A Breif On Cloud computing
- 1. Done By, RAJARAMAN G 3rd year [B.Tech]
- 2. Introduction History on Cloud Cloud Design Types Of Cloud Service SaaS Virtualization PaaS IaaS CaaS IDaaS Comparison Of SaaS, PaaS, IaaS The Pros and Cons Of Cloud The Future Of Cloud
- 3. Cloud computing defines taking services and moving them outside an organizations firewall on shared systems. Is a metaphor for the Internet. Refer to Internet based development and services. Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources Access your data anytime and anywhere.
- 4. When we think of cloud computing, we come across the thought when it was invented. It was a gradual evolution that started in the 1950s with mainframe computing. After some time, around 1970, the concept of virtual machines (VMs) was created. In the 1990s, telecommunications companies started offering virtualized private network connections. In 21st century cloud computing came into existence.
- 5. o Grid computing: Solving large problems with parallel computing. o Utility computing: Offering computing resources as a metered service. o SaaS: Network-based subscriptions to applications. o Cloud computing: Anytime, anywhere access to IT resources delivered dynamically as a service
- 7. The cloud follows some basic characteristics: RESOURCE SCALING ELASTICITY LESS COST HIGH SECURITY VIRTUALIZATIONHOMOGENITY HIGH SPEED RECOVERY BROAD ACCESS OF NETWORK
- 8. The four dimensions of the Cloud Cube Model are shown in Figure 1.2 and listed here: • Physical location of the data: Internal (I) / External (E) determines your organization's boundaries. • Ownership: Measure of not only the technology ownership, but of interoperability, ease of data transfer, and degree of vendor application lock-in. • Security boundary: Perimeterised /De-perimiterised is a measure of whether the operation is inside or outside the security boundary or network firewall. • Sourcing: In sourced or Outsourced means whether the service is provided by the customer or the service provider.
- 10. People are risk averse and loss averse. People value what they own more than what they are given. People favor things that are free. People discount future risk and favor instant gratification. People value what they own more than what they are given. Measuring cloud computing costs The cost of a cloud computing deployment is roughly estimated to be CostCLOUD = Σ(UnitCostCLOUD x (Revenue – CostCLOUD))
- 11. Clients can connect to a cloud service in a number of different ways. These are the two most common means: • A Web browser • A proprietary application There are three basic methods for securely connecting over a connection: • Use a secure protocol to transfer data such as SSL , FTPS or connect using a secure shell such as SSH to connect a client to the cloud. • Create a virtual connection using a virtual private network (VPN), or with a remote data transfer protocol such as Microsoft RDP or Citrix ICA, where the data is protected by a tunneling mechanism. • Encrypt the data so that even if the data is intercepted or sniffed, the data will not be meaningful.
- 12. o If any cloud-computing system resource is difficult to plan for, it is network capacity. The three aspects of N/W capacity: o Network traffic to and from the network interface at the server, be it a physical or virtual interface or server o Network traffic from the cloud to the network interface o Network traffic from the cloud through your ISP to your local network interface. To measure network traffic at a server's network interface, you need to employ is known as a network monitor, which is a form of packet analyzer. Microsoft includes a utility called the Microsoft Network Monitor as part of its server utilities.
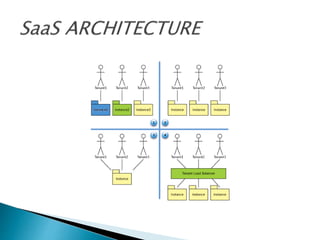
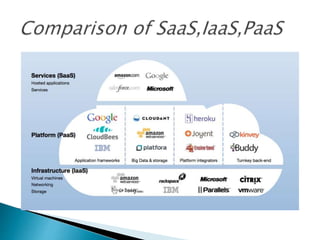
- 13. The 3 types of service are: SaaS: Provides Applications. PaaS: Deploy Customer Created Applications. IaaS: Rent Processing , N/W Resources. Software as a Service(SaaS) Platform as a Service(PaaS) Infracture as a Service(IaaS)
- 15. Here I compare SaaS arch with marketing strategies:
- 16. The emergence of SaaS as an effective software-delivery mechanism creates an opportunity to change their focus from deploying and supporting applications to managing the services that those applications provide. SaaS as a concept is often associated with the application service providers (ASPs) of the 1990s A typical SaaS application is offered either directly by the vendor or by an intermediary party called an aggregator, which bundles SaaS offerings from different vendors and offers them as part of a unified application platform.
- 17. Managing the Risks of Software Acquisition SaaS applications don't require the deployment of a large infrastructure at the client's location, which eliminates or drastically reduces the upfront commitment of resources. Managing IT Focus Testing and installing patches, managing upgrades, monitoring performance, ensuring high availability, and so forth—is handled by the provider.
- 18. The 4 levels of SaaS given below: 1st Level: Ad-Hoc/Custom – One Instance per customer 2nd Level: Configurable per customer 3rd Level: configurable & Multi-Tenant-Efficient 4th Level: Scalable, Configurable & Multi-Tenant- Efficient
- 19. SaaS applications are distinguished by their conceptual locations on three different continua. Licensing: On-premise applications typically are licensed in perpetuity, with a single up-front cost for each user or owned outright. SaaS applications often are licensed with a usage- based transaction model, in which the customer is only billed for the number of service transactions used. In between is the familiar time-based subscription model, in which the customer pays a flat fee per seat for a particular time period and is allowed unlimited use of the service during that period.
- 20. Location: SaaS applications are installed at the SaaS hoster's location, while on-premise applications are, of course, installed within your own IT environment. In between is the appliance model, in which the vendor supplies a hardware/software component as a "black box" that is installed at your location, instead of the others. Management: Traditionally, the IT department is responsible for providing IT service to users, which means being familiar with network, server, and application platforms, providing support and troubleshooting and resolving IT security, reliability, performance, and availability problems.
- 21. The model of SaaS continua is shown below :
- 22. Political considerations: Decision can be short-circuited by resistance within an organization, if people insist that certain functionality remain internal, under the control of IT.
- 23. Technical considerations: SaaS applications typically provide some flexibility for customer configuration, but this approach has its limitations. If an important application requires specialized technical knowledge to operate and support, or requires customization that a SaaS vendor cannot offer, it might not be possible to pursue a SaaS solution for the application. Financial considerations: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) of a SaaS application, compared to that of an equivalent on-premise application. Legal considerations: Some industries are subject to regulatory law in different parts of the world, which imposes various reporting and recordkeeping requirements that your potential SaaS solution candidates cannot satisfy. Consider the regulatory environments in all the different jurisdictions in which your organization operates and how they affect your application needs.
- 24. Interface with the infrastructure via the APIs. Flexibility and elasticity Pay as much as used and needed Transparent to users and applications Built on clusters of PC servers CPU, storage, server capacity, load balancing, and databases
- 25. Cloud computing layers additional technologies such as self- service provisioning onto virtualization. The VM role for Windows Azure is similar to other server roles. VMs on Windows Azure run a version of the Windows Server OS. The difference with the VM role is that you can create, and customize the server to meet your needs. The end user has the same experience on a virtual machine as they would have on dedicated hardware. Virtual machines do not require specialized hypervisor- specific hardware.
- 27. Reduce the data centre footprint. Easier to create new machines, backup machines, etc… Faster server provisioning. Increase uptime. Extend the life of older applications. Help move things to the cloud. Easy migration of virtual machines. Debug problems.
- 28. Software that manipulates hardware, while cloud refers to a service that results from that manipulation. It is a foundational element of cloud computing and helps deliver on the value of cloud computing. A private cloud, in its own virtualized environment, gives users the best. It Maximize resources, IT budget integration , Multiple systems. This makes servers, workstations, storage and other systems independent of the physical hardware layer.
- 29. Cloud is used most because: Agility improves with users, Cost reductions Security,performace and productivity. Multitenancy enables sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users. Reliability improves with the use of multiple redundant sites. Control of data, and service parameters.
- 31. Amazon- Amazon always excelled at delivering computing capacity at a large scale to its own employees and to consumers. Enomaly- Software that integrates enterprise data centers with commercial cloud computing offerings. Google- Google Apps was the company's attempt to branch out beyond the consumer search market and become a player in the enterprise. Microsoft- Microsoft made its name by developing the operating system for home and work computers. But with all forms of applications moving to the Web-hosted model.
- 34. Cloud storage is a model of data storage where the digital data is stored in logical pools. Based on highly virtualized infrastructure and is like broader cloud computing in terms of accessible interfaces. This typically refers to a hosted object storage service, but the term has broadened to include other types of data storage that are now available as a service, like block storage.
- 35. It has loads of different distributed resources. It reduces the fault occurs during the process. Durability is great. Allows Word and Excel documents to be edited directly from your browser. Provides users with immediate access to a broad range of resources. Storage availability and data protection is intrinsic to object.
- 36. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): ◦ Elastic, marshal 1 to 100+ PCs via WS,Fairly cheap! Powered by Xen – a Virtual Machine: ◦ Different from Vm’ware and VPC as uses “para- virtualization” where the guest OS is modified to use hyper- calls ◦ Hardware contributions by Intel and AMD (AMD-V). ◦ Supports “Live Migration” of a virtual machine between hosts. Linux, Windows, OpenSolaris Management Console/AP
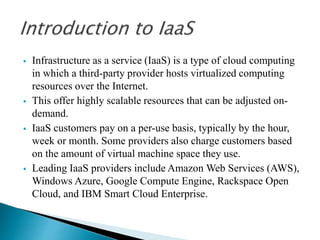
- 37. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing in which a third-party provider hosts virtualized computing resources over the Internet. This offer highly scalable resources that can be adjusted on- demand. IaaS customers pay on a per-use basis, typically by the hour, week or month. Some providers also charge customers based on the amount of virtual machine space they use. Leading IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Windows Azure, Google Compute Engine, Rackspace Open Cloud, and IBM Smart Cloud Enterprise.
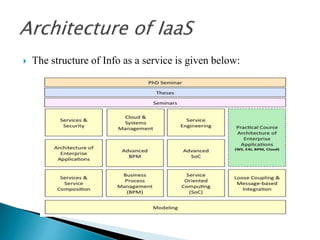
- 38. The structure of Info as a service is given below:
- 40. Scalability No single point of failure Physical security of data centre locations Reduces TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) Flexible offering Location independence
- 41. • On-demand self-service: A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as compute time, n/w connectivity and storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction. • Broad network access • Resource pooling: Examples of computing resources include storage, processing (compute), memory, network bandwidth, and virtual machines. Rapid elasticity: To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be purchased in any quantity at any time.
- 42. Private cloud: The cloud infrastructure is operated solely for an organization. It may be managed by the organization or a third party and may exist on premise or off premise. Community cloud: The cloud infrastructure is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy). It may be managed by the organizations or a third party and may exist on premise or off premise. Public cloud: The cloud infrastructure is made available to the general public or a large industry group and is owned by an organization selling cloud services. Hybrid cloud: The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability.
- 43. Pros: High degree of control over facilities. Guaranteed capacity and easier expansion planning. Potential for greater power efficiency through specialization. Easier security management with a single-tenant facility. Cons: Limited geographic expansion abilities. More limited connectivity options. Tendency to run lower-tier facilities. Distracting to the core business. Very capital intensive.
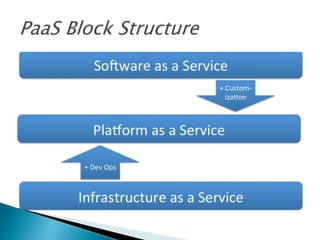
- 44. The ultimate goal of a PaaS is to make it easier for you to run your website or web application no matter how much traffic it gets. A platform as a service should handle scaling seamlessly for you so you can just focus on your website and the code running it. As a programmer, you leverage pre-existing code rather than starting from scratch and writing everything. The most well-known software platforms for desktop software are Windows and Mac OS.
- 47. • A platform may even provide a way to accomplish things that would otherwise not be possible at all. • Additional features such as email distribution lists, contact form handler and other tools that make it easier to run a website are part of almost every hosting service. • Web platforms today provide a significant level of automation, control, and tools. • Hosting layer is analogous to desktop computer hardware and the platform layer is analogous to a desktop operating system.
- 48. There is always a conflict between the developers and the System Engineers. Developers are keen on getting their environments up without waiting. System Engineers care about performance and stability. Creates a peaceful environment for both parties.
- 50. PaaS is a category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run and manage Web applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure. Public PaaS: Derived from software as a service(SaaS), and is situated in cloud computing between SaaS and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Mobile PaaS: Initiated in 2012, mobile PaaS (mPaaS) provides development capabilities for mobile app designers and developers.
- 51. Public PaaS providers and private PaaS vendors include: Active State AWS Elastic Beanstalk Cloud Foundry Engine Yard Google App Engine Microsoft Azure Web Sites Oracle Pivotal Software Red Hat Wave Maker
- 52. Pros: Automatic Updates. Decreased Costs. Teams Can Collaborate From A far. Assured Compatibility. Cons: Limited Scalability. Lock-In.
- 53. The establishment and proof of an identity is a central network function. An identity is a set of characteristics or traits that make something recognizable or known. To establish your identity on a network, you might be asked to provide a name and password, which is called a single-factor authentication method. Identity protection is one of the more expensive and complex areas of network computing. Identity as a Service provides an easy mechanism for integrating identity services into individual applications with minimal development effort, by allowing the identification logic and storage of an identity's attributes to be maintained externally.
- 54. Compliance as a Service (CaaS) appears in discussions, few examples of this kind of service exist as a general product for a cloud computing architecture. A Compliance as a Service application would need to serve as a trusted third party, because this is a man-in-the-middle type of service. CaaS may need to be architected as its own layer of a SOA architecture in order to be trusted. A CaaS would need to be able to manage cloud relationships, understand security policies and procedures, know how to handle information and privacy, be aware of geography, provide an response and allow for the system to be queried.
- 57. Limit flexibility and innovation. Issues relating to policy and access. Enables services to be used without any understanding of their infrastructure. Performance and Bandwidth Cost. Interoperability and Portability. Reduced time for implementation. Disaster recovery.
- 58. PROS: Improved performance. Reduced costs. Almost Unlimited Storage. Backup and Recovery. CONS: Requires a constant Internet connection. Features might be limited. Very Slow.
- 59. Grid Computing was the last research-led centralised approach. More application availability on the cloud. More hybrid cloud adoption. Increased development for the cloud. The research findings provide some surprising and useful insights into what current and potential users see as the most important benefits of cloud technologies.
![Done By,
RAJARAMAN G
3rd year [B.Tech]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing-150708155326-lva1-app6891/85/A-Breif-On-Cloud-computing-1-320.jpg)