Ad
48742447 11g-sql-fundamentals-ii-additional-practices-and-solutions
- 1. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices and Solutions D49994GC10 Edition 1.0 August 2007 D52149 ® Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 2. Copyright © 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. Disclaimer This course provides an overview of features and enhancements planned in release 11g. It is intended solely to help you assess the business benefits of upgrading to 11g and to plan your IT projects. This course in any form, including its course labs and printed matter, contains proprietary information that is the exclusive property of Oracle. This course and the information contained herein may not be disclosed, copied, reproduced, or distributed to anyone outside Oracle without prior written consent of Oracle. This course and its contents are not part of your license agreement nor can they be incorporated into any contractual agreement with Oracle or its subsidiaries or affiliates. This course is for informational purposes only and is intended solely to assist you in planning for the implementation and upgrade of the product features described. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described in this document remain at the sole discretion of Oracle. This document contains proprietary information and is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may copy and print this document solely for your own use in an Oracle training course. The document may not be modified or altered in any way. Except where your use constitutes "fair use" under copyright law, you may not use, share, download, upload, copy, print, display, perform, reproduce, publish, license, post, transmit, or distribute this document in whole or in part without the express authorization of Oracle. The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. If you find any problems in the document, please report them in writing to: Oracle University, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, California 94065 USA. This document is not warranted to be error-free. Restricted Rights Notice If this documentation is delivered to the United States Government or anyone using the documentation on behalf of the United States Government, the following notice is applicable: U.S. GOVERNMENT RIGHTS The U.S. Government’s rights to use, modify, reproduce, release, perform, display, or disclose these training materials are restricted by the terms of the applicable Oracle license agreement and/or the applicable U.S. Government contract. Trademark Notice Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Author Chaitanya Koratamaddi Technical Contributors and Reviewers Claire Bennett Ken Cooper Yanti Chang Laszlo Czinkoczki Burt Demchick Gerlinde Frenzen Joel Goodman Laura Garza Richard Green Nancy Greenberg Akira Kinutani Wendy Lo Isabelle Marchand Timothy Mcglue Alan Paulson Srinivas Putrevu Bryan Roberts Clinton Shaffer Abhishek Singh Jenny Tsai Smith James Spiller Lori Tritz Lex van der Werff Marcie Young Editors Nita Pavitran Arijit Ghosh Raj Kumar Graphic Designer Satish Bettegowda Publisher Michael Sebastian Almeida Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 3. iii Contents Preface I Introduction Lesson Objectives I-2 Lesson Agenda I-3 Course Objectives I-4 Course Prerequisites I-5 Course Agenda I-6 Lesson Agenda I-7 Human Resources (HR) Schema Used in This Course I-8 Appendixes Used in This Course I-9 Development Environments I-10 Lesson Agenda I-11 Review of Using Oracle SQL Developer I-12 Creating a Database Connection I-13 Creating a Schema Object I-14 Using the SQL Worksheet I-15 Executing SQL Statements I-16 Saving SQL Statements I-17 Executing SQL Scripts I-18 Lesson Agenda I-19 SQL Statements in SQL*Plus I-20 Review of Restricting Data I-21 Review of Sorting Data I-22 Review of SQL Functions I-23 Review of Single-Row Functions I-24 Review of Types of Group Functions I-25 Review of Using Subqueries I-26 Review of Manipulating Data I-27 Lesson Agenda I-28 Oracle Database 11g SQL Documentation I-29 Additional Resources I-30 Summary I-31 Practice I: Overview I-32 Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 4. iv 1 Controlling User Access Objectives 1-2 Lesson Agenda 1-3 Controlling User Access 1-4 Privileges 1-5 System Privileges 1-6 Creating Users 1-7 User System Privileges 1-8 Granting System Privileges 1-9 Lesson Agenda 1-10 What Is a Role? 1-11 Creating and Granting Privileges to a Role 1-12 Changing Your Password 1-13 Lesson Agenda 1-14 Object Privileges 1-15 Granting Object Privileges 1-17 Passing On Your Privileges 1-18 Confirming Granted Privileges 1-19 Lesson Agenda 1-20 Revoking Object Privileges 1-21 Summary 1-23 Practice 1: Overview 1-24 2 Managing Schema Objects Objectives 2-2 Lesson Agenda 2-3 ALTER TABLE Statement 2-4 Adding a Column 2-6 Modifying a Column 2-7 Dropping a Column 2-8 SET UNUSED Option 2-9 Lesson Agenda 2-11 Adding a Constraint Syntax 2-12 Adding a Constraint 2-13 ON DELETE CASCADE 2-14 Deferring Constraints 2-15 Difference Between INITIALLY DEFERRED and INITIALLY IMMEDIATE 2-16 Deferring Constraints: Example 2-17 Dropping a Constraint 2-18 Disabling Constraints 2-19 Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 5. v Enabling Constraints 2-20 Cascading Constraints 2-22 Renaming Table Columns and Constraints 2-24 Lesson Agenda 2-25 Overview of Indexes 2-26 CREATE INDEX with the CREATE TABLE Statement 2-27 Function-Based Indexes 2-29 Removing an Index 2-30 DROP TABLE … PURGE 2-31 Lesson Agenda 2-32 FLASHBACK TABLE Statement 2-33 Using the FLASHBACK TABLE Statement 2-35 Lesson Agenda 2-36 External Tables 2-37 Creating a Directory for the External Table 2-38 Creating an External Table 2-40 Creating an External Table by Using ORACLE_LOADER 2-42 Querying External Tables 2-44 Creating an External Table by Using ORACLE_DATAPUMP: Example 2-45 Summary 2-46 Practice 2: Overview 2-47 3 Managing Objects with Data Dictionary Views Objectives 3-2 Lesson Agenda 3-3 Data Dictionary 3-4 Data Dictionary Structure 3-5 How to Use the Dictionary Views 3-7 USER_OBJECTS and ALL_OBJECTS Views 3-8 USER_OBJECTS View 3-9 Lesson Agenda 3-10 Table Information 3-11 Column Information 3-12 Constraint Information 3-14 USER_CONSTRAINTS: Example 3-15 Querying USER_CONS_COLUMNS 3-16 Lesson Agenda 3-17 View Information 3-18 Sequence Information 3-19 Confirming Sequences 3-20 Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 6. vi Index Information 3-21 USER_INDEXES: Examples 3-22 Querying USER_IND_COLUMNS 3-23 Synonym Information 3-24 Lesson Agenda 3-25 Adding Comments to a Table 3-26 Summary 3-27 Practice 3: Overview 3-28 4 Manipulating Large Data Sets Objectives 4-2 Lesson Agenda 4-3 Using Subqueries to Manipulate Data 4-4 Retrieving Data Using a Subquery as Source 4-5 Inserting Using a Subquery as a Target 4-7 Using the WITH CHECK OPTION Keyword on DML Statements 4-9 Lesson Agenda 4-11 Overview of the Explicit Default Feature 4-12 Using Explicit Default Values 4-13 Copying Rows from Another Table 4-14 Lesson Agenda 4-15 Overview of Multitable INSERT Statements 4-16 Types of Multitable INSERT Statements 4-18 Multitable INSERT Statements 4-19 Unconditional INSERT ALL 4-21 Conditional INSERT ALL: Example 4-23 Conditional INSERT ALL 4-24 Conditional INSERT FIRST: Example 4-25 Conditional INSERT FIRST 4-26 Pivoting INSERT 4-28 Lesson Agenda 4-31 MERGE Statement 4-32 MERGE Statement Syntax 4-33 Merging Rows: Example 4-34 Lesson Agenda 4-37 Tracking Changes in Data 4-38 Example of the Flashback Version Query 4-39 VERSIONS BETWEEN Clause 4-41 Summary 4-42 Practice 4: Overview 4-43Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 7. vii 5 Managing Data in Different Time Zones Objectives 5-2 Lesson Agenda 5-3 Time Zones 5-4 TIME_ZONE Session Parameter 5-5 CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP 5-6 Comparing Date and Time in a Session’s Time Zone 5-7 DBTIMEZONE and SESSIONTIMEZONE 5-9 TIMESTAMP Data Types 5-10 TIMESTAMP Fields 5-11 Difference Between DATE and TIMESTAMP 5-12 Comparing TIMESTAMP Data Types 5-13 Lesson Agenda 5-14 INTERVAL Data Types 5-15 INTERVAL Fields 5-17 INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH: Example 5-18 INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND Data Type: Example 5-20 Lesson Agenda 5-21 EXTRACT 5-22 TZ_OFFSET 5-23 FROM_TZ 5-25 TO_TIMESTAMP 5-26 TO_YMINTERVAL 5-27 TO_DSINTERVAL 5-28 Daylight Saving Time 5-29 Summary 5-31 Practice 5: Overview 5-32 6 Retrieving Data Using Subqueries Objectives 6-2 Lesson Agenda 6-3 Multiple-Column Subqueries 6-4 Column Comparisons 6-5 Pairwise Comparison Subquery 6-6 Nonpairwise Comparison Subquery 6-8 Lesson Agenda 6-10 Scalar Subquery Expressions 6-11 Scalar Subqueries: Examples 6-12 Lesson Agenda 6-14 Correlated Subqueries 6-15Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 8. viii Using Correlated Subqueries 6-17 Lesson Agenda 6-19 Using the EXISTS Operator 6-20 Find Employees Who Have at Least One Person Reporting to Them 6-21 Find All Departments That Do Not Have Any Employees 6-22 Correlated UPDATE 6-23 Using Correlated UPDATE 6-24 Correlated DELETE 6-26 Using Correlated DELETE 6-27 Lesson Agenda 6-28 WITH Clause 6-29 WITH Clause: Example 6-30 Summary 6-32 Practice 6: Overview 6-34 7 Regular Expression Support Objectives 7-2 Lesson Agenda 7-3 What Are Regular Expressions? 7-4 Benefits of Using Regular Expressions 7-5 Using the Regular Expressions Functions and Conditions in SQL and PL/SQL 7-6 Lesson Agenda 7-7 What Are Metacharacters? 7-8 Using Metacharacters with Regular Expressions 7-9 Lesson Agenda 7-11 Regular Expressions Functions and Conditions: Syntax 7-12 Performing a Basic Search Using the REGEXP_LIKE Condition 7-13 Replacing Patterns Using the REGEXP_REPLACE Function 7-14 Finding Patterns Using the REGEXP_INSTR Function 7-15 Extracting Substrings Using the REGEXP_SUBSTR Function 7-16 Lesson Agenda 7-17 Subexpressions 7-18 Using Subexpressions with Regular Expression Support 7-19 Why Access the nth Subexpression? 7-20 REGEXP_SUBSTR: Example 7-21 Lesson Agenda 7-22 Using the REGEXP_COUNT Function 7-23 Regular Expressions and Check Constraints: Examples 7-24 Summary 7-25 Practice 7: Overview 7-26Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 9. ix Appendix A: Practice Solutions Appendix B: Table Descriptions Appendix C: Using the SQL Developer GUI Appendix D: Using SQL*Plus Appendix E: Generating Reports by Grouping Related Data Appendix F: Hierarchical Retrieval Appendix G: Writing Advanced Scripts Appendix H: Oracle Database Architectural Components Index Additional Practices Additional Practice Solutions Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 10. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 11. Preface Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 12. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 13. Preface - 3 Profile Before You Begin This Course Before you begin this course, you should have working experience with SQL. How This Course Is Organized Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II is an instructor-led course featuring lectures and hands-on exercises. Online demonstrations and written practice sessions reinforce the concepts and skills that are introduced. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 14. Preface - 4 Related Publications Oracle Publications Title Part Number Oracle® Database Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) B28320-01 Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g – Release 1 (11.1) B28286-01 Oracle® Database Concepts 11g Release 1 (11.1) B28318-01 Oracle® Database Advanced Application Developer’s Guide – 11g Release 1 (11.1) B28424-01 SQL*Plus® User’s Guide and Reference Release 11.1 B31189-01 Oracle Database SQL Developer User's Guide Release 1.2 E10406-01 Additional Publications • System release bulletins • Installation and user’s guides • read.me files • International Oracle User’s Group (IOUG) articles • Oracle Magazine Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 15. Preface - 5 Typographic Conventions What follows are two lists of typographical conventions that are used specifically within text or within code. Typographic Conventions Within Text Convention Object or Term Example Uppercase Commands, Use the SELECT command to view functions, information stored in the LAST_NAME column names, column of the EMPLOYEES table. table names, PL/SQL objects, schemas Lowercase, Filenames, where: role is the name of the role italic syntax variables, to be created. usernames, passwords Initial cap Trigger and Assign a When-Validate-Item trigger to button names the ORD block. Choose Cancel. Italic Books, names of For more information on the subject see courses and Oracle SQL Reference manuals, and Manual emphasized words or phrases Do not save changes to the database. Quotation marks Lesson module This subject is covered in Lesson 3, titles referenced “Working with Objects.” within a course Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 16. Preface - 6 Typographic Conventions (continued) Typographic Conventions Within Code Convention Object or Term Example Uppercase Commands, SELECT employee_id functions FROM employees; Lowercase, Syntax variables CREATE ROLE role; italic Initial cap Forms triggers Form module: ORD Trigger level: S_ITEM.QUANTITY item Trigger name: When-Validate-Item . . . Lowercase Column names, . . . table names, OG_ACTIVATE_LAYER filenames, (OG_GET_LAYER ('prod_pie_layer')) PL/SQL objects . . . SELECT last_name FROM employees; Bold Text that must CREATE USER scott be entered by a IDENTIFIED BY tiger; user Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 17. __________________ Additional Practices __________________ Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 18. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 2 The following exercises can be used for extra practice after you have discussed data manipulation language (DML) and data definition language (DDL) statements in the lessons titled “Managing Schema Objects” and “Manipulating Large Data Sets.” Note: Run the lab_ap_cre_special_sal.sql, lab_ap_cre_sal_history.sql, and lab_ap_cre_mgr_history.sql scripts in the labs folder to create the SPECIAL_SAL, SAL_HISTORY, and MGR_HISTORY tables. 1. The Human Resources department wants to get a list of underpaid employees, salary history of employees, and salary history of managers based on an industry salary survey. So they have asked you to do the following: Write a statement to do the following: - Retrieve details such as the employee ID, hire date, salary, and manager ID of those employees whose employee ID is more than or equal to 200 from the EMPLOYEES table. - If the salary is less than $5,000, insert details such as the employee ID and salary into the SPECIAL_SAL table. - Insert details such as the employee ID, hire date, and salary into the SAL_HISTORY table. - Insert details such as the employee ID, manager ID, and salary into the MGR_HISTORY table. 2. Query the SPECIAL_SAL, SAL_HISTORY, and MGR_HISTORY tables to view the inserted records. SALARY_HISTORY SPECIAL_SAL Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 19. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 3 3. Nita, the DBA, needs you to create a table, which has a primary key constraint, but she wants to name the index to have a different name than the constraint. Create the LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX table based on the following table instance chart. Name the index for the PRIMARY KEY column as LOCATIONS_PK_IDX. 4. Query the USER_INDEXES table to display the INDEX_NAME for the LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX table. Column Name Deptno Dname Primary Key Yes Data Type Number VARCHAR2 Length 4 30 MGR_HISTORY Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 20. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 4 The following exercises can be used for extra practice after you have discussed datetime functions. You work for a global company and the new vice president of operations wants to know the different time zones of all the company branches. The new vice president has requested the following information: 5. Alter the session to set the NLS_DATE_FORMAT to DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS. 6. a. Write queries to display the time zone offsets (TZ_OFFSET) for the following time zones: Australia/Sydney Chile/Easter Island b. Alter the session to set the TIME_ZONE parameter value to the time zone offset of Australia/Sydney. c. Display SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP for this session. Note: The output might be different based on the date when the command is executed. d. Alter the session to set the TIME_ZONE parameter value to the time zone offset of Chile/Easter Island. Note: The results of the preceding question are based on a different date, and in some cases, they will not match the actual results that the students get. Also, the time zone offset of the various countries may differ, based on daylight saving time. e. Display SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP for this session. Note: The output may be different based on the date when the command is executed. f. Alter the session to set NLS_DATE_FORMAT to DD-MON-YYYY. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 21. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 5 Note • Observe in the preceding question that CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP are all sensitive to the session time zone. Observe that SYSDATE is not sensitive to the session time zone. • The results of the preceding question are based on a different date, and in some cases, they will not match the actual results that the students get. Also the time zone offset of the various countries may differ, based on daylight saving time. 7. The Human Resources department wants a list of employees who are up for review in January, so they have requested you to do the following: Write a query to display the last names, month of the date of hire, and hire date of those employees who have been hired in the month of January, irrespective of the year of hire. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 22. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 6 The following exercises can be used for extra practice after you have discussed advanced subqueries. 8. The CEO needs a report on the top three earners in the company for profit sharing. You are responsible to provide the CEO with a list. Write a query to display the top three earners in the EMPLOYEES table. Display their last names and salaries. 9. The benefits for the state of California have been changed based on a local ordinance. So the benefits representative has asked you to compile a list of the people who are affected. Write a query to display the employee ID and last names of the employees who work in the state of California. Hint: Use scalar subqueries. 10. Nita, the DBA, wants to remove old information from the database. One of the things she thinks is unnecessary is the old employment records. She has asked you to do the following: Write a query to delete the oldest JOB_HISTORY row of an employee by looking up the JOB_HISTORY table for the MIN(START_DATE) for the employee. Delete the records of only those employees who have changed at least two jobs. Hint: Use a correlated DELETE command. 11. The vice president of Human Resources needs the complete employment records for the annual employee recognition banquet speech. The vice president makes a quick phone call to stop you from following the DBA’s orders. Roll back the transaction. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 23. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 7 12. The sluggish economy is forcing management to take cost reduction actions. The CEO wants to review the highest paid jobs in the company. You are responsible to provide the CEO with a list based on the following specifications: Write a query to display the job IDs of those jobs whose maximum salary is above half the maximum salary in the entire company. Use the WITH clause to write this query. Name the query MAX_SAL_CALC. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
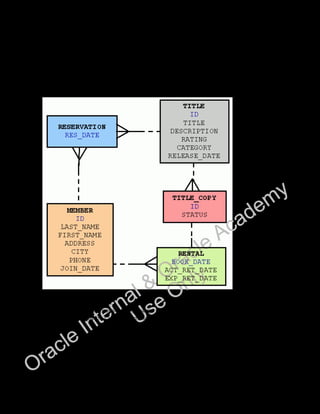
- 24. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 8 Additional Practices: Case Study In the case study for the SQL Fundamentals I course, you built a set of database tables for a video application. In addition, you inserted, updated, and deleted records in a video store database and generated a report. The following is a diagram of the tables and columns that you created for the video application: Note: First, run the dropvid.sql script in the labs folder to drop tables if they already exist. Then run the buildvid.sql script in the labs folder to create and populate the tables. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 25. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 9 Additional Practices: Case Study (continued) 1. Verify that the tables were created properly by running a report to show the list of tables and their column definitions. 2. Verify the existence of the MEMBER_ID_SEQ and TITLE_ID_SEQ sequences in the data dictionary. 3. You want to create some users who have access only to their own rentals. Create a user called Carmen and grant her the privilege to select from the RENTAL table. Note: Make sure to prefix the user name with your database account. For example, if you are the user oraxx, then create a user called oraxx_Carmen.Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 26. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 10 Additional Practices: Case Study (continued) 4. Add a price column (number 4,2) to the TITLE table to store how much it costs to rent the title. 5. Add a CATEGORY table to store CATEGORY_ID and CATEGORY_DESCRIPTION. The table has a foreign key with the CATEGORY column in the TITLE table. 6. Select all the tables from the data dictionary. 7. There is no real need to store reservations any longer. You can drop the table. 8. Create a RENTAL_HISTORY table to store the details of a rental by member for the last 6 months. (Hint: You can copy the RENTAL table.) 9. Show a list of the top 10 titles rented in the last month grouped by category. 10. You want to calculate the late fee (price of title/day) if the member brings back the video 6 days late. 11. Show a list of members who have rented 2 or more times. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 27. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practices - 11 Additional Practices: Case Study (continued) 12. Show a list of titles who have a status of rented. 13. Show a list of members who have “99” in their phone numbers. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 28. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 29. _______________ Additional Practice Solutions _______________ Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 30. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 2 The following exercises can be used for extra practice after you have discussed data manipulation language (DML) and data definition language (DDL) statements in the lessons titled “Managing Schema Objects” and “Manipulating Large Data Sets.” Note: Run the lab_ap_cre_special_sal.sql, lab_ap_cre_sal_history.sql, and lab_ap_cre_mgr_history.sql scripts in the labs folder to create the SPECIAL_SAL, SAL_HISTORY, and MGR_HISTORY tables. 1. The Human Resources department wants to get a list of underpaid employees, salary history of employees, and salary history of managers based on an industry salary survey. So they have asked you to do the following: Write a statement to do the following: - Retrieve details such as the employee ID, hire date, salary, and manager ID of those employees whose employee ID is more than or equal to 200 from the EMPLOYEES table. - If the salary is less than $5,000, insert details such as the employee ID and salary into the SPECIAL_SAL table. - Insert details such as the employee ID, hire date, and salary into the SAL_HISTORY table. - Insert details such as the employee ID, manager ID, and salary into the MGR_HISTORY table. INSERT ALL WHEN SAL < 5000 THEN INTO special_sal VALUES (EMPID, SAL) ELSE INTO sal_history VALUES(EMPID,HIREDATE,SAL) INTO mgr_history VALUES(EMPID,MGR,SAL) SELECT employee_id EMPID, hire_date HIREDATE, salary SAL, manager_id MGR FROM employees WHERE employee_id >=200; 2. Query the SPECIAL_SAL, SAL_HISTORY, and the MGR_HISTORY tables to view the inserted records. SELECT * FROM special_sal; SELECT * FROM sal_history; SELECT * FROM mgr_history; Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 31. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 3 3. Nita, the DBA, needs you to create a table, which has a primary key constraint, but she wants to name the index to have a different name than the constraint. Create the LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX table based on the following table instance chart. Name the index for the PRIMARY KEY column as LOCATIONS_PK_IDX. CREATE TABLE LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX (location_id NUMBER(4) PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX (CREATE INDEX locations_pk_idx ON LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX(location_id)), location_name VARCHAR2(20)); 4. Query the USER_INDEXES table to display the INDEX_NAME for the LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX table. SELECT INDEX_NAME, TABLE_NAME FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE TABLE_NAME = ‘LOCATIONS_NAMED_INDEX’; Column Name Deptno Dname Primary Key Yes Data Type Number VARCHAR2 Length 4 30 Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 32. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 4 The following exercises can be used for extra practice after you have discussed datetime functions. You work for a global company and the new vice president of operations wants to know the different time zones of all the company branches. The new vice president has requested the following information: 5. Alter the session to set NLS_DATE_FORMAT to DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS. ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT = ‘DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS’; 6. a. Write queries to display the time zone offsets (TZ_OFFSET) for the following time zones: - Australia/Sydney SELECT TZ_OFFSET (‘Australia/Sydney’) from dual; - Chile/Easter Island SELECT TZ_OFFSET (‘Chile/EasterIsland’) from dual; b. Alter the session to set the TIME_ZONE parameter value to the time zone offset of Australia/Sydney. ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE = ‘+10:00’; c. Display SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP for this session. Note: The output may be different based on the date when the command is executed. SELECT SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LOCALTIMESTAMP FROM DUAL; d. Alter the session to set the TIME_ZONE parameter value to the time zone offset of Chile/Easter Island. Note: The results of the preceding question are based on a different date, and in some cases, they will not match the actual results that the students get. Also, the time zone offset of the various countries may differ, based on daylight saving time. ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE = ‘-06:00’; e. Display SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP for this session. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 33. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 5 Note: The output may be different based on the date when the command is executed. SELECT SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LOCALTIMESTAMP FROM DUAL; f. Alter the session to set NLS_DATE_FORMAT to DD-MON-YYYY. ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT = ‘DD-MON-YYYY’; Note • Observe in the preceding question that CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP are all sensitive to the session time zone. Observe that SYSDATE is not sensitive to the session time zone. • The results of the preceding question are based on a different date, and in some cases, they will not match the actual results that the students get. Also, the time zone offset of the various countries may differ, based on daylight saving time. 7. The Human Resources department wants a list of employees who are up for review in January, so they have requested you to do the following: Write a query to display the last names, month of the date of hire, and hire date of those employees who have been hired in the month of January, irrespective of the year of hire. SELECT last_name, EXTRACT (MONTH FROM HIRE_DATE), HIRE_DATE FROM employees WHERE EXTRACT (MONTH FROM HIRE_DATE) = 1; Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 34. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 6 The following exercises can be used for extra practice after you have discussed advanced subqueries. 8. The CEO needs a report on the top three earners in the company for profit sharing. You are responsible to provide the CEO with a list. Write a query to display the top three earners in the EMPLOYEES table. Display their last names and salaries. SELECT last_name, salary FROM employees e WHERE 3 > (SELECT COUNT (*) FROM employees WHERE e.salary < salary); 9. The benefits for the state of California have been changed based on a local ordinance. So the benefits representative has asked you to compile a list of the people who are affected. Write a query to display the employee ID and last names of the employees who work in the state of California. Hint: Use scalar subqueries. SELECT employee_id, last_name FROM employees e WHERE ((SELECT location_id FROM departments d WHERE e.department_id = d.department_id ) IN (SELECT location_id FROM locations l WHERE state_province = ‘California’)); 10. Nita, the DBA, wants to remove old information from the database. One of the things she thinks is unnecessary is the old employment records. She has asked you to do the following: Write a query to delete the oldest JOB_HISTORY row of an employee by looking up the JOB_HISTORY table for the MIN(START_DATE)for the employee. Delete the records of only those employees who have changed at least two jobs. Hint: Use a correlated DELETE command. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 35. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 7 DELETE FROM job_history JH WHERE employee_id = (SELECT employee_id FROM employees E WHERE JH.employee_id = E.employee_id AND START_DATE = (SELECT MIN(start_date) FROM job_history JH WHERE JH.employee_id = E.employee_id) AND 3 > (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM job_history JH WHERE JH.employee_id = E.employee_id GROUP BY EMPLOYEE_ID HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2)); 11. The vice president of Human Resources needs the complete employment records for the annual employee recognition banquet speech. The vice president makes a quick phone call to stop you from following the DBA’s orders. Roll back the transaction. ROLLBACK; 12. The sluggish economy is forcing management to take cost reduction actions. The CEO wants to review the highest paid jobs in the company. You are responsible to provide the CEO with a list based on the following specifications: Write a query to display the job IDs of those jobs whose maximum salary is above half the maximum salary in the entire company. Use the WITH clause to write this query. Name the query MAX_SAL_CALC. WITH MAX_SAL_CALC AS (SELECT job_title, MAX(salary) AS job_total FROM employees, jobs WHERE employees.job_id = jobs.job_id GROUP BY job_title) SELECT job_title, job_total FROM MAX_SAL_CALC WHERE job_total > (SELECT MAX(job_total) * 1/2 FROM MAX_SAL_CALC) ORDER BY job_total DESC; Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 36. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 8 Additional Practices: Case Study Solutions In the case study for the SQL Fundamentals I course, you built a set of database tables for a video application. In addition, you inserted, updated, and deleted records in a video store database and generated a report. The following is a diagram of the tables and columns that you created for the video application: Note: First, run the dropvid.sql script in the labs folder to drop tables if they already exist. Then run the buildtab.sql script in the labs folder to create and populate the tables. Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only
- 37. Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals II Additional Practice Solutions - 9 Additional Practices: Case Study Solutions (continued) 1. Verify that the tables were created properly by running a report to show the list of tables and their column definitions. SELECT table_name,column_name,data_type,nullable FROM user_tab_columns WHERE table_name IN('MEMBER','TITLE','TITLE_COPY','RENTAL','RESERVATION'); 2. Verify the existence of the MEMBER_ID_SEQ and TITLE_ID_SEQ sequences in the data dictionary. SELECT sequence_name FROM user_sequences; 3. You want to create some users who have access only to their own rentals. Create a user called Carmen and grant her the privilege to select from the RENTAL table. Note: Make sure to prefix the user name with your database account. For example, if you are the user oraxx, then create a user called oraxx_Carmen. CREATE USER oraxx_carmen IDENTIFIED BY oracle ; GRANT select ON rental TO oraxx_carmen; 4. Add a price column (number 4,2) to the TITLE table to store how much it costs to rent the title. ALTER TABLE title ADD(price NUMBER(6)) 5. Add a CATEGORY table to store CATEGORY_ID and CATEGORY_DESCRIPTION. The table has a foreign key with the CATEGORY column in the TITLE table. CREATE TABLE CATEGORY ( "CATEGORY_ID" NUMBER(6,0) NOT NULL ENABLE, "CATEGORY_DESCRIPTION" VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE), CONSTRAINT "CATEGORY_PK" PRIMARY KEY ("CATEGORY_ID")) 6. Select all the tables from the data dictionary. SELECT table_name FROM user_tables order by table_name; 7. There is no real need to store reservations any longer. You can drop the table. DROP TABLE reservation cascade constraints; 8. Create a RENTAL_HISTORY table to store the details of a rental by member for the last 6 months. (Hint: You can copy the RENTAL table.) CREATE TABLE rental_history as select * from rental where '1' = '1' Oracle Internal & Oracle Academy Use Only