B.sc cs-ii-u-3.2-basic computer programming and micro programmed control
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes1,015 views
The document describes the implementation and organization of a microprogrammed control unit. It discusses the main components which include the control memory containing microinstructions, control address register (CAR) for specifying the address of the next microinstruction, and a next address generator or microprogram sequencer for determining the address sequence. It also explains microoperations, mapping of instructions to routines in control memory, conditional branching, and provides an example of a microprogram routine for fetching instructions from memory.
1 of 27
Downloaded 23 times

![Control Unit Implementation[1]
2
• Hardwired
• Microprogrammed
Instruction code
Combinational
Logic Circuits
Memory
Sequence Counter
.
.
Control
signals
Control
signals
Next Address
Generator
(sequencer)
CAR Control
Memory
CDR Decoding
Circuit
Memory
.
.
CAR: Control Address Register
CDR: Control Data RegisterInstruction code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-2-320.jpg)









![Mapping of Instruction[2]
• Each computer instruction has its own
microprogram routine stored in a given
location of the control memory
• Mapping
– Transformation from instruction code bits to
address in control memory where routine is located
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-12-320.jpg)

![Address Sequencing[2]
• Address sequencing capabilities required in
control unit
– Incrementing CAR
– Unconditional or conditional branch, depending on
status bit conditions
– Mapping from bits of instruction to address for
control memory
– Facility for subroutine call and return
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-14-320.jpg)

![Microprogram Example[3]
16
Computer
Configuration
MUX
AR
10 0
PC
10 0
Address Memory
2048 x 16
MUX
DR
15 0
Arithmetic
logic and
shift unit
AC
15 0
SBR
6 0
CAR
6 0
Control memory
128 x 20
Control unit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-16-320.jpg)
![Microprogram Example
17
Microinstruction Format
EA is the effective address
Symbol OP-code Description
ADD 0000 AC ← AC + M[EA]
BRANCH 0001 if (AC < 0) then (PC ← EA)
STORE 0010 M[EA] ← AC
EXCHANGE 0011 AC ← M[EA], M[EA] ← AC
Computer instruction format
I Opcode
15 14 11 10
Address
0
Four computer instructions
F1 F2 F3 CD BR AD
3 3 3 2 2 7
F1, F2, F3: Microoperation fields
CD: Condition for branching
BR: Branch field
AD: Address field](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-17-320.jpg)
![Microinstruction Fields
18
F1 Microoperation Symbol
000 None NOP
001 AC ← AC + DR ADD
010 AC ← 0 CLRAC
011 AC ← AC + 1 INCAC
100 AC ← DR DRTAC
101 AR ← DR(0-10) DRTAR
110 AR ← PC PCTAR
111 M[AR] ← DR WRITE
F2 Microoperation Symbol
000 None NOP
001 AC ← AC - DR SUB
010 AC ← AC ∨ DR OR
011 AC ← AC ∧ DR AND
100 DR ← M[AR] READ
101 DR ← AC ACTDR
110 DR ← DR + 1 INCDR
111 DR(0-10) ← PC PCTDR
F3 Microoperation Symbol
000 None NOP
001 AC ← AC ⊕ DR XOR
010 AC ← AC’ COM
011 AC ← shl AC SHL
100 AC ← shr AC SHR
101 PC ← PC + 1 INCPC
110 PC ← AR ARTPC
111 Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-18-320.jpg)

![Fetch Routine
21
Fetch routine
- Read instruction from memory
- Decode instruction and update PC
AR ← PC
DR ← M[AR], PC ← PC + 1
AR ← DR(0-10), CAR(2-5) ← DR(11-14), CAR(0,1,6) ← 0
Symbolic microprogram for fetch routine:
ORG 64
PCTAR U JMP NEXT
READ, INCPC U JMP NEXT
DRTAR U MAP
FETCH:
Binary microporgram for fetch routine:
1000000 110 000 000 00 00 1000001
1000001 000 100 101 00 00 1000010
1000010 101 000 000 00 11 0000000
Binary
address F1 F2 F3 CD BR AD
Microinstructions for fetch routine:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-21-320.jpg)


![Design of Control Unit[4]
24
microoperation fields
3 x 8 decoder
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
F1
3 x 8 decoder
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
F2
3 x 8 decoder
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
F3
Arithmetic
logic and
shift unit
AND
ADD
DRTAC
AC
Load
From
PC
From
DR(0-10)
Select 0 1
Multiplexers
AR
Load Clock
AC
DR
DRTAR
PCTAR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150317034836-conversion-gate01/85/B-sc-cs-ii-u-3-2-basic-computer-programming-and-micro-programmed-control-24-320.jpg)



Ad
Recommended
Computer arithmetic



Computer arithmeticBalakrishna Chowdary All the data about computer arithmetic .. i searched for it in slide share but no result.. so i made it for u guys..
Microprocessor square wave



Microprocessor square waveFthi Arefayne This document is a laboratory manual for the subject Microprocessor & Microcontroller Lab in the 3rd year 5th semester of the B.Tech programme at SRM University. It was prepared by Assistant Professor A Bhargavi Haripriya of the Department of Biomedical Engineering. The manual contains pin diagrams, instruction sets and programs for the 8085, 8086 and 8051 microprocessors and microcontrollers to be performed by students in the lab.
Android Os (operating system) 



Android Os (operating system) Ruhil Arora Android is an open source, Linux-based operating system developed by Google. It has seen many versions released since 2008 that have added new features and functionality while improving performance and security. Some key versions include Android 1.5 Cupcake, 2.0 Eclair, 2.2 Froyo, 2.3 Gingerbread, 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich, 4.4 KitKat, 5.0 Lollipop, 6.0 Marshmallow, 7.0 Nougat, and 8.0 Oreo. The latest versions focus on enhancing the user experience, battery life, and security. Android is available through the Google Play store and has an open development environment, while iOS is proprietary to Apple
Computer Organization and 8085 microprocessor notes



Computer Organization and 8085 microprocessor notesLakshmi Sarvani Videla The CPU is made up of 3 major parts: the register set, control unit, and arithmetic logic unit. The register set stores intermediate values during program execution. The control unit generates control signals and selects operations for the ALU. The ALU performs arithmetic and logic operations. Computer architecture includes instruction formats, addressing modes, instruction sets, and CPU register organization. Registers are organized in a bus structure to efficiently transfer data and perform microoperations under control of the control unit. Common instruction fields are the operation code, address fields, and addressing mode fields. Instructions can be classified by the number of address fields as zero-address, one-address, two-address, or three-address instructions. Common addressing modes specify how operands
Interfacing LCD with 8051 Microcontroller



Interfacing LCD with 8051 MicrocontrollerPantech ProLabs India Pvt Ltd An LCD display is specifically designed to interface with microcontrollers and not standard ICs. It can display letters, symbols, and user-defined characters. Interfacing an LCD with an 8051 microcontroller involves understanding the LCD's pins and commands, and using C or assembly code to control write and read operations to the LCD. More details on interfacing LCDs with 8051 microcontrollers can be found on the listed websites.
Interrupt



InterruptSiddique Ibrahim Interrupts allow input/output devices to alert the processor when they are ready. When an interrupt request occurs, the processor saves its context and jumps to an interrupt service routine. It then acknowledges the interrupt and restores its context before returning to the original instruction. Processors have mechanisms for prioritizing interrupts and enabling/disabling them to avoid infinite loops or unintended requests.
Instruction codes



Instruction codespradeepa velmurugan An instruction code consists of an operation code and operand(s) that specify the operation to perform and data to use. Operation codes are binary codes that define operations like addition, subtraction, etc. Early computers stored programs and data in separate memory sections and used a single accumulator register. Modern computers have multiple registers for temporary storage and performing operations faster than using only memory. Computer instructions encode an operation code and operand fields to specify the basic operations to perform on data stored in registers or memory.
Addressing sequencing



Addressing sequencingrajshreemuthiah The document discusses address sequencing in a microprogram control unit. It begins by defining key terms like control address register, which stores the initial address of the first microinstruction. It then explains that the next address generator is responsible for selecting the next address from control memory based on the current microinstruction. Microinstructions are stored in control memory in groups that make up routines corresponding to each machine instruction. The document also discusses control memory, hardwired control vs microprogrammed control, and examples of next address generation and status bits.
Central Processing Unit User View



Central Processing Unit User ViewAnuj Modi This document summarizes the central processing unit (CPU) and its organization. The CPU has three main parts: the register set, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and control unit. It describes two common CPU organizations: general register organization and stack organization. General register organization uses multiple registers and a register set with a register file and ALU. The stack organization uses a last-in, first-out stack and stack pointer register. It also discusses addressing modes that provide programming versatility and reduce the number of bits in instruction addresses.
My seminar ppt SPACE MOUSE



My seminar ppt SPACE MOUSESudeep Kumar The document discusses the Space Mouse, a 3D controller used to manipulate objects in 3D environments. It describes what a Space Mouse is, its components and how it works, features like programmable buttons, technical specifications, origins at a German aerospace research establishment, applications in CAD/CAM/CAE software, and advantages like reduced drawing times and natural hand position.
Memory Organization



Memory OrganizationKamal Acharya This slide contain the introduction to memory , hierarchy, types, virtual memory,associative memory and cache memory.
androidstudio.pptx



androidstudio.pptxSundaresanB5 Android Studio is the official IDE for developing Android applications. It was announced by Google in 2013 and is based on JetBrains' IntelliJ IDEA software. Android Studio replaced Eclipse Android Development Tools as Google's primary IDE for native Android development. It supports building Android and Android Wear apps and integrates Google Cloud services. The stable version is continuously updated with new features to support the latest Android development needs.
Instruction cycle



Instruction cycleshweta-sharma99 The instruction cycle describes the process a computer follows to execute each machine language instruction. It involves 4 phases: 1) Fetch - the instruction is fetched from memory and placed in the instruction register. 2) Decode - the instruction is analyzed and decoded. 3) Execute - the processor executes the instruction by performing the specified operation. 4) The program counter is then incremented to point to the next instruction, and the cycle repeats. Each phase involves transferring data between the program counter, instruction register, memory, and other components via a common bus under the control of a timing unit. The instruction specifies the operation to be performed, such as a memory reference, register operation, or I/O access.
Graphical User Interface 



Graphical User Interface Bivek Pakuwal Graphical User Interface (GUI) is a visual way for users to interact with a computer program using graphical elements like windows, icons, menus, etc. rather than text-based commands. A GUI makes programs easier to use by presenting commands visually and allowing users to perform actions by clicking on screen elements rather than memorizing commands. Well-designed GUIs help users avoid complex text commands by providing intuitive graphical layouts and controls.
A c program of Phonebook application



A c program of Phonebook applicationsvrohith 9 This program is a simple application that you can find on your mobile as a contacts app. This allows the users to save contacts under a name.
C presentation



C presentationAPSMIND TECHNOLOGY PVT LTD. A small journey in programming using C Language. In This Presentation i provide a small introduction about C Language.
Our Company APSMIND TECHNLOGY PVT LTD actually provide Application/software development training using various language like C, C++, java, .Net, PHP etc.
We also ,develop application and website for various client as for their requirement.
Computer registers



Computer registersDeepikaT13 This document discusses computer registers and their functions. It describes 8 key registers - Data Register, Address Register, Accumulator, Instruction Register, Program Counter, Temporary Register, Input Register and Output Register. It explains what each register stores and its role. For example, the Program Counter holds the address of the next instruction to be executed, while the Accumulator is used for general processing. The registers are connected via a common bus to transfer information between memory and registers for processing instructions.
Android architecture



Android architectureKartik Kalpande Patil This document provides an overview of Android and mobile application development. It discusses the history of Android, including its origins at Android Inc. and acquisition by Google. It describes the core components of the Android software stack and architecture. The document outlines the Android development process and tools used to build, run, test and publish Android apps. It also discusses advantages and disadvantages of developing for mobile platforms.
HDL Implementation of Vending Machine Report with Verilog Code



HDL Implementation of Vending Machine Report with Verilog CodePratik Patil A vending machine is a machine which dispenses items such as snacks, beverages, lottery tickets, consumer products to customers automatically, after the customer inserts currency or credit into the machine. Nowadays, Vending Machines are well known among Japan, Malaysia and Singapore. The quantity of machines in these countries is on the top worldwide. This is due to the modern lifestyles which require fast food processing with high quality. This paper describes the designing of Vending Machine with Auto-Billing Features. The objective here is to design Vending Machine Controller which accepts money inputs (i and j) in any sequence and delivers the products when the required amount has been deposited and gives back the change. Here an additional facility is provided to the user. It is possible to withdraw the deposited money in between if the customer wishes so by pressing a push button. The Verilog Code for the proposed Vending Machine model is developed and the Simulation results are successfully verified using Xilinx ISE 9.2i tool.
Chapter 03 arithmetic for computers



Chapter 03 arithmetic for computersBảo Hoang This document discusses computer arithmetic and floating point representation. It begins with an introduction to computer arithmetic and covers topics like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and their algorithms. It then discusses floating point representation which uses scientific notation to represent real numbers. Key aspects covered include single and double precision formats, normalized and denormalized numbers, overflow and underflow, and biased exponent representation. Examples are provided to illustrate floating point addition and multiplication. The document also discusses floating point instructions in MIPS and the need for accurate arithmetic in floating point operations.
memory reference instruction



memory reference instructionDeepikaT13 This document discusses memory reference instructions (MRI) and their implementation using microoperations. It defines MRI as instructions that operate on data stored in memory. Seven common MRI are described: AND to AC, ADD to AC, LDA, STA, BUN, BSA, and ISZ. Each MRI is broken down into its constituent microoperations, which are controlled by timing signals. The microoperations transfer data between memory, registers, and logic circuits. A control flow chart illustrates the sequencing of microoperations for each instruction type.
Memory reference instruction



Memory reference instructionSanjeev Patel The document discusses memory reference instructions in a processor. It explains that bits 12-14 in the instruction register determine the memory reference instruction type, which can be AND to AC, ADD to AC, LDA, STA, BUN, BSA, or ISZ. It then describes the operation of each instruction type, including which decoder line is activated and the timing signals used to access memory and update registers.
Introduction to Microprocessor and Microcontroller.pdf



Introduction to Microprocessor and Microcontroller.pdfEngineering Funda The document discusses microprocessors and microcontrollers. It defines a microprocessor as a central processing unit on a single chip that performs arithmetic and logical operations, while a microcontroller contains additional components like memory, timers and I/O ports on a single chip. The document lists differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers like fixed vs flexible memory and I/O, and provides examples of each. It also outlines criteria for choosing a microcontroller like meeting task needs efficiently, development support available, and future availability.
Functions ppt ch06



Functions ppt ch06Terry Yoast The chapter discusses user-defined functions in C++, including:
- Value-returning functions that use the return statement to return a value of a specific data type.
- Void functions that do not return a value.
- Function prototypes that declare a function without defining its body, allowing a function to be called before it is defined.
- Value and reference parameters, where reference parameters pass a reference to the variable rather than a copy.
- The scope of identifiers as either local to a function or global across the entire program.
Standard IO Interface



Standard IO Interfacetamizh arthanari Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. It allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, scale and re-provision resources at will, and save money by opting to pay as they use. Cloud computing allows companies to avoid or minimize up-front infrastructure costs, and focus on projects that differentiate their businesses instead of on infrastructure.
Interrupt presentaion



Interrupt presentaionTanXeela Sheikh The document discusses interrupts, which occur when a process is executing on the CPU and another process requests to run. This interrupts the running process. There are three main types of interrupts: internal, external, and software interrupts. The interrupt cycle involves suspending the current process, saving its context, running the interrupt handler, restoring context, and continuing the original process. Interrupts are prioritized, with hardware commands having the highest priority and I/O devices the lowest. This priority scheme allows more important interrupts to preempt lower priority ones.
Computer architecture addressing modes and formats



Computer architecture addressing modes and formatsMazin Alwaaly Computer architecture addressing modes and formats seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Android app development ppt



Android app development pptsaitej15 This document provides an overview of Android app development. It discusses what Android is, its history and architecture. It describes the core components of an Android app like activities, services, content providers and intents. It also discusses Android Studio as the IDE, system requirements, how to develop a first app, common programming languages and learning resources. The goal is to introduce the key concepts for developing Android apps.
OER an Schule & Hochschule



OER an Schule & Hochschulee-teaching.org Übersicht zu organisationalen Aspekten und strategischen Ansätzen
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Central Processing Unit User View



Central Processing Unit User ViewAnuj Modi This document summarizes the central processing unit (CPU) and its organization. The CPU has three main parts: the register set, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and control unit. It describes two common CPU organizations: general register organization and stack organization. General register organization uses multiple registers and a register set with a register file and ALU. The stack organization uses a last-in, first-out stack and stack pointer register. It also discusses addressing modes that provide programming versatility and reduce the number of bits in instruction addresses.
My seminar ppt SPACE MOUSE



My seminar ppt SPACE MOUSESudeep Kumar The document discusses the Space Mouse, a 3D controller used to manipulate objects in 3D environments. It describes what a Space Mouse is, its components and how it works, features like programmable buttons, technical specifications, origins at a German aerospace research establishment, applications in CAD/CAM/CAE software, and advantages like reduced drawing times and natural hand position.
Memory Organization



Memory OrganizationKamal Acharya This slide contain the introduction to memory , hierarchy, types, virtual memory,associative memory and cache memory.
androidstudio.pptx



androidstudio.pptxSundaresanB5 Android Studio is the official IDE for developing Android applications. It was announced by Google in 2013 and is based on JetBrains' IntelliJ IDEA software. Android Studio replaced Eclipse Android Development Tools as Google's primary IDE for native Android development. It supports building Android and Android Wear apps and integrates Google Cloud services. The stable version is continuously updated with new features to support the latest Android development needs.
Instruction cycle



Instruction cycleshweta-sharma99 The instruction cycle describes the process a computer follows to execute each machine language instruction. It involves 4 phases: 1) Fetch - the instruction is fetched from memory and placed in the instruction register. 2) Decode - the instruction is analyzed and decoded. 3) Execute - the processor executes the instruction by performing the specified operation. 4) The program counter is then incremented to point to the next instruction, and the cycle repeats. Each phase involves transferring data between the program counter, instruction register, memory, and other components via a common bus under the control of a timing unit. The instruction specifies the operation to be performed, such as a memory reference, register operation, or I/O access.
Graphical User Interface 



Graphical User Interface Bivek Pakuwal Graphical User Interface (GUI) is a visual way for users to interact with a computer program using graphical elements like windows, icons, menus, etc. rather than text-based commands. A GUI makes programs easier to use by presenting commands visually and allowing users to perform actions by clicking on screen elements rather than memorizing commands. Well-designed GUIs help users avoid complex text commands by providing intuitive graphical layouts and controls.
A c program of Phonebook application



A c program of Phonebook applicationsvrohith 9 This program is a simple application that you can find on your mobile as a contacts app. This allows the users to save contacts under a name.
C presentation



C presentationAPSMIND TECHNOLOGY PVT LTD. A small journey in programming using C Language. In This Presentation i provide a small introduction about C Language.
Our Company APSMIND TECHNLOGY PVT LTD actually provide Application/software development training using various language like C, C++, java, .Net, PHP etc.
We also ,develop application and website for various client as for their requirement.
Computer registers



Computer registersDeepikaT13 This document discusses computer registers and their functions. It describes 8 key registers - Data Register, Address Register, Accumulator, Instruction Register, Program Counter, Temporary Register, Input Register and Output Register. It explains what each register stores and its role. For example, the Program Counter holds the address of the next instruction to be executed, while the Accumulator is used for general processing. The registers are connected via a common bus to transfer information between memory and registers for processing instructions.
Android architecture



Android architectureKartik Kalpande Patil This document provides an overview of Android and mobile application development. It discusses the history of Android, including its origins at Android Inc. and acquisition by Google. It describes the core components of the Android software stack and architecture. The document outlines the Android development process and tools used to build, run, test and publish Android apps. It also discusses advantages and disadvantages of developing for mobile platforms.
HDL Implementation of Vending Machine Report with Verilog Code



HDL Implementation of Vending Machine Report with Verilog CodePratik Patil A vending machine is a machine which dispenses items such as snacks, beverages, lottery tickets, consumer products to customers automatically, after the customer inserts currency or credit into the machine. Nowadays, Vending Machines are well known among Japan, Malaysia and Singapore. The quantity of machines in these countries is on the top worldwide. This is due to the modern lifestyles which require fast food processing with high quality. This paper describes the designing of Vending Machine with Auto-Billing Features. The objective here is to design Vending Machine Controller which accepts money inputs (i and j) in any sequence and delivers the products when the required amount has been deposited and gives back the change. Here an additional facility is provided to the user. It is possible to withdraw the deposited money in between if the customer wishes so by pressing a push button. The Verilog Code for the proposed Vending Machine model is developed and the Simulation results are successfully verified using Xilinx ISE 9.2i tool.
Chapter 03 arithmetic for computers



Chapter 03 arithmetic for computersBảo Hoang This document discusses computer arithmetic and floating point representation. It begins with an introduction to computer arithmetic and covers topics like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and their algorithms. It then discusses floating point representation which uses scientific notation to represent real numbers. Key aspects covered include single and double precision formats, normalized and denormalized numbers, overflow and underflow, and biased exponent representation. Examples are provided to illustrate floating point addition and multiplication. The document also discusses floating point instructions in MIPS and the need for accurate arithmetic in floating point operations.
memory reference instruction



memory reference instructionDeepikaT13 This document discusses memory reference instructions (MRI) and their implementation using microoperations. It defines MRI as instructions that operate on data stored in memory. Seven common MRI are described: AND to AC, ADD to AC, LDA, STA, BUN, BSA, and ISZ. Each MRI is broken down into its constituent microoperations, which are controlled by timing signals. The microoperations transfer data between memory, registers, and logic circuits. A control flow chart illustrates the sequencing of microoperations for each instruction type.
Memory reference instruction



Memory reference instructionSanjeev Patel The document discusses memory reference instructions in a processor. It explains that bits 12-14 in the instruction register determine the memory reference instruction type, which can be AND to AC, ADD to AC, LDA, STA, BUN, BSA, or ISZ. It then describes the operation of each instruction type, including which decoder line is activated and the timing signals used to access memory and update registers.
Introduction to Microprocessor and Microcontroller.pdf



Introduction to Microprocessor and Microcontroller.pdfEngineering Funda The document discusses microprocessors and microcontrollers. It defines a microprocessor as a central processing unit on a single chip that performs arithmetic and logical operations, while a microcontroller contains additional components like memory, timers and I/O ports on a single chip. The document lists differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers like fixed vs flexible memory and I/O, and provides examples of each. It also outlines criteria for choosing a microcontroller like meeting task needs efficiently, development support available, and future availability.
Functions ppt ch06



Functions ppt ch06Terry Yoast The chapter discusses user-defined functions in C++, including:
- Value-returning functions that use the return statement to return a value of a specific data type.
- Void functions that do not return a value.
- Function prototypes that declare a function without defining its body, allowing a function to be called before it is defined.
- Value and reference parameters, where reference parameters pass a reference to the variable rather than a copy.
- The scope of identifiers as either local to a function or global across the entire program.
Standard IO Interface



Standard IO Interfacetamizh arthanari Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. It allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, scale and re-provision resources at will, and save money by opting to pay as they use. Cloud computing allows companies to avoid or minimize up-front infrastructure costs, and focus on projects that differentiate their businesses instead of on infrastructure.
Interrupt presentaion



Interrupt presentaionTanXeela Sheikh The document discusses interrupts, which occur when a process is executing on the CPU and another process requests to run. This interrupts the running process. There are three main types of interrupts: internal, external, and software interrupts. The interrupt cycle involves suspending the current process, saving its context, running the interrupt handler, restoring context, and continuing the original process. Interrupts are prioritized, with hardware commands having the highest priority and I/O devices the lowest. This priority scheme allows more important interrupts to preempt lower priority ones.
Computer architecture addressing modes and formats



Computer architecture addressing modes and formatsMazin Alwaaly Computer architecture addressing modes and formats seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Android app development ppt



Android app development pptsaitej15 This document provides an overview of Android app development. It discusses what Android is, its history and architecture. It describes the core components of an Android app like activities, services, content providers and intents. It also discusses Android Studio as the IDE, system requirements, how to develop a first app, common programming languages and learning resources. The goal is to introduce the key concepts for developing Android apps.
Viewers also liked (8)
OER an Schule & Hochschule



OER an Schule & Hochschulee-teaching.org Übersicht zu organisationalen Aspekten und strategischen Ansätzen
Lernvideos von Studierenden für Studierende - Präsentation Roy Franke



Lernvideos von Studierenden für Studierende - Präsentation Roy Frankee-teaching.org Am Kompetenz- und Ausbildungszentrum für bankfachliche Ausbildung CYP in der Schweiz werden Lernvideos als didaktisches Mittel direkt im Unterricht eingesetzt. Lernende bekommen die Aufgabe selbständig zu einem fachlichen Thema zuerst ein Drehbuch zu verfassen und danach mittels Legetechnik und einem Tablet einen 3 minütigen Lernfilm zu erstellen. Von über 200 erstellten Lernfilmen wurden die 8 besten Lernfilme für die Teilnahme am nationalen Lernfilmfestival lernfilm.ch nominiert. Im Online-Event auf e-teaching.org (Aufzeichnung verfügbar über https://www.e-teaching.org/community/communityevents/ringvorlesung/lernvideos-von-studierenden-fuer-studierende-lecture/) zu dem diese Präsentation gehört, berichtet Roy Franke von seinen Erfahrungen, der positiven Resonanz und Herausforderungen bei der Umsetzung.
overview of register transfer, micro operations and basic computer organizati...



overview of register transfer, micro operations and basic computer organizati...Rai University This document provides an overview of register transfer, micro-operations, and basic computer organization and design. It discusses how digital systems can be characterized by their registers and operations. Micro-operations are the elementary operations performed on register data during each clock cycle. A computer's organization is defined by its registers, micro-operation set, and control signals. Registers are designated symbolically and can represent whole registers, portions, or individual bits. Basic register transfer operations include unconditional and conditional loading of data between registers. Micro-operations include data transfer, arithmetic, logic, and shift operations.
MCA-I-COA- overview of register transfer, micro operations and basic computer...



MCA-I-COA- overview of register transfer, micro operations and basic computer...Rai University This document provides an overview of register transfer, micro operations, and basic computer organization and design. It discusses the key concepts of a stored program, instructions, and how instructions are executed through an instruction cycle that involves fetching, decoding, and executing instructions via a sequence of microoperations controlled by a sequence counter register. It also describes the register architecture and instruction set of the Mano computer model, which uses a basic set of registers and a hierarchical 1+3 bit instruction format to support 25 instructions for arithmetic, logic, data movement, program control, and I/O operations.
BIT I WiSe 2014 | Basisinformationstechnologie I - 04: Rechnertechnologie I



BIT I WiSe 2014 | Basisinformationstechnologie I - 04: Rechnertechnologie IInstitute for Digital Humanities, University of Cologne BIT I WiSe 2014 | Basisinformationstechnologie I - 04: Rechnertechnologie I
BIT I WiSe 2014 | Basisinformationstechnologie I - 04: Rechnertechnologie I



BIT I WiSe 2014 | Basisinformationstechnologie I - 04: Rechnertechnologie IInstitute for Digital Humanities, University of Cologne
Ad
Similar to B.sc cs-ii-u-3.2-basic computer programming and micro programmed control (20)
basic computer programming and micro programmed control



basic computer programming and micro programmed controlRai University The document discusses microprogrammed control unit implementation. It describes that a microprogrammed control unit uses microinstructions stored in read-only control memory to generate control signals for executing microoperations. Each computer instruction is mapped to a routine in control memory containing a sequence of microinstructions. The microinstructions include fields that specify microoperations to perform and the address of the next microinstruction. A control address register holds the address of the current microinstruction, and a next address generator determines the next address based on branching conditions.
2024_lecture10__come321..................................



2024_lecture10__come321..................................ghada507476 Computer system architecture
mano
Chapter7.pptx



Chapter7.pptxradhushri This document discusses microprogrammed control in computer organization. It covers topics like microprogrammed control units, microinstructions, control memory, address sequencing, mapping instructions to control memory, and the design of control units using microcode. The key aspects are that a microprogrammed control unit uses microinstructions stored in control memory to generate the control signals needed to execute machine instructions through a sequence of microoperations.
MICROPROGRAMMEDCONTROL-3.pptx



MICROPROGRAMMEDCONTROL-3.pptxPhoenixEagles The document discusses microprogrammed control and compares it to hard-wired control implementations. It covers terminology like microprogram, microinstruction, control memory, and sequencing. It explains microinstruction sequencing capabilities like branching. It provides examples of symbolic microprograms and microinstruction formats.
Chapter 7 of Computer system and architecture



Chapter 7 of Computer system and architecturemayank7067038682 computer system and architecture's chapter 7
Computer_Architecture_3rd_Edition_by_Moris_Mano_Ch_07.ppt



Computer_Architecture_3rd_Edition_by_Moris_Mano_Ch_07.pptRafiyaKouser2 Microprogrammed control units use microprograms stored in control memory to generate control signals for executing machine instructions. A microprogram consists of a sequence of microinstructions, each containing a control word and sequencing word. The control unit implements instruction mapping, sequencing, branching, and subroutines using the microprogram stored in its writable control memory.
Microprogrammed of organisation and architecture of computer.pptx



Microprogrammed of organisation and architecture of computer.pptxSahithBeats Microprogrammed control units use microprograms stored in control memory to generate control signals for executing machine instructions. A microprogram consists of a sequence of microinstructions, each containing control bits and sequencing information. Common components of microprogrammed control units include control memory to store the microprogram, a sequencer to determine the next microinstruction address, and decoding logic to generate control signals from microinstruction fields.
COA 2.1 Microprogrammed control systems of btech 2nd year students.pptx



COA 2.1 Microprogrammed control systems of btech 2nd year students.pptxSahithBeats Microprogrammed control units use microprograms stored in control memory to generate control signals for executing machine instructions. A microprogram consists of a sequence of microinstructions, each containing fields for control operations, sequencing, and constants. The control unit implements microprogram sequencing logic to determine the next microinstruction address based on conditions and branching in the microprogram. This allows microprograms to be written to control all aspects of instruction execution.
Control Memory



Control Memorymahesh kumar prajapat The document describes the control unit of a processor and how it is implemented using either hardwired control or microprogrammed control. It provides terminology related to microprogrammed control including microinstruction, control word, sequencing word, control memory, sequencer, and microinstruction format. It explains how the address sequencer works in a microprogrammed control unit to sequence through microinstructions stored in control memory.
Computer Organization & Architecture (COA)Unit 4



Computer Organization & Architecture (COA)Unit 4parthivrathodlits This document provides information about the Computer Organization and Architecture course for the 4th semester of the B.E. program at Laxmi Institute of Technology, Sarigam. It includes details about the course content which covers topics such as computer data representation, assembly language programming, CPU, and memory organization. The document then focuses on the topics of control memory, address sequencing, and microprogram examples. It provides explanations of control memory, the advantages of microprogrammed control, and the addressing capabilities required for control memory. Finally, it includes the format and coding for microinstructions along with examples.
microprocessor presentation.pptx



microprocessor presentation.pptxPuskar Bhandari This document discusses symbolic and binary microprograms. A symbolic microprogram uses symbols in microinstructions like an assembly language, while a binary microprogram represents a symbolic microprogram in binary using a microprogram assembler. It provides examples of fields in microinstructions and their symbolic and binary codes to define the functions of a microprocessor at a low level.
Lecture 21



Lecture 21RahulRathi94 The document discusses the control unit of a computer. It covers control memory, microinstruction sequencing, the microinstruction format, design of the control unit, and the address sequencer. The address sequencer uses a multiplexer to select the next address from various sources like incrementing the current address, returning from a subroutine, branching to a new address, or mapping from the machine instruction.
Computer architecture control unit



Computer architecture control unitMazin Alwaaly Computer architecture control unit seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Design of control unit.pptx



Design of control unit.pptxShubham014 The document discusses the design of control units in computers. It describes two main types of control unit implementations: hardwired control units and microprogrammed control units. Hardwired control units use combinational logic circuits to generate control signals, while microprogrammed control units store sequences of control instructions called microprograms in a read-only control memory. The document provides details on the components and functioning of microprogrammed control units, and compares the advantages and disadvantages of the two approaches.
Control unit-implementation



Control unit-implementationWBUTTUTORIALS The document discusses control unit implementation in computer architectures. It describes the 6-step instruction cycle and micro-operations that generate control signals to activate data path components like registers and ALU according to the machine state and control data. Micro-operations are made up of micro-actions that control individual components. The timing of micro-operations is controlled through a machine cycle divided into timing states. An example RISC-S architecture and its instruction set and micro-operations are provided.
Ad
More from Rai University (20)
Brochure Rai University 



Brochure Rai University Rai University Rai University provides high quality education for MSc, Law, Mechanical Engineering, BBA, MSc, Computer Science, Microbiology, Hospital Management, Health Management and IT Engineering.
Mm unit 4point2



Mm unit 4point2Rai University The document discusses various types of retailers including specialty stores, department stores, supermarkets, convenience stores, and discount stores. It then covers marketing decisions for retailers related to target markets, product assortment, store services, pricing, promotion, and store location. The document also discusses wholesaling, including the functions of wholesalers, types of wholesalers, and marketing decisions faced by wholesalers.
Mm unit 4point1



Mm unit 4point1Rai University This document discusses marketing channels and channel management. It defines marketing channels as sets of interdependent organizations that make a product available for use. Channels perform important functions like information gathering, stimulating purchases, negotiating prices, ordering, financing inventory, storage, and payment. Channel design considers customer expectations, objectives, constraints, alternatives that are evaluated. Channel management includes selecting, training, motivating, and evaluating channel members. Channels are dynamic and can involve vertical, horizontal, and multi-channel systems. Conflicts between channels must be managed to balance cooperation and competition.
Mm unit 4point3



Mm unit 4point3Rai University The document discusses integrated marketing communication and its various elements. It defines integrated marketing communication as combining different communication modes like advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct marketing to provide a complete communication portfolio to audiences. It also discusses the communication process and how each element of the marketing mix communicates to customers. The document provides details on the key components of an integrated marketing communication mix and how it can be used to build brand equity.
Mm unit 3point2



Mm unit 3point2Rai University Pricing is a key element in determining the profitability and success of a business. The price must be set correctly - if too high, demand may decrease and the product may be priced out of the market, but if too low, revenue may not cover costs. Pricing strategies should consider the product lifecycle stage, costs, competitors, and demand factors. Common pricing methods include penetration pricing for new products, market skimming for premium products, value pricing based on perceived worth, and cost-plus pricing which adds a markup to costs. Price affects demand through price elasticity, with elastic demand more sensitive to price changes.
Mm unit 3point1



Mm unit 3point1Rai University The document discusses various aspects of branding such as definitions of a brand, brand positioning, brand name selection, brand sponsorship, brand development strategies like line extensions and brand extensions, challenges in branding, importance of packaging, labeling, and universal product codes. It provides examples of well-known brands and analyzes their branding strategies. The key points covered are creating emotional value for customers, building relationships and loyalty, using brands to project aspirational lifestyles and values to command premium prices.
Mm unit 2point2



Mm unit 2point2Rai University This document outlines the key stages in the new product development (NPD) process. It begins with generating ideas for new products, which can come from internal or external sources. Ideas are then screened using criteria like market size and development costs. Successful concepts are developed and test marketed to customers. If testing goes well, the product proceeds to commercialization with a full market launch. The NPD process helps companies focus their resources on projects most likely to be rewarding and brings new products to market more quickly. It describes common challenges in NPD like defining specifications and managing resources and timelines, and how to overcome them through planning and cross-functional involvement.
Mm unit 2 point 1



Mm unit 2 point 1Rai University A product is an item offered for sale that can be physical or virtual. It has a life cycle and may need to be adapted over time to remain relevant. A product needs to serve a purpose, function well, and be effectively communicated to users. It also requires a name to help it stand out.
A product hierarchy has multiple levels from core needs down to specific items. These include the need, product family, class, line, type, and item or stock keeping unit.
Products go through a life cycle with stages of development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Marketing strategies must adapt to each stage such as heavy promotion and price changes in introduction and maturity.
Mm unit 1point3



Mm unit 1point3Rai University This document discusses barriers between marketing researchers and managerial decision makers. It identifies three types of barriers: behavioral, process, and organizational. Specific behavioral barriers discussed include confirmatory bias, the difficulty balancing creativity and data, and the newcomer syndrome. Process barriers include unsuccessful problem definition and research rigidity. Organizational barriers include misuse of information asymmetries. The document also discusses ethical issues in marketing research such as deceptive practices, invasion of privacy, and breaches of confidentiality.
Mm unit 1point2



Mm unit 1point2Rai University The document discusses best practices for organizing, writing, and presenting a marketing research report. It provides guidance on structuring the report with appropriate headings, formatting the introduction and conclusion/recommendation sections, effectively utilizing visuals like tables and graphs, and tips for an ethical and impactful oral presentation of the findings. The goal is to clearly communicate the research results and insights to the client to inform their decision-making.
Mm unit 1point1



Mm unit 1point1Rai University This document discusses marketing research and its key steps and methods. Marketing research involves collecting, analyzing and communicating information to make informed marketing decisions. There are 5 key steps in marketing research: 1) define the problem, 2) collect data, 3) analyze and interpret data, 4) reach a conclusion, 5) implement the research. Common data collection methods include interviews, surveys, observations, and experiments. The data is then analyzed using statistical techniques like frequency, percentages, and means to interpret the findings and their implications for marketing decisions.
Bdft ii, tmt, unit-iii, dyeing & types of dyeing,



Bdft ii, tmt, unit-iii, dyeing & types of dyeing,Rai University Dyeing is a method of imparting color to textiles by applying dyes. There are two major types of dyes - natural dyes extracted from plants/animals/minerals and synthetic dyes made in a laboratory. Dyes can be applied at different stages of textile production from fibers to yarns to fabrics to finished garments. Common dyeing methods include stock dyeing, yarn dyeing, piece dyeing, and garment dyeing. Proper dye and method selection are needed for good colorfastness.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.4 publicrevenue-presentation-130208082149-phpapp02



Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.4 publicrevenue-presentation-130208082149-phpapp02Rai University The government requires public revenue to fund its political, social, and economic activities. There are three main sources of public revenue: tax revenue, non-tax revenue, and capital receipts. Tax revenue is collected through direct taxes like income tax, which are paid directly to the government, and indirect taxes like sales tax, where the burden can be shifted to other parties. Non-tax revenue sources include profits from public enterprises, railways, postal services, and the Reserve Bank of India. While taxes provide wide coverage and influence production, they can also reduce incentives to work and increase inequality.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.3 public expenditure



Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.3 public expenditureRai University Public expenditure has increasingly grown over time to fulfill three main roles: protecting society, protecting individuals, and funding public works. The growth can be attributed to several causes like increased income, welfare state ideology, effects of war, increased resources and ability to finance expenditures, inflation, and effects of democracy, socialism, and development. There are also canons that govern public spending like benefits, economy, and approval by authorities. The effects of public expenditure include impacts on consumption, production through efficiency, incentives and allocation, and distribution of resources.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.2 public finance



Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.2 public financeRai University Public finance involves the taxing and spending activities of government. It focuses on the microeconomic functions of government and examines taxes and spending. Government ideology can view the community or individual as most important. In the US, the federal government has more spending flexibility than states. Government spending has increased significantly as a percentage of GDP from 1929 to 2001. Major items of federal spending have shifted from defense to entitlements like Social Security and Medicare. Revenues mainly come from individual income taxes, payroll taxes, and corporate taxes at the federal level and property, sales, and income taxes at the state and local levels.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.1 introduction



Bsc agri 2 pae u-4.1 introductionRai University This document provides an overview of public finance. It defines public finance as the study of how governments raise money through taxes and spending, and how these activities affect the economy. It discusses why public finance is needed to provide public goods and services, redistribute wealth, and correct issues like pollution. The key aspects of public finance covered are government spending, revenue sources like income taxes, and how fiscal policy around spending and taxation can influence economic performance.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-3.3 inflation



Bsc agri 2 pae u-3.3 inflationRai University The document discusses the classical theory of inflation and how it relates to money supply. It states that inflation is defined as a rise in the overall price level in an economy. The quantity theory of money explains that inflation is primarily caused by increases in the money supply as controlled by the central bank. When the money supply grows faster than the amount of goods and services, it leads to too much money chasing too few goods and a rise in prices, or inflation. The document also notes that hyperinflation, which is a very high rate of inflation, can occur when governments print too much money to fund spending.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-3.2 introduction to macro economics



Bsc agri 2 pae u-3.2 introduction to macro economicsRai University This document provides an introduction to macroeconomics. It defines macroeconomics as the study of national economies and the policies that governments use to affect economic performance. It discusses key issues macroeconomists address such as economic growth, business cycles, unemployment, inflation, international trade, and macroeconomic policies. It also outlines different macroeconomic theories including classical, Keynesian, and unified approaches.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-3.1 marketstructure



Bsc agri 2 pae u-3.1 marketstructureRai University Market structure identifies how a market is composed in terms of the number of firms, nature of products, degree of monopoly power, and barriers to entry. Markets range from perfect competition to pure monopoly based on imperfections. The level of competition affects consumer benefits and firm behavior. While models simplify reality, they provide benchmarks to analyze real world situations, where regulation may influence firm actions.
Bsc agri 2 pae u-3 perfect-competition



Bsc agri 2 pae u-3 perfect-competitionRai University This document discusses the concept of perfect competition in economics. It defines perfect competition as a market with many small firms, identical products, free entry and exit of firms, and complete information. The document outlines the key features of perfect competition including: a large number of buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, no barriers to entry or exit, and profit maximization by firms. It also discusses the short run and long run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive firm, including cases where firms experience super normal profits, normal profits, or losses.
Recently uploaded (20)
Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s Guide



Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s GuideGS Virdi Dive into the fundamentals of P–N junctions, the heart of every diode and semiconductor device. In this concise presentation, Dr. G.S. Virdi (Former Chief Scientist, CSIR-CEERI Pilani) covers:
What Is a P–N Junction? Learn how P-type and N-type materials join to create a diode.
Depletion Region & Biasing: See how forward and reverse bias shape the voltage–current behavior.
V–I Characteristics: Understand the curve that defines diode operation.
Real-World Uses: Discover common applications in rectifiers, signal clipping, and more.
Ideal for electronics students, hobbyists, and engineers seeking a clear, practical introduction to P–N junction semiconductors.
Geography Sem II Unit 1C Correlation of Geography with other school subjects



Geography Sem II Unit 1C Correlation of Geography with other school subjectsProfDrShaikhImran The correlation of school subjects refers to the interconnectedness and mutual reinforcement between different academic disciplines. This concept highlights how knowledge and skills in one subject can support, enhance, or overlap with learning in another. Recognizing these correlations helps in creating a more holistic and meaningful educational experience.
Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptx



Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptxArya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. The Pala kings were people-protectors. In fact, Gopal was elected to the throne only to end Matsya Nyaya. Bhagalpur Abhiledh states that Dharmapala imposed only fair taxes on the people. Rampala abolished the unjust taxes imposed by Bhima. The Pala rulers were lovers of learning. Vikramshila University was established by Dharmapala. He opened 50 other learning centers. A famous Buddhist scholar named Haribhadra was to be present in his court. Devpala appointed another Buddhist scholar named Veerdeva as the vice president of Nalanda Vihar. Among other scholars of this period, Sandhyakar Nandi, Chakrapani Dutta and Vajradatta are especially famous. Sandhyakar Nandi wrote the famous poem of this period 'Ramcharit'.
Real GitHub Copilot Exam Dumps for Success



Real GitHub Copilot Exam Dumps for SuccessMark Soia Download updated GitHub Copilot exam dumps to boost your certification success. Get real exam questions and verified answers for guaranteed performance
pulse ppt.pptx Types of pulse , characteristics of pulse , Alteration of pulse



pulse ppt.pptx Types of pulse , characteristics of pulse , Alteration of pulsesushreesangita003 what is pulse ?
Purpose
physiology and Regulation of pulse
Characteristics of pulse
factors affecting pulse
Sites of pulse
Alteration of pulse
for BSC Nursing 1st semester
for Gnm Nursing 1st year
Students .
vitalsign
Presentation on Tourism Product Development By Md Shaifullar Rabbi



Presentation on Tourism Product Development By Md Shaifullar RabbiMd Shaifullar Rabbi Presentation on Tourism Product Development By Md Shaifullar Rabbi, Assistant Manager- SABRE Bangladesh.
Link your Lead Opportunities into Spreadsheet using odoo CRM



Link your Lead Opportunities into Spreadsheet using odoo CRMCeline George In Odoo 17 CRM, linking leads and opportunities to a spreadsheet can be done by exporting data or using Odoo’s built-in spreadsheet integration. To export, navigate to the CRM app, filter and select the relevant records, and then export the data in formats like CSV or XLSX, which can be opened in external spreadsheet tools such as Excel or Google Sheets.
SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptx



SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptxRonisha Das SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS - XTASY 2025
BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...



BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection https://app.box.com/s/n8nl163m8v9ou7xil944pod44a5wi43h
Metamorphosis: Life's Transformative Journey



Metamorphosis: Life's Transformative JourneyArshad Shaikh *Metamorphosis* is a biological process where an animal undergoes a dramatic transformation from a juvenile or larval stage to a adult stage, often involving significant changes in form and structure. This process is commonly seen in insects, amphibians, and some other animals.
Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)



Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)Sritoma Majumder Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)
Grade 2 - Mathematics - Printable Worksheet



Grade 2 - Mathematics - Printable WorksheetSritoma Majumder Grade 2 - Mathematics - Printable Worksheet
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 817 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 97 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 817 (As of 05/3/2025)
• Texas: 688 (+20)(62% of these cases are in Gaines County).
• New Mexico: 67 (+1 )(92.4% of the cases are from Eddy County)
• Oklahoma: 16 (+1)
• Kansas: 46 (32% of the cases are from Gray County)
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 97 (+2)
• Texas: 89 (+2) - This is 13.02% of all TX cases.
• New Mexico: 7 - This is 10.6% of all NM cases.
• Kansas: 1 - This is 2.7% of all KS cases.
DEATHS: 3
• Texas: 2 – This is 0.31% of all cases
• New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.54% of all cases
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 967 (Confirmed and suspected):
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD (As of 4/2/2025)
• Mexico – 865 (+58)
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 844 (+58) cases, 3 hospitalizations, 1 fatality
• Canada: 1531 (+270) (This reflects Ontario's Outbreak, which began 11/24)
‒Ontario, Canada – 1243 (+223) cases, 84 hospitalizations.
• Europe: 6,814
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 795 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 95 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
Contact Lens:::: An Overview.pptx.: Optometry



Contact Lens:::: An Overview.pptx.: OptometryMushahidRaza8 A comprehensive guide for Optometry students: understanding in easy launguage of contact lens.
Don't forget to like,share and comments if you found it useful!.
Herbs Used in Cosmetic Formulations .pptx



Herbs Used in Cosmetic Formulations .pptxRAJU THENGE The content is for the educational purpose for Pharmacy and Cosmetic students.
03#UNTAGGED. Generosity in architecture.



03#UNTAGGED. Generosity in architecture.MCH What makes space feel generous, and how architecture address this generosity in terms of atmosphere, metrics, and the implications of its scale? This edition of #Untagged explores these and other questions in its presentation of the 2024 edition of the Master in Collective Housing. The Master of Architecture in Collective Housing, MCH, is a postgraduate full-time international professional program of advanced architecture design in collective housing presented by Universidad Politécnica of Madrid (UPM) and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH).
Yearbook MCH 2024. Master in Advanced Studies in Collective Housing UPM - ETH
Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptx



Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptxArya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...



BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
B.sc cs-ii-u-3.2-basic computer programming and micro programmed control
- 1. Basic Computer Programming and Micro Programmed Control Course: B.Sc-CS-II Subject: Computer Organization And Architecture Unit-3 1
- 2. Control Unit Implementation[1] 2 • Hardwired • Microprogrammed Instruction code Combinational Logic Circuits Memory Sequence Counter . . Control signals Control signals Next Address Generator (sequencer) CAR Control Memory CDR Decoding Circuit Memory . . CAR: Control Address Register CDR: Control Data RegisterInstruction code
- 3. Microprogrammed Control Unit • Control signals – Group of bits used to select paths in multiplexers, decoders, arithmetic logic units • Control variables – Binary variables specify microoperations • Certain microoperations initiated while others idle • Control word – String of 1’s and 0’s represent control variables 3
- 4. Microprogrammed Control Unit • Control memory – Memory contains control words • Microinstructions – Control words stored in control memory – Specify control signals for execution of microoperations • Microprogram – Sequence of microinstructions 4
- 5. Control Memory • Read-only memory (ROM) • Content of word in ROM at given address specifies microinstruction • Each computer instruction initiates series of microinstructions (microprogram) in control memory • These microinstructions generate microoperations to – Fetch instruction from main memory – Evaluate effective address – Execute operation specified by instruction – Return control to fetch phase for next instruction 5 Control memory (ROM) Control word (microinstruction) Address
- 6. Microprogrammed Control Organization • Control memory – Contains microprograms (set of microinstructions) – Microinstruction contains • Bits initiate microoperations • Bits determine address of next microinstruction • Control address register (CAR) – Specifies address of next microinstruction 6 Control word Next Address Generator (sequencer) CAR Control Memory (ROM) CDR External input
- 7. Microprogrammed Control Organization • Next address generator (microprogram sequencer) – Determines address sequence for control memory • Microprogram sequencer functions – Increment CAR by one – Transfer external address into CAR – Load initial address into CAR to start control operations 7
- 8. Microprogrammed Control Organization • Control data register (CDR)- or pipeline register – Holds microinstruction read from control memory – Allows execution of microoperations specified by control word simultaneously with generation of next microinstruction • Control unit can operate without CDR 8 Control word Next Address Generator (sequencer) CAR Control Memory (ROM) External input
- 9. Microprogram Routines • Routine – Group of microinstructions stored in control memory • Each computer instruction has its own microprogram routine to generate microoperations that execute the instruction 9
- 10. Microprogram Routines • Subroutine – Sequence of microinstructions used by other routines to accomplish particular task • Example – Subroutine to generate effective address of operand for memory reference instruction • Subroutine register (SBR) – Stores return address during subroutine call 10
- 11. Conditional Branching • Branching from one routine to another depends on status bit conditions • Status bits provide parameter info such as – Carry-out of adder – Sign bit of number – Mode bits of instruction • Info in status bits can be tested and actions initiated based on their conditions: 1 or 0 • Unconditional branch – Fix value of status bit to 1 11
- 12. Mapping of Instruction[2] • Each computer instruction has its own microprogram routine stored in a given location of the control memory • Mapping – Transformation from instruction code bits to address in control memory where routine is located 12
- 13. Mapping of Instruction • Example – Mapping 4-bit operation code to 7-bit address 13 OP-codes of Instructions ADD AND LDA 0000 0001 0010 Address 0 0000 00 0 0001 00 0 0010 00 Mapping bits 0 xxxx 00 ADD Routine AND Routine LDA Routine Control memory
- 14. Address Sequencing[2] • Address sequencing capabilities required in control unit – Incrementing CAR – Unconditional or conditional branch, depending on status bit conditions – Mapping from bits of instruction to address for control memory – Facility for subroutine call and return 14
- 15. Address Sequencing 15 Instruction code Mapping logic Multiplexers Control memory (ROM) Subroutine Register (SBR) Branch logic Status bits Microoperations Control Address Register (CAR) Incrementer MUX select select a status bit Branch address
- 16. Microprogram Example[3] 16 Computer Configuration MUX AR 10 0 PC 10 0 Address Memory 2048 x 16 MUX DR 15 0 Arithmetic logic and shift unit AC 15 0 SBR 6 0 CAR 6 0 Control memory 128 x 20 Control unit
- 17. Microprogram Example 17 Microinstruction Format EA is the effective address Symbol OP-code Description ADD 0000 AC ← AC + M[EA] BRANCH 0001 if (AC < 0) then (PC ← EA) STORE 0010 M[EA] ← AC EXCHANGE 0011 AC ← M[EA], M[EA] ← AC Computer instruction format I Opcode 15 14 11 10 Address 0 Four computer instructions F1 F2 F3 CD BR AD 3 3 3 2 2 7 F1, F2, F3: Microoperation fields CD: Condition for branching BR: Branch field AD: Address field
- 18. Microinstruction Fields 18 F1 Microoperation Symbol 000 None NOP 001 AC ← AC + DR ADD 010 AC ← 0 CLRAC 011 AC ← AC + 1 INCAC 100 AC ← DR DRTAC 101 AR ← DR(0-10) DRTAR 110 AR ← PC PCTAR 111 M[AR] ← DR WRITE F2 Microoperation Symbol 000 None NOP 001 AC ← AC - DR SUB 010 AC ← AC ∨ DR OR 011 AC ← AC ∧ DR AND 100 DR ← M[AR] READ 101 DR ← AC ACTDR 110 DR ← DR + 1 INCDR 111 DR(0-10) ← PC PCTDR F3 Microoperation Symbol 000 None NOP 001 AC ← AC ⊕ DR XOR 010 AC ← AC’ COM 011 AC ← shl AC SHL 100 AC ← shr AC SHR 101 PC ← PC + 1 INCPC 110 PC ← AR ARTPC 111 Reserved
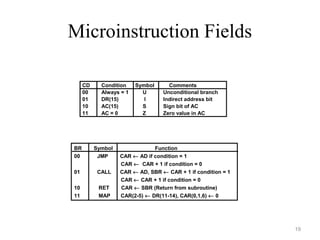
- 19. Microinstruction Fields 19 CD Condition Symbol Comments 00 Always = 1 U Unconditional branch 01 DR(15) I Indirect address bit 10 AC(15) S Sign bit of AC 11 AC = 0 Z Zero value in AC BR Symbol Function 00 JMP CAR ← AD if condition = 1 CAR ← CAR + 1 if condition = 0 01 CALL CAR ← AD, SBR ← CAR + 1 if condition = 1 CAR ← CAR + 1 if condition = 0 10 RET CAR ← SBR (Return from subroutine) 11 MAP CAR(2-5) ← DR(11-14), CAR(0,1,6) ← 0
- 20. Symbolic Microinstruction 20 Sample Format Label: Micro-ops CD BR AD Label may be empty or may specify symbolic address terminated with colon Micro-ops consists of 1, 2, or 3 symbols separated by commas CD one of {U, I, S, Z} U: Unconditional Branch I: Indirect address bit S: Sign of AC Z: Zero value in AC BR one of {JMP, CALL, RET, MAP} AD one of {Symbolic address, NEXT, empty}
- 21. Fetch Routine 21 Fetch routine - Read instruction from memory - Decode instruction and update PC AR ← PC DR ← M[AR], PC ← PC + 1 AR ← DR(0-10), CAR(2-5) ← DR(11-14), CAR(0,1,6) ← 0 Symbolic microprogram for fetch routine: ORG 64 PCTAR U JMP NEXT READ, INCPC U JMP NEXT DRTAR U MAP FETCH: Binary microporgram for fetch routine: 1000000 110 000 000 00 00 1000001 1000001 000 100 101 00 00 1000010 1000010 101 000 000 00 11 0000000 Binary address F1 F2 F3 CD BR AD Microinstructions for fetch routine:
- 22. Symbolic Microprogram 22 • Control memory: 128 20-bit words • First 64 words: Routines for 16 machine instructions • Last 64 words: Used for other purpose (e.g., fetch routine and other subroutines) • Mapping: OP-code XXXX into 0XXXX00, first address for 16 routines are 0(0 0000 00), 4(0 0001 00), 8, 12, 16, 20, ..., 60 ORG 0 NOP READ ADD ORG 4 NOP NOP NOP ARTPC ORG 8 NOP ACTDR WRITE ORG 12 NOP READ ACTDR, DRTAC WRITE ORG 64 PCTAR READ, INCPC DRTAR READ DRTAR I U U S U I U I U U I U U U U U U U U CALL JMP JMP JMP JMP CALL JMP CALL JMP JMP CALL JMP JMP JMP JMP JMP MAP JMP RET INDRCT NEXT FETCH OVER FETCH INDRCT FETCH INDRCT NEXT FETCH INDRCT NEXT NEXT FETCH NEXT NEXT NEXT ADD: BRANCH: OVER: STORE: EXCHANGE: FETCH: INDRCT: Label Microops CD BR AD Partial Symbolic Microprogram
- 23. Binary Microprogram 23 Address Binary Microinstruction Micro Routine Decimal Binary F1 F2 F3 CD BR AD ADD 0 0000000 000 000 000 01 01 1000011 1 0000001 000 100 000 00 00 0000010 2 0000010 001 000 000 00 00 1000000 3 0000011 000 000 000 00 00 1000000 BRANCH 4 0000100 000 000 000 10 00 0000110 5 0000101 000 000 000 00 00 1000000 6 0000110 000 000 000 01 01 1000011 7 0000111 000 000 110 00 00 1000000 STORE 8 0001000 000 000 000 01 01 1000011 9 0001001 000 101 000 00 00 0001010 10 0001010 111 000 000 00 00 1000000 11 0001011 000 000 000 00 00 1000000 EXCHANGE 12 0001100 000 000 000 01 01 1000011 13 0001101 001 000 000 00 00 0001110 14 0001110 100 101 000 00 00 0001111 15 0001111 111 000 000 00 00 1000000 FETCH 64 1000000 110 000 000 00 00 1000001 65 1000001 000 100 101 00 00 1000010 66 1000010 101 000 000 00 11 0000000 INDRCT 67 1000011 000 100 000 00 00 1000100 68 1000100 101 000 000 00 10 0000000
- 24. Design of Control Unit[4] 24 microoperation fields 3 x 8 decoder 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 F1 3 x 8 decoder 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 F2 3 x 8 decoder 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 F3 Arithmetic logic and shift unit AND ADD DRTAC AC Load From PC From DR(0-10) Select 0 1 Multiplexers AR Load Clock AC DR DRTAR PCTAR
- 25. Microprogram Sequencer 25 3 2 1 0 S1 MUX1 External (MAP) SBR Load Incrementer CAR Input logic I0 T MUX2 Select 1 I S Z Test Clock Control memory Microops CD BR AD L I1 S0 . . .. . .
- 26. Input Logic for Microprogram Sequencer 26 Input logicI0 I 1 T MUX2 Select 1 I S Z Test CD Field of CS From CPU BR field of CS L(load SBR with PC) for subroutine Call S0 S1 for next address selection I1I0T Meaning Source of Address S1S0 L 000 In-Line CAR+1 00 0 001 JMP CS(AD) 01 0 010 In-Line CAR+1 00 0 011 CALL CS(AD) and SBR <- CAR+1 01 1 10x RET SBR 10 0 11x MAP DR(11-14) 11 0 L S1 = I1 S0 = I0I1 + I1’T L = I1’I0T Input Logic
- 27. References 1. Computer Organization and Architecture, Designing for performance by William Stallings, Prentice Hall of India. 2. Modern Computer Architecture, by Morris Mano, Prentice Hall of India. 3. Computer Architecture and Organization by John P. Hayes, McGraw Hill Publishing Company. 4. Computer Organization by V. Carl Hamacher, Zvonko G. Vranesic, Safwat G. Zaky, McGraw Hill Publishing Company.











