Cognitive models unit 3
- 1. chapter 12 cognitive models ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 2. Cognitive models • goal and task hierarchies • linguistic • physical and device • architectural ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 3. Cognitive models • They model aspects of user: – understanding – knowledge – intentions – processing • Common categorisation: – Competence vs. Performance – Computational flavour – No clear divide ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 4. Goal and task hierarchies • Mental processing as divide-and-conquer • Example: sales report produce report gather data . find book names . . do keywords search of names database . . . … further sub-goals . . sift through names and abstracts by hand . . . … further sub-goals . search sales database - further sub-goals layout tables and histograms - further sub-goals write description - further sub-goals ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 5. goals vs. tasks • goals – intentions what you would like to be true • tasks – actions how to achieve it • GOMS – goals are internal • HTA – actions external – tasks are abstractions ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 6. Issues for goal hierarchies • Granularity – Where do we start? – Where do we stop? • Routine learned behaviour, not problem solving – The unit task • Conflict – More than one way to achieve a goal • Error ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 7. Techniques • Goals, Operators, Methods and Selection (GOMS) • Cognitive Complexity Theory (CCT) • Hierarchical Task Analysis (HTA) - Chapter 15 ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 8. GOMS Goals – what the user wants to achieve Operators – basic actions user performs Methods – decomposition of a goal into subgoals/operators Selection – means of choosing between competing methods ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 9. GOMS example GOAL: CLOSE-WINDOW . [select GOAL: USE-MENU-METHOD . MOVE-MOUSE-TO-FILE-MENU . PULL-DOWN-FILE-MENU . CLICK-OVER-CLOSE-OPTION GOAL: USE-CTRL-W-METHOD . PRESS-CONTROL-W-KEYS] For a particular user: Rule 1: Select USE-MENU-METHOD unless another rule applies Rule 2: If the application is GAME, select CTRL-W-METHOD ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 10. Cognitive Complexity Theory • Two parallel descriptions: – User production rules – Device generalised transition networks • Production rules are of the form: – if condition then action • Transition networks covered under dialogue models ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 11. Example: editing with vi • Production rules are in long-term memory • Model working memory as attribute-value mapping: (GOAL perform unit task) (TEXT task is insert space) (TEXT task is at 5 23) (CURSOR 8 7) • Rules are pattern-matched to working memory, e.g., LOOK-TEXT task is at %LINE %COLUMN is true, with LINE = 5 COLUMN = 23. ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 12. Active rules: SELECT-INSERT-SPACE INSERT-SPACE-MOVE-FIRST INSERT-SPACE-DOIT INSERT-SPACE-DONE Four rules to model inserting a space New working memory (GOAL insert space) (NOTE executing insert space) (LINE 5) (COLUMN 23) SELECT-INSERT-SPACE matches current working memory (SELECT-INSERT-SPACE IF (AND (TEST-GOAL perform unit task) (TEST-TEXT task is insert space) (NOT (TEST-GOAL insert space)) (NOT (TEST-NOTE executing insert space))) THEN ( (ADD-GOAL insert space) (ADD-NOTE executing insert space) (LOOK-TEXT task is at %LINE %COLUMN)))ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 13. Notes on CCT • Parallel model • Proceduralisation of actions • Novice versus expert style rules • Error behaviour can be represented • Measures – depth of goal structure – number of rules – comparison with device description ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 14. Problems with goal hierarchies • a post hoc technique • expert versus novice • How cognitive are they? ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 15. Linguistic notations • Understanding the user's behaviour and cognitive difficulty based on analysis of language between user and system. • Similar in emphasis to dialogue models • Backus–Naur Form (BNF) • Task–Action Grammar (TAG) ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
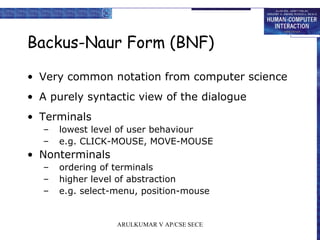
- 16. Backus-Naur Form (BNF) • Very common notation from computer science • A purely syntactic view of the dialogue • Terminals – lowest level of user behaviour – e.g. CLICK-MOUSE, MOVE-MOUSE • Nonterminals – ordering of terminals – higher level of abstraction – e.g. select-menu, position-mouse ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 17. Example of BNF • Basic syntax: – nonterminal ::= expression • An expression – contains terminals and nonterminals – combined in sequence (+) or as alternatives (|) draw line ::= select line + choose points + last point select line ::= pos mouse + CLICK MOUSE choose points ::= choose one | choose one + choose points choose one ::= pos mouse + CLICK MOUSE last point ::= pos mouse + DBL CLICK MOUSE pos mouse ::= NULL | MOVE MOUSE+ pos mouse ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
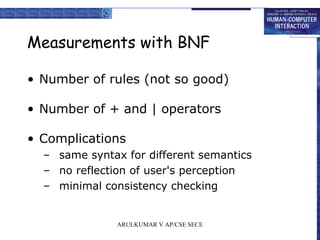
- 18. Measurements with BNF • Number of rules (not so good) • Number of + and | operators • Complications – same syntax for different semantics – no reflection of user's perception – minimal consistency checking ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 19. Task Action Grammar (TAG) • Making consistency more explicit • Encoding user's world knowledge • Parameterised grammar rules • Nonterminals are modified to include additional semantic features ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 20. Consistency in TAG • In BNF, three UNIX commands would be described as: copy ::= cp + filename + filename | cp + filenames + directory move ::= mv + filename + filename | mv + filenames + directory link ::= ln + filename + filename | ln + filenames + directory • No BNF measure could distinguish between this and a less consistent grammar in which link ::= ln + filename + filename | ln + directory + filenames ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 21. Consistency in TAG (cont'd) • consistency of argument order made explicit using a parameter, or semantic feature for file operations • Feature Possible values Op = copy; move; link • Rules file-op[Op] ::= command[Op] + filename + filename | command[Op] + filenames + directory command[Op = copy] ::= cp command[Op = move] ::= mv command[Op = link] ::= ln ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 22. Other uses of TAG • User’s existing knowledge • Congruence between features and commands • These are modelled as derived rules ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 23. Physical and device models • The Keystroke Level Model (KLM) • Buxton's 3-state model • Based on empirical knowledge of human motor system • User's task: acquisition then execution. – these only address execution • Complementary with goal hierarchies ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 24. Keystroke Level Model (KLM) • lowest level of (original) GOMS • six execution phase operators – Physical motor: K - keystroking P - pointing H - homing D - drawing – Mental M - mental preparation – System R - response • times are empirically determined. Texecute = TK + TP + TH + TD + TM + TR ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 25. KLM example GOAL: ICONISE-WINDOW [select GOAL: USE-CLOSE-METHOD . MOVE-MOUSE-TO- FILE-MENU . PULL-DOWN-FILE-MENU . CLICK-OVER-CLOSE-OPTION GOAL: USE-CTRL-W-METHOD PRESS-CONTROL-W-KEY] • compare alternatives: • USE-CTRL-W-METHOD vs. • USE-CLOSE-METHOD • assume hand starts on mouse USE-CLOSE-METHOD P[to menu] 1.1 B[LEFT down] 0.1 M 1.35 P[to option] 1.1 B[LEFT up] 0.1 Total 3.75 s USE-CTRL-W-METHOD H[to kbd] 0.40 M 1.35 K[ctrlW key] 0.28 Total 2.03 s ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 26. Architectural models • All of these cognitive models make assumptions about the architecture of the human mind. • Long-term/Short-term memory • Problem spaces • Interacting Cognitive Subsystems • Connectionist • ACT ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE
- 27. Display-based interaction • Most cognitive models do not deal with user observation and perception • Some techniques have been extended to handle system output (e.g., BNF with sensing terminals, Display-TAG) but problems persist • Exploratory interaction versus planning ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE









![GOMS example
GOAL: CLOSE-WINDOW
. [select GOAL: USE-MENU-METHOD
. MOVE-MOUSE-TO-FILE-MENU
. PULL-DOWN-FILE-MENU
. CLICK-OVER-CLOSE-OPTION
GOAL: USE-CTRL-W-METHOD
. PRESS-CONTROL-W-KEYS]
For a particular user:
Rule 1: Select USE-MENU-METHOD unless another
rule applies
Rule 2: If the application is GAME,
select CTRL-W-METHOD
ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cognitivemodelsunit3-171219094645/85/Cognitive-models-unit-3-9-320.jpg)









![Consistency in TAG (cont'd)
• consistency of argument order made explicit
using a parameter, or semantic feature for file
operations
• Feature Possible values
Op = copy; move; link
• Rules
file-op[Op] ::= command[Op] + filename + filename
| command[Op] + filenames + directory
command[Op = copy] ::= cp
command[Op = move] ::= mv
command[Op = link] ::= ln
ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cognitivemodelsunit3-171219094645/85/Cognitive-models-unit-3-21-320.jpg)



![KLM example
GOAL: ICONISE-WINDOW
[select
GOAL: USE-CLOSE-METHOD
. MOVE-MOUSE-TO- FILE-MENU
. PULL-DOWN-FILE-MENU
. CLICK-OVER-CLOSE-OPTION
GOAL: USE-CTRL-W-METHOD
PRESS-CONTROL-W-KEY]
• compare alternatives:
• USE-CTRL-W-METHOD vs.
• USE-CLOSE-METHOD
• assume hand starts on mouse
USE-CLOSE-METHOD
P[to menu] 1.1
B[LEFT down] 0.1
M 1.35
P[to option] 1.1
B[LEFT up] 0.1
Total 3.75 s
USE-CTRL-W-METHOD
H[to kbd] 0.40
M 1.35
K[ctrlW key] 0.28
Total 2.03 s
ARULKUMAR V AP/CSE SECE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cognitivemodelsunit3-171219094645/85/Cognitive-models-unit-3-25-320.jpg)

