Ad
3 database-jdbc(1)
- 1. Accessing a Database in Java How to use JDBC and Application Design for O-R Mapping By Sayed Abdul bari harifal
- 2. JDBC Overview 1. Get a Connection to the database. 2. Create a Statement using the Connection. 3. Execute the Statement with SQL string. 4. Use the results.
- 3. JDBC Overview creates Statements for database actions selects a specific Connection type and instantiates it
- 4. JDBC Code /** BAD CODE. We'll fix this later. */ static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://dbserver/world"; static final String USER = "student"; static final String PASSWORD = "secret"; // 1. Get a Connection to the database. Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection( URL, USER, PASSWORD ); // 2. Create a Statement Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); // 3. Execute the Statement with SQL command. ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM ..."); // 4. Use the Result. while ( rs.next( ) ) { String name = rs.getString("name");
- 5. Connecting to a Database in Java (1) java.sql.Connection is a standard interface for connecting to any database. Each database type requires its own jdbc driver that implements this interface. MySQL driver mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar Derby driver: derby.jar or derbyclient.jar HSQLDB driver: hsqldb.jar DriverManager selects the driver based on URL.
- 6. DriverManager returns a Connection DriverManager getConnection( url, user, passwd) : Connection <<interface>> Connection createStatement(): Statement close( ) isClosed( ): boolean getCatalog( ): String MySqlConnection creates url = "jdbc:mysql://hostname/database" HSQLConnection
- 7. Patterns Question DriverManager getConnection( url, user, passwd) : Connection <<interface>> Connection createStatement(): Statement close( ) isClosed( ): boolean getCatalog( ): String MySqlConnection creates What design pattern is used by DriverManager? HSQLConnection
- 8. Where is the Database Driver? Driver is in a JAR file. JAR file must be on the CLASSPATH. Use one of these: 1. add as an external jar file to your IDE project 2. add the JAR to your CLASSPATH CLASSPATH = /my/path/mysql-connector.jar;. 3. add JAR using the Java command line: java -cp /my/path/mysql-connector.jar ... 4. Put JAR file in the JRE/lib/ext directory: C:/java/jre1.6.0/lib/ext/mysql-connector.jar
- 9. Can't find the Driver? DriverManager finds a registered database driver. How? 1. Automatically. This should happen with type 4 & 5. 2. Load the driver class in your program: Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 3. Add driver to the jdbc.drivers property System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 4. Specify jdbc.drivers property on command line: java -Djdbc.drivers="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ...
- 10. Database URL String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://dbserver:3306/world"; The format of a database URL is: Protocol Sub-protocol Hostname Port DatabaseName Port is the TCP port number where the database server is listening. 3306 is the default port for MySQL Use hostname "localhost" for the local machine.
- 11. Database URL Example: These 4 URL refer to the same database "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/world" "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" "jdbc:mysql:///world" "jdbc:mysql:/world" The hostname and port are optional. For MySQL driver: defaults are localhost and port 3306
- 12. JDBC Driver You can get a JDBC driver (network connector) for most databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQLite ... 5 Types of JDBC drivers Type 1: JDBC-to-ODBC bridge driver for Microsoft ODBC. Java JDBC includes the bridge driver: sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver. Type 2: Native-API driver (written in C or C++ using JNI) Type 3: Pure Java client-to-server driver, use a standard network protocol. The server translates requests to server-specific protocol. Type 4: Pure Java drivers implementing a database-specific network protocol. Java programs can connect directly to the database. Type 5: The latest.
- 13. Exercise: Install JDBC Driver Download the mysql-connector-*.jar file use http://se.cpe.ku.ac.th/download/mysql alternate: http://www.mysql.com Install it in your software "library" directory, e.g. C:/lib/mysql JDBC Connector for MySQL: mysql-connector-java-5.x.y.zip
- 14. Executing SQL Commands To execute an SQL command, use the Connection object to create an SQL Statement object. Statement interface defines methods for executing commands. Statement statement = connection.createStatement( ); // execute an UPDATE command int count = statement.executeUpdate( "UPDATE City SET population=30000 WHERE name='Bangsaen'" ); System.out.println( "Modified " + count + " records");
- 15. Executing SQL Queries A statement.executeQuery( ) returns a ResultSet. ResultSet is a scrollable set of values. Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); // execute a SELECT command ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( "SELECT * FROM city WHERE id = "+id ); rs.first(); // scroll to first result do { String name = rs.getString(1);// get 1st field int population = rs.getInt("population"); ... } while( rs.next() );
- 16. Search for a City Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print( "Name of city to find? " ); String name = console.nextLine().trim(); // This is not safe... String query = "SELECT * FROM city WHERE Name='" +name+ "'"; ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query ); Use a statement you already created.
- 17. ResultSet Methods ResultSet contains one "row" for each result returned from the query. ResultSet contains get methods for column data: "get" by column number -- starts at 1 (not 0)! "get" by column name -- field names in table/query. String query = "SELECT * FROM Country WHERE ..."; ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query ); // go to first row of results rs.first( ); // display the values System.out.println( rs.getString( 1 ) ); System.out.println( rs.getInt( "population" ) ); get by column number get by name
- 18. ResultSet Methods A ResultSet contains one "row" for each result returned from the query. Indices start from 1 (not 0)! go to next row of results. "false" if no more. go to previous row. "false" if 1st result. go to first row of results. go to last row of results. go to k-th row of results. get int value of field "name" get int value of k-th column in a record ResultSet next() : boolean previous() : boolean first() : boolean last() : boolean absolute( k ) getInt( name: String ) getInt( index: int ) ...
- 19. Question What design pattern does ResultSet use? Hint: ResultSet lets you access the results one-by-one without knowing how the results are organized. ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( "..." ); while ( rs.next( ) ) { String name = rs.getString("name"); int population = rs.getInt("popuation"); System.out.println( name +" "+population ); }
- 20. ResultSet Methods for Getting Data ResultSet "get" methods return column data: getLong( 3 ) : get by column index (most efficient) getLong( "population" ) : get by field name (safest) getInt( ), getLong( ) - get Integer field value getFloat( ), getDouble() - get floating pt. value getString( ) - get Char or Varchar field value getDate( ) - get Date or Timestamp field value getBoolean( ) - get a Bit field value getBytes( ) - get Binary data getBigDecimal( ) - get Decimal field as BigDecimal getBlob( ) - get Binary Large Object getObject( ) - get any field value
- 21. ResultSet and Type Compatibility SQL data types don't exactly match Java data types. See Java API and JDBC tutorial for conversion rules. For all compatibilities, see: /tutorial/jdbc/basics/retrieving.html int pop1 = rs.getInt( "population" ); long pop2 = rs.getLong( "population" ); // float - int conversion is possible, too float area = rs.getFloat( "surfacearea" ); // convert char(n) to String String region = rs.getString( "region" );
- 22. How to Execute SQL Commands The Statement interface defines many execute methods: Resultset rs = statement.executeQuery("SELECT ..."); use for statements that return data values (SELECT) int count = statement.executeUpdate("UPDATE ..."); use for INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE boolean b = statement.execute("DROP TABLE test"); use to execute any SQL statement(s)
- 23. Security Problem Scanner scanner = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.print( "Name of city to find? "); String name = scanner.nextLine( ); String query = String.format( "SELECT * FROM city WHERE name='%s'", name ); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query );
- 24. Security Problem (2) String name = "Bangkok"; String query = String.format( "SELECT * FROM city WHERE name='%s'", name ); Becomes: query="SELECT * FROM city WHERE name='Bangkok' " ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query );
- 25. Hack The Code String query = String.format( "SELECT * FROM City WHERE name='%s'" , name); "SELECT * FROM City WHERE name='x' OR 'a'='a'" Name of City to Find? x' OR 'a'='a
- 26. SQL Injection String query = String.format( "SELECT * FROM city WHERE name='%s' ", name ); Becomes: "SELECT * FROM city WHERE name='Bangkok' ; DELETE FROM city WHERE 'x'='x' " ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query ); City to find? Bangkok'; DELETE FROM city WHERE 'x'='x
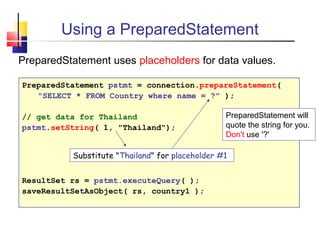
- 27. Using a PreparedStatement PreparedStatement uses placeholders for data values. PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement( "SELECT * FROM Country where name = ?" ); // get data for Thailand pstmt.setString( 1, "Thailand"); ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery( ); saveResultSetAsObject( rs, country1 ); PreparedStatement will quote the string for you. Don't use '?' Substitute "Thailand" for placeholder #1
- 28. Reuse a PreparedStatement You can reuse a PreparedStatement with new data. // get data for Laos pstmt.setString( 1, "Laos"); rs = pstmt.executeQuery( ); saveResultSetAsObject( rs, country2 ); Substitute "Laos" for placeholder #1
- 29. Create a Class to Manage DB Connection Create ConnectionManager with a static factory method ConnectionManager - connection : Connection +getConnection( ) : Connection +close( ) : void // example how to use Statement statement = ConnectionManager.getConnection().createStatement( );
- 30. Simple version of manager (1) public class ConnectionManager { // literal constants in Java code is baaaad code. // we will change to a configuration file later. private static String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://hostname/world"; private static String user = "student"; private static String password = "student"; /* a single shared database connection */ private static Connection connection = null; private ConnectionManager() { /* no object creation */ }
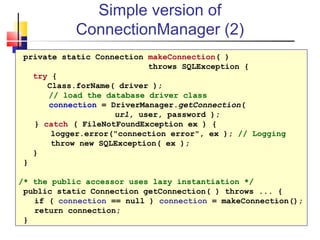
- 31. Simple version of ConnectionManager (2) /* the public accessor uses lazy instantiation */ public static Connection getConnection( ) throws ... { if ( connection == null ) connection = makeConnection(); return connection; }
- 32. Simple version of ConnectionManager (2) private static Connection makeConnection( ) throws SQLException { try { Class.forName( driver ); // load the database driver class connection = DriverManager.getConnection( url, user, password ); } catch ( FileNotFoundException ex ) { logger.error("connection error", ex ); // Logging throw new SQLException( ex ); } } /* the public accessor uses lazy instantiation */ public static Connection getConnection( ) throws ... { if ( connection == null ) connection = makeConnection(); return connection; }
- 33. Simple version of ConnectionManager (3) public class DataAccessException extends RuntimeException { public DataAccessException(String arg) { super(arg); } } Catch, Log, and rethrow any exception. Necessary to avoid Exceptions in app. Translate low-level exception into higher layer exception What is a DataAccessException? translate checked exceptions into unchecked exception to simplify code.
- 34. ConnectionManager using Properties private static Connection makeConnection( ) throws ... { Properties props = PropertyManager.getProperties( ); String url = props.getProperty("jdbc.url"); // load the database driver class connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, props); } • Give All the properties to DriverManager. • DriverManager uses jdbc.drivers to locate the JDBC Driver class! • No "ClassNotFoundException"
- 35. ConnectionManager Using Properties public class ConnectionManager { // literal constants in Java code is baaad. // we will change to a configuration file later. private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://hostname/world"; private static String user = "student"; private static String password = "student"; DELETE THIS
- 36. How to do Object Persistence Choices for How to do Object Persistence? 1. write your own DAO using JDBC 2. Use an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) Framework Hibernate, TopLink, MyBatis, Apache Cayenne 1. Use a Standard Persistence API. Java Persistence Architecture (JPA) standard used in JavaEE implemented by EclipseLink, Hibernate, OpenJPA Java Data Objects (JD) implemented by DataNucleus.org "standard" means you can change the implementation without changing your code
- 37. The World Application Insert class diagram or ER diagram
- 38. CityDao for World Application CityDao find( id: Integer ): City findByName( name: String ): City[*] find( query: String ) : City[*] save( Country ) : boolean delete( Country ) : boolean The primary key is an integer city ID. Search by name is used in our application, so I add a method for it.
- 39. CityDao using JDBC (1) public class CityDao { private static final Logger logger = ...; // log4J private static final CountryDao countryDao; private static HashMap<Integer,City> cache = ...; /** retrieve a city by its id */ public City findById( Integer id ) { if ( cache.containsKey(id) ) return cache.get(id); List<City> list = find("WHERE id = "+id); return list.get(0); } /** retrieve a city by name */ public List<City> findByName( String name ) { name = sanitize( name ); List<City> list = find("WHERE name = '"+name+"'"); return list; }
- 40. CityDao using JDBC (2) /** find cities using a general query, use a * WHERE ..., HAVING ..., or other selection clause */ public List<City> find( String query ) { List<City> list = new ArrayList<City>( ); Statement stmt = ConnectionManager .getConnection( ).createStatement(); String sqlquery = "SELECT * FROM city c " + query; try { logger.debug("executing query: " + sqlquery ); ResultSet rs = stmt .executeQuery( sqlquery ); while ( rs.next() ) { City c = resultSetToCity( rs ); list.add( c ); } } catch ( SQLException sqle ) { logger.error( "error executing: "+sqlquery, sqle); } finally { if (stmt!=null) try { stmt.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { /* forget it */ } return list;
- 41. CityDao using JDBC (3) /** convert a ResultSet entry to a City object */ private City resultSetToCity(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { City city = null; Integer id = rs.getInt("id"); // is this city already in cache? if so, use it if ( cache.contains(id) ) city = cache.get(id); else city = new City(); city.setId(id); city.setName( rs.getString("Name") ); city.setDistrict( rs.getString("District") ); city.setPopulation( rs.getInt("Population") ); String countrycode = rs.getString("countrycode");
- 42. CityDao using JDBC (4) // add this city to the cache if ( ! cache.containsKey(id) ) cache.put(id, city); // now get reference to the country this city refers logger.info("get country for city "+city.getName() ); Country country = countryDao.findById( countrycode ); city.setCountry( country ); return city; }
- 43. Why CityDao Needs a Cache What if the application requests cityDao.find("Bangkok") two times? We should return the same object each time. Necessary to avoid infinite loops: 1. cityDao uses JDBC and gets data for Bangkok 2. the countrycode for Bangkok is "THA". cityDao must convert this to a country object reference. 3. cityDao calls countryDao.findById( "THA" ) 4. countryDao finds Thailand, and the capital city has a cityID = 3320. It must convert this to a city reference. 5. countryDao calls cityDao.findById( 3320 ) 6. cityDao uses JDBC and gets data for Bangkok again
- 44. CityDao: delete public boolean delete( City city ) { if ( city == null || city.getId() == null ) return false; Long id = city.getId( ); Statement statement = ConnectionManager.getStatement( ); int count = 0; if ( statement == null ) return false; String query = "DELETE FROM city WHERE id=" + id; try { count = statement.executeUpdate( query ); } catch ( SQLException sqle ) { logger.error( "error executing: "+query, sqle ); } finally { ConnectionManager.closeStatement( statement ); } // is city in the cache? if ( cache.containsKey(id) ) cache.remove( id ); return count > 0; }
- 45. CityDao: save and update public boolean save( City city ) { Long id = city.getId( ); if ( id == null ) this is a new city, save it ; else { if ( cache.containsKey( id ) ) this city is already in database, update it else this city is not in the database, save it but check that no other city has this id } We can use save( ) for both saving a new object and updating an existing object.
- 46. UI /** prompt for a city name and display city info */ private void citySearch( ) { out.print("Input name of city: "); String name = in.next().trim(); // run the query City city = cityDao.findByName( name ); if ( city == null ) { out.println("Sorry, no match or query error"); } else { out.println("Name: "+city.getName( ) ); out.println("District: "+city.getDistrict( ) ); out.println("Country: " +city.getCountry( ).getName( ) ); ... } }
- 47. UI search for country private void countrySearch() { out.print("Input name of country: "); String name = in.next().trim(); // perform the query List<Country> results = countyDao.findByName( name ); if ( results == null ) ... // failed for( Country country : results ) { out.printf("Name: %sn", country.getName() ); out.printf("Capital: %sn", country.getCapital() ); out.printf("Region: %sn", country.getRegion() );
- 48. Exercise Finish the CityDao and CountryDao. Write JUnit tests to verify they are correct. What happens if you enter invalid country name?
- 49. Use a Configuration File Purpose: Configuration data such as database URL, username, password, should be in a file not in the Java code. Put this data in a configuration file. Example: world.config # World database properties jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/world user=student password=secret jdbc.drivers=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- 50. Loading Properties The java.util.Properties class can read or write "properties" files in this format. (can also write XML). // get name of the configuration file String config = "world.config"; // allow user to change this: java -dworld.config=... config = System.getProperty("world.config", config ); // load the properties Properties properties = new Properties( ); try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( config ); properties.load( fis ); fis.close( ); } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { ... }
- 51. Use Properties in ConnectionManager public class ConnectionManager { private void makeConnection( ) { Properties properties = PropertyManager.getProperties(); String jdbc_driver = properties.getProperty("jdbc.drivers"); String url = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url"); // pass all remaining properties to DriverManager // including user and password properties try { class.forName( jdbc_driver ); connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,properties); } catch ( SQLException sqle ) { log exception and rethrow as DataAccessException } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { ...
- 52. Properties Filename is a property, too Use a System property to get configuration file name. // get name of the configuration file String configfile = System.getProperty( "world.config" ); if ( configfile == null ) configfile = DEFAULT_CONFIG_FILE; C> java -Dworld.config=c:/temp/config.txt world.jar This enables user to change the filename at runtime:
- 53. java.util.Properties (a HashTable) Properties p = new Properties( ) create new java.util.Properties object String value = p.getProperty( name ) get a named property; returns null if not found. String value = p.getProperty( name, default_value ) get a property, returns default_value if not found.
- 54. System Properties String value = System.getProperty( name ) get a system property Properties p = System.getProperties( ) get all the system properties
- 55. Details of Statement and ResultSet
- 56. Understanding statement objects A Statement object is tied to a Connection. Use an re-use a statement object for many database commands. If the Connection is closed, the statement object is invalid (disconnected). Statement object consumes resources close it when you are finished Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); statement.executeQuery( "SELECT * FROM ... " ); ... statement.close( );
- 57. Understanding ResultSet ResultSet is tied to a statement and a database connection. if statement or connection is closed, results are gone if another command is executed, results are gone ResultSet can change (!) after performing the query ResultSet can update a database Statement stmt = connection.createStatement( ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE ); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query );
- 58. Using ResultSet to update a database Specify ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE when creating Statement. Requires (a) support by database driver, (b) UPDATE privilege on tables // rs is scrollable, will not show changes made // by others, and will be updatable Statement statement = connection.createStatement( ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE ); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery( query ); rs.next(); int population = rs.getInt("population"); // add 10,000 to the population rs.updateInt( "population", population+10000 ); rs.updateRow( );
- 59. RowSet RowSet is like ResultSet, but... data not tied to database connection. can be cached. can be updated by re- connecting to database can store other kinds of data, such as from file or spreadsheet <<interface>> ResultSet <<interface>> RowSet <<interface>> CachedRowSet <<interface>> WebRowSet
- 60. RowSet Question Suppose part of your application is expecting a ResultSet, but you change the lower layers to return a RowSet instead. Do the upper layers of the application need to change? <<interface>> ResultSet <<interface>> RowSet <<interface>> CachedRowSet <<interface>> WebRowSet
- 61. JTable Swing object looks like a spreadsheet table. A JTable
- 62. JTable Class Diagram JTable displays data returned by a TableModel. JTable TableModel describes data in the table AbstractTableModel getColumnCount( ) : int getColumnName( index ) : String getColumnClass( index ) : Class getRowCount( ) : int getValueAt( row, col ) : Object
- 63. Design a TableModel for Queries Design a TableModel to manage a ResultSet JTable ResultSetTableModel ResultSetTableModel(statement) runQuery( query : String ) AbstractTableModel getColumnCount( ) : int getColumnName( index ) : String getColumnClass( index ) : Class getRowCount( ) : int getValueAt( row, col ) : Object
- 64. Implementing TableModel ResultSet contains some of the data we need. class ResultSetTableModel { private Statement statement; private ResultSet rs; public Object getValueAt(int row, int col) { if ( rs == null ) return null; rs.absolute( row + 1 ); rs.getObject( col ); } public int getRowCount() { if ( rs == null ) return 0; rs.last(); // move to last row rowCount = rs.getRow(); return rowCount; }
- 65. Implementing TableModel (2) ResultSet is missing some information. public int getColumnCount( ) { } public String getColumnName( int col ) { }
- 66. ResultSet Meta-data ResultSet has a getMetaData( ) method that returns a ResultSetMetaData object. ResultSetMetaData describes the ResultSet. try { ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery( query ); ResultSetMetaData metadata = resultSet.getMetaData(); int numberOfColumns = metadata.getColumnCount(); for(int col=1; col<=numberOfColumns; col++) { // get name and SQL datatype for each column String name = metadata.getColumnName( col ); int type = metadata.getColumnType( col ); int typeName = metadata.getColumnTypeName( col ); } catch( SQLException sqle ) { ... }
- 67. Closing the Connection It is advisable to close Connection object when done. This frees resources and ensures data integrity. Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(...); /* use the database */ ... /* done using database */ public void close( ) { if ( connection == null ) return; try { connection.close(); } catch ( SQLException sqle ) { /* ignore it */ } finally { connection = null; } }
- 68. Connection Sharing A database connection consumes resources. All instances can share the same Connection object. To enforce this use the Singleton Pattern: use a factory method to get connection the method always returns the same instance of the connection
- 69. Let the IDE build your Country Class public class Country { private String name; private String continent; private String region; private float surfaceArea; private long population; private float lifeExpectancy; private long gnp; private String governmentForm; private String capital; /** auto-generated constructor public Country(String name,... { this.name = name; this.continent = continent; Eclipse: Source menu
- 70. Summary JDBC specifies standard interfaces for communicating with different databases. To use JDBC you need a JDBC or ODBC driver for the database. The application must load a database-specific driver. DriverManager will choose driver when creating a Connection. a Connection object manages the connection to a database. a Statement object is used to submit database statements and get results. A query returns a ResultSet containing data and meta-data. A ResultSet can be read-only or updateable depending on the Statement object (specified in Statement constructor). properly close a Statement or Connection when finished to release resources and ensure data integrity.
- 71. Important Design Concepts JDBC specifies standard interfaces for databases. Any database can use JDBC by writing classes that implement these interfaces. To re-use a connection in different classes, use the Singleton Pattern and a Factory Method for getting the connection object. Use a finally clause on try - catch blocks to ensure that some code is always executed. Inside the try - catch, you must not use 'return' since this would bypass the "finally" clause. Use 'break'.
- 72. Learning More Sun Java Tutorial: JDBC Database Access Java API for the java.sql package: DriverManager Connection Statement ResultSet ResultSetMetaData DatabaseMetaData (describes the database)
- 73. Resources MySQL http://dev.mysql.com/ Learning SQL http://www.w3schools.com/sql/ nice tutorial and command reference Learning JDBC JDBC Trail in Sun's Java Tutorial. Dietel, Java How To Program, Chapter 25. ... and zillions of resources on the web
- 74. Resources SQL Explorer for Eclipse http://www.sqlexplorer.org Eclipse Update: http://eclipsesql.sourceforge.net/ Standalone app: http://sourceforge.net/projects/eclipsesql http://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2005/05/11/sqle xplorer.html Eclipse Data Tools Platform (Eclipse Project) http://www.eclipse.org/datatools
- 75. Resources Netbeans database tutorials http://netbeans.org/kb/docs/ide/mysql.html http://netbeans.org/kb/docs/web/mysql-webapp.html



































![CityDao for World Application
CityDao
find( id: Integer ): City
findByName( name: String ): City[*]
find( query: String ) : City[*]
save( Country ) : boolean
delete( Country ) : boolean
The primary key is an integer city ID.
Search by name is used in our application, so I add a method
for it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-database-jdbc1-170226180724/85/3-database-jdbc-1-38-320.jpg)








































































































![Pixologic ZBrush Crack Plus Activation Key [Latest 2025] New Version](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/fashionevolution2-250322112409-f76abaa7-250428124909-b51264ff-250504160528-fc2bb1c5-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)












![Download Wondershare Filmora Crack [2025] With Latest](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/neo4j-howkgsareshapingthefutureofgenerativeaiatawssummitlondonapril2024-240426125209-2d9db05d-250419-250428115407-a04afffa-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
