Ad
3-Python Python oho pytho hdiwefjhdsjhds
- 1. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 1 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals "The only way to learn a new programming language is by writing programs in it." - Dennis Ritchie You will learn the following topics in this Tutorial S. No. Topics 1 Python Character Set 2 Tokens Keywords Identifiers / Variable Literals / Values Delimiters Operators Variable 3 Concepts of L-Value and R-Value 4 Comments 5 Statement 6 Clarity and simplicity of expression 7 Blocks and Indentation 8 The input ( ) function 9 The print ( ) function 10 Program Testing and Debugging 11 Errors and Exceptions 12 A) Compile – Time errors 13 A) Syntax Error 14 B) Semantic Errors
- 2. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 2 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Python Character Set: A character can represents any letter, digit, or any other sign. Following are some of the python character set. LETTERS A to Z and a to z DIGITS 0 -9 SPECIAL SYMBOLS Space, + -* ^ *+ ,- =! = < > . ‗ ‗ ; : & #, under score(_) etc. WHITE SPACE Blank space, horizontal tab ( - > ), carriage return , Newline, Form feed. OTHER CHARACTERS Python can process all ASCII and Unicode characters as part of data or literals. Tokens: The smallest individual unit in a program is known as token or lexical unit. 1) Keywords: Keywords are special identifiers with predefined meanings that cannot change. As these words have specific meaning for interpreter, they cannot be used for any other purpose. TOKENS Keywords Identifier or Varuables Literals Delimiters Operators
- 3. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 3 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Some Commonly Used Keywords: 2) Identifiers / Variable: Identifiers are names given to identify something. Identifiers are fundamental building blocks of a program and are used as general terminology for the names given to different part of the program that is variables, objects, classes, functions, lists, dictionaries etc. NOTE: An identifier must not be a keyword of Python There are some rules you have to follow for naming identifiers: An identifier starts with a letter A to Z or a to z or an underscore (_) followed by zero or more letters, underscores and digits (0 to 9). Python does not allow special characters Identifier must not be a keyword of Python. Python is a case sensitive programming language. Thus, Sname and sname are two different identifiers in Python. and exec not continue if return except else as finally or def import try class lambda assert for Pass del in while global yield break from print elif is with raise class
- 4. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 4 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Some valid identifiers: Mybook, file123, z2td, date_2, _no Some invalid identifier: Some invalid variable name which produces syntax errors are as follows >>> 98Sep_sco SyntaxError: invalid syntax because variable start with a digit >>> Your Age SyntaxError: invalid syntax because variable contains space >>> while SyntaxError: invalid syntax because variable is a reserve word >>> myname@ SyntaxError: invalid syntax because variable contains a special character 3) Literals / Values: Literals in Python can be defined as number, text, or other data that represent values to be stored in variables. The data items which never change their value throughout the program run. There are several kinds of literals: String Literals Numeric Literals Boolean Literals Special Literal None Literal Collections
- 5. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 5 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals 4) Delimiters: Used to implement the grammatical and structure of Syntax. Delimiters are used in various areas of the Python language. They are used to build expressions, string literals, tuples, dictionaries or lists. Following are the python delimiters. 5) Operators: Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result.
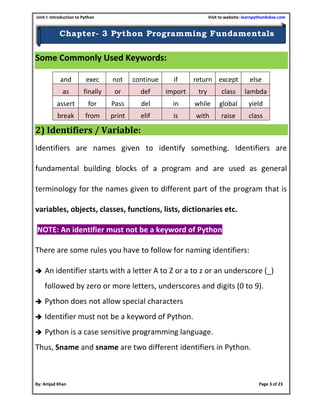
- 6. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 6 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Variable: Variable is an identifier whose value can change. For example variable age can have different value for different person. Variable name should be unique in a program. Variables must always be assigned values before they are used in the program, otherwise it will lead to an error. Wherever a variable name occurs in the program, the interpreter replaces it with the value of that particular variable. Value of a variable can be string (for example, ‘A’, ‘Excellent’), number (for example 98.5) or any combination of alphanumeric (alphabets and numbers for example ‘B10’) characters. In Python, we can use an assignment statement to create new variables and assign specific values to them. The basic assignment statement has this form: <variable> = <expr> Here, <variable> is an identifier and <expr> is an expression. Operators Operators type ( ) [ ] { } Grouping + - * / // % ** Arithmetic Operator == != <> <= >= Is In Relational Operators And Not Or Logical Operators & | ~ ^ << >> Bit-wise Operators
- 7. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 7 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals For Example: Class = 12 # Variable created of numeric (integer) type Remark = "Keep it up!" # Variable created of string type Percentage = 98.5 # Variable created of numeric (floating point) type Multiple Assignments: Assigning same value to multiple variables: x = y = z = 100 It will assign value 100 to all three variables x, y and z. Assigning multiple value to multiple variables p, q, r = 10, 20, 30 It will assign the value order wise that is value 10 assign to variable p, value 20 assign to variable q and value 30 assign to variable r. Example: Write a Python program to find the sum of two numbers. num1 = 100 num2 = 200 result = num1 + num2 print(result) Output: 300 Example: Write a Python program to find the area of a triangle given that its base is 20 units and height is 40 units. base = 20 height = 40
- 8. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 8 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals area = 0.5 *base * height print(area) Output: 400 Concepts of L-Value and R-Value Lvalue refers to object to which you can assign value. It refers to memory location. It can appear LHS or RHS of assignment Rvalue refers to the value we assign to any variable. It can appear on RHS of assignment For example: Num1 = 10 # Num1 is an L-value Num2 = 20 # Num2 is an L-value sum = Num1 + Num2 # (Num1 +Num2) is an R-value print(sum) Output: 30 Comments: (Code tells you how, comments should tell you why) Comments are used to add a remark or a note in the source code. Comments are not executed by interpreter. In Python, a single line comment starts with # (hash sign). Python supports 3 ways to enter comments:
- 9. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 9 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Full line comment Inline comment Multiline comment Full line comment : Physical lines between with # Example: #This is program of volume of cylinder Inline comment: It start in the middle of the physical line Example area = length*breadth # calculating area of rectangle Multiline comment: You can put a multiple line or a block commment Example: A. adding in the beginning of every line (using #) # Program name: area of circle # Date: 20/07/18 #Language : Python Example : B. Multiline comment (using “ “ “) triple quotes ‘ ’ ’ Created by: learnpython4cbse.com Date : 07/11/2020 Topic : Use of triple – qouted multi line string ‘ ’ ’
- 10. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 10 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Statement It is a programming instruction that does something i.e. some action takes place. Instructions that a Python interpreter can execute are called statements Example: print (“Welcome to python”) The above statement call print function Multi-Line/ Continuation Statements: Statements in Python typically end with a new line. Python does, however, allow the use of the line continuation character () at the end of the line to continue the statement onto the next line. For example, # Assigns more values to the variables Mark1, Mark2, Mark3, Mark4, Mark5 = 70, 80, 87, 89, 78 Total = Mark1 + Mark2 + Mark3 + Mark4 + Mark5 print ("Total mark is:", Total) Output: Total mark is: 404
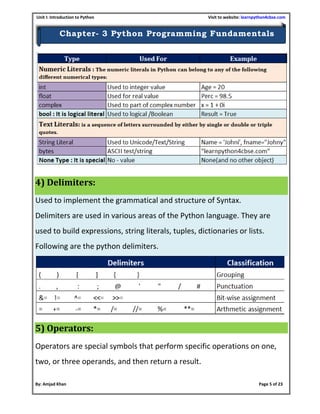
- 11. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 11 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals NOTE: Statements contained within the [ ], { }, or ( ) brackets do not need to use the line continuation character. For example: days = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', ‘Thursday', 'Friday'] Clarity and simplicity of expression Parenthesis should be used to show the precedence of the operators and to enclose a sub-expression. This removes the ambiguities and misinterpretation leading to wrong outputs. Example, Z = (a * a) + (3 * a * b) – (c * c) For example, import math Root = (–b + math. sqrt (b * b – 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a) It is better to break this expression i.e. import math D = math. sqrt (b * b – 4 * a * c) X = 2 * a Root = (–b + D) / X No two operators can occur one after the other. The operators should have operands before and after them. In case there are many sub-expressions in an expression, then we break it up into individual sub- expressions.
- 12. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 12 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Blocks and Indentation A group of statements which are part of another statement or a function are called block or code – block or suite in Python. It’s best to use four spaces of indent for each code block level. If you use another number of spaces (2, 6, 8), that’s fine. The important thing is that all the code in the code block must have the same number of spaces. Note: You cannot unnecessarily indent a statement; Python will raise error for that. Consider the following Example: if n1<n2: Temp =n1 n1=n2 n2=Temp print (“I Understand Block”) Example: Write a program to input a number (N) and find the sum of all numbers till N and its average. Also, find the sum of all even and odd numbers till N. The program also justifies the indentation for both looping and branching to find the correct result. Solution: Block of if statement with all its statements at same indentation level
- 13. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 13 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals # Program to find sum of natural numbers, average of natural numbers, # sum of even numbers and odd numbers c1 = c2 = avg1 = avg2 = sum1 = sum2 = 0 i = 1 n = int(input("Enter the value of n: ")) while (i <= n): # while loop body started if (i % 2 == 0): # Conditional construct # Two lines body in true part sum1 = sum1 + i c1 = c1 + 1 else: # Two lines body in false part sum2 = sum2 + i c2 = c2 + 1; i+=1 # while loop counter # Calculation part avg1 = sum1 / c1; avg2 = sum2 / c2; sum = sum1 + sum2; avg = sum / n; print ("*************************************") print ("The sum of natural numbers is => ", sum) print ("The avg of natural numbers is => ", avg) print ("The sum of even numbers is => ", sum1) print ("The sum of odd numbers is => ", sum2) print ("The avg of even numbers is => ", avg1) print ("The avg of odd numbers is => ", avg2) print ("*************************************") if part indentation else part indentation while part indentation
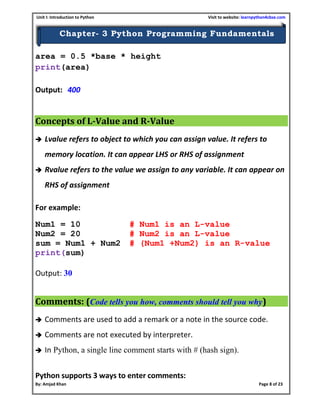
- 14. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 14 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Function indentation Indent the function body when a function starts. # Function to find sum of two numbers def Sum ( ): # Multiline in a block using function a = 20 b = 40 result = a + b print("Sum of two numbers is:", result) Sum ( ) The input ( ) function The input ( ) function prompts the user to enter data. It accepts all user input as string. The user may enter a number or a string but the input ( ) function treats them as strings only. The syntax for input ( ) is: input ([Prompt]) Prompt is the string we may like to display on the screen prior to taking the input, and it is optional. For example, Function body statements
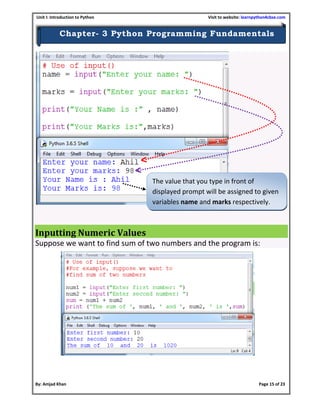
- 15. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 15 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Inputting Numeric Values Suppose we want to find sum of two numbers and the program is: The value that you type in front of displayed prompt will be assigned to given variables name and marks respectively.
- 16. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 16 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals When we execute the above program, the program doesn’t add the two numbers together; it just puts one right after the other as 1020 The solution to the above problem is: Python offers two functions int ( ) and float ( ) to be used with input ( ) to convert the values received through input ( ) into int and float types. Accept an Integer input from User We need to convert an input string value into an integer using a int( ) function. num1 = int (input("Enter first number: ")) num2 = int(input("Enter second number: ")) sum = num1 + num2 print ('The sum of ', num1, ' and ', num2, ' is ',sum) OUTPUT: Enter first number: 10 Enter second number: 30 The sum of 10 and 30 is 40 Accept an float input from User You need to convert user input to the float number using the float() function as we did for the integer value. num1 = float (input("Enter first number: ")) num2 = float(input("Enter second number: ")) sum = num1 + num2 print ('The sum of ', num1, ' and ', num2, ' is ',sum) OUTPUT: Enter first number: 10.5 Enter second number: 30.5 Both input values are converted into integer type Both input values are converted into float type
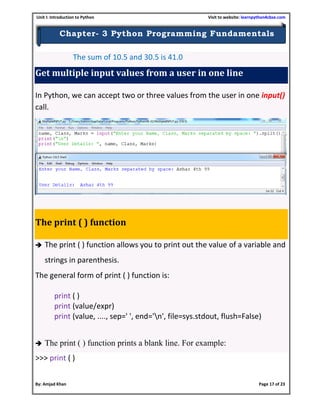
- 17. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 17 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals The sum of 10.5 and 30.5 is 41.0 Get multiple input values from a user in one line In Python, we can accept two or three values from the user in one input() call. The print ( ) function The print ( ) function allows you to print out the value of a variable and strings in parenthesis. The general form of print ( ) function is: print ( ) print (value/expr) print (value, ...., sep=' ', end='n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False) The print ( ) function prints a blank line. For example: >>> print ( )
- 18. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 18 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals The print ( ) function prints the value of variable or expression. For example: >>> N1 = 20 >>> N2 = 30 >>> Sum = N1 + N2 >>> print (Sum) # prints a value 50 >>> print (N1+N2) # prints a value of an expression i.e., N1+N2 50 >>> Ver = 3.6 >>> Prog = "Python" >>> print (Prog, Ver) # prints two values separated with comma (,) Python 3.6 The print() function contains number of options. You can use either one, two or all at once. For example: − Print a message. >>> print ("The sum is") # prints a message The sum is >>> print ("My Python")
- 19. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 19 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals My Python − Print a value, message or both message and values and vice versa. >>> print ("The sum is", Sum) # prints a message with a value The sum is 50 >>> print (Sum, "is the sum of", N1, "and", N2) # print is alternate way 50 is the sum of 20 and 30 The sep separator is used between the values. It defaults into a space character. For example: >>> print (10,20,30,40,sep='*') # prints a separator * 10*20*30*40 After all values are printed, end is printed. It defaults into a new line. >>> print (10, 20, 30, 40, sep = '*', end = '@') # A new end is assigned @ 10*20*30*40@ Let us take other examples, where a print() function can output multiple things at once, each item separated by a comma. # The following code prints: The answer to 10+10 is 20 >>>print (" The answer to 10+10 is" , 10+10) # The following code prints: The answer to 10+10 is 10+10 >>>print (" The answer to 10+10 is", "10+10 ")
- 20. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 20 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals # The following code does not work and product Invalid Syntax because the comma (,) is inside the quotation marks and not outside. >>>print (" The answer to 10+10 is ," 10+10) print () with Concatenate Operator (+) The print() function can print two strings either using comma (,) operator, or a concatenate operator (+). For example, >>> print ("My name is Ahil", "Class-XI A.") # Print with space separator. My name is Ahil Class-XI A. Similarly, by using concatenate operator (+), the print() function is: >>> print ("My name is Ashaz" + "Class-XI B.") # Print without separator. My name is AshazClass-XI A. Formatting Data with print() The general Syntax: % width.precision type-char For example: a=2.45567 print("%.2F" %a)
- 21. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 21 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals Program Testing and Debugging A programmer can make mistakes while writing a program, and hence, the program may not execute or may generate wrong output. Program Testing: Program Testing means running the program, executing all its instructions or functions and testing the logic by entering sample data in order to check the output. Debugging: Debugging is the process of finding and correcting the errors in the program code. Errors and Exceptions: An errors and exceptions both disrupt a program and stop its execution. But Errors and Exceptions are not the same. Errors in a program: An error, also termed as ‘a bug’, is anything in the code that prevents a program from compiling and running correctly. Type of errors: There are two types of errors: 1) Compile – time Errors 2) Runtime Errors
- 22. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 22 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals 1) Compile – Time errors: Errors that occur when you violate the rules of writing syntax are known as compile – time errors. Compiled time errors are broadly classified into two categaries. A) Syntax error: Every programming language has its own rules and regulations (syntax). If we overcome the particular language rules and regulations, the syntax error will appear (i.e. an error of language resulting from code that does not conform to the syntax of the programming language). It can be recognized during compilation time. Example a = 0 while a < 10 a = a + 1 print (a) In the above statement, the second line is not correct. Since the while statement does not end with ‘:’. This will flash a syntax error. B) Semantic Errors: It refers the set of rules which give the meaning of statement.
- 23. Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com By: Amjad Khan Page 23 of 23 Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals For Example: X + Y = A will result in a semantically error as an expression cannot come on the left side of an assignment statement. Run time Errors: Errors that occur during the execution of a program are known as run time errors. Logical error: It is a type of runtime error that may simply produce the wrong output or may cause a program to crash while running. It is an error in a program's source code that results in incorrect or unexpected result. The logical error might only be noticed during runtime, because it is often hidden in the source code and are typically harder to find and debug. a = 100 while a < 10: a = a + 1 print (a) In the above example, the while loop will not execute even a single time, because the initial value of ‘a’ is 100.

![Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com
By: Amjad Khan Page 6 of 23
Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals
Variable:
Variable is an identifier whose value can change. For example variable
age can have different value for different person.
Variable name should be unique in a program.
Variables must always be assigned values before they are used in the
program, otherwise it will lead to an error.
Wherever a variable name occurs in the program, the interpreter
replaces it with the value of that particular variable.
Value of a variable can be string (for example, ‘A’, ‘Excellent’), number
(for example 98.5) or any combination of alphanumeric (alphabets and
numbers for example ‘B10’) characters.
In Python, we can use an assignment statement to create new variables
and assign specific values to them.
The basic assignment statement has this form:
<variable> = <expr>
Here, <variable> is an identifier and <expr> is an expression.
Operators Operators type
( ) [ ] { } Grouping
+ - * / // % ** Arithmetic Operator
== != <> <= >= Is In Relational Operators
And Not Or Logical Operators
& | ~ ^ << >> Bit-wise Operators](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-pythonprogrammingfundamentals-241222101920-8a63de8d/85/3-Python-Python-oho-pytho-hdiwefjhdsjhds-6-320.jpg)



![Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com
By: Amjad Khan Page 11 of 23
Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals
NOTE: Statements contained within the [ ], { }, or ( ) brackets do not need
to use the line continuation character.
For example:
days = ['Monday',
'Tuesday',
'Wednesday',
‘Thursday',
'Friday']
Clarity and simplicity of expression
Parenthesis should be used to show the precedence of the operators and
to enclose a sub-expression. This removes the ambiguities and
misinterpretation leading to wrong outputs.
Example,
Z = (a * a) + (3 * a * b) – (c * c)
For example,
import math
Root = (–b + math. sqrt (b * b – 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a)
It is better to break this expression i.e.
import math
D = math. sqrt (b * b – 4 * a * c)
X = 2 * a
Root = (–b + D) / X
No two operators can
occur one after the other.
The operators should have
operands before and after
them. In case there are
many sub-expressions in
an expression, then we
break it up into individual
sub- expressions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-pythonprogrammingfundamentals-241222101920-8a63de8d/85/3-Python-Python-oho-pytho-hdiwefjhdsjhds-11-320.jpg)


![Unit I: Introduction to Python Visit to website: learnpython4cbse.com
By: Amjad Khan Page 14 of 23
Chapter- 3 Python Programming Fundamentals
Function indentation
Indent the function body when a function starts.
# Function to find sum of two numbers
def Sum ( ): # Multiline in a block using function
a = 20
b = 40
result = a + b
print("Sum of two numbers is:", result)
Sum ( )
The input ( ) function
The input ( ) function prompts the user to enter data.
It accepts all user input as string.
The user may enter a number or a string but the input ( ) function
treats them as strings only.
The syntax for input ( ) is:
input ([Prompt])
Prompt is the string we may like to display on the screen prior to taking
the input, and it is optional.
For example,
Function body statements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-pythonprogrammingfundamentals-241222101920-8a63de8d/85/3-Python-Python-oho-pytho-hdiwefjhdsjhds-14-320.jpg)