1. over view and history of c
- 2. History of Programming • The root of all modern languages is ALGOL (introduce in 1960s). • ALGOL uses a structure programming. • ALGOL is popular in Europe • In 1967, Martin Richards developed a language called BCPL (Basic Combined Programming Language) • Primarily BCPL is developed for system software • In 1970, Ken Thompson created a new language called B • B is created for UNIX os at Bell Laboratories. • Both BCPL and B were “typeless” languages
- 3. History of C • C was evolved from ALGOL, BCPL and B. • C was developed by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Laboratories in 1972. • Added new features and concepts like “data types”. • It was developed along with the UNIX operating system. • It was strongly integrated with the UNIX operating system. • In 1983 American National Standards Institute (ANSI) appointed a technical committee to define a standard for C. The committee approved a version of C in December 1989 which is now known as ANSI C. • In 1990 International Standards Organization (ISO) has approved C and this version of C is referred to as C89.
- 4. History of C 1960 ALGOL International Group 1967 BCPL Martin Richards 1970 B Ken Thompson 1972 Traditional C Dennis Ritchie 1978 K&R C Kernighan and Ritchie 1983 ANSI C ANSI Committee 1990 ANSI/ISO C ISO Committee 1999 C99 Standardization Committee
- 5. Importance of C • Rich set of built-in functions • Operators can be used to write any complex program. • The C compiler combines the capabilities of an assembly language with the features of a high-level language. • It is well sited for writing both system software and business packages. • Due to variety of data types and powerful operators programs written in C are efficient and fast. • There are only 32 keywords in C and its strength lies in its built in functions. • C is highly portable.
- 6. Importance of C • Ability to extend itself. • C is a Structured Programming Language (requiring the user to think of a problems in terms of function modules or blocks).
- 7. First C program #include<stdio.h> //Headerfile main() //main function { /*…….printing begins……..*/ printf(“I see, I remember”); /*……printing end…………*/ } ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - • Stdio.h is a header file which is included in our program by writing #include<stdio.h> in first line of program. • main() is function where execution begins. • Every program must have exactly one main function. • “{” opening brace & “}” closing brace. • printf(“ ”); is the only executable instruction. • C is case sensitive.
- 8. Format of simple C program main() //function name { //Starting of program --- --- //Program statements --- } //End of program ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- The main() is a part of every C program. C permits different forms of main statements • main() • int main() • void main() • main(void) • void main(void) • int main(void)
- 9. Executing a ‘C’ Program 1. Creating the program 2. Compiling the program 3. Linking the program with functions that are needed from the C library 4. Executing the program
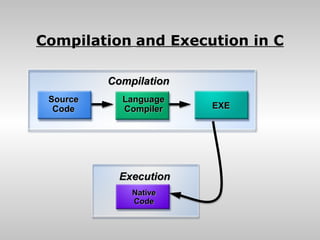
- 10. Compilation and Execution in C Compilation Source Language Code Compiler EXE Execution Native Code
- 11. Thank You Questions & General Discussion
Editor's Notes
- #11: The Common Language Runtime Compilation and Execution The above diagram illustrates the process used to compile and execute managed code, or code that uses the CLR. Source code written in Visual C#, Visual Basic .NET or another language that targets the CLR is first transformed into MSIL by the appropriate language compiler. Before execution, this MSIL is compiled by the Just-in-Time (JIT) complier into native code for the processor on which the code will operate. The default is to JIT compile each method when it is first called, but it is also possible to “preJIT” MSIL code to native code at assembly install-time. With this option, all methods are compiled before the application is loaded so as to avoid the overhead of JIT compilation on each initial method call. You use the Native Image Generator (Ngen.exe) to create a native image from a managed assembly and install it into the native image cache. Once the code is compiled and cached, the CLR does not need to re-compile the MSIL code until the assembly is updated, the Just-In-Time compiled code is removed from the cache, or the machine is restarted. A point worth noting is that all languages targeting the CLR should exhibit a similar performance. While some compilers may produce better MSIL code, large variations in execution speed are unlikely.