OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 01 - Introduction
3 likes1,369 views
Episode 01 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group This episode is about different versions of OpenShift, supported platforms, terminology and architecture of OpenShift. I hope you will find it useful.
1 of 25
Downloaded 62 times
























Ad
Recommended
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 02 - Architecture



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 02 - ArchitectureBehnam Loghmani Episode 02 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about different layers, architecture, security in OpenShift.
I hope you will find it useful.
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 06 - Core Concepts Part II



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 06 - Core Concepts Part IIBehnam Loghmani Episode 06 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about core concepts in OpenShift.
Part 2 includes concepts of Users, Projects, Builds and Image streams
At the end of presentation you can find a link that helps you to setup OpenShift in your local system ( this setup is not a enterprise setup and it's only for creating a small test environment ).
I hope you will find it useful.
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 03 - Infrastructure part I



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 03 - Infrastructure part IBehnam Loghmani Episode 03 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about master's components and high availability masters.
I hope you will find it useful.
Putting Drupal in the Cloud with Red Hat's OpenShift PaaS #DrupalCon/Prague 



Putting Drupal in the Cloud with Red Hat's OpenShift PaaS #DrupalCon/Prague OpenShift Origin Everything you need to know about putting Drupal 7 & Drupal 8 in the cloud using Red Hat's Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) known as OpenShift (1) it's Open Source (2) it runs on any Cloud (2) OpenShift loves Drupal! Sign-up at http://www.openshift.com and get your Drupal on the Cloud now!
Building Domain-specific PaaS with OpenShift Origin: The TRESOR Healthcare P...



Building Domain-specific PaaS with OpenShift Origin: The TRESOR Healthcare P...OpenShift Origin Building Domain-specific PaaS with OpenShift Origin
Presenter: Alexander Grzesik, Softwarearchitekt, Medisite.de
Alexander will discuss customizing OpenShift Origin for the Healthcare industry to meet with specific to German government compliance regulations for cloud security as part of the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology's Trusted Cloud initiative also know as TRESOR - Trusted Ecosystem for Standardized and Open cloud-based Resources.
OpenShift Overview



OpenShift Overviewroundman OpenShift cloud technology high-level overview given at the Athens Area Software Developer Meet-up in Athens, Georgia, January 2014.
Introduction to OpenShift Origin- Private, Public and Community



Introduction to OpenShift Origin- Private, Public and CommunityOpenShift Origin From 2013-04-14 OpenShift Origin Community Day in Portland, Oregon
Presenter: (William) Bill DeCoste (Principal Software Engineer for OpenShift) will introduce Red Hat's PaaS. He'll describe the several flavors of OpenShift ranging from the upstream community project Origin, the EC2-based online offering at http://openshift.redhat.com, to the corresponding commercial offering, OpenShift Enterprise. OpenShift Origin and Online will be demonstrated.
Red Hat OpenShift V3 Overview and Deep Dive



Red Hat OpenShift V3 Overview and Deep DiveGreg Hoelzer OpenShift is a platform as a service product from Red Hat that allows developers to easily deploy and manage applications using containers. It provides developers with a common platform to build, deploy and update applications quickly using containers. For IT operations, OpenShift improves efficiency and infrastructure utilization through automated provisioning and management of application services. Some key customers highlighted include a large enterprise software company, a major online travel agency, and a leading financial analytics software provider.
Build a Basic Cloud Using RDO-manager



Build a Basic Cloud Using RDO-managerK Rain Leander One of the impediments to becoming an active technical contributor in the OpenStack community is setting up an efficient R&D environment which includes deploying a simple cloud. Using RDO-manager, get a basic cloud up and running with the fewest steps and minimal hardware so you can focus on the fun stuff - development
Build Your Own PaaS, Just like Red Hat's OpenShift from LinuxCon 2013 New Orl...



Build Your Own PaaS, Just like Red Hat's OpenShift from LinuxCon 2013 New Orl...OpenShift Origin Learn how to build your platform as a service just like RedHat's OpenShift PaaS - covers all the architecture & internals of OpenShift Origin OpenSource project, how to deploy it & configure it for bare metal, AWS, OpenStack, CloudStack or any IaaS, and the community that's collaborating on the project to deliver the next-generation of secure, scale-able PaaS visit: openshift.com for more information
presented at LinuxCon by Diane Mueller in the CloudOpen track
DevFestMN 2017 - Learning Docker and Kubernetes with Openshift



DevFestMN 2017 - Learning Docker and Kubernetes with OpenshiftKeith Resar Hands-on lab discovering containers (through docker), the need for container orchestration (using Kubernetes), and the place for a container PaaS (via OpenShift)
DEVNET-1183 OpenShift + Kubernetes + Docker



DEVNET-1183 OpenShift + Kubernetes + DockerCisco DevNet You have heard about containers and would like to see more than some hand waving and slideware. Well sit back and enjoy. We'll cover some basic vocabulary and tech for those who are new to the technology. From there on out, it will be all demos! Starting with just deploying a simple Docker image, we will work all the way up to a complete application and scale it on demand. You will leave a great taste of the technology Red Hat and Cisco will be bringing you to get your application development on the right track!
DevOps, PaaS and the Modern Enterprise CloudExpo Europe presentation by Diane...



DevOps, PaaS and the Modern Enterprise CloudExpo Europe presentation by Diane...OpenShift Origin The rise in application complexity is answered by the emergence of DevOps and simplified by adding a PaaS bringing agility, speed, and compliance to the modern Enterprise.
OpenShift 4 installation



OpenShift 4 installationRobert Bohne Red Hat OpenShift 4 allows for automated and customized deployments. The Full Stack Automation method fully automates installation and updates of both the OpenShift platform and Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS host operating system. The Pre-existing Infrastructure method allows OpenShift to be deployed on user-managed infrastructure, where the customer provisions resources like load balancers and DNS. Both methods use the openshift-install tool to generate ignition configs and monitor the cluster deployment.
OpenShift on OpenStack



OpenShift on OpenStackDave Neary OpenShift is a Platform as a Service. It's straightforward to deploy it on top of the Infrastructure as a Service platform OpenStack using Heat templates, in a way which allows it to grow as more resources are required.
This presentation gives an overview of what OpenShift gives to developers, and how to deploy it on top of OpenStack.
Putting The PaaS in OpenStack with Diane Mueller @RedHat 



Putting The PaaS in OpenStack with Diane Mueller @RedHat OpenShift Origin RedHat has created it's own OpenStack distribution that is now in preview and still a bit rough around the edges, but promises to include what is needed to deploy & evaluate a truly & complete Open Cloud environment. In addition, Red Hat wants there to be a widely used open-source community developed PaaS model for the cloud which includes being open to participation by a community of peers.
To really create a open cloud environment and to make it useful, you need to complete the stack with an PaaS. Just getting a cloud environment up and running is no longer enough. The challenge that OpenStack faces is how to get people, applications and services working on OpenStack out of the box.
One approach to the problem is to combining all the necessary pieces that go into building an OpenStack cloud (compute, storage, networking, management) with a platform as a service (PaaS) into your OpenStack distribution.
OpenShift Origin project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0, a permissive and widely-used open source license, which was selected so that the code would be available for use by the broadest range of
individuals and organizations. This is the same license chosen by the OpenStack project, for much the same reason. This license is already well known and understood by individuals and organizations already involved in cloud computing and in enterprise scale open source development.
In this session, I'll discuss RedHat's efforts with OpenStack, Fedora, & OpenShift Origin to create a more complete OpenStack distribution. Our community initiatives to ensure Origin easily and seamlessly integrates on any OpenStack distribution and how to you can add Origin into your own OpenStack distributions.
http://openstacksummitapril2013.sched.org/event/93a0a84f3623c2e1cdf9563b72f9e351#.UW2YmnAnsUU
Openshift Container Platform



Openshift Container PlatformDLT Solutions This document discusses OpenShift Container Platform, a platform as a service (PaaS) that provides a full development and deployment platform for applications. It allows developers to easily manage application dependencies and development environments across basic infrastructure, public clouds, and production servers. OpenShift provides container orchestration using Kubernetes along with developer tools and a user experience to support DevOps practices like continuous integration/delivery.
Kubernetes or OpenShift - choosing your container platform for Dev and Ops



Kubernetes or OpenShift - choosing your container platform for Dev and OpsTomasz Cholewa Kubernetes has become the most popular choice among container orchestrators with strong community and growing numbers of production deployments. There is no shortage of various K8s distros, at the moment 20+ and counting. There are many distributions available that just simply add toolsets and products that embed it and adds more features. In this presentation, you'll learn about OpenShift and how it compares to vanilla Kubernetes - their major differences, best features and how they can help to build a consistent platform for Dev and Ops cooperation.
OpenShift Anywhere given at Infrastructure.Next Talk at #Scale12X



OpenShift Anywhere given at Infrastructure.Next Talk at #Scale12XOpenShift Origin Why IaaS is not enough
What PaaS is & Why It's Magic
How to deploy a PaaS on any IaaS
Where all the scripts are hidden
Putting Private Clouds to Work with PaaS Interop Vegas 2013 presentation by D...



Putting Private Clouds to Work with PaaS Interop Vegas 2013 presentation by D...Diane Mueller Presentation from Interop/Vegas 2013 Private Cloud track
Getting the most out of your Private Cloud means going beyond simply deploying IaaS, maximize your investment and meet your line of business managers & developer's expectations of self-service, on demand cloud resource in today's agile life cycles
LatinoWare 2013 An OpenSource Blueprint for Cloud presented by Diane Mueller,...



LatinoWare 2013 An OpenSource Blueprint for Cloud presented by Diane Mueller,...OpenShift Origin LatinoWare 2013 An OpenSource Blueprint for Cloud presented by Diane Mueller, OpenShift Origin Community Manager 2013-10-17
Openshift + Openstack + Fedora = Awesome



Openshift + Openstack + Fedora = AwesomeMark Atwood - The document discusses deploying OpenShift Origin on OpenStack. It begins with overviews of OpenStack, an open source cloud computing platform, and OpenShift Origin, the open source version of Red Hat's OpenShift Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). It then demonstrates provisioning an OpenStack environment and deploying OpenShift Origin on top of it.
From Zero to Cloud: Revolutionize your Application Life Cycle with OpenShift ...



From Zero to Cloud: Revolutionize your Application Life Cycle with OpenShift ...OpenShift Origin From Zero to Cloud: Revolutionize your Application Life Cycle with OpenShift PaaS
Talk given by Diane Mueller, OpenShift Origin Community Manager at FISL 15 on May 9th, 2014
Openshift: Build, deploy & manage open, standard containers



Openshift: Build, deploy & manage open, standard containersJonh Wendell OpenShift is a container platform for deploying and managing containerized applications. It uses Kubernetes for orchestration and Docker containers. OpenShift provides developers a way to build, deploy and manage applications throughout the lifecycle using containers and provides operations with stability, security and resource management tools. It supports choice of programming languages, continuous deployment and integration, and scaling of applications.
OpenShift Meetup 8th july 2019 at ConSol - OpenShift v4



OpenShift Meetup 8th july 2019 at ConSol - OpenShift v4Robert Bohne Red Hat OpenShift 4 provides a cloud-like platform for containerized applications that can run on hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures. It offers full-stack automation for simplified cluster installation and lifecycle management along with over-the-air updates. OpenShift 4 supports deployment on both infrastructure provisioned and managed by Red Hat as well as customer-managed infrastructure. It leverages containers, microservices, and Kubernetes concepts to empower developers to build, deploy and manage applications.
Red Hat Forum Benelux 2015



Red Hat Forum Benelux 2015Microsoft This document discusses OpenShift v3 and how it can help organizations accelerate development at DevOps speed. It provides an overview of Kubernetes and OpenShift's technical architecture, how OpenShift enables continuous delivery and faster cycle times from idea to production. It also summarizes benefits for developers, integrations, administration capabilities, and the OpenShift product roadmap.
RPM Factory for RDO



RPM Factory for RDOFrédéric Lepied Status of the RPM Factory experiment to become the forge to build the OpenStack RPM packages for the RDO project. Presented at the RDO Day pre-FOSDEM 2016.
OpenStack in an Ever Expanding World of Possibilities - Vancouver 2015 Summit



OpenStack in an Ever Expanding World of Possibilities - Vancouver 2015 SummitLew Tucker Over the past several years we have seen the continued adoption of OpenStack and it’s expansion into new areas: from cloud service providers, enterprise private clouds to large media companies, telecommunication giants, and big science. At the same time, open source based platforms for network functions virtualization (NFV) are fueling a movement toward cloud computing in almost all major telco’s.
In the developer world, open source projects, such as Docker, Mesos, Kubernetes, and Spark are gaining a lot of attention and being integrated into OpenStack through projects Kolla and Magnum.
This session will cover how these projects and activities relate to each other and further expand the utility and adoption OpenStack.
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 05 - Core Concepts Part I



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 05 - Core Concepts Part IBehnam Loghmani Episode 05 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about core concepts in openshift.
Part 1 include concepts of Containers, Images, Pods and services
I hope you will find it useful.
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 04 - Infrastructure part II



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 04 - Infrastructure part IIBehnam Loghmani Episode 04 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about Nodes, Kublet, Image registry and web console of OpenShift.
I hope you will find it useful.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Build a Basic Cloud Using RDO-manager



Build a Basic Cloud Using RDO-managerK Rain Leander One of the impediments to becoming an active technical contributor in the OpenStack community is setting up an efficient R&D environment which includes deploying a simple cloud. Using RDO-manager, get a basic cloud up and running with the fewest steps and minimal hardware so you can focus on the fun stuff - development
Build Your Own PaaS, Just like Red Hat's OpenShift from LinuxCon 2013 New Orl...



Build Your Own PaaS, Just like Red Hat's OpenShift from LinuxCon 2013 New Orl...OpenShift Origin Learn how to build your platform as a service just like RedHat's OpenShift PaaS - covers all the architecture & internals of OpenShift Origin OpenSource project, how to deploy it & configure it for bare metal, AWS, OpenStack, CloudStack or any IaaS, and the community that's collaborating on the project to deliver the next-generation of secure, scale-able PaaS visit: openshift.com for more information
presented at LinuxCon by Diane Mueller in the CloudOpen track
DevFestMN 2017 - Learning Docker and Kubernetes with Openshift



DevFestMN 2017 - Learning Docker and Kubernetes with OpenshiftKeith Resar Hands-on lab discovering containers (through docker), the need for container orchestration (using Kubernetes), and the place for a container PaaS (via OpenShift)
DEVNET-1183 OpenShift + Kubernetes + Docker



DEVNET-1183 OpenShift + Kubernetes + DockerCisco DevNet You have heard about containers and would like to see more than some hand waving and slideware. Well sit back and enjoy. We'll cover some basic vocabulary and tech for those who are new to the technology. From there on out, it will be all demos! Starting with just deploying a simple Docker image, we will work all the way up to a complete application and scale it on demand. You will leave a great taste of the technology Red Hat and Cisco will be bringing you to get your application development on the right track!
DevOps, PaaS and the Modern Enterprise CloudExpo Europe presentation by Diane...



DevOps, PaaS and the Modern Enterprise CloudExpo Europe presentation by Diane...OpenShift Origin The rise in application complexity is answered by the emergence of DevOps and simplified by adding a PaaS bringing agility, speed, and compliance to the modern Enterprise.
OpenShift 4 installation



OpenShift 4 installationRobert Bohne Red Hat OpenShift 4 allows for automated and customized deployments. The Full Stack Automation method fully automates installation and updates of both the OpenShift platform and Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS host operating system. The Pre-existing Infrastructure method allows OpenShift to be deployed on user-managed infrastructure, where the customer provisions resources like load balancers and DNS. Both methods use the openshift-install tool to generate ignition configs and monitor the cluster deployment.
OpenShift on OpenStack



OpenShift on OpenStackDave Neary OpenShift is a Platform as a Service. It's straightforward to deploy it on top of the Infrastructure as a Service platform OpenStack using Heat templates, in a way which allows it to grow as more resources are required.
This presentation gives an overview of what OpenShift gives to developers, and how to deploy it on top of OpenStack.
Putting The PaaS in OpenStack with Diane Mueller @RedHat 



Putting The PaaS in OpenStack with Diane Mueller @RedHat OpenShift Origin RedHat has created it's own OpenStack distribution that is now in preview and still a bit rough around the edges, but promises to include what is needed to deploy & evaluate a truly & complete Open Cloud environment. In addition, Red Hat wants there to be a widely used open-source community developed PaaS model for the cloud which includes being open to participation by a community of peers.
To really create a open cloud environment and to make it useful, you need to complete the stack with an PaaS. Just getting a cloud environment up and running is no longer enough. The challenge that OpenStack faces is how to get people, applications and services working on OpenStack out of the box.
One approach to the problem is to combining all the necessary pieces that go into building an OpenStack cloud (compute, storage, networking, management) with a platform as a service (PaaS) into your OpenStack distribution.
OpenShift Origin project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0, a permissive and widely-used open source license, which was selected so that the code would be available for use by the broadest range of
individuals and organizations. This is the same license chosen by the OpenStack project, for much the same reason. This license is already well known and understood by individuals and organizations already involved in cloud computing and in enterprise scale open source development.
In this session, I'll discuss RedHat's efforts with OpenStack, Fedora, & OpenShift Origin to create a more complete OpenStack distribution. Our community initiatives to ensure Origin easily and seamlessly integrates on any OpenStack distribution and how to you can add Origin into your own OpenStack distributions.
http://openstacksummitapril2013.sched.org/event/93a0a84f3623c2e1cdf9563b72f9e351#.UW2YmnAnsUU
Openshift Container Platform



Openshift Container PlatformDLT Solutions This document discusses OpenShift Container Platform, a platform as a service (PaaS) that provides a full development and deployment platform for applications. It allows developers to easily manage application dependencies and development environments across basic infrastructure, public clouds, and production servers. OpenShift provides container orchestration using Kubernetes along with developer tools and a user experience to support DevOps practices like continuous integration/delivery.
Kubernetes or OpenShift - choosing your container platform for Dev and Ops



Kubernetes or OpenShift - choosing your container platform for Dev and OpsTomasz Cholewa Kubernetes has become the most popular choice among container orchestrators with strong community and growing numbers of production deployments. There is no shortage of various K8s distros, at the moment 20+ and counting. There are many distributions available that just simply add toolsets and products that embed it and adds more features. In this presentation, you'll learn about OpenShift and how it compares to vanilla Kubernetes - their major differences, best features and how they can help to build a consistent platform for Dev and Ops cooperation.
OpenShift Anywhere given at Infrastructure.Next Talk at #Scale12X



OpenShift Anywhere given at Infrastructure.Next Talk at #Scale12XOpenShift Origin Why IaaS is not enough
What PaaS is & Why It's Magic
How to deploy a PaaS on any IaaS
Where all the scripts are hidden
Putting Private Clouds to Work with PaaS Interop Vegas 2013 presentation by D...



Putting Private Clouds to Work with PaaS Interop Vegas 2013 presentation by D...Diane Mueller Presentation from Interop/Vegas 2013 Private Cloud track
Getting the most out of your Private Cloud means going beyond simply deploying IaaS, maximize your investment and meet your line of business managers & developer's expectations of self-service, on demand cloud resource in today's agile life cycles
LatinoWare 2013 An OpenSource Blueprint for Cloud presented by Diane Mueller,...



LatinoWare 2013 An OpenSource Blueprint for Cloud presented by Diane Mueller,...OpenShift Origin LatinoWare 2013 An OpenSource Blueprint for Cloud presented by Diane Mueller, OpenShift Origin Community Manager 2013-10-17
Openshift + Openstack + Fedora = Awesome



Openshift + Openstack + Fedora = AwesomeMark Atwood - The document discusses deploying OpenShift Origin on OpenStack. It begins with overviews of OpenStack, an open source cloud computing platform, and OpenShift Origin, the open source version of Red Hat's OpenShift Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). It then demonstrates provisioning an OpenStack environment and deploying OpenShift Origin on top of it.
From Zero to Cloud: Revolutionize your Application Life Cycle with OpenShift ...



From Zero to Cloud: Revolutionize your Application Life Cycle with OpenShift ...OpenShift Origin From Zero to Cloud: Revolutionize your Application Life Cycle with OpenShift PaaS
Talk given by Diane Mueller, OpenShift Origin Community Manager at FISL 15 on May 9th, 2014
Openshift: Build, deploy & manage open, standard containers



Openshift: Build, deploy & manage open, standard containersJonh Wendell OpenShift is a container platform for deploying and managing containerized applications. It uses Kubernetes for orchestration and Docker containers. OpenShift provides developers a way to build, deploy and manage applications throughout the lifecycle using containers and provides operations with stability, security and resource management tools. It supports choice of programming languages, continuous deployment and integration, and scaling of applications.
OpenShift Meetup 8th july 2019 at ConSol - OpenShift v4



OpenShift Meetup 8th july 2019 at ConSol - OpenShift v4Robert Bohne Red Hat OpenShift 4 provides a cloud-like platform for containerized applications that can run on hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures. It offers full-stack automation for simplified cluster installation and lifecycle management along with over-the-air updates. OpenShift 4 supports deployment on both infrastructure provisioned and managed by Red Hat as well as customer-managed infrastructure. It leverages containers, microservices, and Kubernetes concepts to empower developers to build, deploy and manage applications.
Red Hat Forum Benelux 2015



Red Hat Forum Benelux 2015Microsoft This document discusses OpenShift v3 and how it can help organizations accelerate development at DevOps speed. It provides an overview of Kubernetes and OpenShift's technical architecture, how OpenShift enables continuous delivery and faster cycle times from idea to production. It also summarizes benefits for developers, integrations, administration capabilities, and the OpenShift product roadmap.
RPM Factory for RDO



RPM Factory for RDOFrédéric Lepied Status of the RPM Factory experiment to become the forge to build the OpenStack RPM packages for the RDO project. Presented at the RDO Day pre-FOSDEM 2016.
OpenStack in an Ever Expanding World of Possibilities - Vancouver 2015 Summit



OpenStack in an Ever Expanding World of Possibilities - Vancouver 2015 SummitLew Tucker Over the past several years we have seen the continued adoption of OpenStack and it’s expansion into new areas: from cloud service providers, enterprise private clouds to large media companies, telecommunication giants, and big science. At the same time, open source based platforms for network functions virtualization (NFV) are fueling a movement toward cloud computing in almost all major telco’s.
In the developer world, open source projects, such as Docker, Mesos, Kubernetes, and Spark are gaining a lot of attention and being integrated into OpenStack through projects Kolla and Magnum.
This session will cover how these projects and activities relate to each other and further expand the utility and adoption OpenStack.
Viewers also liked (20)
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 05 - Core Concepts Part I



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 05 - Core Concepts Part IBehnam Loghmani Episode 05 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about core concepts in openshift.
Part 1 include concepts of Containers, Images, Pods and services
I hope you will find it useful.
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 04 - Infrastructure part II



OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 04 - Infrastructure part IIBehnam Loghmani Episode 04 of "OpenShift in a nutshell" presentations in Iran OpenStack community group
This episode is about Nodes, Kublet, Image registry and web console of OpenShift.
I hope you will find it useful.
OpenShift Enterprise 3.1 vs kubernetes



OpenShift Enterprise 3.1 vs kubernetesSamuel Terburg OpenShift is Red Hat's container application platform that provides a full-stack platform for deploying and managing containerized applications. It is based on Docker and Kubernetes and provides additional capabilities for self-service, automation, multi-language support, and enterprise features like authentication, centralized logging, and integration with Red Hat's JBoss middleware. OpenShift handles building, deploying, and scaling applications in a clustered environment with capabilities for continuous integration/delivery, persistent storage, routing, and monitoring.
Build a PaaS with OpenShift Origin



Build a PaaS with OpenShift OriginSteven Pousty This document discusses OpenShift, an open source Platform as a Service (PaaS) from Red Hat. It provides an overview of OpenShift Origin, including that it runs on Linux, uses brokers and nodes to manage containers called gears that deploy user applications using cartridges. It also summarizes how to get involved with the OpenShift community through forums, blogs, GitHub and IRC/email lists. The conclusion encourages attendees to join the community as PaaS can benefit both developers and sysadmins.
OpenShift v3 Internal networking details



OpenShift v3 Internal networking detailsEtsuji Nakai OpenShift v3 uses an overlay VXLAN network to connect pods within a project. Traffic between pods on a node uses Linux bridges, while inter-node communication uses the VXLAN overlay network. Services are exposed using a service IP and iptables rules to redirect traffic to backend pods. For external access, services are associated with router pods using a DNS name, and traffic is load balanced to backend pods by HAProxy in the router pod.
Architecture Overview: Kubernetes with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.1



Architecture Overview: Kubernetes with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.1Etsuji Nakai 2015/03/12 ver1.0 published.
2015/03/26 ver1.1 fixed: flannel's tunnel type to VXLAN.
2015/04/03 ver1.2 fixed: Flannel's mechanism for VXLAN processing.
KubeCon EU 2016: Templatized Application Configuration on OpenShift and Kuber...



KubeCon EU 2016: Templatized Application Configuration on OpenShift and Kuber...KubeAcademy Kubernetes gives developers a platform on which to run images and many configuration objects to control those images, but constructing a cohesive application made up of images and configuration objects is currently a challenge. Reconstructing or sharing that configuration can also be a challenge. This talk will cover the Template feature implemented in OpenShift to simplify the process of defining and repeatably deploying coordinated objects, discuss what is coming to Kubernetes with respect to this capability, and touch on several other existing projects that enable templatizing application definitions.
Sched Link: http://sched.co/6BVH
PaaS POV_To PaaS or Not There really is no question_150601_FINAL_PRINT_READY



PaaS POV_To PaaS or Not There really is no question_150601_FINAL_PRINT_READYRene Claudio Enterprise IT needs to achieve a much higher degree of agility by increasing delivery velocity from requirements to releases. PaaS is a foundational enabler of IT agility by allowing developers to focus on coding while automating operational activities like provisioning and deploying environments. PaaS provides application runtimes and services, enables microservices architectures, and automates operations tasks like infrastructure management, deployments, and scaling. Achieving IT agility starts with a PaaS proof-of-concept to identify workloads that would benefit and determine a roadmap for adoption.
The DevOps PaaS Infusion - May meetup



The DevOps PaaS Infusion - May meetupNorm Leitman The document discusses the Cloudify platform for deploying applications to various cloud environments. Cloudify aims to allow deployment of applications without code changes across any cloud or infrastructure. It uses recipes and a DSL to describe application topology and configuration. Cloudify recipes can deploy various application types and databases. It includes built-in support for common applications, databases, and cloud providers. Cloudify handles provisioning infrastructure through its cloud drivers and deploys applications according to the recipes.
How did Trinity get to Number One in Europe



How did Trinity get to Number One in EuropeJohn Whelan Trinity College in Dublin became the top university in Europe for producing student entrepreneurs. The executive director of Launchbox/Launchpad, John Whelan, explains that Trinity provided experiential and co-curricular supports to inspire and nurture entrepreneurial students. These programs included LaunchPad which helped students start companies like FoodCloud to help small farms donate excess food to the UN World Food Programme, and LaunchBox which assisted startups like SiteSpy and Stand At Mobile World Congress 2016.
Choosing a PaaS for the Enterprise



Choosing a PaaS for the EnterpriseCloud Elements The document discusses the business case for using Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) within enterprises. It outlines the benefits of building applications on a PaaS, such as reducing development costs by 30% and avoiding vendor lock-in. The presentation then discusses characteristics of cloud-optimized applications and examples of common PaaS services. Finally, it provides nine questions enterprises should consider when selecting a PaaS, such as whether it needs to be public or private, and what complementary application services are offered.
An Evaluation of OpenStack Deployment Frameworks



An Evaluation of OpenStack Deployment Frameworksshane_gibson Symantec evaluated several OpenStack deployment frameworks to test provisioning OpenStack clusters from bare metal. They tested Fuel Web, MaaS/JuJu, Crowbar, Foreman, and Rackspace Private Cloud. Crowbar had the fastest time to deploy a full OpenStack cluster and met most of Symantec's requirements. The evaluation provided feedback to vendors on improving automation, resiliency, and managing complex configurations when deploying OpenStack at scale.
Workshop-Build e deploy avançado com Openshift e Kubernetes



Workshop-Build e deploy avançado com Openshift e Kubernetesjuniorjbn Personalizando o ambiente para sua aplicação, editando parâmetros de build e deploy para melhor se adequar a sua aplicação.
OpenShift meetup Bangalore



OpenShift meetup BangaloreSuraj Deshmukh This talk was presented at first OpenShift Bangalore meetup. It showcases what is OpenShift PAAS and how can you deploy app on OpenShift, etc
Openshift/Kubernetes integration with Apache YARN



Openshift/Kubernetes integration with Apache YARNverbal1714 Openshift/Kubernetes integration with Apache YARN
Shows how YARN allows Big Data/Hadoop and other workloads to run side by side on same cluster
Openshift presentation



Openshift presentationArmağan Ersöz PAAS Openshift Presentation : For those who want to focus on their codes rather than dark side of software I mean sysadm :)
[Devconf.cz][2017] Understanding OpenShift Security Context Constraints![[Devconf.cz][2017] Understanding OpenShift Security Context Constraints](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/devconf-170124111354-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Devconf.cz][2017] Understanding OpenShift Security Context Constraints](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/devconf-170124111354-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Devconf.cz][2017] Understanding OpenShift Security Context Constraints](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/devconf-170124111354-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Devconf.cz][2017] Understanding OpenShift Security Context Constraints](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/devconf-170124111354-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Devconf.cz][2017] Understanding OpenShift Security Context ConstraintsAlessandro Arrichiello The document discusses OpenShift security context constraints (SCCs) and how to configure them to allow running a WordPress container. It begins with an overview of SCCs and their purpose in OpenShift for controlling permissions for pods. It then describes issues running the WordPress container under the default "restricted" SCC due to permission errors. The document explores editing the "restricted" SCC and removing capabilities and user restrictions to address the errors. Alternatively, it notes the "anyuid" SCC can be used which is more permissive and standard for allowing the WordPress container to run successfully.
Ultimate DevOps - Jenkins Enterprise & Red Hat OpenShift



Ultimate DevOps - Jenkins Enterprise & Red Hat OpenShiftAndy Pemberton This document discusses using OpenShift and CloudBees Jenkins Platform together for DevOps. OpenShift is a PaaS built on Docker and Kubernetes that allows deploying applications and services. Jenkins can be easily started and integrated with OpenShift to use it as an elastic runtime or deployment target. Jenkins Pipeline allows defining CI/CD pipelines as code. A live demo shows using OpenShift from a Jenkins Pipeline to build and deploy an application. Additional resources are provided to learn more about the OpenShift and CloudBees integration.
Openshift Container Platform on Azure



Openshift Container Platform on AzureGlenn West 1) The document describes an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template for deploying OpenShift Enterprise on Azure. It provisions masters, infra nodes, and worker nodes with load balancing and storage.
2) The ARM template automates the entire deployment process through nested templates for each resource and Bash scripts for configuration. It handles naming, load balancing, storage, networking, and more.
3) The goal is to create a production-ready reference architecture for OpenShift on Azure and automate the deployment process through the ARM template. Current work focuses on deployment, storage, authentication, and documentation. Future work includes additional features and integrations.
Ad
Similar to OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 01 - Introduction (20)
Opensource SDN slides 



Opensource SDN slides ssk OpenDaylight: Open Source Programmable Networking Platform
OpenDaylight is an open platform for network programmability to enable SDN and create a solid foundation for NFV for networks at any size and scale. OpenDaylight software is a combination of components including a fully pluggable controller, interfaces, protocol plug-ins and applications. The Northbound (programmatic) and Southbound (implementation) interfaces are clearly defined and documented APIs. This combination allows vendors and customers alike the ability to utilize a standards-based and widely supported platform without compromising technical creativity and solution innovation. With this common platform both customers and vendors can innovate and collaborate in order to commercialize SDN- and NFV-based solutions
Src : https://www.openstack.org/summit/openstack-summit-hong-kong-2013/session-videos/presentation/opendaylight-an-open-source-sdn-for-your-openstack-cloud
Check the video here : http://youtu.be/Y0P_h6INi_o
OpenDaylight: an open source SDN for your OpenStack cloud



OpenDaylight: an open source SDN for your OpenStack cloudAnees Shaikh Presented at the 2013 OpenStack Summit in Hong Kong.
Authors: Stephan Baucke, Kyle Mestery, Anees Shaikh, Chris Wright
OpenDaylight is an exciting new community-led, open source project focused on accelerating adoption of software-defined networking (SDN) by providing a robust SDN platform on which the industry can build and innovate. An OpenDaylight controller provides flexible management of both physical and virtual networks. The open source nature of the project and its flexible network management capabilities make it an ideal SDN platform to integrate with Neutron.
In this session, OpenDaylight community members from Cisco, IBM, RedHat, and Ericsson will describe the OpenDaylight project goals and platform architecture, as well as the roadmap and progress to date. OpenDaylight brings together a number of virtual networking approaches, and we will discuss integration approaches with OpenStack Neutron that provide flexibility for OpenStack administrators and users. Details of our initial Neutron integration will also be demonstrated for attendees.
Attendees will leave this session with a greater understanding of what OpenDaylight is, and how it can integrate with OpenStack Neutron to provide a powerful SDN-based networking solution for OpenStack Clouds.
OpenStack and OpenDaylight: An Integrated IaaS for SDN/NFV



OpenStack and OpenDaylight: An Integrated IaaS for SDN/NFVCloud Native Day Tel Aviv OpenStack is a free and open-source software platform for cloud computing, mostly deployed as an infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS). OpenDaylight is an open source project under the Linux Foundation with the goal of furthering the adoption and innovation of SDN through the creation of a common industry supported platform.
In this session, I will talk about how OpenStack and OpenDaylight can be combined together to solve real world business cases and networking needs. We will cover:
- What is OpenDaylight
- Use cases for OpenDaylight with OpenStack
- The OpenDaylight NetVirt project
- How OpenDaylight interacts with OpenStack
- The future of OpenDaylight, and how we see it help solving challenges in the networking industry such as NFV, container networking and physical network fabric management -- the open source way.
OpenStack Introduction



OpenStack IntroductionRoozbeh Shafiee This document provides an introduction and overview of OpenStack. It discusses what OpenStack is, how it works, its architecture and components. It also describes how innfinision supports OpenStack and the Iranian OpenStack community. Key points covered include that OpenStack is an open source cloud computing platform, it was founded by Rackspace and NASA, has over 1200 developers, and consists of components like Nova, Swift, Cinder, Neutron and Horizon.
Linux Foundation Collaboration Summit: Hitchhiker's Guide to the Cloud



Linux Foundation Collaboration Summit: Hitchhiker's Guide to the CloudMark Hinkle Imagine it's eight o'clock on a Thursday morning and you awake to see a bulldozer out your window ready to plow over your data center. Normally you may wish to consult the Encyclopedia Galáctica to discern the best course of action but your copy is likely out of date. And while the Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy (HHGTTG) is a wholly remarkable book it doesn't cover the nuances of cloud computing. That's why you need the Hitchhiker's Guide to Cloud Computing (HHGTCC) or at least to attend this talk understand the state of open source cloud computing. Specifically this talk will cover infrastructure-as-a-service, platform-as-a-service and developments in big data and how to more effectively take advantage of these technologies using open source software. Technologies that will be covered in this talk include Apache CloudStack, Chef, CloudFoundry, NoSQL, OpenStack, Puppet and many more.
Open stack architecture overview-meetup-6-6_2013



Open stack architecture overview-meetup-6-6_2013Mirantis This document provides an overview of OpenStack architecture and components. It discusses the goals of OpenStack, including understanding its purpose, ecosystem, definition, history, and projects. It describes the logical architecture and components of OpenStack like Nova, Glance, Swift, Cinder, Quantum, Keystone, and Horizon. It explains how a virtual machine provisioning request flows through different OpenStack components.
Software Defined Networking: The OpenDaylight Project



Software Defined Networking: The OpenDaylight ProjectGreat Wide Open The document discusses OpenDaylight and its Hydrogen release. It provides an overview of OpenDaylight, describing it as an open-source SDN platform built by an open community. The Hydrogen release included 14 projects and delivered capabilities like a controller, virtual tenant networking, and OpenStack integration. Key learnings discussed were the importance of community building and collaboration. Metrics on code volume and contributors for OpenDaylight and other projects were also presented. Future work discussed for the Helium release includes new projects, a focus on code quality and stability, and reducing manual processes.
OpenStack Introduction



OpenStack IntroductionInnfinision Cloud and BigData Solutions This document provides an introduction and overview of OpenStack presented by Roozbeh Shafiee from innfinision Cloud Solutions. The document outlines innfinision's role in supporting OpenStack, describes various OpenStack concepts like architecture, components, and types of clouds, and discusses why OpenStack is used in enterprises. It also promotes contribution and participation in the IRAN OpenStack community.
OpenStack Overview and History



OpenStack Overview and HistoryMirantis The document provides an overview of OpenStack, including its definition, history and initiatives. It describes OpenStack as an open source cloud computing platform that aims to be simple to implement and massively scalable. The overview outlines the core components of OpenStack including compute, networking, storage, identity management and a dashboard. It also discusses related programs in incubation and how the different components communicate and relate to each other.
Introduction to Orchestration and DevOps with OpenStack



Introduction to Orchestration and DevOps with OpenStackAbderrahmane TEKFI I would like to thank all who participates in the webinar, it was a great pleasure to share and contribute,
Below are the links to the record of the Webinar,
All the Webinar:
Just the Demo:
you can also find all the slides the HEAT template file, the CLI and all the materials used in this webinar here:
The OpenStack VM all-in-one: https://www.dropbox.com/s/501ul31o6ilnmv3/coa-aio-newton.ova?dl=0
All the materials: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1dTSe4n2m3VoevIHZGT_q8uZIV7_f9ZJt?usp=sharing
Thanks to Racim and to the ELIANIS TECHNOLOGIES team.
Special thanks to our REDHAT ARCHITECT Sir. Djelloul Bouida for attending the webinar and all our group member.
For those who didn't join our Group, here the link to our Group on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/groups/475301352862998/
Mobile, Open Source, & the Drive to the Cloud



Mobile, Open Source, & the Drive to the CloudDev_Events - The presentation discussed bringing Swift to the server by enabling modern application design patterns through open source projects like Kitura and OpenWhisk.
- Key points included an overview of the Swift language and tools, how to develop a basic web application using Kitura, and how OpenWhisk allows triggering actions through events.
- Sample applications like BluePic and resources like the Swift Package Catalog and IBM Swift developer center were highlighted as ways to get involved with the Swift community.
Mobile, Open Source, and the Drive to the Cloud



Mobile, Open Source, and the Drive to the CloudDev_Events Open technologies are leading the way to a simplified development experience, end to end, from mobile to the cloud. Open source projects including the Swift programming language, OpenWhisk, the serverless, even-driven execution environment, and Cloudant DBaaS, based on Apache CouchDB, are key to this transformation. Separately, these powerful open technologies make mobile and cloud development easier and faster, but in combination, their value to the developer greatly increases. Patrick Bohrer explores the role of these open technologies in driving down the time it takes to build, integrate, and deliver powerful apps that blur the lines between mobile and cloud.
OpenInfra Projects Overview by Ildiko Vancsa.pdf



OpenInfra Projects Overview by Ildiko Vancsa.pdfCloud Study Network The OpenInfra Projects Overview slide deck from the same-titled presentation given by Ildiko Vancsa on March 29, 2024. It offers an in-depth exploration into the dynamic world of open infrastructure projects. As a seasoned expert and the Director of Community at the OpenInfra Foundation, Ildiko provides unique insights into the development, impact, and future directions of critical projects such as StarlingX, Kata Containers, and other edge computing initiatives.
Open Stack Cloud Services



Open Stack Cloud ServicesSaurabh Gupta The document provides an overview of Open Stack cloud services. It discusses key aspects of Open Source, cloud computing, hypervisors, Open Stack, and compares Open Stack to other cloud platforms like CloudStack and Eucalyptus. The document highlights that Open Stack provides the features required for IaaS cloud services, but some integration work is needed to commercialize it. It also notes that while the platforms differ in codebase and hypervisor support, choosing a good management layer allows portability between platforms.
LinuxFest NW 2013: Hitchhiker's Guide to Open Source Cloud Computing



LinuxFest NW 2013: Hitchhiker's Guide to Open Source Cloud ComputingMark Hinkle Presented on April 27th, 2013 at LinuxFest NW
Imagine it’s eight o’clock on a Thursday morning and you awake to see a bulldozer out your window ready to plow over your data center. Normally you may wish to consult the Encyclopedia Galáctica to discern the best course of action but your copy is likely out of date. And while the Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy (HHGTTG) is a wholly remarkable book it doesn’t cover the nuances of cloud computing. That’s why you need the Hitchhiker’s Guide to Cloud Computing (HHGTCC) or at least to attend this talk understand the state of open source cloud computing. Specifically this talk will cover infrastructure-as-a-service, platform-as-a-service and developments in big data and how to more effectively take advantage of these technologies using open source software. Technologies that will be covered in this talk include Apache CloudStack, Chef, CloudFoundry, NoSQL, OpenStack, Puppet and many more.
Specific topics for discussion will include:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service - The Systems Cloud - Get a comparision of the open source cloud platforms including OpenStack, Apache CloudStack, Eucalyptus, OpenNebula
Platform-as-a-Service - The Developers Cloud - Find out what tools are availble to build portable auto-scaling applications including CloudFoundry, OpenShift, Stackato and more.
Data-as-a-Service - The Analytics Cloud - Want to figure out the who, what , where , when and why of big data ? You get an overview of open source NoSQL databases and technologies like MapReduce to help crunch massive data sets in the cloud.
Finally you'll get a overview of the tools that can help you really take advantage of the cloud? Want to auto-scale virtual machiens to serve millions of web pages or want to automate the configuration of cloud computing environments. You'll learn how to combine these tools to provide continous deployment systems that will help you earn DevOps cred in any data center.
[Finally, for those of you that are Douglas Adams fans please accept the deepest apologies for bad analogies to the HHGTTG.]
Cloud Expo East 2013: Essential Open Source Software for Building the Open Cloud



Cloud Expo East 2013: Essential Open Source Software for Building the Open CloudMark Hinkle Cloud computing is more than a buzz-phrase it’s a transformative IT paradigm shift. The emphasis in the cloud is on elasticity, scalability, agility and open. Not just open standards but open APIs and open source. The delivery of software is also going through a paradigm shift. Open source software was often a commoditization of a market leader; Unix to Linux or Oracle to MySQL what’s changing is that the iterative nature, user context and the motto of releasing early and often are driving real innovation in open source.
This session will cover those essential open source technologies for delivering cloud computing in the enterprise.
Speaker Bio:
Mark Hinkle is the Senior Director, Open Source Solutions at Citrix Systems Inc. He joined Citrix as a result of their July 2011 acquisition of Cloud.com where he was their Vice President of Community. He is currently responsible for Citrix open source efforts around the open source cloud computing platform, Apache CloudStack and the Xen Hypervisor. Previously he was the VP of Community at Zenoss Inc., a producer of the open source application, server, and network management software, where he grew the Zenoss Core project to over 100,000 users and 20,000 organizations on all seven continents. He also is a longtime open source expert and author having served as Editor-in-Chief for both LinuxWorld Magazine and Enterprise Open Source Magazine. His blog on open source, technology, and new media can be found at http://www.socializedsoftware.com.
TOWARDS Hybrid OpenStack Clouds in the Real World



TOWARDS Hybrid OpenStack Clouds in the Real WorldAndrew Hickey Tim Bell, Manager of Infrastructure at CERN, and Rackspace's Toby Owen present "TOWARDS Hybrid OpenStack Clouds in the Real World"
Aether: The First Open Source 5G/LTE Connected Edge Cloud Platform



Aether: The First Open Source 5G/LTE Connected Edge Cloud PlatformMyNOG The document discusses Aether, an open source 5G/LTE connected edge cloud platform from the Open Networking Foundation (ONF). It aims to enable digital transformation through a cloud-native platform that supports disaggregated and virtualized mobile networks. Aether provides a common, neutral platform for building distributed edge applications and allows enterprises to deploy private 4G/5G networks. It has global deployments across multiple continents and edges that are centrally orchestrated from the cloud.
Sharad openstack slides



Sharad openstack slidesSharad Aggarwal OpenStack is an open-source cloud computing platform that consists of interrelated projects that provide software for building and managing public and private clouds. The projects include Nova (compute), Swift (object storage), Glance (image repository), Keystone (identity), Quantum (networking), Cinder (block storage), and Horizon (dashboard). OpenStack aims to produce a cloud computing platform that is simple to implement, massively scalable, and feature-rich. It has a large global community of developers and is used by many large companies and organizations.
Beyond OpenStack | OpenStack in Real Life



Beyond OpenStack | OpenStack in Real LifeOpsta OpenStack is a open source software for creating private and public clouds that coordinated collection of software from a few dozen related projects. This presentation give you an introduction about using Public and Private Cloud with OpenStack and how to max it out
OpenStack in Real Life at INET on July 24, 2017
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
AI EngineHost Review: Revolutionary USA Datacenter-Based Hosting with NVIDIA ...



AI EngineHost Review: Revolutionary USA Datacenter-Based Hosting with NVIDIA ...SOFTTECHHUB I started my online journey with several hosting services before stumbling upon Ai EngineHost. At first, the idea of paying one fee and getting lifetime access seemed too good to pass up. The platform is built on reliable US-based servers, ensuring your projects run at high speeds and remain safe. Let me take you step by step through its benefits and features as I explain why this hosting solution is a perfect fit for digital entrepreneurs.
DevOpsDays Atlanta 2025 - Building 10x Development Organizations.pptx



DevOpsDays Atlanta 2025 - Building 10x Development Organizations.pptxJustin Reock Building 10x Organizations with Modern Productivity Metrics
10x developers may be a myth, but 10x organizations are very real, as proven by the influential study performed in the 1980s, ‘The Coding War Games.’
Right now, here in early 2025, we seem to be experiencing YAPP (Yet Another Productivity Philosophy), and that philosophy is converging on developer experience. It seems that with every new method we invent for the delivery of products, whether physical or virtual, we reinvent productivity philosophies to go alongside them.
But which of these approaches actually work? DORA? SPACE? DevEx? What should we invest in and create urgency behind today, so that we don’t find ourselves having the same discussion again in a decade?
How analogue intelligence complements AI



How analogue intelligence complements AIPaul Rowe
Artificial Intelligence is providing benefits in many areas of work within the heritage sector, from image analysis, to ideas generation, and new research tools. However, it is more critical than ever for people, with analogue intelligence, to ensure the integrity and ethical use of AI. Including real people can improve the use of AI by identifying potential biases, cross-checking results, refining workflows, and providing contextual relevance to AI-driven results.
News about the impact of AI often paints a rosy picture. In practice, there are many potential pitfalls. This presentation discusses these issues and looks at the role of analogue intelligence and analogue interfaces in providing the best results to our audiences. How do we deal with factually incorrect results? How do we get content generated that better reflects the diversity of our communities? What roles are there for physical, in-person experiences in the digital world?
AI Changes Everything – Talk at Cardiff Metropolitan University, 29th April 2...



AI Changes Everything – Talk at Cardiff Metropolitan University, 29th April 2...Alan Dix Talk at the final event of Data Fusion Dynamics: A Collaborative UK-Saudi Initiative in Cybersecurity and Artificial Intelligence funded by the British Council UK-Saudi Challenge Fund 2024, Cardiff Metropolitan University, 29th April 2025
https://alandix.com/academic/talks/CMet2025-AI-Changes-Everything/
Is AI just another technology, or does it fundamentally change the way we live and think?
Every technology has a direct impact with micro-ethical consequences, some good, some bad. However more profound are the ways in which some technologies reshape the very fabric of society with macro-ethical impacts. The invention of the stirrup revolutionised mounted combat, but as a side effect gave rise to the feudal system, which still shapes politics today. The internal combustion engine offers personal freedom and creates pollution, but has also transformed the nature of urban planning and international trade. When we look at AI the micro-ethical issues, such as bias, are most obvious, but the macro-ethical challenges may be greater.
At a micro-ethical level AI has the potential to deepen social, ethnic and gender bias, issues I have warned about since the early 1990s! It is also being used increasingly on the battlefield. However, it also offers amazing opportunities in health and educations, as the recent Nobel prizes for the developers of AlphaFold illustrate. More radically, the need to encode ethics acts as a mirror to surface essential ethical problems and conflicts.
At the macro-ethical level, by the early 2000s digital technology had already begun to undermine sovereignty (e.g. gambling), market economics (through network effects and emergent monopolies), and the very meaning of money. Modern AI is the child of big data, big computation and ultimately big business, intensifying the inherent tendency of digital technology to concentrate power. AI is already unravelling the fundamentals of the social, political and economic world around us, but this is a world that needs radical reimagining to overcome the global environmental and human challenges that confront us. Our challenge is whether to let the threads fall as they may, or to use them to weave a better future.
Rusty Waters: Elevating Lakehouses Beyond Spark



Rusty Waters: Elevating Lakehouses Beyond Sparkcarlyakerly1 Spark is a powerhouse for large datasets, but when it comes to smaller data workloads, its overhead can sometimes slow things down. What if you could achieve high performance and efficiency without the need for Spark?
At S&P Global Commodity Insights, having a complete view of global energy and commodities markets enables customers to make data-driven decisions with confidence and create long-term, sustainable value. 🌍
Explore delta-rs + CDC and how these open-source innovations power lightweight, high-performance data applications beyond Spark! 🚀
TrustArc Webinar: Consumer Expectations vs Corporate Realities on Data Broker...



TrustArc Webinar: Consumer Expectations vs Corporate Realities on Data Broker...TrustArc Most consumers believe they’re making informed decisions about their personal data—adjusting privacy settings, blocking trackers, and opting out where they can. However, our new research reveals that while awareness is high, taking meaningful action is still lacking. On the corporate side, many organizations report strong policies for managing third-party data and consumer consent yet fall short when it comes to consistency, accountability and transparency.
This session will explore the research findings from TrustArc’s Privacy Pulse Survey, examining consumer attitudes toward personal data collection and practical suggestions for corporate practices around purchasing third-party data.
Attendees will learn:
- Consumer awareness around data brokers and what consumers are doing to limit data collection
- How businesses assess third-party vendors and their consent management operations
- Where business preparedness needs improvement
- What these trends mean for the future of privacy governance and public trust
This discussion is essential for privacy, risk, and compliance professionals who want to ground their strategies in current data and prepare for what’s next in the privacy landscape.
Cyber Awareness overview for 2025 month of security



Cyber Awareness overview for 2025 month of securityriccardosl1 Cyber awareness training educates employees on risk associated with internet and malicious emails
Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD



Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure ADVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD
Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdf



Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdfSoftware Company Explore the benefits and features of advanced logistics management software for businesses in Riyadh. This guide delves into the latest technologies, from real-time tracking and route optimization to warehouse management and inventory control, helping businesses streamline their logistics operations and reduce costs. Learn how implementing the right software solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a competitive edge in the growing logistics sector of Riyadh.
Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy Consumption



Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy ConsumptionExove How to measure web front-end energy consumption using Firefox Profiler. Presented in DrupalCamp Finland on April 25th, 2025.
tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdf



tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdffjgm517 descaripcion detallada del avance de las tecnologias en mesopotamia, egipto, roma y grecia.
Into The Box Conference Keynote Day 1 (ITB2025)



Into The Box Conference Keynote Day 1 (ITB2025)Ortus Solutions, Corp This is the keynote of the Into the Box conference, highlighting the release of the BoxLang JVM language, its key enhancements, and its vision for the future.
Designing Low-Latency Systems with Rust and ScyllaDB: An Architectural Deep Dive



Designing Low-Latency Systems with Rust and ScyllaDB: An Architectural Deep DiveScyllaDB Want to learn practical tips for designing systems that can scale efficiently without compromising speed?
Join us for a workshop where we’ll address these challenges head-on and explore how to architect low-latency systems using Rust. During this free interactive workshop oriented for developers, engineers, and architects, we’ll cover how Rust’s unique language features and the Tokio async runtime enable high-performance application development.
As you explore key principles of designing low-latency systems with Rust, you will learn how to:
- Create and compile a real-world app with Rust
- Connect the application to ScyllaDB (NoSQL data store)
- Negotiate tradeoffs related to data modeling and querying
- Manage and monitor the database for consistently low latencies
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungen



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungenpanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-und-verwaltung-von-multiuser-umgebungen/
HCL Nomad Web wird als die nächste Generation des HCL Notes-Clients gefeiert und bietet zahlreiche Vorteile, wie die Beseitigung des Bedarfs an Paketierung, Verteilung und Installation. Nomad Web-Client-Updates werden “automatisch” im Hintergrund installiert, was den administrativen Aufwand im Vergleich zu traditionellen HCL Notes-Clients erheblich reduziert. Allerdings stellt die Fehlerbehebung in Nomad Web im Vergleich zum Notes-Client einzigartige Herausforderungen dar.
Begleiten Sie Christoph und Marc, während sie demonstrieren, wie der Fehlerbehebungsprozess in HCL Nomad Web vereinfacht werden kann, um eine reibungslose und effiziente Benutzererfahrung zu gewährleisten.
In diesem Webinar werden wir effektive Strategien zur Diagnose und Lösung häufiger Probleme in HCL Nomad Web untersuchen, einschließlich
- Zugriff auf die Konsole
- Auffinden und Interpretieren von Protokolldateien
- Zugriff auf den Datenordner im Cache des Browsers (unter Verwendung von OPFS)
- Verständnis der Unterschiede zwischen Einzel- und Mehrbenutzerszenarien
- Nutzung der Client Clocking-Funktion
What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...



What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...Vishnu Singh Chundawat The MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a framework designed to manage context and interaction within complex systems. This SlideShare presentation will provide a detailed overview of the MCP Model, its applications, and how it plays a crucial role in improving communication and decision-making in distributed systems. We will explore the key concepts behind the protocol, including the importance of context, data management, and how this model enhances system adaptability and responsiveness. Ideal for software developers, system architects, and IT professionals, this presentation will offer valuable insights into how the MCP Model can streamline workflows, improve efficiency, and create more intuitive systems for a wide range of use cases.
Linux Support for SMARC: How Toradex Empowers Embedded Developers



Linux Support for SMARC: How Toradex Empowers Embedded DevelopersToradex Toradex brings robust Linux support to SMARC (Smart Mobility Architecture), ensuring high performance and long-term reliability for embedded applications. Here’s how:
• Optimized Torizon OS & Yocto Support – Toradex provides Torizon OS, a Debian-based easy-to-use platform, and Yocto BSPs for customized Linux images on SMARC modules.
• Seamless Integration with i.MX 8M Plus and i.MX 95 – Toradex SMARC solutions leverage NXP’s i.MX 8 M Plus and i.MX 95 SoCs, delivering power efficiency and AI-ready performance.
• Secure and Reliable – With Secure Boot, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and LTS kernel support, Toradex ensures industrial-grade security and longevity.
• Containerized Workflows for AI & IoT – Support for Docker, ROS, and real-time Linux enables scalable AI, ML, and IoT applications.
• Strong Ecosystem & Developer Support – Toradex offers comprehensive documentation, developer tools, and dedicated support, accelerating time-to-market.
With Toradex’s Linux support for SMARC, developers get a scalable, secure, and high-performance solution for industrial, medical, and AI-driven applications.
Do you have a specific project or application in mind where you're considering SMARC? We can help with Free Compatibility Check and help you with quick time-to-market
For more information: https://www.toradex.com/computer-on-modules/smarc-arm-family
Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For Devs



Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For DevsBrian McKeiver May 2nd, 2025 talk at StirTrek 2025 Conference.
#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025



#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, transcript, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...



What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...Vishnu Singh Chundawat
OpenShift In a Nutshell - Episode 01 - Introduction
- 1. Presentation By: Behnam Loghmani Winter 2016 IRAN OpenStack Users Group OPENSHIFT IN A NUTSHELL (Episode 01) Introduction
- 2. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir Agenda: ● Cloud Service Models ● What's OpenShift? ● OpenShift Architectures ● Iran OpenStack Community OpenShift Introduction
- 3. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Cloud Service Models
- 4. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction https://www.cloudtec.ch/assets/fm/IT-Consulting/Cloud-Computing/iaas-paas-saas.png
- 5. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction What's OpenShift?
- 6. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction OpenShift is a platform as a service product from Red Hat. OpenShift is Red Hat’s public cloud application development and hosting platform that automates the provisioning, management and scaling of applications so that you can focus on writing the code for your business, startup, or big idea.
- 7. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction OpenShift Versions OPENSHIFT Enterprise OPENSHIFT Online OPENSHIFT Dedicated
- 8. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction OpenShift Origin ● Binary ● Source code ● RPMs
- 9. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction
- 10. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction
- 11. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction
- 12. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction On Debian??! - Memory cgroup support: GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="cgroup_enable=memory" On v1.1.2 - CPU cgroup: cpu.cfs_quota_us and cpu.cfs_quota_us Recompile kernel with “CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH=y” https://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi?bug=789019
- 13. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction OpenShift Online
- 14. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Supported language environments ● Haskell ● Java ● JavaScript ● .Net ● Perl ● PHP ● Python ● Ruby
- 15. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Supported databases ● Microsoft SQL Server ● MongoDB ● MySQL ● PostgreSQL
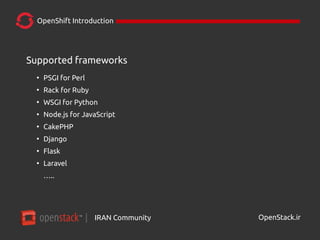
- 16. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Supported frameworks ● PSGI for Perl ● Rack for Ruby ● WSGI for Python ● Node.js for JavaScript ● CakePHP ● Django ● Flask ● Laravel …..
- 17. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction OpenShift Architectures OpenShift v2 / OpenShift v3
- 18. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Applications - In OpenShift v2, an application was a single unit - it consisted of one web framework and no more than one of any given cartridge type. - Linking was limited to within an application and only worked within cartridges designed to work together. - In OpenShift v3 remove "application" as a keyword since "application" can mean something different to everyone. - Flexible linking: means you can link any two arbitrary components together.
- 19. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Cartridges vs Images ● Dependencies ● Collocation ● Source Code ● Build ● Routing
- 20. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Terminology ● Application ● Gear vs Container ● Cartridge vs Image ● Domain vs Project ● Broker vs Master
- 21. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction V2 :
- 22. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction V3 :
- 23. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Iran OpenStack Community
- 24. IRAN Community| OpenStack.ir OpenShift Introduction Stay in Touch and Join Us: ● Home Page: OpenStack.ir ● Meetup Page: Meetup.com/Iran-OpenStack ● Mailing List: [email protected] ● Twitter: @OpenStackIR , #OpenStackIRAN ● IRC Channel on FreeNode: #OpenStack-ir
- 25. Thank You Behnam Loghmani Iran OpenStack Community Member [email protected] OpenStack.ir We need to work together to build a better community


