Ad
1 introduction-to-computer-networking
- 2. DefinitionDefinition A computer network is a group of interconnected computers. It allows computers to communicate with each other and to share resources and information
- 3. ComponentsComponents A minimum of at least 2 computers Cables or wireless communication that connect the computers to each other. A network interface device on each computer (this is called a network interface card or NIC) A ‘Switch’ used to switch the data from one point to another. Network operating system software.
- 4. Types of networkTypes of network The three basic types of networks include: Local Area Network (LAN) Metropolitan Area Network (WAN) Wide Area Network (WAN)
- 5. Local Area Network (LAN) A LAN covers a relatively small area such as a classroom, school, or a single building LANs are inexpensive to install and also provide higher speeds.
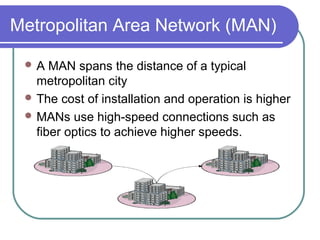
- 6. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) A MAN spans the distance of a typical metropolitan city The cost of installation and operation is higher MANs use high-speed connections such as fiber optics to achieve higher speeds.
- 7. Wide Area Network (WAN) WANs span a larger area than a single city. These use long distance telecommunication networks for connection, thereby increasing the cost. The Internet is a good example of a WAN.
- 8. Network Configuration Classification based on how computers behave in a network Two classifications are: Peer-to-Peer networkPeer-to-Peer network Server based networkServer based network
- 9. Peer-to-Peer Networks In a peer-to-peer network, the networked computers act as equal partners, or peers, to each other. As peers, each computer can take on the client function or the server function alternately.
- 10. Client/Server Networks In a client/server network arrangement, network services are located in a dedicated computer whose only function is to respond to the requests of clients. The server contains the file, print, application, security, and other services in a central computer that is continuously available to respond to client requests.
- 11. Networking hardware Hub – electronic device (with a number of ports) used in a LAN to link groups of computers Repeaters (also called amplifiers) – electronic devices that receive signals and amplify and send them along the network Routers - electronic devices used to ensure messages are sent to their intended destinations Gateway – consists of hardware and/or software that allows communications between dissimilar networks Bridge – consists of hardware and/or software that allows communication between two similar networks
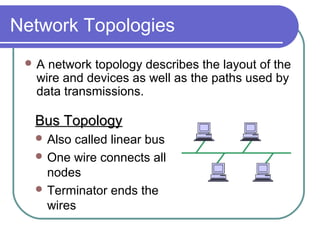
- 12. Network Topologies A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions. Bus TopologyBus Topology Also called linear bus One wire connects all nodes Terminator ends the wires
- 13. Network Topologies Star TopologyStar Topology All nodes connect to a hub Packets sent to hub Hub sends packet to destination Ring TopologyRing Topology Nodes connected in a circle Tokens used to transmit data
- 14. Network Topologies Mesh TopologyMesh Topology All computers connected together Internet is a mesh network Tree TopologyTree Topology Hierarchal Model Combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies.
- 15. Communications Media Communications ChannelCommunications Channel To transfer data from one computer to another requires some type of link through which the data can be transmitted. This link is known as the communications channel. To send data through the channel requires some type of transmission media, which may be either physical or wireless.
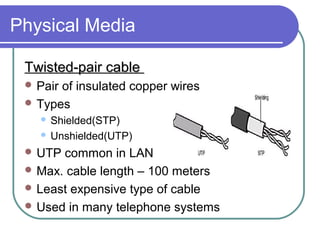
- 16. Physical Media Twisted-pair cableTwisted-pair cable Pair of insulated copper wires Types Shielded(STP) Unshielded(UTP) UTP common in LAN Max. cable length – 100 meters Least expensive type of cable Used in many telephone systems
- 17. Physical Media Co-axial cableCo-axial cable Consists of an insulated center wire grounded by a shield of braided wire Carries data as electromagnetic signals Good resistance against interference Used by the cable television industry
- 18. Physical Media Fiber optic cableFiber optic cable Core – cylinder of glass Bandwidth is greater, so it can carry more data Not subject to interference Transfer rate – more than 100 mbps Expensive
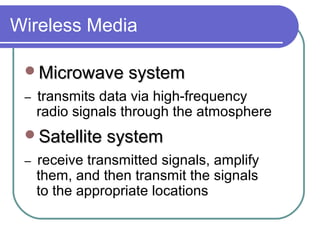
- 19. Wireless Media Microwave systemMicrowave system – transmits data via high-frequency radio signals through the atmosphere Satellite systemSatellite system – receive transmitted signals, amplify them, and then transmit the signals to the appropriate locations
- 20. Wireless Media Cellular technologyCellular technology – uses antennae resembling telephone towers to pick up radio signals within a specific area (cell) Infrared technologyInfrared technology – transmits data as infrared light waves from one device to another, providing wireless links between PCs and peripherals
- 21. InternetworkInternetwork An Internetwork is the connection of two or more distinct computer networks or network segments via a common routing technology. Any interconnection among or between public, private, commercial, industrial, or governmental networks may also be defined as an internetwork.
- 22. Intranet An intranet is a private LAN designed for use by everyone within an organization. An intranet might consist of an internal e-mail system, a message board and one or more Web site portals that contain company news, forms, and personnel information
- 23. Extranet A network that connects people within your company with people who are outside your company--all within a secure, password-protected network that can be accessed from anywhere.
- 24. Internet A computer network consisting of a worldwide network of computer networks that use the TCP/IP network protocols to facilitate data transmission and exchange
- 25. Internet Connections Internet backbone : A set of high-speed networks that carry Internet traffic. These networks are provided by companies such as AT&T, GTE, and IBM Internet service provider (ISP) : A company that provides other companies or individuals with access to the Internet
- 26. Internet Connections There are various technologies available that you can use to connect a home computer to the Internet A phone modem converts computer data into an analog audio signal for transfer over a telephone line, and then a modem at the destination converts it back again into data A digital subscriber line (DSL) uses regular copper phone lines to transfer digital data to and from the phone company’s central office A cable modem uses the same line that your cable TV signals come in on to transfer the data back and forth
- 27. Internet Connections Broadband A connection in which transfer speeds are faster than 128 bits per second DSL connections and cable modems are broadband connections The speed for downloads (getting data from the Internet to your home computer) may not be the same as uploads (sending data from your home computer to the Internet)
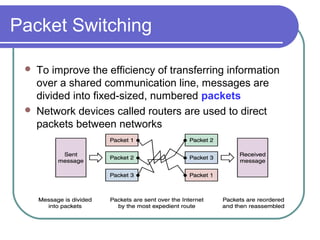
- 28. Packet Switching To improve the efficiency of transferring information over a shared communication line, messages are divided into fixed-sized, numbered packets Network devices called routers are used to direct packets between networks
- 29. Open System Interconnection (OSI) The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model Each layer deals with a particular aspect of network communication
- 30. Network Protocols Network protocols are layered such that each one relies on the protocols that underlie it Sometimes referred to as a protocol stack
- 31. TCP/IP Protocol TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol TCP software breaks messages into packets, hands them off to the IP software for delivery, and then orders and reassembles the packets at their destination IP stands for Internet Protocol IP software deals with the routing of packets through the maze of interconnected networks to their final destination
- 32. Internet Connections Other protocols build on the foundation established by the TCP/IP protocol suite Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Telnet Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- 34. Network Security Firewalls can either be hardware and/or software based. It sits at the gateway between the two networks, usually a private network and a public network such as the internet. All traffic from inside to outside and vice versa, must pass through the firewall. Only authorized traffic as defined by the local security policy, will be allowed to pass. The firewall itself is immune to penetration.