05 control structures 2
- 1. Chapter 5 – Control Structures: Part 2 Outline 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.3 For / Next Repetition Structure 5.4 Examples Using the For / Next Structure 5.5 Select Case Multiple-Selection Structure 5.6 Do / Loop While Repetition Structure 5.7 Do / Loop Until Repetition Structure 5.8 Using the Exit Keyword in a Repetition Structure 5.9 Logical Operators 5.10 Structured Programming Summary
- 2. 5.1 Introduction Problem Solving Requires understanding of: Building blocks Program-construction principles
- 3. 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition Elements needed Control variable Used to determine whether loop continues to iterate Initial value of control variable Increment (or decrement) Describes how control variable is modified during each iteration Condition Tests for final value of control variable
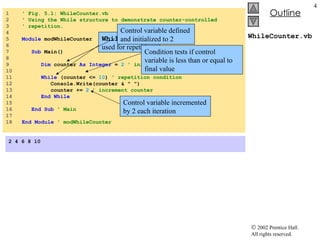
- 4. WhileCounter.vb 1 ' Fig. 5.1: WhileCounter.vb 2 ' Using the While structure to demonstrate counter-controlled 3 ' repetition. 4 5 Module modWhileCounter 6 7 Sub Main() 8 9 Dim counter As Integer = 2 ' initialization 10 11 While (counter <= 10 ) ' repetition condition 12 Console.Write(counter & " ") 13 counter += 2 ' increment counter 14 End While 15 16 End Sub ' Main 17 18 End Module ' modWhileCounter 2 4 6 8 10 While structure used for repetition Control variable defined and initialized to 2 Control variable incremented by 2 each iteration Condition tests if control variable is less than or equal to final value
- 5. 5.3 For / Next Repetition Structure For / Next counter-controlled repetition Structure header initializes control variable, specifies final value and increment For keyword begins structure Followed by control variable initialization To keyword specifies final value Step keyword specifies increment Optional Increment defaults to 1 if omitted May be positive or negative Next keyword marks end of structure Executes until control variable greater (or less) than final value
- 6. ForCounter.vb Program Output 1 ' Fig. 5.2: ForCounter.vb 2 ' Using the For/Next structure to demonstrate counter-controlled 3 ' repetition. 4 5 Module modForCounter 6 7 Sub Main() 8 Dim counter As Integer 9 10 ' initialization, repetition condition and 11 ' incrementing are included in For structure 12 For counter = 2 To 10 Step 2 13 Console.Write(counter & " " ) 14 Next 15 16 End Sub ' Main 17 18 End Module ' modForCounter 2 4 6 8 10 Control variable initialized to 2 To specifies final value of 10 Step increments counter by 2 each iteration Next marks end of loop
- 7. 5.3 For / Next Repetition Structure Fig. 5.3 Components of a typical For/Next header. For counter = 2 To 10 Step 2 For keyword Initial value of control variable Final value of control variable Increment of control variable Control variable name To keyword Step keyword
- 8. 5.4 Examples Using the For / Next Structure Examples Vary the control variable from 1 to 100 in increments of 1 For i = 1 To 100 For i = 1 To 100 Step 1 Vary the control variable from 100 to 1 in increments of –1 For i = 100 To 1 Step –1 Vary the control variable from 7 to 77 in increments of 7 For i = 7 To 77 Step 7 Vary the control variable from 20 to 2 in increments of –2 For i = 20 To 2 Step -2
- 9. 5.4 Examples Using the For / Next Structure Fig. 5.4 Flowcharting a typical For/Next repetition structure. counter = 1 counter < = 10 (implicit) false true Console.WriteLine(counter * 10) counter += 1 (implicit) Establish initial value of control variable Determine if final value of control variable has been reached Body of loop (this can be multiple statements) Increment the control variable
- 10. Sum.vb Program Output 1 ' Fig. 5.5: Sum.vb 2 ' Using For/Next structure to demonstrate summation. 3 4 Imports System.Windows.Forms 5 6 Module modSum 7 8 Sub Main() 9 10 Dim sum = 0 , number As Integer 11 12 ' add even numbers from 2 to 100 13 For number = 2 To 100 Step 2 14 sum += number 15 Next 16 17 MessageBox.Show( "The sum is " & sum, _ 18 "Sum even integers from 2 to 100" , _ 19 MessageBoxButtons. OK , MessageBoxIcon. Information ) 20 End Sub ' Main 21 22 End Module ' modSum Control variable counts by 2, from 2 to 100 Value of number is added in each iteration to determine sum of even numbers Text displayed in dialog Display a MessageBox Indicate button to be OK button Indicate icon to be Information icon Text displayed in title bar
- 11. 5.4 Examples Using the For / Next Structure Fig. 5.6 Icons for message dialogs.
- 12. 5.4 Examples Using the For / Next Structure Fig. 5.7 Button constants for message dialogs.
- 13. Interest.vb 1 ' Fig. 5.8: Interest.vb 2 ' Calculating compound interest. 3 4 Imports System.Windows.Forms 5 6 Module modInterest 7 8 Sub Main() 9 10 Dim amount, principal As Decimal ' dollar amounts 11 Dim rate As Double ' interest rate 12 Dim year As Integer ' year counter 13 Dim output As String ' amount after each year 14 15 principal = 1000.00 16 rate = 0.05 17 18 output = "Year" & vbTab & "Amount on deposit" & vbCrLf 19 20 ' calculate amount after each year 21 For year = 1 To 10 22 amount = principal * ( 1 + rate) ^ year 23 output &= year & vbTab & _ 24 String.Format( "{0:C}" , amount) & vbCrLf 25 Next 26 27 ' display output 28 MessageBox.Show(output, "Compound Interest" , _ 29 MessageBoxButtons. Ok , MessageBoxIcon. Information ) 30 31 End Sub ' Main 32 33 End Module ' modInterest Perform calculation to determine amount in account Append year followed by the formatted calculation result and newline character to end of String output Specify C (for “currency”) as formatting code Type Decimal used for precise monetary calculations
- 14. Program Output
- 15. 5.4 Examples Using the For / Next Structure Fig. 5.9 String formatting codes.
- 16. 5.5 Select Case Multiple-Selection Structure Multiple-Selection Structure Tests expression separately for each value expression may assume Select Case keywords begin structure Followed by controlling expression Compared sequentially with each case Code in case executes if match is found Program control proceeds to first statement after structure Case keyword Specifies each value to test for Followed by code to execute if test is true Case Else Optional Executes if no match is found Must be last case in sequence
- 17. SelectTest.vb 1 ' Fig. 5.10: SelectTest.vb 2 ' Using the Select Case structure. 3 4 Module modEnterGrades 5 6 Sub Main() 7 Dim grade As Integer = 0 ' one grade 8 Dim aCount As Integer = 0 ' number of As 9 Dim bCount As Integer = 0 ' number of Bs 10 Dim cCount As Integer = 0 ' number of Cs 11 Dim dCount As Integer = 0 ' number of Ds 12 Dim fCount As Integer = 0 ' number of Fs 13 14 Console.Write( "Enter a grade, -1 to quit: " ) 15 grade = Console.ReadLine() 16 17 ' input and process grades 18 While grade <> -1 19 20 Select Case grade ' check which grade was input 21 22 Case 100 ' student scored 100 23 Console.WriteLine( "Perfect Score!" & vbCrLf & _ 24 "Letter grade: A" & vbCrLf ) 25 aCount += 1 26 27 Case 90 To 99 ' student scored 90-99 28 Console.WriteLine( "Letter Grade: A" & vbCrLf ) 29 aCount += 1 30 31 Case 80 To 89 ' student scored 80-89 32 Console.WriteLine( "Letter Grade: B" & vbCrLf ) 33 bCount += 1 34 Select Case begins multiple-selection structure Controlling expression First Case executes if grade is exactly 100 Next Case executes if grade is between 90 and 99, the range being specified with the To keyword
- 18. SelectTest.vb 35 Case 70 To 79 ' student scored 70-79 36 Console.WriteLine( "Letter Grade: C" & vbCrLf ) 37 cCount += 1 38 39 Case 60 To 69 ' student scored 60-69 40 Console.WriteLine( "Letter Grade: D" & vbCrLf ) 41 dCount += 1 42 43 ' student scored 0 or 10-59 (10 points for attendance) 44 Case 0 , 10 To 59 45 Console.WriteLine( "Letter Grade: F" & vbCrLf ) 46 fCount += 1 47 48 Case Else 49 50 ' alert user that invalid grade was entered 51 Console.WriteLine( "Invalid Input. " & _ 52 "Please enter a valid grade." & vbCrLf ) 53 End Select 54 55 Console.Write( "Enter a grade, -1 to quit: " ) 56 grade = Console.ReadLine() 57 End While 58 59 ' display count of each letter grade 60 Console.WriteLine( vbCrLf & _ 61 "Totals for each letter grade are: " & vbCrLf & _ 62 "A: " & aCount & vbCrLf & "B: " & bCount _ 63 & vbCrLf & "C: " & cCount & vbCrLf & "D: " & _ 64 dCount & vbCrLf & "F: " & fCount) 65 66 End Sub ' Main 67 68 End Module ' modEnterGrades Optional Case Else executes if no match occurs with previous Case s End Select marks end of structure
- 19. Program Output Enter a grade: 84 Letter Grade: B Enter a grade: 100 Perfect Score! Letter grade : A+ Enter a grade: 7 Invalid Input. Please enter a valid grade. Enter a grade: 95 Letter Grade: A Enter a grade: 78 Letter Grade: C Totals for each letter grade are: A: 2 B: 1 C: 1 D: 0 F: 0
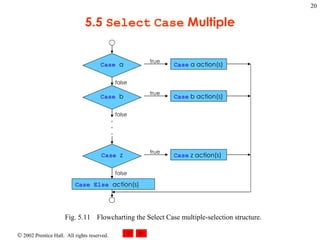
- 20. 5.5 Select Case Multiple Fig. 5.11 Flowcharting the Select Case multiple-selection structure. Case a Case b Case z . . . Case Else action(s) false false false Case a action(s) Case b action(s) Case z action(s) true true true
- 21. 5.6 Do / Loop While Repetition Structure Do / Loop While Repetition Structure Similar to While and Do / While Loop-continuation condition tested after body executes Loop body always executed at least once Begins with keyword Do Ends with keywords Loop While followed by condition
- 22. DoWhile.vb Program Output 1 ' Fig. 5.12: DoWhile.vb 2 ' Demonstrating the Do/Loop While repetition structure. 3 4 Module modDoWhile 5 6 Sub Main() 7 8 Dim counter As Integer = 1 9 10 ' print values 1 to 5 11 Do 12 Console.Write(counter & " " ) 13 counter += 1 14 Loop While (counter <= 5 ) 15 16 End Sub ' Main 17 18 End Module ' modDoWhile 1 2 3 4 5 Do keyword begins structure Loop While ends structure Condition tested after body executes
- 23. 5.7 Do / Loop Until Repetition Structure Fig. 5.13 Flowcharting the Do/Loop While repetition structure. true false action(s) condition
- 24. 5.7 Do / Loop Until Repetition Structure Do / Loop Until Repetition Structure Similar to Do Until / Loop structure Loop-continuation condition tested after body executes Loop body always executed at least once
- 25. LoopUntil.vb Program Output 1 ' Fig. 5.14: LoopUntil.vb 2 ' Using Do/Loop Until repetition structure 3 4 Module modLoopUntil 5 6 Sub Main() 7 8 Dim counter As Integer = 1 9 10 ' print values 1 to 5 11 Do 12 Console.Write(counter & " " ) 13 counter += 1 14 Loop Until counter > 5 15 16 End Sub ' Main 17 18 End Module ' modLoopUntil 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Condition tested after body executes
- 26. 5.7 Do / Loop Until Repetition Structure Fig. 5.15 Flowcharting the Do/Loop Until repetition structure. true false action(s) condition
- 27. 5.8 Using the Exit Keyword in a Repetition Structure Exit Statements Alter the flow of control Cause immediate exit from a repetition structure Exit Do Executed in Do structures Exit For Executed in For structures Exit While Executed in While structures
- 28. ExitTest.vb 1 ' Fig. 5.16: ExitTest.vb 2 ' Using the Exit keyword in repetition structures. 3 4 Imports System.Windows.Forms 5 6 Module modExitTest 7 8 Sub Main() 9 Dim output As String 10 Dim counter As Integer 11 12 For counter = 1 To 10 13 14 ' skip remaining code in loop only if counter = 3 15 If counter = 3 Then 16 Exit For 17 End If 18 19 Next 20 21 output = "counter = " & counter & _ 22 " after exiting For/Next structure" & vbCrLf 23 24 Do Until counter > 10 25 26 ' skip remaining code in loop only if counter = 5 27 If counter = 5 Then 28 Exit Do 29 End If 30 31 counter += 1 32 Loop 33 Loop specified to execute 10 times Exit For statement executes when condition is met, causing loop to exit Program control proceeds to first statement after the structure counter is 3 when loop starts, specified to execute until it is greater than 10 Exit Do executes when counter is 5, causing loop to exit
- 29. Program Output 34 output &= "counter = " & counter & _ 35 " after exiting Do Until/Loop structure" & vbCrLf 36 37 While counter <= 10 38 39 ' skip remaining code in loop only if counter = 7 40 If counter = 7 Then 41 Exit While 42 End If 43 44 counter += 1 45 End While 46 47 output &= "counter = " & counter & _ 48 " after exiting While structure" 49 50 MessageBox.Show(output, "Exit Test" , _ 51 MessageBoxButtons. OK , MessageBoxIcon. Information ) 52 End Sub ' Main 53 54 End Module ' modExitTest counter is 5 when loop starts, specified to execute while less than or equal to 10 Exit While executes when counter is 7, causing loop to exit
- 30. 5.9 Logical Operators Used to form complex conditions by combining simple ones Short-circuit evaluation Execute only until truth or falsity is known AndAlso operator Returns true if and only if both conditions are true OrElse operator Returns true if either or both of two conditions are true
- 31. 5.9 Logical Operators (II) Logical Operators without short-circuit evaluation And and Or Similar to AndAlso and OrElse respectively Always execute both of their operands Used when an operand has a side effect Condition makes a modification to a variable Should be avoided to reduce subtle errors Xor Returns true if and only if one operand is true and the other false
- 32. 5.9 Logical Operators (III) Logical Negation Not Used to reverse the meaning of a condition Unary operator Requires one operand Can usually be avoided by expressing a condition differently
- 33. 5.9 Logical Operators Fig. 5.17 Truth table for the AndAlso (logical AND) operator.
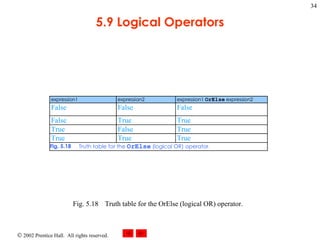
- 34. 5.9 Logical Operators Fig. 5.18 Truth table for the OrElse (logical OR) operator.
- 35. 5.9 Logical Operators Fig. 5.19 Truth table for the boolean logical exclusive OR (Xor) operator. Fig. 5.20 Truth table for operator Not (logical NOT).
- 36. LogicalOperator.vb 1 ' Fig. 5.21: LogicalOperator.vb 2 ' Using logical operators. 3 4 Public Class FrmLogicalOperator 5 Inherits System.Windows.Forms.Form 6 7 ' Visual Studio .NET generated code 8 9 Private Sub FrmLogicalOperator_Load( _ 10 ByVal sender As System.Object, _ 11 ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase .Load 12 13 lblAndAlso.Text = "AndAlso" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _ 14 "False AndAlso False: " & ( False AndAlso False ) & _ 15 vbCrLf & "False AndAlso True: " & _ 16 ( False AndAlso True ) & vbCrLf & _ 17 "True AndAlso False: " & ( True AndAlso False ) & _ 18 vbCrLf & "True AndAlso True: " & ( True AndAlso True ) 19 20 lblOrElse.Text = "OrElse" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _ 21 "False OrElse False: " & ( False OrElse False ) & _ 22 vbCrLf & "False OrElse True: " & ( False OrElse True ) & _ 23 vbCrLf & "True OrElse False: " & ( True OrElse False ) & _ 24 vbCrLf & "True OrElse True: " & ( True OrElse True ) 25 26 lblAnd.Text = "And" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _ 27 "False And False: " & ( False And False ) & vbCrLf & _ 28 "False And True: " & ( False And True ) & vbCrLf & _ 29 "True And False: " & ( True And False ) & vbCrLf & _ 30 "True And True: " & ( True And True ) 31 Code generated by Visual Studio represented by this comment Demonstrate AndAlso operator Demonstrate OrElse operator Demonstrate And operator
- 37. LogicalOperator.vb 32 lblOr.Text = "Or" & vbCrLf & _ 33 vbCrLf & "False Or False: " & ( False Or False ) & _ 34 vbCrLf & "False Or True: " & ( False Or True ) & _ 35 vbCrLf & "True Or False: " & ( True Or False ) & _ 36 vbCrLf & "True Or True: " & ( True Or True ) 37 38 lblXor.Text = "Xor" & vbCrLf & _ 39 vbCrLf & "False Xor False: " & ( False Xor False ) & _ 40 vbCrLf & "False Xor True: " & ( False Xor True ) & _ 41 vbCrLf & "True Xor False: " & ( True Xor False ) & _ 42 vbCrLf & "True Xor True: " & ( True Xor True ) 43 44 lblNot.Text = "Not" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _ 45 "Not False: " & ( Not False ) & vbCrLf & "Not True: " & _ 46 ( Not True ) 47 48 End Sub ' FrmLogicalOperator_Load 49 50 End Class ' FrmLogicalOperator Demonstrate Or operator Demonstrate Xor operator Demonstrate Not operator
- 38. Program Output
- 39. 5.9 Logical Operators Fig. 5.22 Precedence and associativity of the operators discussed so far.
- 40. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Structured Programming Promotes simplicity Produces programs that are easier to understand, test, debug and modify Rules for Forming Structured Programs If followed, an unstructured flowchart cannot be created Only three forms of control needed Sequence Selection If / Then structure sufficient to provide any form of selection Repetition While structure sufficient to provide any form of repetition
- 41. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.23 Visual Basic’s single-entry/single-exit sequence and selection structures. Sequence . . . Selection If / Then structure (single selection) T F If / Then / Else structure (double selection) T F . . . Select Case structure (multiple selection)
- 42. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.24 Visual Basic’s single-entry/single-exit repetition structures. While structure T F F T For / Next structure T F Do / Loop Until structure Do / Loop While structure F T Repetition
- 43. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.24 Visual Basic’s single-entry/single-exit repetition structures. Do While / Loop structure T F Do Until / Loop structure F T F T For Each / Next structure Repetition
- 44. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.25 Rules for forming structured programs.
- 45. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.26 Simplest flowchart. . . . Rule 2 Rule 2 Rule 2 Fig. 5.27 Repeatedly applying rule 2 of Fig. 5.25 to the simplest flowchart.
- 46. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.28 Applying rule 3 of Fig. 5.25 to the simplest flowchart. Rule 3 Rule 3
- 47. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.29 Stacked, nested and overlapped building blocks. Nested building blocks Stacked building blocks Overlapping building blocks (Illegal in structured programs)
- 48. 5.10 Structured Programming Summary Fig. 5.30 Unstructured flowchart.