Design and implementation of path planning algorithm for wheeled mobile robot in a known dynamic environment
Abstract Path planning in mobile robots must ensure optimality of the path. The optimality achieved may be in path, time, energy consumed etc. Path planning in robots also depends on the environment in which it operates like, static or dynamic, known or unknown etc. Global path planning using A* algorithm and genetic algorithm is investigated in this paper. A known dynamic environment, in which a control station will compute the shortest path and communicate to the mobile robot and the mobile robot, will traverse through this path to reach the goal. The control station will keep track of the path traversed by the robot. The mobile robot navigates through the shortest path and if the robot detects any obstacle in the destined path, the mobile robot will update the information about the environment and this information together with the current location will be communicated to the control station. Then the control station, with the updated map of the environment and new starting location and destination recalculates the new shortest path, if any, and will communicate to the mobile robot so that it can reach the destination. The technique has been implemented and tested extensively in real-world experiments and simulation runs. The results demonstrate that the technique effectively calculates the shortest path in known dynamic environment and allows the robot to quickly accomplish the mission.
![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 967
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF PATH PLANNING ALGORITHM
FOR WHEELED MOBILE ROBOT IN A KNOWN DYNAMIC
ENVIRONMENT
Rahul Sharma K
M.Tech Student, Electrical and Electronics Department, Amrita school of engineering, Coimbatore, India
rahulsharmak14@gmail.com
Abstract
Path planning in mobile robots must ensure optimality of the path. The optimality achieved may be in path, time, energy consumed
etc. Path planning in robots also depends on the environment in which it operates like, static or dynamic, known or unknown etc.
Global path planning using A* algorithm and genetic algorithm is investigated in this paper. A known dynamic environment, in which
a control station will compute the shortest path and communicate to the mobile robot and the mobile robot, will traverse through this
path to reach the goal. The control station will keep track of the path traversed by the robot. The mobile robot navigates through the
shortest path and if the robot detects any obstacle in the destined path, the mobile robot will update the information about the
environment and this information together with the current location will be communicated to the control station. Then the control
station, with the updated map of the environment and new starting location and destination recalculates the new shortest path, if any,
and will communicate to the mobile robot so that it can reach the destination. The technique has been implemented and tested
extensively in real-world experiments and simulation runs. The results demonstrate that the technique effectively calculates the
shortest path in known dynamic environment and allows the robot to quickly accomplish the mission.
Index Terms: A* algorithm, A - Star algorithm, path planning, mobile robot
-----------------------------------------------------------------------***-----------------------------------------------------------------------
1. INTRODUCTION
The mobile robot path planning problem is typically
formulated as follows: given a mobile robot and a description
of an environment, plan a path between two specified
locations, a start and end point. The path should be free of
collision and satisfies certain optimization criteria (i.e.,
shortest cost path). According to this definition, path planning
problem is categorized as an optimization problem.
Researchers classify various methods used to solve the path
planning problem based on two factors, (1) the environment
type (i.e., static or dynamic), (2) the path planning algorithms
(i.e., global or local).
The static environment is defined as the environment which
doesn’t contain any moving objects other than a navigating
robot; while the dynamic is the environment which has
dynamic moving objects (i.e., human beings, moving
machines and other moving robots. The global path planning
algorithms requires all terrain to be static and also a complete
knowledge about the search environment. On the other hand,
local path planning means that path planning is being
implemented while the robot is moving; in other words, the
algorithm is capable of producing a new path in response to
environmental changes.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 1 Introduction.
Section 2: Path planning techniques. Section 3: System
architecture. Section 4: Design and implementation. Section 5:
Experimental setup. Section 6: Conclusion.
2. RELATED WORKS
Path finding for a single robot has already been discussed
intensively in the past [1][6][7][8]. For a multi-robot-system
however, the problem is much more complex, especially for
systems with a large number of robots and cluttered
environments. Two different approaches can be distinguished:
Centralized methods and Distributed approaches [2][9]. The
other classification of path planning is online and offline
approaches. In offline path planning the complete information
of the environment will be known before hand. There are
many algorithms designed for offline (global) path planning
namely Dijisktra algorithm, A* algorithm [3], Genetic
algorithm [4] etc. A* star algorithm for finding out shortest
distance is proposed in this paper.
3. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The wheeled mobile robot consists of IR range finders,
position encoders; communication module etc.Three IR range
finders will detect obstacles which are placed at RIGHT,
FRONT and LEFT of the robot as shown in Fig.1. The](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandimplementationofpathplanningalgorithmforwheeledmobilerobotinaknowndynamicenvironment-160802074716/85/Design-and-implementation-of-path-planning-algorithm-for-wheeled-mobile-robot-in-a-known-dynamic-environment-1-320.jpg)

![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 970
Fig -7: Shortest path planning scenario in dynamic
environment
Fig.7 shows the experimental set up of path planning
algorithm in known dynamic environment, where in a third
obstacle is also placed in the grid. During its course to the
goal, the mobile robot detects the third obstacle then it will
localize, itself and obstacles location. This information is
communicated to the central station. The central station will
run the shortest path planning algorithm with the updated
information and this will make the mobile robot traverse
through the shortest path to the goal.
CONCLUSIONS
Path planning in known environment is designed and
implemented. The robot could navigate to the target through
shortest path. It was found that there are deviations from
robots actual path from the desired path. This may be due to
the wheel slippage, position encoder errors, battery charge
fluctuation and difference in friction between wheel and path.
This can be avoided using Simultaneous Localization And
Mapping techniques like Extended Kalman Filter, Particle
Filter etc. The deviation from the path can be predicted using
probabilistic techniques and it can be corrected accordingly.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Author gratefully acknowledges the facilities available at the
Amrita school of engineering, Coimbatore, sincerely thanks to
guide Dr. Gireesh Kumar and Mr. Sivraj P for helping in
theoretical and practical section.
REFERENCES
[1]. Masehian, Ellips, and Davoud Sedighizadeh., Classic and
heuristic approaches in robot motion planning-a chronological
review, World Academy of Science, Engineering and
Technology 29 (2007): 101-106.
[2]. Park, Sujin, Jin Hong Jung, and Seong-Lyun Kim.,
Cooperative path-finding of multi-robots with wireless
multihop communications, Modeling and Optimization in
Mobile, Ad Hoc, and Wireless Networks and Workshops,
2008, WiOPT 2008, 6th International Symposium on. IEEE,
2008.
[3]. Cui, Shi-Gang, Hui Wang, and Li Yang, A Simulation
Study of A-star Algorithm for Robot Path Planning, 16th
international conference on mechatronics technology,PP: 506
– 510, 2012
[4]. Sedighi, Kamran H., Kaveh Ashenayi, Theodore W.
Manikas, Roger L. Wainwright, and Heng-Ming Tai.,
Autonomous local path planning for a mobile robot using a
genetic algorithm, In Evolutionary Computation, 2004,
CEC2004, Congress on, vol. 2, pp. 1338-1345. IEEE, 2004.
[5] T. Akimoto and N. Hagita "Introduction to a Network
Robot System", Proc. intl Symp. Intelligent Sig. Processing
and Communication, 2006
[6]. A. Stentz, "Optimal and efficient path planning for
unknown and dynamic enviroments," Technical report, CMU-
RI-TR-93-20, The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon
University, PA, USA, 1993.
[7]. H. Noborio, K. Fujimura and Y. Horiuchi, "A comparative
study of sensor-based path-planning algorithms in an unknown
maze," Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and
Systems, pp. 909-916, 2000.
[8] L. Podsedkowski, J. Nowakowski, M. Idzikowski and I.
Vizvary, "A new solution method for path planning in
partially known or unkonwn environment for nonholonomic
mobile robots," Elsevier Robotics and Autonomous Systems,
Vol. 34, pp. 145-152, 2001.
[9] M. Szymanski, T. Breitling, J. Seyfried and H . Wörn,
"Distributed shortest-path finding by a mirco-robot swarm,"
Springer Ant Colony Optimization and Swarm Intelligence,
LNCS 4150, pp. 404-411, 2006.
BIOGRAPHIES
Rahul Sharma K is a student at Amrita
University at Coimbatore and presently
doing Master Of Technology in
Embedded System. He received the
B.Tech degree in Electrical and
Electronics Engineering from the
Mahatma Gandhi University. He has an
industrial experience of four years as
Electrical and Instrumentation Engineer. His research interests
include robotics, real time systems and Wireless Sensor
Networks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandimplementationofpathplanningalgorithmforwheeledmobilerobotinaknowndynamicenvironment-160802074716/85/Design-and-implementation-of-path-planning-algorithm-for-wheeled-mobile-robot-in-a-known-dynamic-environment-4-320.jpg)
Recommended




























































More Related Content
What's hot (20)








































Viewers also liked (17)


































Similar to Design and implementation of path planning algorithm for wheeled mobile robot in a known dynamic environment (20)








































More from eSAT Journals (20)








































Recently uploaded (20)






























Design and implementation of path planning algorithm for wheeled mobile robot in a known dynamic environment
- 1. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163 __________________________________________________________________________________________ Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 967 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF PATH PLANNING ALGORITHM FOR WHEELED MOBILE ROBOT IN A KNOWN DYNAMIC ENVIRONMENT Rahul Sharma K M.Tech Student, Electrical and Electronics Department, Amrita school of engineering, Coimbatore, India [email protected] Abstract Path planning in mobile robots must ensure optimality of the path. The optimality achieved may be in path, time, energy consumed etc. Path planning in robots also depends on the environment in which it operates like, static or dynamic, known or unknown etc. Global path planning using A* algorithm and genetic algorithm is investigated in this paper. A known dynamic environment, in which a control station will compute the shortest path and communicate to the mobile robot and the mobile robot, will traverse through this path to reach the goal. The control station will keep track of the path traversed by the robot. The mobile robot navigates through the shortest path and if the robot detects any obstacle in the destined path, the mobile robot will update the information about the environment and this information together with the current location will be communicated to the control station. Then the control station, with the updated map of the environment and new starting location and destination recalculates the new shortest path, if any, and will communicate to the mobile robot so that it can reach the destination. The technique has been implemented and tested extensively in real-world experiments and simulation runs. The results demonstrate that the technique effectively calculates the shortest path in known dynamic environment and allows the robot to quickly accomplish the mission. Index Terms: A* algorithm, A - Star algorithm, path planning, mobile robot -----------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. INTRODUCTION The mobile robot path planning problem is typically formulated as follows: given a mobile robot and a description of an environment, plan a path between two specified locations, a start and end point. The path should be free of collision and satisfies certain optimization criteria (i.e., shortest cost path). According to this definition, path planning problem is categorized as an optimization problem. Researchers classify various methods used to solve the path planning problem based on two factors, (1) the environment type (i.e., static or dynamic), (2) the path planning algorithms (i.e., global or local). The static environment is defined as the environment which doesn’t contain any moving objects other than a navigating robot; while the dynamic is the environment which has dynamic moving objects (i.e., human beings, moving machines and other moving robots. The global path planning algorithms requires all terrain to be static and also a complete knowledge about the search environment. On the other hand, local path planning means that path planning is being implemented while the robot is moving; in other words, the algorithm is capable of producing a new path in response to environmental changes. This paper is organized as follows: Section 1 Introduction. Section 2: Path planning techniques. Section 3: System architecture. Section 4: Design and implementation. Section 5: Experimental setup. Section 6: Conclusion. 2. RELATED WORKS Path finding for a single robot has already been discussed intensively in the past [1][6][7][8]. For a multi-robot-system however, the problem is much more complex, especially for systems with a large number of robots and cluttered environments. Two different approaches can be distinguished: Centralized methods and Distributed approaches [2][9]. The other classification of path planning is online and offline approaches. In offline path planning the complete information of the environment will be known before hand. There are many algorithms designed for offline (global) path planning namely Dijisktra algorithm, A* algorithm [3], Genetic algorithm [4] etc. A* star algorithm for finding out shortest distance is proposed in this paper. 3. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE The wheeled mobile robot consists of IR range finders, position encoders; communication module etc.Three IR range finders will detect obstacles which are placed at RIGHT, FRONT and LEFT of the robot as shown in Fig.1. The
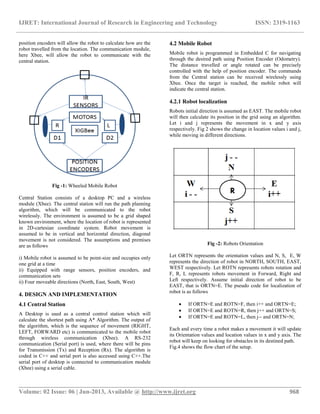
- 2. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163 __________________________________________________________________________________________ Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 968 position encoders will allow the robot to calculate how are the robot travelled from the location. The communication module, here Xbee, will allow the robot to communicate with the central station. Fig -1: Wheeled Mobile Robot Central Station consists of a desktop PC and a wireless module (Xbee). The central station will run the path planning algorithm, which will be communicated to the robot wirelessly. The environment is assumed to be a grid shaped known environment, where the location of robot is represented in 2D-cartesian coordinate system. Robot movement is assumed to be in vertical and horizontal direction, diagonal movement is not considered. The assumptions and premises are as follows i) Mobile robot is assumed to be point-size and occupies only one grid at a time ii) Equipped with range sensors, position encoders, and communication sets ii) Four moveable directions (North, East, South, West) 4. DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION 4.1 Central Station A Desktop is used as a central control station which will calculate the shortest path using A* Algorithm. The output of the algorithm, which is the sequence of movement (RIGHT, LEFT, FORWARD etc) is communicated to the mobile robot through wireless communication (Xbee). A RS-232 communication (Serial port) is used, where there will be pins for Transmission (Tx) and Reception (Rx). The algorithm is coded in C++ and serial port is also accessed using C++.The serial port of desktop is connected to communication module (Xbee) using a serial cable. 4.2 Mobile Robot Mobile robot is programmed in Embedded C for navigating through the desired path using Position Encoder (Odometry). The distance travelled or angle rotated can be precisely controlled with the help of position encoder. The commands from the Central station can be received wirelessly using Xbee. Once the target is reached, the mobile robot will indicate the central station. 4.2.1 Robot localization Robots initial direction is assumed as EAST. The mobile robot will then calculate its position in the grid using an algorithm. Let i and j represents the movement in x and y axis respectively. Fig 2 shows the change in location values i and j, while moving in different directions. Fig -2: Robots Orientation Let ORTN represents the orientation values and N, S, E, W represents the direction of robot in NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, WEST respectively. Let ROTN represents robots rotation and F, R, L represents robots movement in Forward, Right and Left respectively. Assume initial direction of robot to be EAST, that is ORTN=E. The pseudo code for localization of robot is as follows If ORTN=E and ROTN=F, then i++ and ORTN=E; If ORTN=E and ROTN=R, then j++ and ORTN=S; If ORTN=E and ROTN=L, then j-- and ORTN=N; Each and every time a robot makes a movement it will update its Orientation values and location values in x and y axis. The robot will keep on looking for obstacles in its destined path. Fig.4 shows the flow chart of the setup.
- 3. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163 __________________________________________________________________________________________ Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 969 Fig -4: Flow chart 5. EXPERIMENTAL SETUP A grid of size 20cm x 20cm where arranged, in which the obstacles were kept and this is fed to the central station. The central station will calculate the shortest path and this will be communicated to the robot wirelessly. The mobile robot will then start moving through the assigned path. If the robot detects an obstacle in the assigned path, the robot will stop moving; calculate its position and the obstacle position. This information together with the direction information (N, S, E, and W) will be communicated to the central station. The central station will then update its obstacle table and will assign the starting point as the current robot’s position. The central station will rerun the algorithm and the shortest path, if any will be communicated to the robot. A grid of 5x3 is used. An obstacle matrix will provide the information of obstacles present in the known environment. Start node and destination node information is also given. The inputs to the central station includes Starting location (source) Destination Obstacle table indicating the location of obstacle in the grid Fig -5: Output window at central station The output of the central station includes, as shown in Fig.5 Time to calculate (Computation time) Routing (Grid to grid movement) Commands to mobile robots (F- Forward, R-Right, L-Left) Fig -6: Shortest path planning scenario in static environment Fig.6 shows the experimental setup for path planning algorithm in a known dynamic environment. The starting location of the environment is fed as input to the central station. The obstacle table, ie a matrix of size 5x3 is initialized with either 0 or 1 depending upon the presence of obstacle. The destination point or the goal point is also initialized.
- 4. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163 __________________________________________________________________________________________ Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 970 Fig -7: Shortest path planning scenario in dynamic environment Fig.7 shows the experimental set up of path planning algorithm in known dynamic environment, where in a third obstacle is also placed in the grid. During its course to the goal, the mobile robot detects the third obstacle then it will localize, itself and obstacles location. This information is communicated to the central station. The central station will run the shortest path planning algorithm with the updated information and this will make the mobile robot traverse through the shortest path to the goal. CONCLUSIONS Path planning in known environment is designed and implemented. The robot could navigate to the target through shortest path. It was found that there are deviations from robots actual path from the desired path. This may be due to the wheel slippage, position encoder errors, battery charge fluctuation and difference in friction between wheel and path. This can be avoided using Simultaneous Localization And Mapping techniques like Extended Kalman Filter, Particle Filter etc. The deviation from the path can be predicted using probabilistic techniques and it can be corrected accordingly. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Author gratefully acknowledges the facilities available at the Amrita school of engineering, Coimbatore, sincerely thanks to guide Dr. Gireesh Kumar and Mr. Sivraj P for helping in theoretical and practical section. REFERENCES [1]. Masehian, Ellips, and Davoud Sedighizadeh., Classic and heuristic approaches in robot motion planning-a chronological review, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 29 (2007): 101-106. [2]. Park, Sujin, Jin Hong Jung, and Seong-Lyun Kim., Cooperative path-finding of multi-robots with wireless multihop communications, Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc, and Wireless Networks and Workshops, 2008, WiOPT 2008, 6th International Symposium on. IEEE, 2008. [3]. Cui, Shi-Gang, Hui Wang, and Li Yang, A Simulation Study of A-star Algorithm for Robot Path Planning, 16th international conference on mechatronics technology,PP: 506 – 510, 2012 [4]. Sedighi, Kamran H., Kaveh Ashenayi, Theodore W. Manikas, Roger L. Wainwright, and Heng-Ming Tai., Autonomous local path planning for a mobile robot using a genetic algorithm, In Evolutionary Computation, 2004, CEC2004, Congress on, vol. 2, pp. 1338-1345. IEEE, 2004. [5] T. Akimoto and N. Hagita "Introduction to a Network Robot System", Proc. intl Symp. Intelligent Sig. Processing and Communication, 2006 [6]. A. Stentz, "Optimal and efficient path planning for unknown and dynamic enviroments," Technical report, CMU- RI-TR-93-20, The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, PA, USA, 1993. [7]. H. Noborio, K. Fujimura and Y. Horiuchi, "A comparative study of sensor-based path-planning algorithms in an unknown maze," Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 909-916, 2000. [8] L. Podsedkowski, J. Nowakowski, M. Idzikowski and I. Vizvary, "A new solution method for path planning in partially known or unkonwn environment for nonholonomic mobile robots," Elsevier Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol. 34, pp. 145-152, 2001. [9] M. Szymanski, T. Breitling, J. Seyfried and H . Wörn, "Distributed shortest-path finding by a mirco-robot swarm," Springer Ant Colony Optimization and Swarm Intelligence, LNCS 4150, pp. 404-411, 2006. BIOGRAPHIES Rahul Sharma K is a student at Amrita University at Coimbatore and presently doing Master Of Technology in Embedded System. He received the B.Tech degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from the Mahatma Gandhi University. He has an industrial experience of four years as Electrical and Instrumentation Engineer. His research interests include robotics, real time systems and Wireless Sensor Networks.







