Angular - Chapter 2 - TypeScript Programming
- 3. www.webstackacademy.com What is TypeScript? • JavaScript has grown beyond its original idea of front-end language to bring interactivity • As JavaScript code grows, it tends to get messier due to its shortcomings (ex: Not strongly typed) • Some of the key OO features are missing (ex: Classes) • TypeScript was presented to bridge this gap - "JavaScript for application-scale development" • Aligned with ECMA6 specification, whereas JavaScript is aligned with ECMA5 • TypeScript is a compiled languages generates JavaScript as the output program (Transpiler) • Angular programming is done using TypeScript
- 4. www.webstackacademy.com Why use TypeScript? - Advantages • Compiled language: Early defect checking (unlike JavaScript). Leverage tooling benefit. • Strong type checking: No more discounts. Declare a variable and use it only for storing a particular type. • Support for (missing) OO features: Classes, Interfaces, Access modifiers etc.. • Quality: Get it early, scale better • JavaScript Everywhere: Realize it practically • The goal of this chapter is NOT to introduce all the features of the TypeScript. • Let us take a quick hands-on approach to some of the key differentiating features • Certain specific use-cases we can learn during Angular.
- 5. www.webstackacademy.com Writing your first TypeScript program • Writing your first TypeScript requires certain development environment to be available. Major components include TypeScript compiler (tsc), Node.js (node) and Editor (VS code or similar). • All TypeScript files to have *.ts extension (ex: my_program.ts) which generates *.js file as output • The compilation step will throw errors in case of any issue (similar to Java, compiled language) • In case your program is successfully compiled, corresponding my_program.js will be created • U can verify this by performing a "ls" command in your current directory • This is what we mean by TypeScript getting “transpiled” into JavaScript $ tsc my_program.ts // Compile the program $ node my_program.js // Run the program
- 6. www.webstackacademy.com YOUR first TypeScript program – Take a note! • You are executing JavaScript using command line, run-time environment (Node) • This is the fundamental difference what you have done so far (Using browser to run your JavaScript program) • You cannot use any DOM / BOM APIs (ex: document.write() / windows.prompt() etc..) as you are NOT operating in the browser environment • To take use input however there are other options available, will discuss it in later chapters
- 7. www.webstackacademy.comwww.webstackacademy.com TypeScript Features (Major OOP facilities, which you missed in JavaScript)
- 8. www.webstackacademy.com TypeScript – What are the key differences? There are many key differentiating features / facilities available in TypeScript, which are not there in JavaScript. Here is a list, which we need to take a deep dive by getting hands-on • Types: Annotation, Enumeration, Assertion • Functions: Parameter passing & Return type (with types), Arrow Functions (Used in Angular) • OOP: Interface, Classes, Constructors, Access modifiers • Modules: Re-using / sharing modules across different files
- 10. www.webstackacademy.com Type Annotation • Types are annotated using :TypeAnnotation syntax. If any other type is assigned TypeScript compiler will throw error • This strict type-checking is applied for primitive types, array, function parameters, interfaces etc.. • Please note the program will still go ahead and compile, you may still be able to generate JS • By looking into VS editor also will give you some clues about errors • In large scale applications not having strict type checking might create issues • Developer can mistakenly override the values, which may have some unexpected side-effects
- 11. www.webstackacademy.com The “let” and “var” • The keyword let was included in ECMA6, which is similar to var but there are some differences • The main difference is scoping: var is scoped to the nearest function block let is scoped to the nearest enclosing block Both are global if outside any block • Variables declared with let are not accessible before they are declared in their enclosing block, which will throw an exception. Along with that var has got many other side-effects (ex: timer functions), hence in TypeScript it is better to avoid and start using let • Please note when there are issued with let, the TypeScript compiler goes and still generates the JavaScript file. But the main goal is to avoid certain obvious coding mistakes.
- 12. www.webstackacademy.com The “let” and “var” - Example // Note the scope differences function scopeTesting() { var testVar = 100; for (let testLet = 0; testLet <= 10; testLet++) { console.log ("The value of Let " + testLet); console.log ("The value of Var " + testVar); } console.log ("The value of Var" + testLet); console.log ("The value of Var" + testVar); }
- 13. www.webstackacademy.com The Type Annotation // Let usage with type annotation let myNumber: number; let myString: string; // Get early indication of issues myNumber = 'a'; myString = 100; console.log(myNumber); console.log(myString); // Let usage gives error myLetTest = 100; let myLetTest; // Usage of any let anyTest: any; // No issues here anyTest = '123'; anyTest = 123; let myBoolArray: boolean[]; myBoolArray = [true, false]; myBoolArray[0] = 'false'; // Error myBoolArray[1] = 'true'; // Error
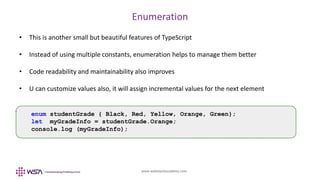
- 14. www.webstackacademy.com Enumeration • This is another small but beautiful features of TypeScript • Instead of using multiple constants, enumeration helps to manage them better • Code readability and maintainability also improves • U can customize values also, it will assign incremental values for the next element enum studentGrade { Black, Red, Yellow, Orange, Green}; let myGradeInfo = studentGrade.Orange; console.log (myGradeInfo);
- 15. www.webstackacademy.com Type Assertion • The goal of type annotation is to ensure developers use right types and prevent mistakes • However TypeScript allows you to override it by a mechanism called 'Type Assertion' • It tells the compiler that you know about the type very well, hence there should not be an issue • At first sight 'Type Assertion' will look similar to 'Type casting' (provided by languages like C) but there is a slight difference between them • Type casting generally requires runtime support. Type assertions are purely a compile time construct • It provides hints to the compiler on how you want your code to be analysed
- 16. www.webstackacademy.com Type Assertion - Example let myNumber: number; // Only number can be stored let myStr: string; // Only string can be stored myNumber = 123; myStr = <string> myNumber; // Type assertion console.log (myNumber); console.log (myStr);
- 17. www.webstackacademy.comwww.webstackacademy.com Functions (Parameter passing, Arrow functions, Overloading)
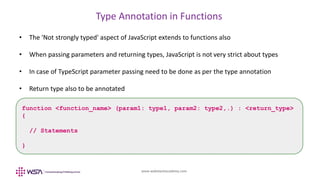
- 18. www.webstackacademy.com Type Annotation in Functions • The 'Not strongly typed' aspect of JavaScript extends to functions also • When passing parameters and returning types, JavaScript is not very strict about types • In case of TypeScript parameter passing need to be done as per the type annotation • Return type also to be annotated function <function_name> (param1: type1, param2: type2,.) : <return_type> { // Statements }
- 19. www.webstackacademy.com Type Annotation - Example function simpleExample (numExample: number, strExample: string) : void { // Function statements } Please note functions in TypeScript support a type called 'void' which returns nothing
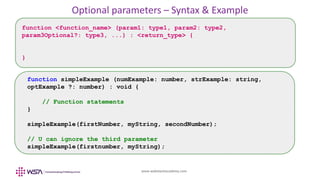
- 20. www.webstackacademy.com Functions – Optional parameters • As you may be aware, JavaScript not only discounts type-checking of parameters, the same happens with number of parameters you pass • For example, a function that calculates a sum of given numbers. U can pass any number of arguments to it • During run-time you have used arguments array and arguments.length parameters to determine what exactly got passed • In TypeScript you have similar facility in terms of making certain function parameters optional • Optional parameters are mentioned with ?: and you can ignore if you don't want to pass
- 21. www.webstackacademy.com Optional parameters – Syntax & Example function <function_name> (param1: type1, param2: type2, param3Optional?: type3, ...) : <return_type> { } function simpleExample (numExample: number, strExample: string, optExample ?: number) : void { // Function statements } simpleExample(firstNumber, myString, secondNumber); // U can ignore the third parameter simpleExample(firstnumber, myString);
- 22. www.webstackacademy.com Function - Overloading Optional parameters also helps to achieve 'functional overloading‘. However functions need to be declared before actual invocation // Function declaration function myOverload (topAndBottom: number, leftAndRight: number); function myOverload (top: number, right: number, bottom: number, left: number); function myOverload(a: number, b?: number, c?: number, d?: number) { // Function definition or implementation } let myNum1: number, myNum2: number, myNum3: number, myNum4: number; myOverload(myNum1, myNum2); // Overloading example-1 myOverload(myNum1, myNum2, myNum3, myNum4); // Overloading example-2 myOverload(myNum1, myNum2, myNum3); // This will give you an error
- 23. www.webstackacademy.com Functions – Arrow Functions • Arrow functions are another way to invoke functions • Commonly known as fat arrow (=>) function or lambda functions (C#) • Using arrow functions you can reduce / get rid of 'function' keyword • Also have better meaning of arguments • Lexical scoping, get rid of “this” business!
- 24. www.webstackacademy.com Function – Arrow Function – Model1 // JavaScript model let typeOne = function(message) { console.log ("JavaScript way of function...normal function"); console.log (message); } // Arrow function let typeTwo = (message: string) => { console.log("TypeScript way of function...arrow function..") console.log(message); } let messageOne = 'Test1'; typeOne(messageOne); let messageTwo = 'Test2'; typeTwo(messageTwo);
- 25. www.webstackacademy.com Function – Arrow Function – Model2 let betterFunction = (string: message) => { console.log("TypeScript way of function...arrow function..") return message.length; } let myStringLength = betterFunction("webstack academy");
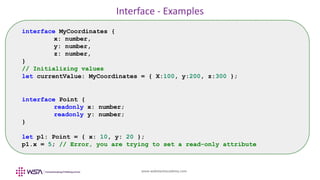
- 27. www.webstackacademy.com Interfaces • TypeScript's type-checking (core feature) focuses on the shape of the values. This is called “duck typing” or “structural subtyping” • Interfaces are majorly helpful to give name to these types, helps in using these user-defined items across the project • Promotes readability, modularity and project wide re-use • TypeScript also supports read only interfaces interface <interface_name> { // Attributes and types }
- 28. www.webstackacademy.com Interface - Examples interface MyCoordinates { x: number, y: number, z: number, } // Initializing values let currentValue: MyCoordinates = { X:100, y:200, z:300 }; interface Point { readonly x: number; readonly y: number; } let p1: Point = { x: 10, y: 20 }; p1.x = 5; // Error, you are trying to set a read-only attribute
- 29. www.webstackacademy.com Exercise • Write a arrow function to take following student assessment information as inputs: Attendance (Obtained) -> 20% weightage Assignment mark (Obtained) -> 30% weightage Project mark (Obtained) -> 20% weightage Module test mark (Obtained) -> 30% weightage • Calculate overall marks and grade and return the same Overall marks >= 70 -> Excellent 65 <= Overall marks < 70 – Very good 60 <= Overall marks < 65 – Good < 60 – Average • Define & Use interfaces for parameter passing • Total information need to be maintained as enumeration
- 30. www.webstackacademy.comwww.webstackacademy.com Classes (Inheritance, Constructors, Access modifiers)
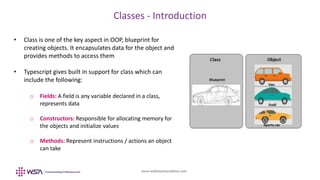
- 31. www.webstackacademy.com Classes - Introduction • Class is one of the key aspect in OOP, blueprint for creating objects. It encapsulates data for the object and provides methods to access them • Typescript gives built in support for class which can include the following: o Fields: A field is any variable declared in a class, represents data o Constructors: Responsible for allocating memory for the objects and initialize values o Methods: Represent instructions / actions an object can take
- 32. www.webstackacademy.com Class - Example class MyInputs { x: number; y: number; add() { console.log("The addition is " + (this.x + this.y)); } sub() { console.log("The subtraction is " + (this.x - this.y)); } } let currentInput = new MyInputs(); currentInput.x = 100; currentInput.y = 50; currentInput.add(); currentInput.sub();
- 33. www.webstackacademy.com Constructors Constructors are used to initialize the newly created object. This can be made optional by making constructor parameters are optional ones class MyInputs { x: number; y: number; constructor (val1: number, val2: number){ this.x = val1; this.y = val2; } // Define further methods here…. } // Object initialization happens via constructors let currentInput = new MyInputs(100,50);
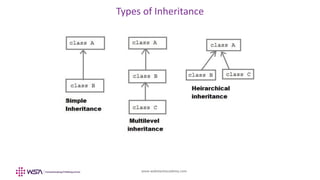
- 34. www.webstackacademy.com Inheritance using class • Inheritance is the ability of a program to create new classes from an existing class • The class that is extended to create newer classes is called the parent class/super class • The newly created classes are called the child/sub classes. • TypeScript supports inheritance using 'extends’keyword. It inherits all properties and methods. • Private members and constructors are not inherited class <child_class> extends <parent_class>
- 36. www.webstackacademy.com Inheritance - Example class StudentClass { // Generic student information & methods } // Inheritance class WSAStudentClass extends StudentClass { // WSA student specific information & methods } // This will get properties of StudentClass & WSAStudentClass let myStudent = new WSAStudentClass();
- 37. www.webstackacademy.com Multi level inheritance • Inheritance can happen at multiple levels, beyond current parent-child mechanism. There are multiple ways inheritance can work • Single: Every class can at the most extend from one parent class • Multiple: A class can inherit from multiple classes. TypeScript doesn’t support multiple inheritance • Multi-level: Inheritance happening at multiple levels (Ex: Grandparent -> Parent -> Child) • In multi-level inheritance a same method can be defined in a child class, which is called as method overriding
- 38. www.webstackacademy.com Method overriding - Example class StudentClass { printStudentData() } class WSAStudentClass extends StudentClass { printStudentData() } let myStudent = new WSAStudentClass(); // Method in derived class will be called myStudent.printStudentData();
- 39. www.webstackacademy.com Exercise • Enhance the snippet given in the previous slide and demonstrate method overriding • Write a program to demonstrate multi-level inheritance as follows: • Dhirubhai Ambani started Reliance with retail & textile segments with 1 Billion networth • Mukesh Ambani inherited it and added petroleum segment. Made 10 Billion networth • Akash Ambani inherited it and added JIO segment. Made 90 Billion networth • Add methods to print various owners, segments and networth values at different times • Demonstrate method overriding
- 40. www.webstackacademy.com Access modifiers • A class can control the visibility of its data members to members of other classes. This capability is termed as Data Hiding or Encapsulation • Object Orientation uses the concept of Access modifiers or Access specifiers to implement the concept of Encapsulation. The access modifiers supported by TypeScript are: • Public: A public data member has universal accessibility. Data members in a class are public by default. • Private: Private data members are accessible only within the class that defines these members. If an external class member tries to access a private member, the compiler throws an error. • Protected: A protected data member is accessible by the members within the same class as that of the former and also by the members of the child classes.
- 41. www.webstackacademy.com Access modifiers class MyInputs { private xValue : number; private yValue : number; public zValue : number; add() { console.log(“Add is " + (this.xValue + this.yValue)); } sub() { console.log(“Sub is " + (this.xValue - this.yValue)); } } // Can be accessed from outside // Can only access via method
- 42. www.webstackacademy.com Exercise • Define a class (Student) with following fields: Student name Phone number Basic placement eligibility (Eligible / Not Eligible) -> Private City • Inherit the class (WSAStudent) with additional fields as follows: Course name Course status Course fee Balance fee Course fee payment status (Paid / Unpaid) -> Private Define the following methods: getPlacementStatus(): A student is eligible for only if he has basic eligibility & paid his full fees payFee(): Pay partial fee payment printStudentData(): Print complete student information Use enumerations, interface, constructor wherever required
- 43. www.webstackacademy.comwww.webstackacademy.com Modules (Modularizing and re-using across multiple files)
- 44. www.webstackacademy.com Modules • In large scale application development, all the program code can’t be in the same file. In order to have better modularity and maintainability it will be spanned across multiple files. • For example, a class declaration will be available in one file and other file will be making use of it by creating an object. In similar way functions, simple variables, objects etc.. Can be exported and imported between modules • In such scenarios the class declaration need to be exported to other module, which will import and make use of it • In TypeScript it is achieved with the help of ‘modules’. In Angular also we will come across multiple scenarios where we will be making use of such modules from other files export class <class_name> { } import { <class_name> } from ‘<relative_path>’
- 46. www.webstackacademy.com Exercise • Create a module in Path1 • Create a module in Path2 • Export a variable from Path1 (say X = 10) • Export a function from Path2 (say a Square() function) • WAP to import a variable from Path1 and apply the Function from Path2 (Square (X)) • Print the result in the main program file Briefly discuss: Absolute path & relative path in Linux
- 47. www.webstackacademy.com WebStack Academy #83, Farah Towers, 1st Floor, MG Road, Bangalore – 560001 M: +91-809 555 7332 E: [email protected] WSA in Social Media:












![www.webstackacademy.com
The Type Annotation
// Let usage with type annotation
let myNumber: number;
let myString: string;
// Get early indication of issues
myNumber = 'a';
myString = 100;
console.log(myNumber);
console.log(myString);
// Let usage gives error
myLetTest = 100;
let myLetTest;
// Usage of any
let anyTest: any;
// No issues here
anyTest = '123';
anyTest = 123;
let myBoolArray: boolean[];
myBoolArray = [true, false];
myBoolArray[0] = 'false'; // Error
myBoolArray[1] = 'true'; // Error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002angulartypescriptprogramming-190503095243/85/Angular-Chapter-2-TypeScript-Programming-13-320.jpg)