Ad
3-inheritanc-and-variation.pdf HSC BIOLOGY 3-inheritanc-and-variation
- 1. L No1 Genetic Basis of Inheritance 1. Define Heredity, variations, genetics. Ans: Heredity; Transmission of characters from 1 generation to other is called as heredity. Variation: Difference between parent and offsprings and among the offspring of the same parent is called as variations. Genetics: The branch of biology which deals with study of heredity and variation is called as genetics. 2. Enlist Mendel’s 7 contrasting traits. Ans: Q3.Mendel selected pea plant for his experiment . Explain. Ans: Mendel selected pea plant for the following reasons. 1. Annual plant with very short span of 3-4 months 2. Small herbaceous plant with many seeds 3. Self pollinating plant which can be cross fertilized artificially 4. Its seeds are viable 5. It does not exhibit intermediate characters. 6. Its flowers are large conspicuous easy for emasculation. Marking scheme: any 4 points each point 0.5 marks hence 2 marks
- 2. 4. State and explain Mendel’s first law of Inheritance. 7M Ans:Mendel’s first law of inheritance is Law of Dominance Law of Dominance: In a cross between 2 organisms pure for any pair of contrasting characters, the character that appear in F1 generation is called dominant and the one which is suppressed is called recessive. Explanation: 1. 1. Mendel selected a variety of tall pea female parent and another dwarf male pea parent. 2. In F1 generation he got all tall pea plants 3. On selfing he received 3 tall and 1 dwarf pea plant 4. The genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 with TT, Tt, tt genotype respectively Graphic Representation 5. 5. Explain Monohybrid cross with suitable example? 3M Ans: Monohybrid Cross: a cross between 2 pure parents in which inheritance pattern of only 1 pair of contrasting characters is studied is called monohybrid cross. Explanation: 1. Mendel selected a variety of tall pea female parent and another dwarf male pea parent. 6. In F1 generation he got all tall pea plants 7. On selfing he received 3 tall and 1 dwarf pea plant 8. The genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 with TT, Tt, tt genotype respectively
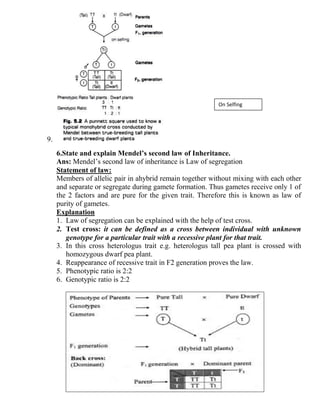
- 3. 9. 6.State and explain Mendel’s second law of Inheritance. Ans: Mendel’s second law of inheritance is Law of segregation Statement of law: Members of allelic pair in ahybrid remain together without mixing with each other and separate or segregate during gamete formation. Thus gametes receive only 1 of the 2 factors and are pure for the given trait. Therefore this is known as law of purity of gametes. Explanation 1. Law of segregation can be explained with the help of test cross. 2. Test cross: it can be defined as a cross between individual with unknown genotype for a particular trait with a recessive plant for that trait. 3. In this cross heterologus trait e.g. heterologus tall pea plant is crossed with homozygous dwarf pea plant. 4. Reappearance of recessive trait in F2 generation proves the law. 5. Phenotypic ratio is 2:2 6. Genotypic ratio is 2:2 On Selfing
- 4. Phenotypic ratio: 2 : 2 Heterozygous tall homozygous Dwarf Genotypic ratio 2 : 2 Tt tt 7. All test cross are back cross but all back cross are not test cross. Give reason. (2m) Ans: 1. Test cross: It can be defined as a cross between individual with unknown genotype for a particular trait with a recessive plant for that trait. 2. Back cross: cross between F1 generation and any of its homozygous parent is called as back cross. 3. Cross of F1 generation and dominant parent will produce all tall offspring with 50% homozygous tall and 50% heterozygous tall. 4. But cross of F1 generation with recessive parent will create 50% tall and 50% homozygous dwarf.
- 5. Q8. A heterozygous tall plant of pea is crossed with a dwarf plant of pea. Caculate phenotypic ratio of the progeny. (3M) Ans: P generation: heterozygous tall X Dwarf Phenotype: Tall Dwarf Genotype: Tt tt Gamete T t t t F1 generation: Tt On crossing F1 with recessive parent i.e Tt X tt T t t Tt tall tt dwarf t Tt tall tt dwarf Phenotypic ratio: 2 : 2 Heterozygous tall homozygous Dwarf Genotypic ratio 2 : 2 Tt tt Marking Scheme: Genotype of parents= 0.5m, gametes of parents= 0.5 m, checker board=1m, phenotypic ratio= 1m Q9. State and explain Law of Independent Assortment with a suitable example.(7M) Ans: Law of independent assortment
- 6. When the two homozygous individuals differ from each other, in 2 or more pairs of contrasting characters or genes are crossed, then the inheritance of one pair of character is independent of the other character. Explanation: 1. Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having yellow round seeds (YYRR)with a plant having green wrinkled seeds (yyrr) 2. The plants of F1 generation are all heterozygous. (YyRr). 3. The 4 types of alleles are separated into 4 types of gametes. (YR), (Yr), (yR), (yr) 4. In addition to parental combination of yellow round and green wrinkled, 2 new combinations of yellow wrinkled and green round seeds are produced. 5. The appearance of new combination in F1 generation proves the law. 6. They showed that each pair of contrasting character behaves independently and has no permanent association with a particular character. 7. Graphic representation of dihybrid cross: Marking Scheme: Statement of law=1m, explanation=2m, graphic representation=3M,Ratios=1M Q10. Explain dihybrid cross with the suitable example.(7M) ANS: Dihybrid cross Def: A cross between 2 pure (homozygous) parents in which the inheritance pattern of 2 pairs of contrasting characters is considered simultaneously is called dihybrid cross. Explanation: 1. Mendel selected a variety of pea plants having yellow and round seeds as female parent and another variety have green and wrinkled seeds as male parent. 2. He obtained pure line by selfing for 3 generations. Graphic representation of dihybrid cross:
- 7. Marking Scheme: definition= 1m, explanation=1m, cross till F1 generation=1 marks, F2 generation=3 m, Phenotypic and genotypic ratios= 1m. Q 11. Describe the cross between homozygous tall, round seeded pea plant and a dwarf, wrinkled seeded pea plant. What will be the type of progeny in F2 generation of this cross and in what proportion will it be/ name and state the law which is explained by this example. Ans: 1. Consider a cross between homozygous tall and round seeded pea plant (TTRR) and a dwarf and wrinkled seeded pea plants. (ttrr) 3. The plants of F1 are heterozygois for both characters with the genotype TtRr. 4. The F1 hybrid is allowed to self pollinate 5. The gametes which are produced is TR, Tr, tR, tr 6. In addition to parental combination of tall wrinked and dwarf round, are produced.
- 8. : Phenotypic ratio: 9:3:3:1 Genotypic Ratio: 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1 The law which is explained in this example is law of Independent Assortment. Statement of Law “ When 2 homozygous individuals differ from each other, in 2 / more pairs of contrasting characters or genes are crossed then the inheritance of 1 pairof characteris independentof the other pair of the character.” Marking scheme: Dihybrid cross=1m, Explanation=1m, F2 generation= 2.5m, types of progeny 1 m, name of law=0.5 m, statement of law =1m Q12. In in-complete dominance and co-dominance , genotypic and phenotypic ratios are identical. Explain how co-dominance differs from incomplete dominance in phenotypic nature of their hybrids. (3M) Ans: Incomplete dominance : 1. In incomplete dominance both the genes of an allelomorphic pair express themselves partially . 2. One gene cannot suppress the expression of the other completely. 3. There is an intermediate expression in F1 hybrid.
- 9. Co-dominance 1. In codominance both the genes of an allelomorphic pair express themselves equally in F1 hybrids. 2. These alleles express themselves independently even if present together in hybrids. 3. Difference : In both incomplete dominance and codominance, phenotypic and genotypic ratios are identical, but ina case of incomplete dominance the phenotype of hybrids are intermediate between the phenotypes of the parents, while in codominance both genes are expressed equally. Marking Scheme: Codominance:explanation and definition 1mark, Incomplete dominance:explanation and definition 1mark, difference between them 1 mark+=3mark
- 10. Q13. A pea plant pure for yellow seed colour is crossed with a pea plant for green seed colour. In F1 generation all pea plants were with yellow seeds. Which law of Mendel is applicable. (1mark) Ans: Law of Dominance or Mendel’s First law of Inheritance is applicable. Q14. Write a note on multiple alleles considering example of human blood groups.3M Ans:Multiple Alleles “More than 2 alternative form of gene in a population occupying same locus on a chromosome or its homologue are known as multiple alleles.” Explanation: a) The gene I controls ABO blood groups b) It Has 3 alleles IA , IB , i c) Allele IA and IB produce different type of sugar/ antigen d) Allele i do not produce any antigen/ sugar. e) The blood group chart is as follows Marking scheme: Def-1m, explanation-1m, chart -1m.
- 11. Q15. What is test cross? 1M. Ans: When F1 hybrid is back crossed with its recessive parent, it is called test cross. Q16. Why the ratio in pleiotropy is 2:1? Explain it with example.(3M) Ans:Pleiotropy: “ When a single gene controls 2 or more different traits, it is called pleiotropic genes and this phenomenon is called as pleiotropy. Its ratio is 2:1 instead of 3:1 Explanation: 1. According to mendel’s principle of unit character 1 gene controls 1 character, but sometimes single gene produces 2 related or unrelated phenotypic expressions. 2. Example: Sickle cell Anaemia Sickle cell anaemia- Hbs (Recessive) Normal healthy gene-HbA (Dominant) Carrier –HbA HbS (Heterozygous) 3. The carrier heterozygotes show sign of mild anaemia as their RBC’s become sickle shaped in oxygen deficiency. They are said to have sickle cell trait but are considered normal. 4. Homozygotes (HbA HbS ) develop severe anemia and die. Hence Sickle cell anemia is lethal. 5. Marriage between 2 carriers will lead to produce 1 normal, 2 carriers and 1 anemic child which dies. 6. Hence the ratio is 2:1 7. Therefore marriages of 2 heterozygote carriers should be avoided. Marking scheme: Description=1.5m, chart-1.5 m 1. Law of dominance is not universally applicable. Give Reason 2. The law of dominance is not universally applicable because as in intra allelic interaction neither gene is dominant nor recessive. 3. Sometimes both gene have equal potential to express as found in incomplete dompnance and co dominance.it modifies the mendalian ratio of 3:1 to 1:2:1. Chromosomla Basis of Inheritance
- 12. Q2. Explain structure of chromosome in detail.(3M) (Diagram 1m, all highlighted words explanation 2m) Ans: 1. A metaphasic chromosome has 2 identical haves called sister chromatids. 2. Each chromatid is in turn made up of sub-chromatids called chromonemata. 3. The chromatids lie side by side & are held together at one point called the centromere. 4. The centromere is also called the primary constriction. 5. Secondary constrictions are also present. 6. The part of the chromosome beyond the nucleolar organiseris short, spherical & is called satellite. 7. The tip of the chromosome is called telomere. 8. The surface of the chromosome bears number of small swellings called chromomeres. Q3. State and explain types of chromosomes.(3M) Ans: METACENTRIC CHROMOSOMES Metacentric chromosomes have the centromere in the center, such that both sections are of equal length..It appears V shaped during anaphase. SUBMETACENTRIC CHROMOSOMES Submetacentric chromosomes have the centromere slightly offset from the center leading to a slight asymmetry in the length of the two sections.. It appears L shaped during anaphase. ACROCENTRIC CHROMOSOMES Acrocentric chromosomes have a centromere which is severely offset from the center leading to one very long and one very short section.. It appears J shaped during anaphase. TELOCENTRIC CHROMOSOMES
- 13. Telocentric chromosomes have the centromere at the very end of the chromosome. Humans do not possess telocentric chromosomes but they are found in other species such as mice. It appears rod shaped during anaphase. Q4. Distinguish between X and Y chromosome. (2m) (any 4 points) Sr No P.O.D X- Chromosome Y-Chromosome 1. Length It is longer than Y chromosome It is shorter than X chromosome 2. Euchromatin Large amount of euchromatin present Small amount of euchromatin. 3. Heterochromatin Small amount of heterochromatin Large amount of heterochromatin present 4. Genetically active As more number of genetically active genes are present hence it is more genetically active As less number of genetically active genes are present hence it is less genetically active 5. Genes Non homologus region of X chromosome contains X linked genes. Non homologus region of Y- chromosome contains Y- linked genes. Q5. What is sex linkage? Explain the inheritance of colorblindness & hemophilia with the suitable example.(7M) Ans: Sex linkage: Transmission of body characters from parents to offspring along with sex chromosome is called sex inheritance or sex linkage. A] Inheritance of color blindness: 1. It is a sex linked disease in which person cannot distinguish between red & green color. Both the color appears grey to him. 2. It is caused by recessive gene, which prevents the proper formation of color sensitive cells in the retina necessary for distinction of red & green. 3. The genes for normal vision (dominant) & colorblindness (recessive) are located on non- homologous region of X- chromosome. Their alleles are absent in Y- chromosome. 4. If gene for normal vision is represented by XC & gene for color-blindness is represented by Xc , then the genotype of different individuals can be represented as follows:- Sex Normal Colourblind Carrier
- 14. Male XC Y Xc Y - Female XC XC Xc Xc Xc XC Explanation : The inheritance of colourblindness can be studided by following examples: 1. If a colourblindman (Xc Y) marries a female with normal vision (XC XC ) all the offsprings will have normal vision.The sons will have normal vision and daughters will be all carriers. 2. If a carrier female (Xc XC ) marries a male with normal vision then all daughters will have normal vision of which half will be carriers. 3. Half the sons will be colourblind and half of them will have normal vision 4. Hence it is clear that the colourblind father transmits the disease to his grandson through his carrier daughter 5. This inheritance from father to grandson through his daughter is called CRISS CROSS INHERITANCE. Chart Phenotypic Ratio of F1 Generation: Xc XC : XC Y Carrier female Normal Male 50% 50% Phenotypic Ratio of F2 Generation: XC XC : XC Xc : XC Y : Xc Y 50% 50%
- 15. Normal female Carrier female Normla male Colourblind male 25% 25% 25% 25% B] Inheritance of Haemophilia 1. Haemophilia is a hereditary disease in which blood falls to clot or clots very slowly. 2. Person who carries the recessive gene for haemophilia has deficiency of clotting factors in blood. So minor injuries causes continuous bleeding. Hence it is also called as bleeder’s disease. 3. The genes for normal clotting (dominant) and haemophiluic (recessive) are located on non homologus region of X chromosome. But their alleles are absent in Y-chromosomes 4. Genes for normal clotting of blood is represented by XH & gene for haemophilic by Xh. The genotype of different individuals can be represented as follows: Sex Normal Colourblind Carrier Male XH Y Xh Y - Female XH XH Xh Xh Xh XH Explanation : The inheritance of haemophilia can be studied by following examples: 1. If haemophilic male (Xh Y) marries a normal female (XH XH ) then all the offsprings will have normal clotting of blood. The son’s will have normal blood clotting but the daughters will be carriers for the disease. The carriers have normal clotting of blood. 2. If carrier female (XH Xh ) marries a Male with normal clotting of blood (XH Y), then all daughters will have normal clotting of blood but half of them will be carriers of the disease. 3. Half the son will be haemophilic & remaining half will have normal clotting of blood. 4. Haemophilia also shows CRISS CROSS INHERITANCE. 5. Hence, father transmits the disease to his grandson through his carrier daughter Charts:
- 16. Phenotypic Ratio of F1 Generation: Xh XH : XH Y Carrier female Normal Male 50% 50% Phenotypic Ratio of F2 Generation: XH XH : XH Xh : XH Y : Xh Y Normal female Carrier female Normal male haemophilic male 25% 25% 25% 25% ( marking scheme: Def of sex linkage 1m, Colourblindness:1m, explanation of eg:1m, colourblidness chart:1m, haemophilia:1m, explanation of eg:1m, haemophilia chart 1m) Q6. Why do sex linked traits appear more in males than in females. (1M) Ans: In males, there is only 1 X-chromosome, hence recessive gene get a chance to express itself.
- 17. Q7. With the help of chart explain the method of sex determination in honeybees.(3M) / Drone of honeybees show haploid number of chromosomes. Illustrate. (chart:1.5m, explanation :1.5m) Ans: Sex determination in honeybees. 1. In honeybees, sex is determined by the number of sets of chromosomes received by an individual. Such type of sex determination is called haploid-0diploid sex determination system. 2. The fertilized egg develops as a female offspring 9 may be queen or worker bee). It shows diploid number of chromosomes i.e 2n=32. 3. An unfertilized egg develops as a male (drone) by means of parthenogenesis. Thus the drones have haploid n=16 number of chromosomes. The drones produces sperm by mitosis. Chart; Q8. Describe the structure of sex chromosome. (3M) (1.5m: explanation, 1.5m: diagram) Ans: X- chromosome: 1. It is longer & contains large amount of euchromatin & small amount of heterochromatin 2. It is common in males & females. 3. Its non homologous part contains X-linked genes that show criss cross inheritance. Y- Chromosome 1. It is shorter than X- chromosome. 2. It contains small amount of euchromatin & large amount of heterochromatin
- 18. 3. Its non homologous part contains Y-linked genes that show straight inheritance. Ans: Q9. Give any 2 sex linked traits. Ans: X- linked diseases are:- a) Colourblindness b) Haemophilia c) Myopia d) Muscular dystrophy e) night blindness Q10. What will be the phenotype of progeny, if a carrier hemophilic female marries a normal male? Explain. Ans: if a carrier hemophilic female marries a normal male then: 1. If carrier female (XH Xh ) marries a Male with normal clotting of blood (XH Y), then all daughters will have normal clotting of blood but half of them will be carriers of the disease. 2. Half the son will be haemophilic & remaining half will have normal clotting of blood. Phenotypic Ratio : XH XH : XH Xh : XH Y : Xh Y Non homologous region of Y Non homologous region of X Homologous region of X Homologous region of Y
- 19. Normal female Carrier female Normal male haemophilic male 25% 25% 25% 25% Q11. What is a cris cross inheritance. (1M) Ans: The inheritance of characters from the father to his grandson through his carrier daughter is called Criss Cross inheritance. Q12. Sketch & label structure of chromosome. (2M) (any 4 labels) Ans: Q14. Give the genotype of Turner’s syndrome. Ans: 44A+ XO is the genotype of Turner’s syndrome Q15. Explain sex chromosomal abnormalities Ans: A] Turner’s syndrome 1. It was described by HH Turner. 2. Person with Turner’s syndrome have 45 chromosomes with only 1 X sex chromosome, such a genotype is represented as (44+ XO) Symptoms of Turner syndrome are: Phenotype is female short stature infertility, webbed neck, No secondary sexual characters. B] Klinefelter’s Syndrome 1. It is caused due to an extra chromosome i.e. extra X chromosome. So the genotype is XXY so they are sometimes described as feminized males. 2. The sufferer has 47 chromosomes instead of 46 Symptoms: 1. Patients are tall, thin sterile 2. Normal intelligence
- 20. 3. Spermatogenesis is absent Q13. Explain the mechanism of sex determination in human being.
- 21. When Y bearing sperm fertilizes the egg the male child is conceived having the combination of 44 + XY. Hence father is responsible for the sex of the child and not the mother. Q16. Distinguish Between Crossing over & linkage Ans












![Telocentric chromosomes have the centromere at the very end of the chromosome. Humans do not
possess telocentric chromosomes but they are found in other species such as mice. It appears rod shaped
during anaphase.
Q4. Distinguish between X and Y chromosome. (2m) (any 4 points)
Sr
No
P.O.D X- Chromosome Y-Chromosome
1. Length It is longer than Y chromosome It is shorter than X chromosome
2. Euchromatin Large amount of euchromatin
present
Small amount of euchromatin.
3. Heterochromatin Small amount of
heterochromatin
Large amount of heterochromatin
present
4. Genetically
active
As more number of genetically
active genes are present hence
it is more genetically active
As less number of genetically
active genes are present hence it is
less genetically active
5. Genes Non homologus region of X
chromosome contains X linked
genes.
Non homologus region of Y-
chromosome contains Y- linked
genes.
Q5. What is sex linkage? Explain the inheritance of colorblindness & hemophilia
with the suitable example.(7M)
Ans: Sex linkage: Transmission of body characters from parents to offspring along with sex
chromosome is called sex inheritance or sex linkage.
A] Inheritance of color blindness:
1. It is a sex linked disease in which person cannot distinguish between red & green color.
Both the color appears grey to him.
2. It is caused by recessive gene, which prevents the proper formation of color sensitive cells
in the retina necessary for distinction of red & green.
3. The genes for normal vision (dominant) & colorblindness (recessive) are located on non-
homologous region of X- chromosome. Their alleles are absent in Y- chromosome.
4. If gene for normal vision is represented by XC
& gene for color-blindness is represented by
Xc
, then the genotype of different individuals can be represented as follows:-
Sex Normal Colourblind Carrier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-inheritanc-and-variation-250109084427-33979b4e/85/3-inheritanc-and-variation-pdf-HSC-BIOLOGY-3-inheritanc-and-variation-13-320.jpg)

![Normal female Carrier female Normla male Colourblind
male
25% 25% 25% 25%
B] Inheritance of Haemophilia
1. Haemophilia is a hereditary disease in which blood falls to clot or clots very slowly.
2. Person who carries the recessive gene for haemophilia has deficiency of clotting factors in
blood. So minor injuries causes continuous bleeding. Hence it is also called as bleeder’s
disease.
3. The genes for normal clotting (dominant) and haemophiluic (recessive) are located on non
homologus region of X chromosome. But their alleles are absent in Y-chromosomes
4. Genes for normal clotting of blood is represented by XH & gene for haemophilic by Xh.
The genotype of different individuals can be represented as follows:
Sex Normal Colourblind Carrier
Male XH
Y Xh
Y -
Female XH
XH
Xh
Xh
Xh
XH
Explanation :
The inheritance of haemophilia can be studied by following examples:
1. If haemophilic male (Xh
Y) marries a normal female (XH
XH
) then all the offsprings will
have normal clotting of blood. The son’s will have normal blood clotting but the
daughters will be carriers for the disease. The carriers have normal clotting of blood.
2. If carrier female (XH
Xh
) marries a Male with normal clotting of blood (XH
Y), then all
daughters will have normal clotting of blood but half of them will be carriers of the
disease.
3. Half the son will be haemophilic & remaining half will have normal clotting of blood.
4. Haemophilia also shows CRISS CROSS INHERITANCE.
5. Hence, father transmits the disease to his grandson through his carrier daughter
Charts:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-inheritanc-and-variation-250109084427-33979b4e/85/3-inheritanc-and-variation-pdf-HSC-BIOLOGY-3-inheritanc-and-variation-15-320.jpg)



![Normal female Carrier female Normal male haemophilic male
25% 25% 25% 25%
Q11. What is a cris cross inheritance. (1M)
Ans: The inheritance of characters from the father to his grandson through his carrier
daughter is called Criss Cross inheritance.
Q12. Sketch & label structure of chromosome. (2M) (any 4 labels)
Ans:
Q14. Give the genotype of Turner’s syndrome.
Ans: 44A+ XO is the genotype of Turner’s syndrome
Q15. Explain sex chromosomal abnormalities
Ans: A] Turner’s syndrome
1. It was described by HH Turner.
2. Person with Turner’s syndrome have 45 chromosomes with only 1 X sex chromosome,
such a genotype is represented as (44+ XO)
Symptoms of Turner syndrome are:
Phenotype is female
short stature
infertility,
webbed neck,
No secondary sexual characters.
B] Klinefelter’s Syndrome
1. It is caused due to an extra chromosome i.e. extra X chromosome. So the genotype is XXY
so they are sometimes described as feminized males.
2. The sufferer has 47 chromosomes instead of 46
Symptoms:
1. Patients are tall, thin sterile
2. Normal intelligence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-inheritanc-and-variation-250109084427-33979b4e/85/3-inheritanc-and-variation-pdf-HSC-BIOLOGY-3-inheritanc-and-variation-19-320.jpg)





































































