Software Engineering - Lecture 02
Download as pptx, pdf3 likes2,356 views
The document discusses various software life cycle models, outlining their characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Key models include the waterfall model, incremental development, prototyping, the spiral model, and the unified process, each offering different approaches to software development. It emphasizes the importance of requirements engineering, design, validation, and software evolution in producing effective software systems.
1 of 43
Downloaded 127 times










































Ad
Recommended
Software Engineering - Lecture 01
Software Engineering - Lecture 01Asifuzzaman Hridoy This document discusses an introductory software engineering lecture. It introduces a simple programming problem of calculating student grades from test marks. It then discusses typical approaches students may take to solve the problem and the importance of understanding the problem. The document defines software engineering and outlines some of its objectives, characteristics of software, what makes good software, common software applications, and challenges in the field.
Ch03-Software Engineering Model
Ch03-Software Engineering ModelBala Ganesh The document discusses various prescriptive software development models including the waterfall model, spiral model, incremental model, rapid application development (RAD) model, and evolutionary prototyping model. It provides details on the phases and characteristics of each model as well as when each model is most appropriate to use. The document also discusses tailored development models and emerging models like the unified process.
The Software Development Process
The Software Development ProcessCesar Augusto Nogueira The document discusses the software development process and defines key terms. It states that a software process organizes development activities and includes roles, workflows, procedures and standards. Following a defined process makes software development more orderly, predictable and repeatable. However, some view following a process as unnecessary overhead. The reality is that not following a process can lead to more rework that outweighs any initial time savings. The document also discusses software life cycle models, such as waterfall and iterative models, and how a good process is repeatable, predictable, adaptable, learnable and measurable.
process models- software engineering
process models- software engineeringArun Nair This document discusses various process models for software engineering:
- The waterfall model defines sequential phases of requirements, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. It is inflexible to change.
- Iterative models allow repetition of phases to incrementally develop software. The incremental model delivers functionality in increments.
- Evolutionary models like prototyping and spiral development use iterative evaluation and refinement of prototypes to evolve requirements and manage risk.
- Other models include component-based development, formal methods, aspect-oriented development, and the Unified Process with iterative development of use cases. Personal and team software processes focus on self-directed teams, planning, metrics, and process improvement.
Software life cycle comparison
Software life cycle comparisonSuvek Shakya This document discusses and compares different software lifecycle models: Waterfall, Prototype, Spiral, and Agile. The Waterfall model is sequential with clear phases but inflexible. The Prototype model allows for early feedback but suffers from poor documentation. The Spiral model combines design and prototyping. Finally, the Agile model is iterative and test-driven but may increase complexity.
Lecture 3 software process model
Lecture 3 software process modelIIUI The document discusses different software process models. It begins by describing the "build and fix" model, where software is constructed without planning and then repeatedly fixed based on user feedback. This approach is problematic for large projects. The document then introduces prescriptive process models which prescribe ordered activities and tasks. The waterfall model and V-model are described as examples of prescriptive linear sequential models. Finally, incremental process models are covered, which deliver software in prioritized increments to provide early user value.
Software development process models
Software development process modelsMuhammed Afsal Villan The document discusses various software development process models, explaining their structures, advantages, and limitations. Key models include the Waterfall, Incremental, Rapid Application Development (RAD), Prototyping, Spiral, and Concurrent Development models, each serving specific project needs and contexts. It emphasizes the importance of adapting models to enhance software quality and manage risks effectively.
Ch02 process a generic view
Ch02 process a generic viewDr. C.V. Suresh Babu The document discusses software engineering processes and process frameworks. It describes common framework activities like requirements analysis, design, coding, testing and deployment. It also discusses umbrella activities, process models, the CMMI process model, process patterns, process assessment methods, and process improvement approaches like the Personal Software Process and Team Software Process which emphasize measurement and continuous improvement. The primary goal of any software process discussed is to deliver high quality software on time through effective requirements analysis, design, coding, testing and reducing rework.
Software Process Models
Software Process ModelsHassan A-j This document discusses different process models used in software development. It describes the key phases and characteristics of several common process models including waterfall, prototyping, V-model, incremental, iterative, spiral and agile development models. The waterfall model involves sequential phases from requirements to maintenance without iteration. Prototyping allows for user feedback earlier. The V-model adds verification and validation phases. Incremental and iterative models divide the work into smaller chunks to allow for iteration and user feedback throughout development.
Sdlc model
Sdlc modelaligarhking The document outlines the steps in the software development life cycle (SDLC), including initial communication, requirement gathering, feasibility analysis, system analysis, software design, coding, testing, integration, implementation, and maintenance. It describes each step in the SDLC process such as gathering requirements from stakeholders, analyzing feasibility, designing the software system, writing code, testing at various stages, integrating the software, implementing it for users, and maintaining it with updates. The SDLC provides a framework for software development projects by describing the key activities that occur at each phase.
SDLC Models
SDLC Modelsakash250690 The document presents information on the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), including:
1) It describes the seven main phases of the SDLC - planning, analysis, design, development, testing, implementation, and maintenance.
2) It discusses several SDLC models like waterfall, iterative, prototyping, spiral and V-model and compares their strengths and weaknesses.
3) It emphasizes the important role of testing in the SDLC and describes different testing types done during the phases.
Slides chapter 2
Slides chapter 2Priyanka Shetty A software process provides stability, control, and organization for software development. It consists of a series of predictable steps that lead to a timely, high-quality product. Key elements include framework activities like planning, modeling, requirements analysis, design, construction, testing, and deployment. The specific tasks and level of rigor for each activity may vary based on the project. Process assessment ensures the process meets criteria for successful software engineering. The primary goal of any process is high-quality software delivered on time through reduced rework.
3. ch 2-process model
3. ch 2-process modelDelowar hossain This document discusses software process models. It defines a software process as a framework for activities required to build high-quality software. A process model describes the phases in a product's lifetime from initial idea to final use. The document then describes a generic process model with five framework activities - communication, planning, modeling, construction, and deployment. It provides an example of identifying task sets for different sized projects. Finally, it discusses the waterfall process model as the first published model, outlining its sequential phases and problems with being rarely linear and requiring all requirements up front.
Software System Engineering - Chapter 2
Software System Engineering - Chapter 2Fadhil Ismail The document discusses different software development models including the linear sequential/waterfall model, prototyping, RAD model, and evolutionary software process models. It provides details on each model, including their advantages and disadvantages. Specific evolutionary models covered are the incremental model, spiral model, WINWIN spiral model, component assembly model, and concurrent development model.
Software Development Life Cycle-SDLC
Software Development Life Cycle-SDLCAdeel Rasheed The document discusses the software development life cycle (SDLC) process. It includes 6 main steps: 1) requirement gathering, 2) software analysis, 3) software design, 4) coding, 5) testing, and 6) implementation. For each step, the document provides details on the objectives and activities involved. It also lists advantages of following the SDLC process such as increased quality, improved tracking, and decreased risks. Finally, it provides a coding example for a basic calculator application to illustrate one step of the process.
Software engineering model
Software engineering modelManish Chaurasia The document discusses various software development life cycle (SDLC) models including waterfall, prototyping, spiral, RAD and V-model. It provides advantages and disadvantages of each model. In conclusion, the RAD model is identified as the best model to implement for a software project since it emphasizes delivering projects in smaller pieces to encourage user involvement and provide greater flexibility.
Software Development Methodologies
Software Development MethodologiesNicholas Davis The document discusses various software development methodologies, including agile, waterfall, prototyping, iterative, spiral, rapid application development, and extreme programming. It outlines the software development life cycle (SDLC) in detail, covering phases from system investigation to evaluation, and emphasizes the importance of testing and user acceptance. Additionally, it evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the SDLC process.
Evolutionary process models se.ppt
Evolutionary process models se.pptbhadjaashvini1 Evolutionary process models allow developers to iteratively create increasingly complete versions of software. Examples include the prototyping paradigm, spiral model, and concurrent development model. The prototyping paradigm uses prototypes to elicit requirements from customers. The spiral model couples iterative prototyping with controlled development, dividing the project into framework activities. The concurrent development model concurrently develops components with defined interfaces to enable integration. These evolutionary models allow flexibility and accommodate changes but require strong communication and updated requirements.
Lecture 5 software process model (3)
Lecture 5 software process model (3)IIUI The document discusses the Unified Process (UP) model for software development. It describes how the UP was created by combining the best features of individual object-oriented analysis and design methods. The UP includes five phases - Inception, Elaboration, Construction, Transition, and Production. The Inception Phase involves planning and requirements activities. The Elaboration Phase refines use cases and expands the architectural design. The Construction Phase focuses on building the software. The Transition Phase involves user testing and feedback. The Production Phase involves monitoring the deployed software.
Intro to Software Engineering - Life Cycle Models
Intro to Software Engineering - Life Cycle ModelsRadu_Negulescu This document discusses various software life cycle models and their characteristics. It begins by defining a software life cycle and life cycle model. It then examines the build-and-fix, waterfall, V-model, prototyping, spiral model, incremental/iterative model, extreme programming, and formal methods life cycle models. Key factors in selecting a life cycle model are also discussed, such as application domain, schedule constraints, and risk tolerance. The document concludes by comparing agile and plan-driven methods and introducing the Capability Maturity Model for assessing the maturity of an organization's software development processes.
1.sdlc
1.sdlcDeepak Sharma This document discusses different software development life cycle (SDLC) models. It describes the waterfall model as the first introduced process model where each phase must be completed before the next begins. The spiral model is presented as a combination of waterfall and risk analysis, with iterative cycles to reduce risk. The iterative enhancement model implements parts of software in cycles to identify further requirements through review.
Chapter 01
Chapter 01ans ali raza This document provides an overview of key concepts in the field of software engineering. It defines software engineering as the application of systematic and disciplined approaches to software development, operation, and maintenance. The document discusses the importance of software engineering in producing reliable and economical software. It also summarizes essential attributes of good software such as maintainability, dependability, efficiency, and acceptability. Additionally, the document outlines a generic software engineering process framework involving activities like communication, planning, modeling, construction, and deployment. It notes that the process should be adapted to the specific project.
SDLC
SDLCPooja Chaddha The document provides an overview of the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It describes the main phases of SDLC as feasibility analysis, requirement analysis and specification, design, coding, testing, and maintenance. For each phase, it outlines the key activities and objectives. It also discusses different approaches to SDLC, including waterfall, prototyping, iterative, and object-oriented approaches.
System Development Life Cycle
System Development Life CycleInternational Islamic University The document discusses the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), which is a framework for developing software in a systematic and efficient manner. It involves several phases from planning and requirements analysis to development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. SDLC helps estimate timelines, test software thoroughly, and develop applications in a disciplined way. The key phases include initiation, planning, requirements analysis, design, development, integration and testing, implementation, deployment, and maintenance.
MODELS USED IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
MODELS USED IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENTPaYal Umraliya A software process model is an abstract representation of a process that guides the coordination and control of tasks needed to develop software. Common models include waterfall, prototype, rapid application development, evolutionary development, incremental, iterative, spiral, and component-based development. The waterfall model involves sequential phases from requirements to maintenance without iteration. Iterative models allow for incremental development and feedback through multiple iterations. The spiral model combines iterative development with risk analysis through iterations called spirals.
Software Devlopment Life Cycle
Software Devlopment Life CycleVivek Gupta The document discusses several software development life cycle (SDLC) models including waterfall, V-shaped, prototyping, rapid application development (RAD), incremental, spiral, and agile models. It provides details on the key steps, strengths, weaknesses, and scenarios for using each model. Quality assurance is important for any SDLC and includes elements like defect tracking, unit testing, code reviews, and integration/system testing.
Software development methodologies
Software development methodologiesAnkita Lachhwani The document outlines various software development methodologies, emphasizing their frameworks for planning and controlling the development process. Key methodologies include the Waterfall model, Prototype model, Incremental model, Spiral model, RAD model, and V-model, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages. It also highlights their roles within the systems development life cycle and the significance of user involvement and risk management.
Software Process Model
Software Process ModelDyanara Pritz Menia This document discusses three software process models: the waterfall model, incremental development, and reuse-oriented software engineering. The waterfall model represents the software development process as sequential phases such as requirements, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. Incremental development interleaves these phases and develops the system in a series of versions that add new functionality. Reuse-oriented engineering focuses on integrating existing reusable components rather than developing everything from scratch.
Rpl 2- sw process model
Rpl 2- sw process modelf' yagami 1. Dokumen tersebut membahas beberapa model proses pengembangan perangkat lunak seperti model siklus hidup klasik, prototyping, spiral, generasi keempat, dan model kombinasi.
2. Setiap model memiliki kelebihan dan kekurangan tertentu dalam pengembangan perangkat lunak.
3. Tidak ada model yang sempurna sehingga seringkali digunakan pendekatan kombinasi dari beberapa model.
An introduction to agile and beyond
An introduction to agile and beyondSander Hoogendoorn Sander Hoogendoorn is a principal technology officer and global agile thought leader at Capgemini who gave a presentation on agile and beyond. He discussed how waterfall models do not work well and advocated for agile approaches. The presentation covered the basics of agile, including iterations, backlogs, and working in iterations to deliver working software frequently. It also discussed visualizing agile processes and progress through tools. The goal is to continuously improve processes through retrospectives.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Software Process Models
Software Process ModelsHassan A-j This document discusses different process models used in software development. It describes the key phases and characteristics of several common process models including waterfall, prototyping, V-model, incremental, iterative, spiral and agile development models. The waterfall model involves sequential phases from requirements to maintenance without iteration. Prototyping allows for user feedback earlier. The V-model adds verification and validation phases. Incremental and iterative models divide the work into smaller chunks to allow for iteration and user feedback throughout development.
Sdlc model
Sdlc modelaligarhking The document outlines the steps in the software development life cycle (SDLC), including initial communication, requirement gathering, feasibility analysis, system analysis, software design, coding, testing, integration, implementation, and maintenance. It describes each step in the SDLC process such as gathering requirements from stakeholders, analyzing feasibility, designing the software system, writing code, testing at various stages, integrating the software, implementing it for users, and maintaining it with updates. The SDLC provides a framework for software development projects by describing the key activities that occur at each phase.
SDLC Models
SDLC Modelsakash250690 The document presents information on the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), including:
1) It describes the seven main phases of the SDLC - planning, analysis, design, development, testing, implementation, and maintenance.
2) It discusses several SDLC models like waterfall, iterative, prototyping, spiral and V-model and compares their strengths and weaknesses.
3) It emphasizes the important role of testing in the SDLC and describes different testing types done during the phases.
Slides chapter 2
Slides chapter 2Priyanka Shetty A software process provides stability, control, and organization for software development. It consists of a series of predictable steps that lead to a timely, high-quality product. Key elements include framework activities like planning, modeling, requirements analysis, design, construction, testing, and deployment. The specific tasks and level of rigor for each activity may vary based on the project. Process assessment ensures the process meets criteria for successful software engineering. The primary goal of any process is high-quality software delivered on time through reduced rework.
3. ch 2-process model
3. ch 2-process modelDelowar hossain This document discusses software process models. It defines a software process as a framework for activities required to build high-quality software. A process model describes the phases in a product's lifetime from initial idea to final use. The document then describes a generic process model with five framework activities - communication, planning, modeling, construction, and deployment. It provides an example of identifying task sets for different sized projects. Finally, it discusses the waterfall process model as the first published model, outlining its sequential phases and problems with being rarely linear and requiring all requirements up front.
Software System Engineering - Chapter 2
Software System Engineering - Chapter 2Fadhil Ismail The document discusses different software development models including the linear sequential/waterfall model, prototyping, RAD model, and evolutionary software process models. It provides details on each model, including their advantages and disadvantages. Specific evolutionary models covered are the incremental model, spiral model, WINWIN spiral model, component assembly model, and concurrent development model.
Software Development Life Cycle-SDLC
Software Development Life Cycle-SDLCAdeel Rasheed The document discusses the software development life cycle (SDLC) process. It includes 6 main steps: 1) requirement gathering, 2) software analysis, 3) software design, 4) coding, 5) testing, and 6) implementation. For each step, the document provides details on the objectives and activities involved. It also lists advantages of following the SDLC process such as increased quality, improved tracking, and decreased risks. Finally, it provides a coding example for a basic calculator application to illustrate one step of the process.
Software engineering model
Software engineering modelManish Chaurasia The document discusses various software development life cycle (SDLC) models including waterfall, prototyping, spiral, RAD and V-model. It provides advantages and disadvantages of each model. In conclusion, the RAD model is identified as the best model to implement for a software project since it emphasizes delivering projects in smaller pieces to encourage user involvement and provide greater flexibility.
Software Development Methodologies
Software Development MethodologiesNicholas Davis The document discusses various software development methodologies, including agile, waterfall, prototyping, iterative, spiral, rapid application development, and extreme programming. It outlines the software development life cycle (SDLC) in detail, covering phases from system investigation to evaluation, and emphasizes the importance of testing and user acceptance. Additionally, it evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the SDLC process.
Evolutionary process models se.ppt
Evolutionary process models se.pptbhadjaashvini1 Evolutionary process models allow developers to iteratively create increasingly complete versions of software. Examples include the prototyping paradigm, spiral model, and concurrent development model. The prototyping paradigm uses prototypes to elicit requirements from customers. The spiral model couples iterative prototyping with controlled development, dividing the project into framework activities. The concurrent development model concurrently develops components with defined interfaces to enable integration. These evolutionary models allow flexibility and accommodate changes but require strong communication and updated requirements.
Lecture 5 software process model (3)
Lecture 5 software process model (3)IIUI The document discusses the Unified Process (UP) model for software development. It describes how the UP was created by combining the best features of individual object-oriented analysis and design methods. The UP includes five phases - Inception, Elaboration, Construction, Transition, and Production. The Inception Phase involves planning and requirements activities. The Elaboration Phase refines use cases and expands the architectural design. The Construction Phase focuses on building the software. The Transition Phase involves user testing and feedback. The Production Phase involves monitoring the deployed software.
Intro to Software Engineering - Life Cycle Models
Intro to Software Engineering - Life Cycle ModelsRadu_Negulescu This document discusses various software life cycle models and their characteristics. It begins by defining a software life cycle and life cycle model. It then examines the build-and-fix, waterfall, V-model, prototyping, spiral model, incremental/iterative model, extreme programming, and formal methods life cycle models. Key factors in selecting a life cycle model are also discussed, such as application domain, schedule constraints, and risk tolerance. The document concludes by comparing agile and plan-driven methods and introducing the Capability Maturity Model for assessing the maturity of an organization's software development processes.
1.sdlc
1.sdlcDeepak Sharma This document discusses different software development life cycle (SDLC) models. It describes the waterfall model as the first introduced process model where each phase must be completed before the next begins. The spiral model is presented as a combination of waterfall and risk analysis, with iterative cycles to reduce risk. The iterative enhancement model implements parts of software in cycles to identify further requirements through review.
Chapter 01
Chapter 01ans ali raza This document provides an overview of key concepts in the field of software engineering. It defines software engineering as the application of systematic and disciplined approaches to software development, operation, and maintenance. The document discusses the importance of software engineering in producing reliable and economical software. It also summarizes essential attributes of good software such as maintainability, dependability, efficiency, and acceptability. Additionally, the document outlines a generic software engineering process framework involving activities like communication, planning, modeling, construction, and deployment. It notes that the process should be adapted to the specific project.
SDLC
SDLCPooja Chaddha The document provides an overview of the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It describes the main phases of SDLC as feasibility analysis, requirement analysis and specification, design, coding, testing, and maintenance. For each phase, it outlines the key activities and objectives. It also discusses different approaches to SDLC, including waterfall, prototyping, iterative, and object-oriented approaches.
System Development Life Cycle
System Development Life CycleInternational Islamic University The document discusses the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), which is a framework for developing software in a systematic and efficient manner. It involves several phases from planning and requirements analysis to development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. SDLC helps estimate timelines, test software thoroughly, and develop applications in a disciplined way. The key phases include initiation, planning, requirements analysis, design, development, integration and testing, implementation, deployment, and maintenance.
MODELS USED IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
MODELS USED IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENTPaYal Umraliya A software process model is an abstract representation of a process that guides the coordination and control of tasks needed to develop software. Common models include waterfall, prototype, rapid application development, evolutionary development, incremental, iterative, spiral, and component-based development. The waterfall model involves sequential phases from requirements to maintenance without iteration. Iterative models allow for incremental development and feedback through multiple iterations. The spiral model combines iterative development with risk analysis through iterations called spirals.
Software Devlopment Life Cycle
Software Devlopment Life CycleVivek Gupta The document discusses several software development life cycle (SDLC) models including waterfall, V-shaped, prototyping, rapid application development (RAD), incremental, spiral, and agile models. It provides details on the key steps, strengths, weaknesses, and scenarios for using each model. Quality assurance is important for any SDLC and includes elements like defect tracking, unit testing, code reviews, and integration/system testing.
Software development methodologies
Software development methodologiesAnkita Lachhwani The document outlines various software development methodologies, emphasizing their frameworks for planning and controlling the development process. Key methodologies include the Waterfall model, Prototype model, Incremental model, Spiral model, RAD model, and V-model, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages. It also highlights their roles within the systems development life cycle and the significance of user involvement and risk management.
Software Process Model
Software Process ModelDyanara Pritz Menia This document discusses three software process models: the waterfall model, incremental development, and reuse-oriented software engineering. The waterfall model represents the software development process as sequential phases such as requirements, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. Incremental development interleaves these phases and develops the system in a series of versions that add new functionality. Reuse-oriented engineering focuses on integrating existing reusable components rather than developing everything from scratch.
Viewers also liked (20)
Rpl 2- sw process model
Rpl 2- sw process modelf' yagami 1. Dokumen tersebut membahas beberapa model proses pengembangan perangkat lunak seperti model siklus hidup klasik, prototyping, spiral, generasi keempat, dan model kombinasi.
2. Setiap model memiliki kelebihan dan kekurangan tertentu dalam pengembangan perangkat lunak.
3. Tidak ada model yang sempurna sehingga seringkali digunakan pendekatan kombinasi dari beberapa model.
An introduction to agile and beyond
An introduction to agile and beyondSander Hoogendoorn Sander Hoogendoorn is a principal technology officer and global agile thought leader at Capgemini who gave a presentation on agile and beyond. He discussed how waterfall models do not work well and advocated for agile approaches. The presentation covered the basics of agile, including iterations, backlogs, and working in iterations to deliver working software frequently. It also discussed visualizing agile processes and progress through tools. The goal is to continuously improve processes through retrospectives.
Software ee1
Software ee1Aman Adhikari Software engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with all aspects of software production. It involves theories, methods and tools to support the software development process from initial specification through maintenance. Key activities include specification, development, validation and evolution of software to meet changing needs. While techniques vary depending on the application type, fundamental principles like managed processes, dependability, requirements management and reuse apply universally.
Lecture 19 design concepts
Lecture 19 design conceptsIIUI This document discusses software design concepts, including defining software design, key elements of a software design model, guidelines for translating requirements to design, and principles of good software design. It notes that software design encompasses principles, concepts and practices that lead to high-quality systems and products. The design model provides details on data structures, architecture, interfaces and components needed to implement a system. It also lists guidelines for modular and traceable design, as well as principles like accommodating change and minimizing errors.
Lecture 05 Software Quality Management
Lecture 05 Software Quality ManagementAchmad Solichin The document provides an overview of software quality management, emphasizing the importance of establishing frameworks and quality plans at both organizational and project levels to ensure high-quality software development. It discusses key activities such as quality checks, reviews, and inspections, along with the relevance of ISO 9001 standards in guiding quality processes. The document also highlights various software quality attributes and the complexities involved in defining and managing these qualities effectively.
Process model in Software engeneering
Process model in Software engeneering International Center for Chemical & Biological Sciences This document proposes a "Linear-Pilot Process Model" that combines elements of the waterfall model and prototyping. It is intended for situations where a software house has expert but few developers, the client is new but mature, and the deadline is flexible but the client wants a dummy of each phase. The model aims to address the lack of reversibility in the waterfall model by applying prototyping in each phase. An example is given of a client who wants to see dummy projects of each phase from a small but expert software house.
02 software process_models
02 software process_modelsUniversity of Computer Science and Technology The document describes several software process models: the 4 block SDLC model, waterfall model, evolutionary development model, incremental development model, reuse-oriented development model, rapid application development model, and software prototyping models including evolutionary prototyping and throw-away prototyping. It also outlines Boehm's spiral model and notes this as a homework task.
SDLC and Software Process Models
SDLC and Software Process ModelsNana Sarpong The document discusses software development life cycles (SDLC). It describes the typical stages of an SDLC including feasibility study, requirements analysis, system design, development, testing, implementation, and maintenance. Several SDLC models are mentioned, including waterfall, spiral, iterative, prototyping, and RAD (rapid application development). The waterfall model is described as having distinct sequential stages with no overlap between phases. Prototyping and RAD methodologies are also explained in further detail.
Software engineering mca
Software engineering mcaAman Adhikari This document outlines the syllabus for a Software Engineering course, including 11 topics that will be covered over several hours: Introduction to Software Engineering, Software Design, Using APIs, Software Tools and Environments, Software Processes, Software Requirements and Specifications, Software Validation, Software Evolution, Software Project Management, Formal Methods, and Specialized Systems Development. The main texts to be used are listed as two Software Engineering books by Sommerville and Pressman.
Software process model
Software process modelMuhammad Yousuf Abdul Qadir The document discusses various software process models, including the build and fix model, waterfall model, incremental model, and evolutionary models like prototyping and spiral. It highlights the importance of process models in managing software development complexity, ensuring quality, and adapting to changing requirements. Each model has its unique advantages and limitations, providing a framework for software engineers to deliver high-quality applications efficiently.
Lecture 02 Software Process Model
Lecture 02 Software Process ModelAchmad Solichin The document outlines various software process models and principles of software engineering, emphasizing the importance of value to users, simplicity in design, and clarity of vision. It discusses different models such as the waterfall, incremental, prototyping, and spiral models, highlighting their benefits and problems. Additionally, it covers methodologies like Rapid Application Development and the Unified Process, detailing their phases and workflows.
Project based learning methodologies for Embedded Systems and Intelligent Sys...
Project based learning methodologies for Embedded Systems and Intelligent Sys...Lakshmi Narain College of Technology & Science Bhopal The document describes project based learning methodologies for embedded systems design. It discusses how project based learning differs from traditional teaching approaches in engaging students through extended inquiry projects. It outlines the roles of instructors in facilitating student-led projects and of students in taking responsibility. Examples of embedded hardware and software development processes on platforms like 8051, AVR and ARM are provided. The document also discusses design complexities and related work before concluding that the methodology presents an approach combining traditional and project based learning for teaching embedded and intelligent systems.
Chapter 2 software_development_life_cycle_models
Chapter 2 software_development_life_cycle_modelsPiyush Gogia This document discusses various software development life cycle models. It begins by defining the software life cycle as the period from when a software product is conceived to when it is no longer available for use, typically including requirements, design, implementation, testing, installation, operation and maintenance, and retirement phases.
It then examines the "build and fix" model, waterfall model, iterative enhancement model, rapid application development model, evolutionary process model, prototyping model, spiral model, and unified process. For each model, it provides a brief overview and discusses their advantages and disadvantages. It concludes by noting that the selection of a life cycle model depends on the requirements, development team, users, and project type and associated risks.
Architecture design of a virtual embedded system ppt
Architecture design of a virtual embedded system pptRajeev Mohanty The document discusses embedded systems and virtualization techniques. It begins with an introduction to embedded systems, their basic principles and characteristics. Examples of embedded systems are provided. The document then discusses the state of the art in multi-agent systems, embedded systems, and virtualization techniques. It describes insulation, para-virtualization, and full virtualization. The document proposes a solution using an agent-based model and describes a prototype implementation of a virtualized embedded system using a Linux kernel and KVM that provides the benefits of virtualization for embedded systems.
Software Architecture Design for Begginers
Software Architecture Design for BegginersChinh Ngo Nguyen This document provides an introduction to software architecture design. It discusses key concepts like the relationship between requirements and architecture, architecture styles, quality attributes, and tradeoff analysis. The document is divided into multiple parts that cover topics such as an overview of software architecture, common architecture styles, quality attributes, and some rules of thumb for architecture design.
Sdlc models
Sdlc modelsSivaprasanthRentala1975 The document discusses various software life cycle models, including waterfall, V-model, incremental, prototype, spiral, RAD and 4GT. It provides descriptions of each model's phases, advantages and disadvantages. The waterfall and V-model are presented as classic sequential models. Incremental and spiral models iterate through phases to allow for flexibility. Prototype and RAD models emphasize early prototypes. Risk analysis is a key part of the spiral model.
software engineering notes for cse/it fifth semester
software engineering notes for cse/it fifth semesterrajesh199155 The document provides an overview of software engineering principles and practices. It discusses:
1) The scope and necessity of software engineering to systematically develop large, complex software products. Without principles, developing large programs would be difficult and error-prone.
2) The "software crisis" caused by ineffective development leading to cost overruns and inefficient resource usage. Proper use of principles can help solve this.
3) The difference between a program developed by an individual and a commercial software product developed by a team for multiple users, requiring careful design, documentation and adherence to principles.
4) How early exploratory development styles focused on error correction after coding, while modern styles emphasize error prevention through defined stages like
Chapter 5 software design
Chapter 5 software designPiyush Gogia The document discusses software design and key concepts related to software design including:
1) Software design is the process of planning the architecture, components, interfaces, and other characteristics of a software system.
2) Good software design aims for high cohesion and loose coupling between modules. It involves conceptual design, technical design, and refinement of the design.
3) Modularity, coupling, and cohesion are important design principles. Modularity enhances manageability while loose coupling and high cohesion are design goals.
Software design methodologies
Software design methodologiesDr. C.V. Suresh Babu The document discusses various software development methodologies and life cycle models that have been used since the 1950s. It provides detailed descriptions of the waterfall model, spiral model, evolutionary prototyping, and staged delivery approaches. Each methodology takes different approaches to requirements analysis, design, development, testing, and deployment. The document emphasizes the importance of choosing a life cycle model that fits the needs of the specific project.
Software engineering lecture notes
Software engineering lecture notesSiva Ayyakutti The document discusses different software engineering process models including:
1. The waterfall model which is a linear sequential model where each phase must be completed before moving to the next.
2. Prototyping models which allow requirements to be refined through building prototypes.
3. RAD (Rapid Application Development) which emphasizes short development cycles through reuse and code generation.
4. Incremental models which deliver functionality in increments with early increments focusing on high priority requirements.
5. The spiral model which has multiple iterations of planning, risk analysis, engineering and evaluation phases.
Project based learning methodologies for Embedded Systems and Intelligent Sys...
Project based learning methodologies for Embedded Systems and Intelligent Sys...Lakshmi Narain College of Technology & Science Bhopal
Ad
Similar to Software Engineering - Lecture 02 (20)
04_Materi Software Proses-Models(1).pptx
04_Materi Software Proses-Models(1).pptxMarwondoMarwondo The document outlines essential activities in software processes, including specification, design and implementation, validation, and evolution. It discusses various software process models such as the waterfall model, incremental development, prototyping, and the spiral model, emphasizing their characteristics and suitability for different situations. Additionally, it highlights the challenges and benefits associated with evolutionary models and reuse-oriented software engineering.
Ch4
Ch4Saad Gabr The document introduces software process models and describes three generic models: waterfall, evolutionary development, and component-based development. It also covers the Rational Unified Process model and discusses how computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools can support software processes. Key activities like requirements, design, implementation, testing, and evolution are defined.
Soft Eng - Software Process
Soft Eng - Software ProcessJomel Penalba The document introduces software process models including the waterfall model, evolutionary development, and component-based software engineering. It describes the Rational Unified Process model and discusses key process activities like requirements engineering, design, implementation, testing, and evolution. Computer-aided software engineering tools are introduced as a way to support various activities in the software development process.
Ch4
Ch4phanleson The document introduces software process models and describes three generic models: waterfall, evolutionary development, and component-based development. It also outlines the software development process including requirements engineering, design, implementation, testing, and evolution. The Rational Unified Process model is introduced as a modern iterative process model. Computer-aided software engineering tools are discussed as a way to support software process activities.
Software Process Models
Software Process ModelsJesse Manalansan The document introduces software process models including the waterfall model, evolutionary development, and component-based software engineering. It describes the Rational Unified Process model and discusses key process activities like requirements engineering, design, implementation, testing, and evolution. Computer-aided software engineering tools are introduced as a way to support various activities in the software development process.
Software Process in Software Engineering SE3
Software Process in Software Engineering SE3koolkampus The document introduces software process models and describes three generic models: waterfall, evolutionary development, and component-based development. It also covers the Rational Unified Process model and discusses how computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools can support software development processes.
Software development life cycle
Software development life cycleNishant Srivastava The document discusses various software development life cycle models, including:
- The waterfall model, which progresses through sequential stages from requirements to maintenance. It allows for predictability but not flexibility.
- Iterative models like prototyping and incremental development, which allow delivering functionality in phases to get early user feedback.
- The V-model which emphasizes verification and validation activities at each stage.
- Agile methods like Scrum and eXtreme Programming which are iterative, incremental and emphasize adaptability over heavy documentation.
what is software Engineering for students
what is software Engineering for studentsAssadLeo1 Software engineering is the discipline of creating significant software systems that meet criteria for timeliness, budget, performance, and correct operation, playing a critical role in the economies of developed nations. It encompasses theories, methods, and tools for cost-effective development, distinguishing between generic and customized products with varying attributes like maintainability and efficiency. The document also covers process models including waterfall and evolutionary approaches, emphasizing the importance of documentation, visibility, and professional responsibilities in software engineering.
Elementary Probability theory Chapter 2.pptx
Elementary Probability theory Chapter 2.pptxethiouniverse The document discusses various software process models including waterfall, iterative, incremental, evolutionary (prototyping and spiral), and component-based development models. It describes the key activities and characteristics of each model and discusses when each may be applicable. The waterfall model presents a linear sequential flow while evolutionary models like prototyping and spiral are iterative and incremental to accommodate changing requirements.
ISE_Lecture Week 2-SW Process Models.ppt
ISE_Lecture Week 2-SW Process Models.pptHumzaWaris1 The document discusses various software development processes. It begins by defining a software process as a framework that describes the activities performed at each stage of a project. It then categorizes common activities as software specification, development, validation, and evolution. The document goes on to describe plan-driven and agile processes, and notes that most practical processes include elements of both. It provides details on specific process models like waterfall, V-model, prototyping, incremental development, component-based development, and spiral model.
01lifecycles
01lifecyclesAbdihakim Dalmar - The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework that uses UML. It consists of four main phases - Inception, Elaboration, Construction, and Transition - which iterate over many cycles.
- The phases focus on establishing feasibility, implementing core architecture, adding remaining elements, and deployment/testing. Artifacts like use cases and UML diagrams are produced.
- Agile methods like RUP are iterative, incremental, and emphasize flexibility over heavy documentation. This allows risks to be reduced by revealing problems earlier compared to traditional waterfall models.
Lecture - 11-15.pptx
Lecture - 11-15.pptxFarHana74914 The document discusses software processes for coping with change, including prototyping and incremental delivery approaches. Prototyping can help reduce costs by anticipating changes early. Incremental delivery breaks a system into prioritized parts for iterative development and delivery of value. Boehm's spiral model also takes a risk-driven iterative approach representing the software process as a spiral of objectives, risks, development, and planning loops. While influential, the spiral model is rarely used directly in practice.
Chapter-2 ppt for the MBA 4rh seme6y.pdf
Chapter-2 ppt for the MBA 4rh seme6y.pdfVikasRai405977 The document discusses several software engineering process models. It begins by defining a generic process model with five framework activities: communication, planning, modeling, construction, and deployment. It then describes different types of process flows (linear, iterative, evolutionary, parallel). Next, it discusses prescriptive process models in more detail, including the waterfall model, incremental process models, and evolutionary models like prototyping and spiral. For each model, it provides an overview and highlights advantages and disadvantages.
Ch2.Part2.Modified.ppt
Ch2.Part2.Modified.pptMelisa521270 The document discusses software processes and managing change. It describes prototyping as a way to clarify requirements and explore design options before significant rework is required. Incremental development and delivery are presented as ways to accommodate change at low cost by developing and deploying the system in prioritized increments. The Rational Unified Process is introduced as an iterative process with phases for inception, elaboration, construction, and transition, with activities like requirements management and component-based design carried out within each phase through multiple iterations.
software Processes
software ProcessesSeif Shaame The document discusses software processes and models. It describes objectives of introducing process models and activities like requirements engineering, design, testing and evolution. Generic process models covered are waterfall, evolutionary development and component-based engineering. Iterative models like incremental delivery and spiral development are also introduced. The Rational Unified Process model and role of computer-aided software engineering in supporting process activities are also summarized.
Chapter 2.pptx
Chapter 2.pptxAmnaAhsaan1 Miss Aster Noor introduces the concepts of software processes and process models. The chapter covers software process models like waterfall, incremental development, and integration/configuration. It discusses the core process activities of requirements engineering, development, testing, and evolution. The chapter aims to explain why processes must adapt to changes and how process improvement affects quality.
Software process life cycles
Software process life cycles
sathish sak The document discusses various software process life cycle models, including:
- Waterfall model which progresses in linear stages from requirements to maintenance. It values predictability but is inflexible to changes.
- Prototyping model which adds prototyping stages to explore risks before full development.
- V model which mirrors each development phase with a testing phase. It emphasizes verification and validation.
- Iterative and incremental models like RUP which develop software iteratively in phases and increments, releasing early and often. This is more flexible and reduces risks compared to waterfall.
- Agile methods are also iterative and incremental but emphasize lightweight processes, adaptation, and flexibility over heavy documentation.
The
Ch 02 s.e software process models 1
Ch 02 s.e software process models 1Badar Waseer The document discusses different software process models. It describes the waterfall model, which involves sequential phases of requirement analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. The waterfall model suggests a systematic approach but real projects rarely follow sequential phases and instead involve overlap and feedback between phases. The document also briefly describes the build-and-fix model, which develops software without specifications or design and relies on repeated modifications until requirements are met.
Ch17
Ch17phanleson This document discusses rapid software development methods like agile development and extreme programming (XP). It explains that agile methods use iterative development with customer involvement to quickly deliver working software. XP in particular emphasizes practices like test-driven development, pair programming, and frequent small releases. The document also covers rapid application development tools and the use of prototypes to help define requirements before full system development.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
VCE Literature Section A Exam Response Guide
VCE Literature Section A Exam Response Guidejpinnuck This practical guide shows students of Unit 3&4 VCE Literature how to write responses to Section A of the exam. Including a range of examples writing about different types of texts, this guide:
*Breaks down and explains what Q1 and Q2 tasks involve and expect
*Breaks down example responses for each question
*Explains and scaffolds students to write responses for each question
*Includes a comprehensive range of sentence starters and vocabulary for responding to each question
*Includes critical theory vocabulary lists to support Q2 responses
F-BLOCK ELEMENTS POWER POINT PRESENTATIONS
F-BLOCK ELEMENTS POWER POINT PRESENTATIONSmprpgcwa2024 F-block elements are a group of elements in the periodic table that have partially filled f-orbitals. They are also known as inner transition elements. F-block elements are divided into two series:
1.Lanthanides (La- Lu) These elements are also known as rare earth elements.
2.Actinides (Ac- Lr): These elements are radioactive and have complex electronic configurations.
F-block elements exhibit multiple oxidation states due to the availability of f-orbitals.
2. Many f-block compounds are colored due to f-f transitions.
3. F-block elements often exhibit paramagnetic or ferromagnetic behavior.4. Actinides are radioactive.
F-block elements are used as catalysts in various industrial processes.
Actinides are used in nuclear reactors and nuclear medicine.
F-block elements are used in lasers and phosphors due to their luminescent properties.
F-block elements have unique electronic and magnetic properties.
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...Kweku Zurek This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Service PIN codes (LIST)
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptx
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptxSourav Kr Podder Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Celebration Quiz
How to Manage Different Customer Addresses in Odoo 18 Accounting
How to Manage Different Customer Addresses in Odoo 18 AccountingCeline George A business often have customers with multiple locations such as office, warehouse, home addresses and this feature allows us to associate with different addresses with each customer streamlining the process of creating sales order invoices and delivery orders.
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students SanctionedKweku Zurek University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
Filipino 9 Maikling Kwento Ang Ama Panitikang Asiyano
Filipino 9 Maikling Kwento Ang Ama Panitikang Asiyanosumadsadjelly121997 Filipino 9 Maikling Kwento Ang Ama Panitikang Asiyano
HistoPathology Ppt. Arshita Gupta for Diploma
HistoPathology Ppt. Arshita Gupta for Diplomaarshitagupta674 Hello everyone please suggest your views and likes so that I uploaded more study materials
In this slide full HistoPathology according to diploma course available like fixation
Tissue processing , staining etc
A Visual Introduction to the Prophet Jeremiah
A Visual Introduction to the Prophet JeremiahSteve Thomason These images will give you a visual guide to both the context and the flow of the story of the prophet Jeremiah. Feel free to use these in your study, preaching, and teaching.
Code Profiling in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 Slides
Code Profiling in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 SlidesCeline George Profiling in Odoo identifies slow code and resource-heavy processes, ensuring better system performance. Odoo code profiling detects bottlenecks in custom modules, making it easier to improve speed and scalability.
Great Governors' Send-Off Quiz 2025 Prelims IIT KGP
Great Governors' Send-Off Quiz 2025 Prelims IIT KGPIIT Kharagpur Quiz Club Prelims of the Great Governors' Send-Off Quiz 2025 hosted by the outgoing governors.
QMs: Aarushi, Aatir, Aditya, Arnav
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02Mauricio Alexandre Silva Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
Tanja Vujicic - PISA for Schools contact Info
Tanja Vujicic - PISA for Schools contact InfoEduSkills OECD Tanja Vujicic, Senior Analyst and PISA for School’s Project Manager at the OECD spoke at the OECD webinar 'Turning insights into impact: What do early case studies reveal about the power of PISA for Schools?' on 20 June 2025
PISA for Schools is an OECD assessment that evaluates 15-year-old performance on reading, mathematics, and science. It also gathers insights into students’ learning environment, engagement and well-being, offering schools valuable data that help them benchmark performance internationally and improve education outcomes. A central ambition, and ongoing challenge, has been translating these insights into meaningful actions that drives lasting school improvement.
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...Ultimatewinner0342 🧠 Lazy Sunday Quiz | General Knowledge Trivia by SMC Quiz Club – Silchar Medical College
Presenting the Lazy Sunday Quiz, a fun and thought-provoking general knowledge quiz created by the SMC Quiz Club of Silchar Medical College & Hospital (SMCH). This quiz is designed for casual learners, quiz enthusiasts, and competitive teams looking for a diverse, engaging set of questions with clean visuals and smart clues.
🎯 What is the Lazy Sunday Quiz?
The Lazy Sunday Quiz is a light-hearted yet intellectually rewarding quiz session held under the SMC Quiz Club banner. It’s a general quiz covering a mix of current affairs, pop culture, history, India, sports, medicine, science, and more.
Whether you’re hosting a quiz event, preparing a session for students, or just looking for quality trivia to enjoy with friends, this PowerPoint deck is perfect for you.
📋 Quiz Format & Structure
Total Questions: ~50
Types: MCQs, one-liners, image-based, visual connects, lateral thinking
Rounds: Warm-up, Main Quiz, Visual Round, Connects (optional bonus)
Design: Simple, clear slides with answer explanations included
Tools Needed: Just a projector or screen – ready to use!
🧠 Who Is It For?
College quiz clubs
School or medical students
Teachers or faculty for classroom engagement
Event organizers needing quiz content
Quizzers preparing for competitions
Freelancers building quiz portfolios
💡 Why Use This Quiz?
Ready-made, high-quality content
Curated with lateral thinking and storytelling in mind
Covers both academic and pop culture topics
Designed by a quizzer with real event experience
Usable in inter-college fests, informal quizzes, or Sunday brain workouts
📚 About the Creators
This quiz has been created by Rana Mayank Pratap, an MBBS student and quizmaster at SMC Quiz Club, Silchar Medical College. The club aims to promote a culture of curiosity and smart thinking through weekly and monthly quiz events.
🔍 SEO Tags:
quiz, general knowledge quiz, trivia quiz, SlideShare quiz, college quiz, fun quiz, medical college quiz, India quiz, pop culture quiz, visual quiz, MCQ quiz, connect quiz, science quiz, current affairs quiz, SMC Quiz Club, Silchar Medical College
📣 Reuse & Credit
You’re free to use or adapt this quiz for your own events or sessions with credit to:
SMC Quiz Club – Silchar Medical College & Hospital
Curated by: Rana Mayank Pratap
Vitamin and Nutritional Deficiencies.pptx
Vitamin and Nutritional Deficiencies.pptxVishal Chanalia Vitamin and nutritional deficiency occurs when the body does not receive enough essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, needed for proper functioning. This can lead to various health problems, including weakened immunity, stunted growth, fatigue, poor wound healing, cognitive issues, and increased susceptibility to infections and diseases. Long-term deficiencies can cause serious and sometimes irreversible health complications.
How to use search fetch method in Odoo 18
How to use search fetch method in Odoo 18Celine George The search_fetch is a powerful ORM method used in Odoo for some specific addons to combine the functionality of search and read for more efficient data fetching. It might be used to search for records and fetch specific fields in a single call. It stores the result in the cache memory.
INDUCTIVE EFFECT slide for first prof pharamacy students
INDUCTIVE EFFECT slide for first prof pharamacy studentsSHABNAM FAIZ The inductive effect is the electron-withdrawing or electron-donating effect transmitted through sigma (σ) bonds in a molecule due to differences in electronegativity between atoms.
---
🔹 Definition:
The inductive effect is the permanent shifting of electrons in a sigma bond caused by the electronegativity difference of atoms, resulting in partial charges within the molecule.
Software Engineering - Lecture 02
- 1. Course Code: 331 Lecture 02
- 2. Software Life Cycle “What happens in the „life‟ of software”
- 3. The software process A structured set of activities required to develop a software system. Many different software processes but all involve: Specification – defining what the system should do; Design and implementation – defining the organization of the system and implementing the system; Validation – checking that it does what the customer wants; Evolution – changing the system in response to changing customer needs. A software process model is an abstract representation of a process. It presents a description of a process from some particular perspective.
- 4. Software process models The waterfall model Plan-driven model. Separate and distinct phases of specification and development. Incremental development Specification, development and validation are interleaved. May be plan-driven or agile. Reuse-oriented software engineering The system is assembled from existing components. May be plan-driven or agile. In practice, most large systems are developed using a process that incorporates elements from all of these models. There are no right or wrong software processes.
- 5. Code and Fix (1950–)
- 6. Code and Fix: Issues No process steps – no specs, docs, tests… No separation of concerns – no teamwork No way to deal with complexity
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13. Characteristics The classic life cycle - oldest and most widely used paradigm Known as “Linear sequential model” Activities „flow‟ from one phase to another If there are corrections, return to a previous phase and „flow‟ from there again Major advantages: Good for planning and well-defined/repeated projects
- 14. Drawbacks Real projects rarely follow a sequential flow Hard to state all requirements explicitly No maintenance or evolution involved Customer must have patience Any blunder can be disastrous Leads to “blocking states”
- 16. Problem Cost
- 18. Incremental Model Each linear sequence produces a particular “increment” to the software First increment typically core product; more features added by later increments Allows flexible allocation of resources
- 19. Characteristics Software separated into different “increments” complete working portions Focus on delivery of operational product with each increment - can be evaluated Useful when insufficient staff and can be planned to manage technical risks, e.g. waiting for new hardware
- 20. Benefits The cost of accommodating changing customer requirements is reduced. It is easier to get customer feedback on the development work that has been done. More rapid delivery and deployment of useful software to the customer is possible.
- 21. Drawbacks The process is not visible. Managers need regular deliverables to measure progress. If systems are developed quickly, it is not cost-effective to produce documents that reflect every version of the system. System structure tends to degrade as new increments are added. Unless time and money is spent on refactoring to improve the software, regular change tends to corrupt its structure. Incorporating further software changes becomes increasingly difficult and costly.
- 22. Prototyping
- 23. Prototypes
- 26. Prototypes A horizontal prototype tests a particular layer (typically the GUI) of the system A vertical prototype tests a particular functionality across all layers
- 27. Characteristics Developer and customer determine objectives and draft requirements Prototype quickly produced and evaluated by customer Prototype then refined, and re-evaluated Process iterated, before final product development Advantages: Customer participation and better requirements
- 28. Drawbacks Customer may see prototype as working model and expects fast results Developer compromised when producing prototype quickly, e.g. different operating system or programming language
- 30. Spiral Model System is developed in series of evolutionary releases Milestones for each iteration of the spiral Process does not end with delivery Reflects iterative nature of development
- 31. Characteristics Originally proposed by Boehm, couples iterative nature of prototyping and the systematic aspects of waterfall model Software is developed in series of incremental releases Each iteration produces a more complete product Better management through risk analysis(Modeling)
- 32. Drawbacks May be difficult to convince customers that evolution is controllable Demands risk assessment expertise - major risk will cause problems if not identified Relatively new and not widely used - cannot determine performance
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
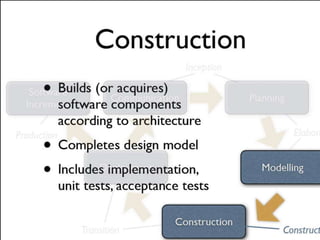
- 40. Unified Process Draws on best features of conventional process models Emphasizes software architecture and design Integrates with UML modeling techniques (more on this later)
- 41. Fourth Generation Techniques (4GT) Requirem ents gathering "Design" Strategy Implementation using 4GL Testing
- 42. 4GT Characteristics Use of software tools that allow software engineer to specify s/w characteristics at higher level The tools generate codes based on specification More time in design and testing - increase productivity Tools may not be easy to use, codes generated may not be efficient
- 43. Key points Software processes are the activities involved in producing a software system. Software process models are abstract representations of these processes. General process models describe the organization of software processes. Examples of these general models include the „waterfall‟ model, incremental development, and reuse-oriented development. Requirements engineering is the process of developing a software specification. Design and implementation processes are concerned with transforming a requirements specification into an executable software system. Software validation is the process of checking that the system conforms to its specification and that it meets the real needs of the users of the system. Software evolution takes place when you change existing software systems to meet new requirements. The software must evolve to remain useful. End
