01 - Introduction to Version Control
- 1. INTRODUCTION TO VERSION CONTROL
- 2. PURPOSE OF CURRENT TRAINING The basics AND Making first steps 2
- 3. CONTENTS What is version control History and evolution of version control Instruments and their classification Approaches Domain vocabulary What else you might want to know 3
- 4. WHAT IS VERSION CONTROL Place to store your source code Historical record of what you have done over time Approach which allows working together without getting in each others' way (allows to collaborate more effectively) Another “trendy” word combination Something that every software developer should deal with 4
- 5. VERSION CONTROL. SYNONYMS Source code management Source control Revision control ~SCM = Software configuration Files Numbers management 5 VERSION CONTROL
- 6. NOT VERSION CONTROL Simple Asset management documents, files, packages, tra cked by filesystem What exact versions of libraries Dependency management are required Music, pictures, drawings, book Digital storage s Installation managers, package Package management dependencies Installations management Installation is not a version 6
- 7. HISTORY AND EVOLUTION OF VERSION CONTROL make utility (early 70's) BitKeeper (1999) Bell labs paper describing the GNU Arch (2001) distributed original diff algorithm (1972) Monotone (2003) CDC update tool (early 70's. darcs (2003) contained revision control, change git (2005) sets, build management, file diffs) Mercurial (2005) SCCS source code control system Bazzar (2005) (1972) CCC version control system (1975) proprietary ClearCase (1992) RCS revision control system (1980) VSS (1994) patch utility (around 1988) Perforce (1995) CVS Concurrent Version System Vault (2002) (1986), CVSNT (1998) AccuRev (2002) 7 Subversion (started in 1999) TFS (2005)
- 8. VCS CLASSIFICATION (BY REPOSITORY MODEL) Centralized (client-server model) • Subversion • CVS • VSS, TFS, Vault • ClearCase • AccuRev Distributed • Git • Mercurial • Bazzar • Perforce • BitKeeper 8
- 9. CONCURRENCY MODELS combined merge Release/lock 9
- 10. VCS CLASSIFICATION (BY CONCURRENCY MODEL) Merge • CVS • Git • Mercurial • Bazzar Release/lock • VSS • TFS • Vault Combined • Subversion • AccuRev • Perforce 10 • ClearCase
- 11. DISTRIBUTED VS CENTRALIZED. Centralized Distributed 11
- 12. CENTRALIZED MODEL 12
- 13. DISTRIBUTED MODEL 13
- 14. DISTRIBUTED VS CENTRALIZED. DIFFERENCES Centralized Distributed Single repository Multiple repositories Commit requires connection Commit does not require (no staging area). connection (due to staging area) Impossible to commit changes Possible to commit changes to to another user another user All history in one place Impossible to get all history Reintegrating the branch might Easier branches management be a pain (especially reintegration) Considered to be not so fast as Considered to be faster than DVCS CVCS Easy access management No access management 14 Chosen for enterprise Chosen for open source development development
- 17. CONCURRENCY MODELS. Lock-unlock Merge Everything is read-only You can edit everything Need to edit? Locally 1. Get lock And commit changes later 2. Edit Everything will be fine 3. Release lock Unless somebody edited the same files Don’t forget to release lock Otherwise you’ll need some luck Otherwise you screwed up You are: Others would not be able to 1. Lucky (source has been merged edit locked files automatically) 2. Not lucky (conflict happened) There is a good thing though Conflicts require resolution You won’t need to merge But it has nothing to do with 17 conflictology This is about merging manually
- 18. LOCK-MODIFY-UNLOCK 3. Sally tries to edit 1. GET LOCK 4. Locked! 2. Read It’s impossible to edit until Harry releases the lock 5. Write (save) 8. Read 6. RELEASE 7. GET LOCK THE LOCK 18
- 19. ANTI VSS CAMPAIGN 19
- 20. COPY-MODIFY-MERGE (#1) 20
- 21. COPY-MODIFY-MERGE (#2) 21
- 22. PRACTICAL VERSION CONTROL What VCS to start with? How to start working with subversion? Subversion Get Subversion from official site Why? and install it 1. It’s most popular Init new repository with 2. Enterprise chooses it svnadmin create command 3. EPAM has chosen it too Create initial project structure (/trunk, /tags/, /branches) 4. It has almost all what VCS should have Check created project out to the directory with the source 5. It’s possible to use svn and git code together if you wish Add files with svn add Are you software developer? command Most likely you would need to Commit files with svn commit deal with subversion command 22
- 23. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. START WORKING WITH VCS checkin add commit push release lock TO REPOSITORY checkout delete update,fetch pull get lock FROM REPOSITORY 23
- 24. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. CVCS WORKFLOW EXAMPLE WC (working copy) Repository svn add svn commit 24 svn update
- 25. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. DVCS WORKFLOW EXAMPLE 25
- 26. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. RESPOSITORY INVARIANT OPERATIONS add delete move svn add, svn delete, svn rename, … rename copy mkdir VCS is not able of flexible filesystem changes tracking It is preferably that instead of applying FS commands corresponding VCS command be applied In other case files will be tracked by VCS as non-versioned or missing. Subversion does not have specific commands for tags and branches 26 creation, svn copy is used instead.
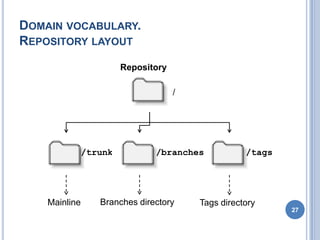
- 27. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. REPOSITORY LAYOUT Repository / /trunk /branches /tags Mainline Branches directory Tags directory 27
- 28. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. CHANGELISTS You have bunch of committed However, it has limitations files 1. Changelists are applicable Which corresponds to the only to particular working standalone feature copy You might want to track this 2. Changelists can be assigned fileset only to files Then it’s time to use changelists 3. At most one changelist It is done by svn changelist assignment on one file command How could it be useful? It sets or unsets the changelist It helps in logical association of a particular organization of files being working copy file committed You’ll be able to see changelists For example in case, when running svn status command one large feature should be committed in several steps 28
- 29. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. REVISIONS Revisions 29 Working copy (WC)
- 30. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. CHANGESET AND SNAPSHOT changeset changeset changeset 30 Tree snapshots
- 31. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. PATCHING svn diff > patchfile.patch create patch patch apply patch WC (working copy) patch -p0 < patchfile.patch 31
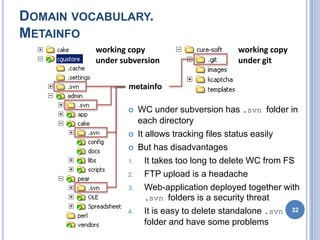
- 32. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. METAINFO working copy working copy under subversion under git metainfo WC under subversion has .svn folder in each directory It allows tracking files status easily But has disadvantages 1. It takes too long to delete WC from FS 2. FTP upload is a headache 3. Web-application deployed together with .svn folders is a security threat 4. It is easy to delete standalone .svn 32 folder and have some problems
- 33. WORKING COPY FILE STATUS working revision .svn timestamp (last updated) Unchanged, and current Unchanged, and out of date 14 18 = 14 ~ Locally changed, and current Locally changed, and out of date 33
- 34. DOMAIN VOCABULARY. REVERT AND BLAME How to get rid of recent Subversion tracks users changes in WC? committing changes Make revert This could be very helpful Why not update? sometimes Update does not override WC Because you want to find changes someone responsible Revert will discard all One can find who changed changes and return WC to specific lines the working revision By running svn blame Unless you have committed It will show all user logins last your changes edited specific line of code Revert will not help in that Developer! Be aware case. Don’t commit buggy code But svn merge –rHEAD:N will They’ll find you anyway 34
- 35. SUBVERSION VS CVS Subversion CVS Commits are atomic Commits are not atomic Renames and copies are Renames and copies are supported not supported Changesets messaging Changes are file-specific (per-commit message) (per-file commit message) Full permissions support Permissions via hooks Difficulties with binary files versioning Easy binary files versioning 35
- 36. WORKING TOOLS Subversion client Command line GUI Subversion TortoiseSVN IDE server embedded support Plugins IntelliJ Netbeans AnkhSVN Subclipse IDEA 36
- 37. VERSION CONTROL FOR NON-PROGRAMMERS There are version control tools even for designers: Adobe version cue PixelNovel Timeline There is version control functionality embedded in: 37 Microsoft Word OpenOffice.org Writer
- 38. ISN'T VERSION CONTROL TOO COMPLEX? 38
- 39. ISN'T VERSION CONTROL TOO COMPLEX? Basic working cycle You can avoid using version control Update your working copy svn update But it can’t last long Make changes You will need to collaborate eventually svn add It might be tricky sometimes svn delete But you can avoid most problems svn copy svn move Recommendations: Examine your changes Stick to basic working cycle svn status Learn basic working cycle svn diff commands svn revert Practice on sandbox project Merge others' changes Read “Version control with svn merge subversion” book svn resolved DVCSs have more steep learning Commit your changes curve anyway svn commit 39
- 40. DOES SCM = VERSION CONTROL? No Version control is just the main SCM process What is SCM then? There are several cumbersome definitions If you want it simple, it is just more broad topic then just version control And it is one of the CMMI process areas 40
- 41. RECOMMENDED READING 1. Version control with Subversion By Ben Collins- Sussman, Brian W. Fitzpatrick, C. Michael Pilato 48
- 42. RECOMMENDED READING 2. Version Control with Git by Jon Loeliger 49
- 43. RECOMMENDED READING 3. Pragmatic Version Control: Using Subversion, 2nd edition by Mike Mason 50
- 44. USEFUL LINKS 1. http://svnbook.red-bean.com/ - official subversion reference/book “Version Control with Subversion” 2. http://progit.org/ - book about git “Pro git” 3. http://www.ericsink.com/ - one of the best blogs about version control 4. http://www.versioncontrolblog.com/ - another great blog about version control 5. http://better-scm.berlios.de/comparison/comparison.html - VCS comparison table 6. http://www.cmcrossroads.com/ - biggest resource about SCM 7. http://git-scm.org/course/svn.html - git for svn users 51
Editor's Notes
- #2: Рад приветствовать на сегодняшнем тренинге, посвященном контролю версий. В прошлом тренинге я налил воды (излагались довольно абстрактные вещи), но на то он и вводный тренинг. Обо всем – и ни о чем. Как первая лекция в университете после долгих каникул. Так как вода уже есть, теперь будем… добавлять муки и месить тесто.В понедельник у вас уши вянули от словосочетания «конфигурационный менеджмент», так как я использовал его СЛИШКОМ часто. Теперь у вас будут вянуть уши от словосочетания «контроль версий». Но вы не пугайтесь. Сегодня будет не только теория, но и практика.
- #6: В википедии есть статья, которая называется отнюдь не version control, a revision control. Такое название акцентирует внимание на хранении информации таким способом, когда каждому отдельному состянию присваивается отдельный номер – номер ревизии. Это напрямую связано с числами и нумерацией. Но суть в том, что контроль версий – это кое что больше, чем просто присваивание номеров.Часто контроль версий называют контролем исходного кода (source control), делая акцент на том, что учету и хранению подлежат в первую очередь текстовые файлы. Но возможности СКВ нынче выходят и за эти пределы. Наиболее странным алиасом, синонимом КВ является употребление словосочетания source code management. Это странно вдвойне:Контроль версий – это не только хранение текстовых файлов с исходным кодомSCM – это аббревиатура, которая может неоднозначно расшифровываться (Software Configuration Management). Суть в том, что контроль версий входит в рассмотрение дисциплины SCM, но в качестве одной из составляющих (пусть и одной из главных). Всё это - контроль версий
- #7: Asset management examples:version control in sharepointSharepoint workspacesDropboxPlain folders (filesystem)Для управления зависимостями используются как отдельные репозитории, так и комбинации разных версий. К примеру, работа приложения зависит от набора версий различных библиотек – нужно следить за этими версиями и конфигурировать приложение используя только правильные версии. Цифровые хранилища книг, чертежей, музыки, фильмов. Казалось бы, как можно перепутать контроль версий с цифровыми библиотеками? На самом деле у цифровых библиотек есть довольно важная особенность – исчерпывающая параметризация и описание хранимых артефактов. И как мы увидим чуть позже, в следующем тренинге, комбинация этих параметров – уже напрямую связано с понятием версий и контролем версий.Управление пакетами. Очень похоже на управление зависимостями.Если мы создадим инсталляционный пакет, это не будет считаться полноценной версией. И для того, чтобы управлять версиями, недостаточно просто создать инсталляцию или заархивировать набор файлов. Это связано со сборками, развертыванием и релиз менеджментом.
- #10: Кроме классификации по модели репозитория существует еще классификация моделей версионированияОсновные две модели версионирования: С пом. БлокировокС пом. СлиянийКомбинированная
- #19: Вsvnможно похищать блокировку
- #20: Разработчики СКВ sourcegear vault в свое время начали рекламную кампанию открыто противопоставляя себя vss. И намекая на то, что концепция, заложенная в vssуже устарела.
- #22: Наиболее оптимальный подход – это комбинированая модель версионирования. Как в subversion. Copy-modify-merge – для исходных и текстовых файлов, lock-unlock – для бинарных файлов.
- #24: Добавление,изменение, обновление содержимого репозиторияУдаление или получение содержимого репозитория
- #30: Ревизии – это номера, которыми обозначаются отдельные состояния содержимого репозитория