be highlighted and condensed into bullet points. Bar charts or line graphs can then display tallied answers or trends over time. Percentages can also represent parts of a whole, such as the proportion of people answering a question in the same way.
TYPES ON CHARTS 



TYPES ON CHARTS Charan kumar The document defines different types of charts and their uses. Column charts display changes over time and compare items in a group. Bar charts focus on comparing item values rather than time. Line charts show trends over intervals of time. Pie charts show the size of items in a data series. Scatter charts illustrate the relationship between numeric values. Area charts signify magnitude of change over time and contribution to a whole. Stock charts display high, low, and close values in the stock market.
Ways of presenting information



Ways of presenting informationIbrahem Abdel Ghany Diagrams, charts, tables, and graphs are common ways to present information graphically. Diagrams can summarize processes and ideas more effectively than words. Charts such as bar charts and line graphs represent numerical data visually. Tables display key information, usually numbers, and can summarize data or start discussions. Graphs show patterns and trends when precise numbers are not needed.
Charts, Graphs and Tables



Charts, Graphs and TablesLiliyaNersesyan This document provides information about different types of charts and graphs used to represent data visually, including pie charts, line graphs, bar charts, and tables. It explains what each of these graphical representations are through definitions and examples. Pie charts show percentages, line graphs show changes over time, bar charts show comparisons of discrete categories, and tables arrange data into rows and columns. The document is intended to teach about various ways to visually display quantitative information through graphical formats.
Dot Plot Presentation



Dot Plot PresentationDr. Amjad Ali Arain Topic: Dot Plot Presentation
Student Name: Misbah
Class: B.Ed. 2.5
Project Name: “Young Teachers' Professional Development (TPD)"
"Project Founder: Prof. Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Faculty of Education, University of Sindh, Pakistan
Interpreting charts and graphs



Interpreting charts and graphslesliejohnson441 This document discusses how to interpret charts and graphs. It explains that graphics provide information in a compact way compared to text. It identifies the most common types of graphs as line graphs, bar graphs, and pie charts. It also discusses tables and diagrams. The document emphasizes that graphics contain important information that supports the reading material, so readers should take time to carefully analyze charts, graphs, and tables.
Charts in MS Excel



Charts in MS ExcelRishi Kumar Gupta This document discusses different types of charts that can be created in Microsoft Excel. It describes pie charts, column charts, line charts, bar charts, area charts, scatter charts, and other chart types. For each type of chart, it provides an example image and brief explanation of when and how it can be used. The document is intended to teach about the various charting capabilities in MS Excel.
Types of Chart



Types of Chartchartblocks Curious about the different types of chart? This presentation demonstrates the variety of charts and their purpose. All these charts have been created using Chartblocks online chart building tool.
Understanding visual information:Figure, Graph, Table, and Diagram



Understanding visual information:Figure, Graph, Table, and DiagramMusfera Nara Vadia This document discusses different types of visual information including figures, graphs, tables, and diagrams. It defines two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures. It also describes the most common types of graphs such as pie charts, bar graphs, scatter plots, and line graphs. Tables are explained as presenting lists of numbers or text in columns to synthesize information or present raw data. Diagrams are defined as using graphic images to present theoretical arguments visually.
Types Of Charts



Types Of Chartswmassie This document discusses six common types of charts used in business: column chart, stacked bar chart, line chart, XY scatter plot, pie chart, and exploded pie chart. It defines each chart and provides examples to illustrate the type of data each chart is best suited to display. The column chart compares groups of data. The stacked bar chart shows the contribution of parts to a whole. The line chart indicates trends over time. The XY scatter plot shows correlations between two variables. The pie chart displays the percentage of parts in a whole. The exploded pie chart emphasizes portions of a pie chart.
Charts And Graphs



Charts And GraphsHimadri Shekhar This document discusses different types of charts and graphs that can be used to visually represent data. It provides examples of pie charts, bar charts, column charts, line charts, area charts, and scatter plots. Reasons for creating charts include making trends easily recognizable, allowing quick perception of information, and aiding data interpretation. Charts can be incorporated into business reports, web pages, posters, and other documents. Proper selection of charts is important to illustrate different types of data, such as time series data displayed in line graphs or comparisons shown in bar charts.
Charts and graphs in excel



Charts and graphs in excelIqra Nehal this ppt is about charts in ms excel.there are many types of chart used in ms excel but in this ppt some common types are defined,as line chart,bar,column,area ,scatter chart etc...
Charts and graphs



Charts and graphsAda Marie Tayao This document discusses various types of charts and graphs, including organizational charts, classification charts, timelines, flowcharts, and tabular charts. It provides examples of each type of chart. The document also discusses the purpose of charts, how to design effective charts, and software that can be used to create charts and graphs, such as OpenOffice Calc and Microsoft Excel.
Top 8 Different Types Of Charts In Statistics And Their Uses



Top 8 Different Types Of Charts In Statistics And Their UsesStat Analytica This document discusses different types of charts used in statistics to visually represent data, including bar charts, line charts, pie charts, histograms, scatter plots, exponential graphs, and trigonometric graphs. Bar charts and line charts are useful for comparing data across categories and showing trends over time. Pie charts show proportions of data as slices of a circle. Histograms group data into bins to summarize continuous or discrete measurements. Scatter plots show the relationship between two numeric variables using positioned dots. Exponential and trigonometric graphs visually represent their respective functions and are used in engineering and research.
Types of Charts



Types of ChartsLoyd Calangan The document describes different types of charts that can be used to visualize data, including column charts, bar charts, line charts, pie charts, XY charts, area charts, doughnut charts, surface charts, bubble charts, stock charts, and cylinder, cone or pyramid charts. It provides examples of subtypes for some chart types and explains what each chart shows or compares.
Choosing the Right Graphs



Choosing the Right GraphsOdogray There are several types of graphs that can be created in Excel, each suited to displaying different types of data. Bar graphs and line graphs are commonly used to show changes in numerical data over time or between categories. Scatter plots show trends in large data sets, while pie charts represent percentages and are used to show how parts of a whole are divided.
The uses of Tables & graphs



The uses of Tables & graphsFranco Jesús This document discusses how to improve the clarity of tables and graphs in research articles. It provides rules for constructing clear tables, such as splitting large tables and standardizing layout. When presenting tables, common problems to avoid are poorly positioning them on the page and manipulating spacing. Both tables and their contents should be explained in the text. The document also covers best practices for visualizations like pie charts, bar charts, and line graphs, noting tables are best for exact numbers while graphs show trends.
TID Chapter 5 Introduction To Charts And Graph



TID Chapter 5 Introduction To Charts And GraphWanBK Leo This document discusses different types of charts and graphs that can be used to represent data visually. It describes common chart types like pie charts, bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots. The document explains how each type of chart is best used depending on the nature of the data and the insights that need to be conveyed. It also provides guidance on creating charts in Excel and includes an example of a hands-on exercise for practicing generating different chart types from sample data sets.
Charts in Microsoft Excel



Charts in Microsoft ExcelRosary High School, Vadodara Charts in Excel can display data in a more visually appealing and easy to understand format compared to tables of numbers. There are many components that make up a chart, including axes, data series, plot area, legend and more. Excel offers different types of charts, such as column, bar, line, area, pie, doughnut, scatter, radar, surface and stock charts, each suited to displaying certain types of data trends over time or in relation to other factors.
Charts in excel



Charts in excelJithin Krishnan Area charts display changes in magnitude over time using colored areas below lines. They can be 2D or 3D, stacked to show contribution, or 100% stacked to show percentage contribution over time. Scatter charts show relationships between numeric variables and are used for scientific data. Bubble charts are like scatter charts but show three variables where the third determines bubble size. Stock charts illustrate price fluctuations over time using high, low, close values or including open and volume values.
Introduction to Statistics information.pptx



Introduction to Statistics information.pptxHarshiHarshika1 It helps to you understand about statistics and helps in acquiring knowledge and helps to analysing the answers , and in the present generation helps to study about statistics
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Presenting information presentation.



Presenting information presentation.danielle93 This document discusses different ways to present information visually, including tally charts, key points, bar charts, line graphs, and percentages. Tally charts can record responses to questions, using lines to show answers. Key points from sources should be highlighted and condensed into bullet points. Bar charts or line graphs can then display tallied answers or trends over time. Percentages can also represent parts of a whole, such as the proportion of people answering a question in the same way.
TYPES ON CHARTS 



TYPES ON CHARTS Charan kumar The document defines different types of charts and their uses. Column charts display changes over time and compare items in a group. Bar charts focus on comparing item values rather than time. Line charts show trends over intervals of time. Pie charts show the size of items in a data series. Scatter charts illustrate the relationship between numeric values. Area charts signify magnitude of change over time and contribution to a whole. Stock charts display high, low, and close values in the stock market.
Ways of presenting information



Ways of presenting informationIbrahem Abdel Ghany Diagrams, charts, tables, and graphs are common ways to present information graphically. Diagrams can summarize processes and ideas more effectively than words. Charts such as bar charts and line graphs represent numerical data visually. Tables display key information, usually numbers, and can summarize data or start discussions. Graphs show patterns and trends when precise numbers are not needed.
Charts, Graphs and Tables



Charts, Graphs and TablesLiliyaNersesyan This document provides information about different types of charts and graphs used to represent data visually, including pie charts, line graphs, bar charts, and tables. It explains what each of these graphical representations are through definitions and examples. Pie charts show percentages, line graphs show changes over time, bar charts show comparisons of discrete categories, and tables arrange data into rows and columns. The document is intended to teach about various ways to visually display quantitative information through graphical formats.
Dot Plot Presentation



Dot Plot PresentationDr. Amjad Ali Arain Topic: Dot Plot Presentation
Student Name: Misbah
Class: B.Ed. 2.5
Project Name: “Young Teachers' Professional Development (TPD)"
"Project Founder: Prof. Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Faculty of Education, University of Sindh, Pakistan
Interpreting charts and graphs



Interpreting charts and graphslesliejohnson441 This document discusses how to interpret charts and graphs. It explains that graphics provide information in a compact way compared to text. It identifies the most common types of graphs as line graphs, bar graphs, and pie charts. It also discusses tables and diagrams. The document emphasizes that graphics contain important information that supports the reading material, so readers should take time to carefully analyze charts, graphs, and tables.
Charts in MS Excel



Charts in MS ExcelRishi Kumar Gupta This document discusses different types of charts that can be created in Microsoft Excel. It describes pie charts, column charts, line charts, bar charts, area charts, scatter charts, and other chart types. For each type of chart, it provides an example image and brief explanation of when and how it can be used. The document is intended to teach about the various charting capabilities in MS Excel.
Types of Chart



Types of Chartchartblocks Curious about the different types of chart? This presentation demonstrates the variety of charts and their purpose. All these charts have been created using Chartblocks online chart building tool.
Understanding visual information:Figure, Graph, Table, and Diagram



Understanding visual information:Figure, Graph, Table, and DiagramMusfera Nara Vadia This document discusses different types of visual information including figures, graphs, tables, and diagrams. It defines two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures. It also describes the most common types of graphs such as pie charts, bar graphs, scatter plots, and line graphs. Tables are explained as presenting lists of numbers or text in columns to synthesize information or present raw data. Diagrams are defined as using graphic images to present theoretical arguments visually.
Types Of Charts



Types Of Chartswmassie This document discusses six common types of charts used in business: column chart, stacked bar chart, line chart, XY scatter plot, pie chart, and exploded pie chart. It defines each chart and provides examples to illustrate the type of data each chart is best suited to display. The column chart compares groups of data. The stacked bar chart shows the contribution of parts to a whole. The line chart indicates trends over time. The XY scatter plot shows correlations between two variables. The pie chart displays the percentage of parts in a whole. The exploded pie chart emphasizes portions of a pie chart.
Charts And Graphs



Charts And GraphsHimadri Shekhar This document discusses different types of charts and graphs that can be used to visually represent data. It provides examples of pie charts, bar charts, column charts, line charts, area charts, and scatter plots. Reasons for creating charts include making trends easily recognizable, allowing quick perception of information, and aiding data interpretation. Charts can be incorporated into business reports, web pages, posters, and other documents. Proper selection of charts is important to illustrate different types of data, such as time series data displayed in line graphs or comparisons shown in bar charts.
Charts and graphs in excel



Charts and graphs in excelIqra Nehal this ppt is about charts in ms excel.there are many types of chart used in ms excel but in this ppt some common types are defined,as line chart,bar,column,area ,scatter chart etc...
Charts and graphs



Charts and graphsAda Marie Tayao This document discusses various types of charts and graphs, including organizational charts, classification charts, timelines, flowcharts, and tabular charts. It provides examples of each type of chart. The document also discusses the purpose of charts, how to design effective charts, and software that can be used to create charts and graphs, such as OpenOffice Calc and Microsoft Excel.
Top 8 Different Types Of Charts In Statistics And Their Uses



Top 8 Different Types Of Charts In Statistics And Their UsesStat Analytica This document discusses different types of charts used in statistics to visually represent data, including bar charts, line charts, pie charts, histograms, scatter plots, exponential graphs, and trigonometric graphs. Bar charts and line charts are useful for comparing data across categories and showing trends over time. Pie charts show proportions of data as slices of a circle. Histograms group data into bins to summarize continuous or discrete measurements. Scatter plots show the relationship between two numeric variables using positioned dots. Exponential and trigonometric graphs visually represent their respective functions and are used in engineering and research.
Types of Charts



Types of ChartsLoyd Calangan The document describes different types of charts that can be used to visualize data, including column charts, bar charts, line charts, pie charts, XY charts, area charts, doughnut charts, surface charts, bubble charts, stock charts, and cylinder, cone or pyramid charts. It provides examples of subtypes for some chart types and explains what each chart shows or compares.
Choosing the Right Graphs



Choosing the Right GraphsOdogray There are several types of graphs that can be created in Excel, each suited to displaying different types of data. Bar graphs and line graphs are commonly used to show changes in numerical data over time or between categories. Scatter plots show trends in large data sets, while pie charts represent percentages and are used to show how parts of a whole are divided.
The uses of Tables & graphs



The uses of Tables & graphsFranco Jesús This document discusses how to improve the clarity of tables and graphs in research articles. It provides rules for constructing clear tables, such as splitting large tables and standardizing layout. When presenting tables, common problems to avoid are poorly positioning them on the page and manipulating spacing. Both tables and their contents should be explained in the text. The document also covers best practices for visualizations like pie charts, bar charts, and line graphs, noting tables are best for exact numbers while graphs show trends.
TID Chapter 5 Introduction To Charts And Graph



TID Chapter 5 Introduction To Charts And GraphWanBK Leo This document discusses different types of charts and graphs that can be used to represent data visually. It describes common chart types like pie charts, bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots. The document explains how each type of chart is best used depending on the nature of the data and the insights that need to be conveyed. It also provides guidance on creating charts in Excel and includes an example of a hands-on exercise for practicing generating different chart types from sample data sets.
Charts in Microsoft Excel



Charts in Microsoft ExcelRosary High School, Vadodara Charts in Excel can display data in a more visually appealing and easy to understand format compared to tables of numbers. There are many components that make up a chart, including axes, data series, plot area, legend and more. Excel offers different types of charts, such as column, bar, line, area, pie, doughnut, scatter, radar, surface and stock charts, each suited to displaying certain types of data trends over time or in relation to other factors.
Charts in excel



Charts in excelJithin Krishnan Area charts display changes in magnitude over time using colored areas below lines. They can be 2D or 3D, stacked to show contribution, or 100% stacked to show percentage contribution over time. Scatter charts show relationships between numeric variables and are used for scientific data. Bubble charts are like scatter charts but show three variables where the third determines bubble size. Stock charts illustrate price fluctuations over time using high, low, close values or including open and volume values.
Similar to Top 7 types of Statistics Graphs for Data Representation (20)
Introduction to Statistics information.pptx



Introduction to Statistics information.pptxHarshiHarshika1 It helps to you understand about statistics and helps in acquiring knowledge and helps to analysing the answers , and in the present generation helps to study about statistics
Graphicalrepresntationofdatausingstatisticaltools2019_210902_105156.pdf



Graphicalrepresntationofdatausingstatisticaltools2019_210902_105156.pdfHimakshi7 The document discusses graphical representation of data using statistical tools. It describes different types of graphs like bar charts, pie charts, scatter plots, and line charts. It explains how to select the appropriate graph based on the type of data and analyze the data. It also discusses limitations of graphs and statistical analysis methods like calculating mean and standard deviation to analyze data in a robust way.
Graphical Displays of Data



Graphical Displays of DataCumberland County Schools This document discusses various methods for graphically displaying data in statistics, including time series graphs, bar charts, histograms, circle graphs, dot plots, stem plots, ogives, and indicators of misleading graphs. It provides examples and descriptions of how to properly interpret and construct each type of graph. Key points include showing change over time with time series graphs, comparing categories with bar charts, displaying continuous or binned data with histograms, showing percentages with circle graphs, listing all values with dot and stem plots, and calculating cumulative frequencies with ogives. Misleading graphs are identified as those that distort scale, lack labels, omit data, or have uneven bins.
Lab file on research methodology



Lab file on research methodologySukhchain Aggarwal This document is a lab file submitted by Sukhchain Aggarwal, a student of B.com, to their professor Harjeet Kaur. It contains an acknowledgement thanking the professors for their guidance. The document then outlines how to create different types of charts in Microsoft Excel, including line charts, bar charts, and pie charts. It provides examples of each chart type using sample data on test scores and the numbers of students in different years. Tables are included showing average, maximum, and minimum values calculated from the data using Excel formulas. Sources consulted for the file are listed in a bibliography.
Macromolecules



Macromoleculesganctil The document discusses different types of graphs used in science: line graphs, bar graphs, and pie graphs. It explains that graphs are useful for organizing and analyzing quantitative data by showing relationships and allowing scientists to identify patterns and make predictions. The key types are defined as follows: line graphs show the relationship between two variables over time; bar graphs compare data categories; and pie graphs divide a whole into percentage parts to visualize proportions. Examples of each type are provided.
Bigdata



Bigdatasakthibalabalamuruga This document provides an overview of different types of charts used for data visualization, including column charts, bar charts, pie charts, doughnut charts, line charts, area charts, scatter charts, spider/radar charts, gauge charts, and comparison charts. It describes the purpose and use of each chart type, highlighting when each type is most effective to visualize different kinds of data relationships. The document aims to help readers select the most appropriate chart type based on their data and visualization goals.
Statistics



Statisticsdiereck This document discusses different types of graphs used to present statistical data. It provides examples and guidelines for bar graphs, pie charts, histograms, line graphs, and pictographs. Bar graphs can show categorical data and frequencies. Pie charts represent qualitative data through wedge-shaped slices. Histograms use bars to depict continuous data grouped into ranges or classes. Line graphs illustrate relationships that change over time. Pictographs use images to demonstrate quantities. Being able to interpret and construct these various graphs is important for analyzing real-world data.
Uses of graph



Uses of graphNimraKhan91 Graphs are pictorial representations that organize data visually. There are four main types of graphs: line graphs, bar graphs, histograms, and pie charts. Graphs are widely used in fields like business, science, and medicine to clarify trends, estimate key values at a glance, see variations in data, and permit visual checks of calculations. They show relationships between variables and are useful for comparing data across groups or tracking changes over time.
Business Anaytics lecture notes1.docx (2).pptx



Business Anaytics lecture notes1.docx (2).pptxkiruthikan18 Fyhckmvbnshsusbdhdhdhdnshdvdudjdbdvdvdbd r e. Endudndndjdidmrbrkd rhdbedv ku hi egg s dn
12 ways to visalize data



12 ways to visalize dataSisense Eliminate bad graphs and charts! Learn how to find the best way to visualize data and get your message across for your business scenario.
Bar Graph



Bar GraphSalahaddin University - Erbil The document discusses different types of bar graphs, including vertical, horizontal, stacked, and grouped bar graphs. It provides examples of how to represent data using bar graphs and tips for creating bar graphs. Some key points covered include that bar graphs show data using rectangular bars of varying heights, they can represent categorical or quantitative data, and they are useful for comparing quantities across different categories.
seminar.pptx



seminar.pptxDilkashMittal1 Graphical representations are useful tools for presenting statistical data in a visual format that is easier to understand compared to textual or tabular representations. They translate complex numerical concepts into simple, concrete forms through the use of diagrams, charts, and plots. Some key advantages of graphical representations are that they facilitate comparisons, help identify relationships and patterns in the data, and attract attention in a time-efficient manner. However, they also have limitations such as only conveying vague ideas, providing limited precision and information, and restricting further data analysis. Common types of graphical representations used in statistics include histograms, frequency polygons, pie charts, scatter plots, and time series graphs.
Artificial Intelligence - Data Analysis, Creative & Critical Thinking and AI...



Artificial Intelligence - Data Analysis, Creative & Critical Thinking and AI...Deboshree Chatterjee This PPT is about AI Values, Data Analysis, and Creative & Critical Thinking in Artificial Intelligence.
Making Sense of Data - 3rd Sector Learning Lab



Making Sense of Data - 3rd Sector Learning LabImprovement Skills Consulting Ltd. This document provides an overview of data visualization techniques that can help non-technical audiences understand and make sense of data. It discusses the importance of selecting the right chart type for the data, such as using histograms to show variation, line graphs for trends over time, and Pareto charts to identify the vital few causes of issues. The document also covers techniques for smoothing time series data, such as moving averages, to identify underlying trends. The goal is to help organizations at all levels make better decisions and improve performance through effective data communication and interpretation.
BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE AND DATA ANALYTICS presentation



BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE AND DATA ANALYTICS presentationMohit Negi SIX SIGMA APPROACH, DIFFERENT TYPES OF CHARTS AND THEIR FUNCTION, DASHBOARD, BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE, DATA VISUALISATION INFORMATION VISUALISATION, PERFORMANCE DASHBOARD, BUSINESS REPORTING, BALANCE SCORECARD
Visual Aids.pptx



Visual Aids.pptxVinothKumarasamy2 The document discusses the importance and uses of visual aids in communication. It notes that visual aids like illustrations, tables, graphs and diagrams are more effective than plain text alone. They help reduce space, increase understanding and make complex ideas and data more easily comprehensible. The document also provides examples of different types of visual aids like tables, bar graphs, flowcharts and maps and discusses when and how they should be used.
Organizing And Presenting Data.pptx



Organizing And Presenting Data.pptxVanessaRobante This PowerPoint presentation is about organizing and presenting data. It will show you which types of graphs to use when presenting your data. Feel free to save and share it! Please do like my PPT THANKS!!
All pictures and descriptions are from Google (I can't find the links).
note: this presentation doesn't have complete information about organizing and presenting data and only shows important pieces of information about organizing and presenting data and the common graphs that are used in data presentation.
Ad
More from Stat Analytica (20)
Visual studio vs visual studio code



Visual studio vs visual studio codeStat Analytica Understanding between Visual Studio vs Visual Studio Code may depend on your work style and features and the language support you need. Here's the difference.
Excel Homework Help



Excel Homework HelpStat Analytica Do you need Excel homework help? Hire our MS Excel experts to get the best Help With Excel Homework. Ask us to do my Excel Homework at affordable prices.
Mba essay writing services



Mba essay writing servicesStat Analytica Statanalytica is a group of experts who are offering the best help with statistics on statistics assignment help and statistics homework help
Prominent steps of how to solve ratios with useful examples



Prominent steps of how to solve ratios with useful examplesStat Analytica Ratio is the comparison between a single term to another term. Learn the useful methods for how to solve ratios. So check all steps.
Ultimate guide to how to finish your homework faster



Ultimate guide to how to finish your homework fasterStat Analytica Procrastinating homework? Follow these tips and guides on How to finish your homework faster without any additional help from anyone.
Top tips on python programming for the absolute beginner



Top tips on python programming for the absolute beginnerStat Analytica Python is an object oriented and leading programming language of the world. Learn python programming for the absolute beginner.
Most prominent methods of how to find outliers in statistics



Most prominent methods of how to find outliers in statisticsStat Analytica This document discusses two prominent methods for finding outliers in statistics: the interquartile range (IQR) method and the Tukey method. Both methods use quartiles to determine a range of values that are not outliers, and then identify outliers as any data points that fall above or below this range. The document provides examples of each method being applied to sample data sets to identify outlier values. It concludes by encouraging the use of these IQR and Tukey methods to solve problems involving outliers.
Statistics for economics its benefits and limitations



Statistics for economics its benefits and limitationsStat Analytica Statistics is playing a crucial role in economics. Here we have defined the benefits and limitation of statistics in economics.
Major types of statistics terms that you should know



Major types of statistics terms that you should knowStat Analytica There are hundreds of statistics terms in the world. But here we have discussed the major statistics terms that is quite helpful for the students.
The Most Important Statistics for R to Get Started With Data Science



The Most Important Statistics for R to Get Started With Data ScienceStat Analytica Do you want to learn R for data science? If yes then here we have metioned the basic statistics for R to get started with data science.
Top 10 statistics tools to get better data insights



Top 10 statistics tools to get better data insightsStat Analytica Want to know the best statistics tools for data analytics and data science? Here we have given the detailed overview of statistics tools.
The Comprehensive Guide on Branches of Mathematics



The Comprehensive Guide on Branches of MathematicsStat Analytica Are you struggling to get all the branches of mathematics? If yes then here is the best ever presentation that will help you to get all the branches of math. Here we have mentioned the basic mathematics branches to the advanced level.
Top 10 importance of mathematics in everyday life



Top 10 importance of mathematics in everyday lifeStat Analytica Would you like to know the importance of mathematics? If yes, then have a look at this presentation to explore the top uses of mathematics in our daily life. Watch the presentation till the end to explore the importance of mathematics.
Classification of Data in Statistics 



Classification of Data in Statistics Stat Analytica The document discusses data classification, which involves organizing data into categories to make it easier to analyze and retrieve. It covers the objectives of classification like arranging large volumes of data and highlighting similarities. The key types are one-way, two-way, and multi-way classification. Classification provides benefits like confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Methods involve scanning, identifying, separating data, and creating a classification policy.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) everything you need to know



Analysis of variance (ANOVA) everything you need to knowStat Analytica Most of the students may struggle with the analysis of variance (ANOVA). Here in this presentation you can clear all your doubts in analysis of variance with suitable examples.
The Basics of Statistics for Data Science By Statisticians



The Basics of Statistics for Data Science By StatisticiansStat Analytica Want to learn data science, but don't know how to start learn data science from scratch? Here in this presentation you will going to learn the basics of statistics for data science. Start learn these basic statistics to get the good command over data science.
Top tips on how to learn math with these simple ways



Top tips on how to learn math with these simple waysStat Analytica Finding it difficult to learn math? If yes, then here are the best ever tips on how to learn math from basic to the advanced level. Follow all these tips to start leaning math and get decent command over math.
What are the uses of excel in our daily life?



What are the uses of excel in our daily life?Stat Analytica Excel is one of the most powerful spreadsheet software in the world. There are plenty of uses of excel in our daily life. Have a look on the top uses of excel in the world. Watch the presentation till the end to explore all the uses of excel.
Top 3 Tips on How to Solve Math Problems



Top 3 Tips on How to Solve Math ProblemsStat Analytica Math is a subject which is simple for some students and also complicated for some students, so we will discuss a topic related to math that How to solve math problems and which types of math problems can we solve quickly by step by step. In many ways, Math problems can be solved, but now the question is how to solve math problems.
If you want math homework help than you can get the math homework helpers here. Homework help in math from our experts and homework help with math gives the perfect math homework help online. My math homework help is the best way to get help me math homework. college math homework help also available here.
The Best Ever Tips on How to Study for Exams



The Best Ever Tips on How to Study for ExamsStat Analytica Only a few week left for the exams. Do you want to get the best ever tips on how to study for exams? Here are the best among the best tricks on how to study for exams. Follow all these tips mentioned in the presentation to do the proper study for exams.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 795 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 95 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
Michelle Rumley & Mairéad Mooney, Boole Library, University College Cork. Tra...



Michelle Rumley & Mairéad Mooney, Boole Library, University College Cork. Tra...Library Association of Ireland
Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s Guide



Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s GuideGS Virdi Dive into the fundamentals of P–N junctions, the heart of every diode and semiconductor device. In this concise presentation, Dr. G.S. Virdi (Former Chief Scientist, CSIR-CEERI Pilani) covers:
What Is a P–N Junction? Learn how P-type and N-type materials join to create a diode.
Depletion Region & Biasing: See how forward and reverse bias shape the voltage–current behavior.
V–I Characteristics: Understand the curve that defines diode operation.
Real-World Uses: Discover common applications in rectifiers, signal clipping, and more.
Ideal for electronics students, hobbyists, and engineers seeking a clear, practical introduction to P–N junction semiconductors.
Unit 6_Introduction_Phishing_Password Cracking.pdf



Unit 6_Introduction_Phishing_Password Cracking.pdfKanchanPatil34 Initial stages of attacks, Phishing, Password Cracking, guidelines to prevent password attacks, Strong password, weak password,
Quality Contril Analysis of Containers.pdf



Quality Contril Analysis of Containers.pdfDr. Bindiya Chauhan Quality control test for containers, rubber closures and secondary packing materials.
One Hot encoding a revolution in Machine learning



One Hot encoding a revolution in Machine learningmomer9505 A brief introduction to ONE HOT encoding a way to communicate with machines
Presentation of the MIPLM subject matter expert Erdem Kaya



Presentation of the MIPLM subject matter expert Erdem KayaMIPLM Presentation of the MIPLM subject matter expert Erdem Kaya
Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...



Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...Library Association of Ireland Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services Clare Doyle - Cork City Libraries
How to track Cost and Revenue using Analytic Accounts in odoo Accounting, App...



How to track Cost and Revenue using Analytic Accounts in odoo Accounting, App...Celine George Analytic accounts are used to track and manage financial transactions related to specific projects, departments, or business units. They provide detailed insights into costs and revenues at a granular level, independent of the main accounting system. This helps to better understand profitability, performance, and resource allocation, making it easier to make informed financial decisions and strategic planning.
Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdf



Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdfSandeep Swamy Exploring Substances:
Acidic, Basic, and
Neutral
Welcome to the fascinating world of acids and bases! Join siblings Ashwin and
Keerthi as they explore the colorful world of substances at their school's
National Science Day fair. Their adventure begins with a mysterious white paper
that reveals hidden messages when sprayed with a special liquid.
In this presentation, we'll discover how different substances can be classified as
acidic, basic, or neutral. We'll explore natural indicators like litmus, red rose
extract, and turmeric that help us identify these substances through color
changes. We'll also learn about neutralization reactions and their applications in
our daily lives.
by sandeep swamy
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 817 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 97 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 817 (As of 05/3/2025)
• Texas: 688 (+20)(62% of these cases are in Gaines County).
• New Mexico: 67 (+1 )(92.4% of the cases are from Eddy County)
• Oklahoma: 16 (+1)
• Kansas: 46 (32% of the cases are from Gray County)
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 97 (+2)
• Texas: 89 (+2) - This is 13.02% of all TX cases.
• New Mexico: 7 - This is 10.6% of all NM cases.
• Kansas: 1 - This is 2.7% of all KS cases.
DEATHS: 3
• Texas: 2 – This is 0.31% of all cases
• New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.54% of all cases
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 967 (Confirmed and suspected):
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD (As of 4/2/2025)
• Mexico – 865 (+58)
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 844 (+58) cases, 3 hospitalizations, 1 fatality
• Canada: 1531 (+270) (This reflects Ontario's Outbreak, which began 11/24)
‒Ontario, Canada – 1243 (+223) cases, 84 hospitalizations.
• Europe: 6,814
CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - Worksheet



CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - WorksheetSritoma Majumder Introduction
All the materials around us are made up of elements. These elements can be broadly divided into two major groups:
Metals
Non-Metals
Each group has its own unique physical and chemical properties. Let's understand them one by one.
Physical Properties
1. Appearance
Metals: Shiny (lustrous). Example: gold, silver, copper.
Non-metals: Dull appearance (except iodine, which is shiny).
2. Hardness
Metals: Generally hard. Example: iron.
Non-metals: Usually soft (except diamond, a form of carbon, which is very hard).
3. State
Metals: Mostly solids at room temperature (except mercury, which is a liquid).
Non-metals: Can be solids, liquids, or gases. Example: oxygen (gas), bromine (liquid), sulphur (solid).
4. Malleability
Metals: Can be hammered into thin sheets (malleable).
Non-metals: Not malleable. They break when hammered (brittle).
5. Ductility
Metals: Can be drawn into wires (ductile).
Non-metals: Not ductile.
6. Conductivity
Metals: Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Non-metals: Poor conductors (except graphite, which is a good conductor).
7. Sonorous Nature
Metals: Produce a ringing sound when struck.
Non-metals: Do not produce sound.
Chemical Properties
1. Reaction with Oxygen
Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides.
These metal oxides are usually basic.
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides.
These oxides are usually acidic.
2. Reaction with Water
Metals:
Some react vigorously (e.g., sodium).
Some react slowly (e.g., iron).
Some do not react at all (e.g., gold, silver).
Non-metals: Generally do not react with water.
3. Reaction with Acids
Metals react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
Non-metals: Do not react with acids.
4. Reaction with Bases
Some non-metals react with bases to form salts, but this is rare.
Metals generally do not react with bases directly (except amphoteric metals like aluminum and zinc).
Displacement Reaction
More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their salt solutions.
Uses of Metals
Iron: Making machines, tools, and buildings.
Aluminum: Used in aircraft, utensils.
Copper: Electrical wires.
Gold and Silver: Jewelry.
Zinc: Coating iron to prevent rusting (galvanization).
Uses of Non-Metals
Oxygen: Breathing.
Nitrogen: Fertilizers.
Chlorine: Water purification.
Carbon: Fuel (coal), steel-making (coke).
Iodine: Medicines.
Alloys
An alloy is a mixture of metals or a metal with a non-metal.
Alloys have improved properties like strength, resistance to rusting.
Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdf



Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdfArab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport This version of the lectures is provided free of charge to graduate students studying the Operations Management course at the MBA level.
LDMMIA Reiki Master Spring 2025 Mini Updates



LDMMIA Reiki Master Spring 2025 Mini UpdatesLDM Mia eStudios As of Mid to April Ending, I am building a new Reiki-Yoga Series. No worries, they are free workshops. So far, I have 3 presentations so its a gradual process. If interested visit: https://www.slideshare.net/YogaPrincess
https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
Blessings and Happy Spring. We are hitting Mid Season.
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan. This chapter provides an in-depth overview of the viscosity of macromolecules, an essential concept in biophysics and medical sciences, especially in understanding fluid behavior like blood flow in the human body.
Key concepts covered include:
✅ Definition and Types of Viscosity: Dynamic vs. Kinematic viscosity, cohesion, and adhesion.
⚙️ Methods of Measuring Viscosity:
Rotary Viscometer
Vibrational Viscometer
Falling Object Method
Capillary Viscometer
🌡️ Factors Affecting Viscosity: Temperature, composition, flow rate.
🩺 Clinical Relevance: Impact of blood viscosity in cardiovascular health.
🌊 Fluid Dynamics: Laminar vs. turbulent flow, Reynolds number.
🔬 Extension Techniques:
Chromatography (adsorption, partition, TLC, etc.)
Electrophoresis (protein/DNA separation)
Sedimentation and Centrifugation methods.
How to Manage Opening & Closing Controls in Odoo 17 POS



How to Manage Opening & Closing Controls in Odoo 17 POSCeline George In Odoo 17 Point of Sale, the opening and closing controls are key for cash management. At the start of a shift, cashiers log in and enter the starting cash amount, marking the beginning of financial tracking. Throughout the shift, every transaction is recorded, creating an audit trail.
Handling Multiple Choice Responses: Fortune Effiong.pptx



Handling Multiple Choice Responses: Fortune Effiong.pptxAuthorAIDNationalRes INTRO TO STATISTICS
INTRO TO SPSS INTERFACE
CLEANING MULTIPLE CHOICE RESPONSE DATA WITH EXCEL
ANALYZING MULTIPLE CHOICE RESPONSE DATA
INTERPRETATION
Q & A SESSION
PRACTICAL HANDS-ON ACTIVITY
apa-style-referencing-visual-guide-2025.pdf



apa-style-referencing-visual-guide-2025.pdfIshika Ghosh Title: A Quick and Illustrated Guide to APA Style Referencing (7th Edition)
This visual and beginner-friendly guide simplifies the APA referencing style (7th edition) for academic writing. Designed especially for commerce students and research beginners, it includes:
✅ Real examples from original research papers
✅ Color-coded diagrams for clarity
✅ Key rules for in-text citation and reference list formatting
✅ Free citation tools like Mendeley & Zotero explained
Whether you're writing a college assignment, dissertation, or academic article, this guide will help you cite your sources correctly, confidently, and consistent.
Created by: Prof. Ishika Ghosh,
Faculty.
📩 For queries or feedback: [email protected]
Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...



Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...Library Association of Ireland
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Michelle Rumley & Mairéad Mooney, Boole Library, University College Cork. Tra...



Michelle Rumley & Mairéad Mooney, Boole Library, University College Cork. Tra...Library Association of Ireland
Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...



Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...Library Association of Ireland
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdf



Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdfArab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan.
Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...



Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...Library Association of Ireland
Top 7 types of Statistics Graphs for Data Representation
- 1. 01 Top 7 Types of Statistics Graphs for Data Representation Statanalytica 01
- 2. Overview Statistics is one of the most crucial parts of our life. Without statistics, data is nothing. We can’t utilize different data without the use of statistics. Therefore the significant role of statistics is to represent the data in a meaningful way. In this way, anyone can understand the data without in-depth knowledge of statistics. Most of the time, the statistics data sets contain massive amounts of values. It is hard to represent these values in the form of lists and articles. That is why the graphs come into existence to represent the aggregate statistic value in clean and well-managed order. Here in this blog, we will share with you the top 7 types of statistics graphs commonly used in statistics. 02 02
- 3. A Pareto diagram is also known as a bar chart. It is the best way to represent the qualitative data. It was developed in the early 1900s by Vilfredo Pareto. He used this graph to conduct his study on wealth and poverty. This chart offers two ways to display the data. You can either represent the data horizontally or vertically. You can use it to compare data, such as amounts, characteristics, times, and frequency. The bar of this graph is emphasized with essential categories. You can quickly get an idea from this bar that which category has the highest amount of data. There are three types of bars in this chart i.e., single, stacked, and grouped. Pareto Diagram or Bar Graph 03 03
- 4. A circle graph is also known as Pie charts. It is also one of the widely used statistics graphs in the world. Statisticians commonly used these graphs to represent the data graphically. As the name suggests, this graph looks like a circular pie with a few slices. Besides, we use this type of statistics graph to represent that qualitative data. Qualitative data means the data is not presented in numerical form. Besides, we put the different categories in each slice of the pie. The size of slices varies upon the data. Some slices might be more significant, and some might be smaller. Pie Chart or Circle Graph 04 04
- 5. The histogram is another best statistics graph to represent the data. We use it to express quantitative data. In this graph, the range of values is known as classes. If the classes contain the lower frequencies, then it would have the shorter as compared with the taller ones that contain, the higher frequency. Most of the students get confused with the bar chart and the histogram. Because both of these look quite similar. But these graphs are different from each other in terms of the data measurement levels. In bar charts, the frequency of categorical data is the primary factor. While in the histogram, the data with ordinal values are the primary factor. Ordinal values are not easily measured i.e., feelings, opinions, suggestions. Histogram 05 05
- 6. A stem and leaf plot is one of the best statistics graphs to represent the quantitative data. This graph breaks each value of a quantitative data set into two pieces. These pieces are often known as the stem and the leaf. Furthermore, the higher places values are known as the stem, and the other places values are known as the leaf. We can list all the data values in a compact form with the help of this graph. It is a device that is used to represent the data set. It evolved in the early 1900s from Arthur Bowley’s work. Most of the statisticians use it for data analysis work. Stem and Leaf Plot 06 06
- 7. It is not that much of a famous statistics graph. Most of the experts say that it is a hybrid of the histogram and a stem and leaf plot. In this type of graph, each value is represented as the dot, and this dot is placed above the appropriate class. We use this graph to represent quantitative data values. Likewise, we use the rectangles and bars in histograms. In the same way, we use the dots which are joined with the help of simple lines. We use these graphs to compare the data of many individuals. Dot Plot 07 07
- 8. Scatterplots graphs are one of the famous statistics graphs that use in most of the powerful statistics software. It is used to display data based on the horizontal axis and vertical axis. I have mentioned earlier that the statistics tools of correlation of regression are used to show trends with the scatterplot. In the scatterplot, the lines or curve is used to show the data. This chart goes upside down and left to right. Scatter means to place the points at different places to each other. It is the statistics chart to uncover the potential of the dataset. Scatterplots 08 08
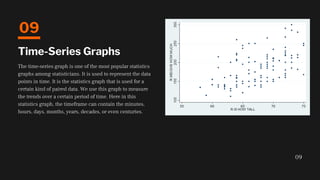
- 9. The time-series graph is one of the most popular statistics graphs among statisticians. It is used to represent the data points in time. It is the statistics graph that is used for a certain kind of paired data. We use this graph to measure the trends over a certain period of time. Here in this statistics graph, the timeframe can contain the minutes, hours, days, months, years, decades, or even centuries. Time-Series Graphs 09 09
- 10. Conclusion All these seven types of statistics graphs are the major ones. Apart from that, there are other types of statistics graphs, too i.e., the statistics bar graphs, statistics misleading graphs, statistics line graphs, and even statistics bad graphs. Most of the statistics students are also well aware of exponentials graphs, logarithmic graphs, trigonometric graphs, cartesian graphs, and frequency distributions graphs. Now you will be more confident about the use of graphs for different kinds of data. At last, I would like to say that you should use the right statistics graph as per your data set. 10 10




