Ad
03_Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection.ppt
- 1. William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8th Edition Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
- 2. Program Concept • Hardwired systems are inflexible • General purpose hardware can do different tasks, given correct control signals • Instead of re-wiring, supply a new set of control signals
- 3. What is a program? • A sequence of steps • For each step, an arithmetic or logical operation is done • For each operation, a different set of control signals is needed
- 4. Function of Control Unit • For each operation a unique code is provided —e.g. ADD, MOVE • A hardware segment accepts the code and issues the control signals • We have a computer!
- 5. Components • The Control Unit and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit constitute the Central Processing Unit • Data and instructions need to get into the system and results out —Input/output • Temporary storage of code and results is needed —Main memory
- 6. Computer Components: Top Level View
- 7. Instruction Cycle • Two steps: —Fetch —Execute
- 8. Fetch Cycle • Program Counter (PC) holds address of next instruction to fetch • Processor fetches instruction from memory location pointed to by PC • Increment PC —Unless told otherwise • Instruction loaded into Instruction Register (IR) • Processor interprets instruction and performs required actions
- 9. Execute Cycle • Processor-memory —data transfer between CPU and main memory • Processor I/O —Data transfer between CPU and I/O module • Data processing —Some arithmetic or logical operation on data • Control —Alteration of sequence of operations —e.g. jump • Combination of above
- 10. Example of Program Execution
- 11. Instruction Cycle State Diagram
- 12. Interrupts • Mechanism by which other modules (e.g. I/O) may interrupt normal sequence of processing • Program —e.g. overflow, division by zero • Timer —Generated by internal processor timer —Used in pre-emptive multi-tasking • I/O —from I/O controller • Hardware failure —e.g. memory parity error
- 14. Interrupt Cycle • Added to instruction cycle • Processor checks for interrupt —Indicated by an interrupt signal • If no interrupt, fetch next instruction • If interrupt pending: —Suspend execution of current program —Save context —Set PC to start address of interrupt handler routine —Process interrupt —Restore context and continue interrupted program
- 15. Transfer of Control via Interrupts
- 16. Instruction Cycle with Interrupts
- 17. Program Timing Short I/O Wait
- 18. Program Timing Long I/O Wait
- 19. Instruction Cycle (with Interrupts) - State Diagram
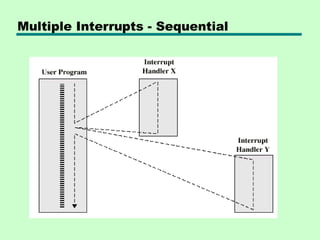
- 20. Multiple Interrupts • Disable interrupts —Processor will ignore further interrupts whilst processing one interrupt —Interrupts remain pending and are checked after first interrupt has been processed —Interrupts handled in sequence as they occur • Define priorities —Low priority interrupts can be interrupted by higher priority interrupts —When higher priority interrupt has been processed, processor returns to previous interrupt
- 21. Multiple Interrupts - Sequential
- 22. Multiple Interrupts – Nested
- 23. Time Sequence of Multiple Interrupts
- 24. Connecting • All the units must be connected • Different type of connection for different type of unit —Memory —Input/Output —CPU
- 25. Computer Modules
- 26. Memory Connection • Receives and sends data • Receives addresses (of locations) • Receives control signals —Read —Write —Timing
- 27. Input/Output Connection(1) • Similar to memory from computer’s viewpoint • Output —Receive data from computer —Send data to peripheral • Input —Receive data from peripheral —Send data to computer
- 28. Input/Output Connection(2) • Receive control signals from computer • Send control signals to peripherals —e.g. spin disk • Receive addresses from computer —e.g. port number to identify peripheral • Send interrupt signals (control)
- 29. CPU Connection • Reads instruction and data • Writes out data (after processing) • Sends control signals to other units • Receives (& acts on) interrupts
- 30. Buses • There are a number of possible interconnection systems • Single and multiple BUS structures are most common • e.g. Control/Address/Data bus (PC) • e.g. Unibus (DEC-PDP)
- 31. What is a Bus? • A communication pathway connecting two or more devices • Usually broadcast • Often grouped —A number of channels in one bus —e.g. 32 bit data bus is 32 separate single bit channels • Power lines may not be shown
- 32. Data Bus • Carries data —Remember that there is no difference between “data” and “instruction” at this level • Width is a key determinant of performance —8, 16, 32, 64 bit
- 33. Address bus • Identify the source or destination of data • e.g. CPU needs to read an instruction (data) from a given location in memory • Bus width determines maximum memory capacity of system —e.g. 8080 has 16 bit address bus giving 64k address space
- 34. Control Bus • Control and timing information —Memory read/write signal —Interrupt request —Clock signals
- 36. Big and Yellow? • What do buses look like? —Parallel lines on circuit boards —Ribbon cables —Strip connectors on mother boards – e.g. PCI —Sets of wires
- 37. Physical Realization of Bus Architecture
- 38. Single Bus Problems • Lots of devices on one bus leads to: —Propagation delays – Long data paths mean that co-ordination of bus use can adversely affect performance – If aggregate data transfer approaches bus capacity • Most systems use multiple buses to overcome these problems
- 41. Bus Types • Dedicated —Separate data & address lines • Multiplexed —Shared lines —Address valid or data valid control line —Advantage - fewer lines —Disadvantages – More complex control – Ultimate performance
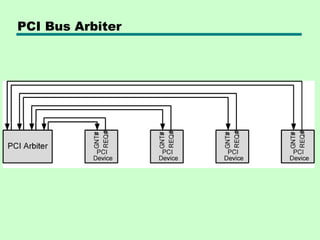
- 42. Bus Arbitration • More than one module controlling the bus • e.g. CPU and DMA controller • Only one module may control bus at one time • Arbitration may be centralised or distributed
- 43. Centralised or Distributed Arbitration • Centralised —Single hardware device controlling bus access – Bus Controller – Arbiter —May be part of CPU or separate • Distributed —Each module may claim the bus —Control logic on all modules
- 44. Timing • Co-ordination of events on bus • Synchronous —Events determined by clock signals —Control Bus includes clock line —A single 1-0 is a bus cycle —All devices can read clock line —Usually sync on leading edge —Usually a single cycle for an event
- 46. Asynchronous Timing – Read Diagram
- 47. Asynchronous Timing – Write Diagram
- 48. PCI Bus • Peripheral Component Interconnection • Intel released to public domain • 32 or 64 bit • 50 lines
- 49. PCI Bus Lines (required) • Systems lines —Including clock and reset • Address & Data —32 time mux lines for address/data —Interrupt & validate lines • Interface Control • Arbitration —Not shared —Direct connection to PCI bus arbiter • Error lines
- 50. PCI Bus Lines (Optional) • Interrupt lines —Not shared • Cache support • 64-bit Bus Extension —Additional 32 lines —Time multiplexed —2 lines to enable devices to agree to use 64-bit transfer • JTAG/Boundary Scan —For testing procedures
- 51. PCI Commands • Transaction between initiator (master) and target • Master claims bus • Determine type of transaction —e.g. I/O read/write • Address phase • One or more data phases
- 52. PCI Read Timing Diagram
- 53. PCI Bus Arbiter
- 55. Foreground Reading • Stallings, chapter 3 (all of it) • www.pcguide.com/ref/mbsys/buses/ • In fact, read the whole site! • www.pcguide.com/