Ad
Advanced data structure
- 1. Advanced Data Structure (using c#) Md. Shakil Ahmed Software Engineer Astha it research & consultancy ltd. Dhaka, Bangladesh
- 2. Introduction Topic Focus: • Trie Tree • Segment Tree • lowest common ancestor (LCA)
- 3. Trie Tree • A trie is an ordered tree data structure that is used to store an associative array where the keys are usually strings.
- 4. Trie Tree Use: • Count Prefixes: This function will count the number of words in the dictionary that have a string prefix as prefix. • Count Words: This function will count the number of words in the dictionary that match exactly with a given string word. • Dictionary: It could be a good data structure for building a memory-efficient dictionary with fast lookups. • Faster Than Hash Table: Looking up data in a trie is faster in the worst case, O(m) time, compared to an imperfect hash table.
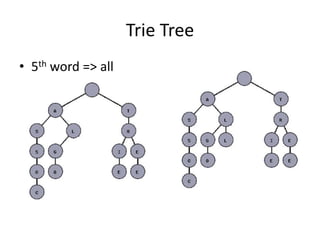
- 5. Trie Tree The next figure shows a trie with the words "tree", "trie", "algo", "assoc", "all", and "also."
- 6. Trie Tree • 1st word => tree
- 7. Trie Tree • 2nd word => trie
- 8. Trie Tree • 3rd word => algo
- 9. Trie Tree • 4th word => assoc
- 10. Trie Tree • 5th word => all
- 11. Trie Tree • 6th word => also
- 12. Trie Tree
- 13. Problem We have some Human name, we can add, delete & search some name. => If number of name is n = 10,00,000, we want to search or delete a name(k is the length of the name), then 1. If we use array, we need O(n*k) complexity. 2. If we sort the array & using binary search then, for search we need O(k * log n) but for delete we need O(n) complexity. 3. If we use trie, we need O(k) complexity for add, search & delete.
- 14. Solution static int[] _count = new int[1000009]; static int[][] _child = new int[1000009][];static int N = 0; static int AddElement(int root, string element, int position) { if (element.Length == position) { _count[root]++; return _count[root]; } else { if (_child[root][element[position] - 'a'] == -1) { _count[N] = 0;_child[N] = new int[26]; for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) _child[N][i] = -1; _child[root][element[position] - 'a'] = N; N++; } return AddElement(_child[root][element[position] - 'a'], element, position + 1); } }
- 15. Solution static void Main(string[] args) { _count[0] = 0; _child[0] = new int[26]; for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) _child[0][i] = -1; N = 1; while (true) { string input = Console.ReadLine(); if (input == null) break; Console.WriteLine(AddElement(0, input.ToLower(), 0)); } }
- 16. Segment Tree • A segment tree is a heap-like data structure that can be used for making update/query operations upon array intervals in logarithmical time. • Query time: O(log n) • Initialize time: O(2 * n) • Update time: O(log n)
- 17. Segment Tree
- 18. Segment Tree E very node v is characterized by tw o param eters B v : beginning of node's w orld (left end ) E v : end of node's w orld (right end) We define the segment tree for the interval [i, j] in the following recursive manner: the first node will hold the information for the interval [i, j] if i<j the left and right son will hold the information for the intervals [i, (i+j)/2] and [(i+j)/2+1, j]
- 19. Segment Tree
- 20. Segment Tree
- 21. Segment Tree
- 23. Segment Tree • Query For 2 to 6
- 24. Segment Tree • Update Element 7 value to 7
- 25. Problem You are given n (1<=n<=100000) integers & 100000 query. Each query you have to change a value of an element Or you have to given the minimum value of a range. => If we use array, then complexity q * n. For the above case it will take, 10000000000 operation, that means 100 sec. => If we use segment tree then complexity is q * log (n). It will take 0.01 sec.
- 26. Solution static int[] element = new int[100009]; static int[] mini = new int[200009];static int[] left = new int[200009];static int[] right = new int[200009]; static int N = 0; static int Init(int start, int end) { if (start == end) { left[N] = -1;right[N] = -1; mini[N] = element[start];N++; return N - 1; } else { int temp = N; N++; left[temp] = Init(start, (start + end) / 2); right[temp] = Init((start + end) / 2 + 1, end); mini[temp] = mini[left[temp]]; if (mini[temp] > mini[right[temp]]) mini[temp] = mini[right[temp]]; return temp; } }
- 27. Solution static int RMQ(int root, int start, int end, int rootStart, int rootEnd) { if (start == rootStart && end == rootEnd) return mini[root]; else if (end <= (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2) return RMQ(left[root], start, end, rootStart, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2); else if ((rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 < start) return RMQ(right[root], start, end, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 + 1, rootEnd); else { int temp1 = RMQ(left[root], start, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2, rootStart, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2); int temp2 = RMQ(right[root], (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 + 1, end, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 + 1, rootEnd); if (temp1 > temp2) temp1 = temp2; return temp1; }}
- 28. Solution static void Update(int root, int index, int value, int rootStart, int rootEnd) { if (rootStart == index && rootEnd == index) mini[root] = value; else { if (index <= (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2) Update(left[root], index, value, rootStart, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2); else Update(right[root], index, value, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 + 1, rootEnd); mini[root] = mini[left[root]]; if (mini[root] > mini[right[root]]) mini[root] = mini[right[root]]; } }
- 29. Solution static void Main(string[] args) for (int q1 = 1; q1 <= q; q1++) { { string input = Console.ReadLine(); input = Console.ReadLine(); string[] inputs = input.Split(' '); int n = Convert.ToInt32(input); int x = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[0]); int y = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[1]); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) int z = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[2]); { input = Console.ReadLine(); if (x == 1) element[i] = Convert.ToInt32(input); Console.WriteLine(RMQ(0, y, z, 0, n } - 1)); else N = 0; Update(0, y, z, 0, n - 1); Init(0, n - 1); } } input = Console.ReadLine(); int q = Convert.ToInt32(input);
- 30. Segment Tree • Segment trees are very powerful, not only because they can be used for RMQ(Range Minimum Query). They are a very flexible data structure, can solve even the dynamic version of RMQ problem, and have numerous applications in range searching problems.
- 31. lowest common ancestor (LCA) • The lowest common ancestor (LCA) is a concept in graph theory and computer science. Let T be a rooted tree with n nodes. The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).
- 32. lowest common ancestor (LCA)
- 33. lowest common ancestor (LCA) • We generate a table.
- 34. lowest common ancestor (LCA) Node 2^0 Parent 2^1 Parent 2^2Parent 1 -1 -1 -1 2 1 -1 -1 3 1 -1 -1 4 2 1 -1 5 4 2 -1 6 3 1 -1 7 5 4 1
- 35. lowest common ancestor (LCA) Node Label 1 1 2 2 3 2 4 3 5 4 6 3 7 5
- 36. lowest common ancestor (LCA)
- 37. lowest common ancestor (LCA)
- 38. Problem You live in a Big country where there are many bi-directional roads connecting the cities. Since the people of the country are quite intelligent, they designed the country such that there is exactly one path to go from one city to another. A path consists of one or more connected roads. Here cities are denoted by integers and each road has a cost of traveling. Now you are given the information about the Country. And you are given some queries, each consists of two cities. You have to find the longest road in the path from one city to another. Input: n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105) denoting the number of cities. Then there will be n-1 lines containing three integers each. They will be given in the form u v w (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, 0 < w ≤ 105, u ≠ v) meaning that there is a road between u and v and the cost of the road is w. The next line contains an integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 25000) denoting the number of queries. Each of the next q lines contains two integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n, x ≠ y).
- 39. Problem Input: 6 Output: 3 6 50 300 2 5 30 2 4 300 300 1 2 100 1 3 200 30 4 14 200 46 25 35 If we solve it only by parent up, then for easy query, we will need O(n) complexity. If we solve it by LCA, then for each query, we will need O(log n) complexity.
- 40. Solution public class Edge { public int node; public int cost;} static List<Edge>[] _connectedNodes = null; static int[] _dfsNumber = null; static int[][] _parent = null; static int[][] _maxCost = null; static void DFS(int node, int parent, int edgeCost, int dfsNumber) { _parent[node][0] = parent; _maxCost[node][0] = edgeCost; _dfsNumber[node] = dfsNumber; for (int i = 0; i < _connectedNodes[node].Count; i++) if (_dfsNumber[_connectedNodes[node][i].node] == -1) DFS(_connectedNodes[node][i].node, node, _connectedNodes[node][i].cost, dfsN umber + 1);
- 41. Solution static void Main(string[] args) { string input = Console.ReadLine(); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { input = Console.ReadLine(); int n = Convert.ToInt32(input); string[] inputs = input.Split(' '); _connectedNodes = new List<Edge>[n + 1]; int x = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[0]); _dfsNumber = new int[n + 1]; int y = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[1]); _parent = new int[n + 1][]; int z = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[2]); _maxCost = new int[n + 1][]; _connectedNodes[x].Add(new Edge { node = y, cost = z }); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) _connectedNodes[y].Add(new Edge { { node = x, cost = z }); _dfsNumber[i] = -1; } _parent[i] = new int[18]; DFS(1, -1, 0, 1); _maxCost[i] = new int[18]; _connectedNodes[i] = new List<Edge>(); }
- 42. Solution for (int j = 1; ; j++) { bool flag = false; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (_parent[i][j - 1] != -1 && _parent[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1] != -1) { _parent[i][j] = _parent[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1]; _maxCost[i][j] = _maxCost[i][j - 1]; if (_maxCost[i][j] < _maxCost[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1]) _maxCost[i][j] = _maxCost[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1]; flag = true; } else _parent[i][j] = -1; } if (!flag)break; }
- 43. Solution input = Console.ReadLine(); int q = Convert.ToInt32(input); for (int q1 = 1; q1 <= q; q1++) { input = Console.ReadLine(); string[] inputs = input.Split(' '); int x = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[0]); int y = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[1]); int max = 0; if (_dfsNumber[x] > _dfsNumber[y]) { int z = x; x = y; y = z; }
- 44. Solution while (_dfsNumber[x] != _dfsNumber[y]) { for (int i = 0; ; i++) { if (_parent[y][i] == -1 || _dfsNumber[_parent[y][i]] < _dfsNumber[x]) { y = _parent[y][i - 1]; break; } else { if (_maxCost[y][i] > max) max = _maxCost[y][i]; } } }
- 45. Solution while (x != y) { else for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++) { { if (_maxCost[x][i] > max) if (_parent[x][i] == _parent[y][i]) { max = _maxCost[x][i]; if (i == 0) if (_maxCost[y][i] > max) { max = _maxCost[y][i]; if (_maxCost[x][i] > max) } max = _maxCost[x][i]; } if (_maxCost[y][i] > max) max = _maxCost[y][i]; } x = _parent[x][i]; Console.WriteLine(max); y = _parent[y][i]; } } } else { x = _parent[x][i - 1]; y = _parent[y][i - 1]; } break; }
- 46. Thanks!













![Solution
static int[] _count = new int[1000009];
static int[][] _child = new int[1000009][];static int N = 0;
static int AddElement(int root, string element, int position)
{ if (element.Length == position)
{ _count[root]++;
return _count[root]; }
else
{ if (_child[root][element[position] - 'a'] == -1)
{ _count[N] = 0;_child[N] = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
_child[N][i] = -1;
_child[root][element[position] - 'a'] = N;
N++;
}
return AddElement(_child[root][element[position] - 'a'], element, position + 1);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-14-320.jpg)
![Solution
static void Main(string[] args)
{
_count[0] = 0;
_child[0] = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
_child[0][i] = -1;
N = 1;
while (true)
{
string input = Console.ReadLine();
if (input == null)
break;
Console.WriteLine(AddElement(0, input.ToLower(), 0));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-15-320.jpg)


![Segment Tree
E very node v is characterized by tw o param eters
B v : beginning of node's w orld (left end )
E v : end of node's w orld (right end)
We define the segment tree for the interval [i, j] in the
following recursive manner:
the first node will hold the information for the interval [i, j]
if i<j the left and right son will hold the information for the
intervals [i, (i+j)/2] and [(i+j)/2+1, j]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-18-320.jpg)







![Solution
static int[] element = new int[100009];
static int[] mini = new int[200009];static int[] left = new int[200009];static
int[] right = new int[200009];
static int N = 0;
static int Init(int start, int end)
{
if (start == end)
{ left[N] = -1;right[N] = -1;
mini[N] = element[start];N++;
return N - 1; }
else
{ int temp = N; N++;
left[temp] = Init(start, (start + end) / 2);
right[temp] = Init((start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
mini[temp] = mini[left[temp]];
if (mini[temp] > mini[right[temp]])
mini[temp] = mini[right[temp]];
return temp; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-26-320.jpg)
![Solution
static int RMQ(int root, int start, int end, int rootStart, int rootEnd)
{
if (start == rootStart && end == rootEnd)
return mini[root];
else if (end <= (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2)
return RMQ(left[root], start, end, rootStart, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2);
else if ((rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 < start)
return RMQ(right[root], start, end, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 + 1, rootEnd);
else
{
int temp1 = RMQ(left[root], start, (rootStart + rootEnd) /
2, rootStart, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2);
int temp2 = RMQ(right[root], (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 + 1, end, (rootStart +
rootEnd) / 2 + 1, rootEnd);
if (temp1 > temp2)
temp1 = temp2;
return temp1;
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-27-320.jpg)
![Solution
static void Update(int root, int index, int value, int rootStart, int rootEnd)
{
if (rootStart == index && rootEnd == index)
mini[root] = value;
else
{
if (index <= (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2)
Update(left[root], index, value, rootStart, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2);
else
Update(right[root], index, value, (rootStart + rootEnd) / 2 +
1, rootEnd);
mini[root] = mini[left[root]];
if (mini[root] > mini[right[root]])
mini[root] = mini[right[root]];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-28-320.jpg)
![Solution
static void Main(string[] args) for (int q1 = 1; q1 <= q; q1++)
{ {
string input = Console.ReadLine(); input = Console.ReadLine();
string[] inputs = input.Split(' ');
int n = Convert.ToInt32(input); int x = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[0]);
int y = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) int z = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[2]);
{
input = Console.ReadLine(); if (x == 1)
element[i] = Convert.ToInt32(input); Console.WriteLine(RMQ(0, y, z, 0, n
} - 1));
else
N = 0; Update(0, y, z, 0, n - 1);
Init(0, n - 1); }
}
input = Console.ReadLine();
int q = Convert.ToInt32(input);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-29-320.jpg)










![Solution
public class Edge
{ public int node; public int cost;}
static List<Edge>[] _connectedNodes = null;
static int[] _dfsNumber = null;
static int[][] _parent = null;
static int[][] _maxCost = null;
static void DFS(int node, int parent, int edgeCost, int dfsNumber)
{
_parent[node][0] = parent;
_maxCost[node][0] = edgeCost;
_dfsNumber[node] = dfsNumber;
for (int i = 0; i < _connectedNodes[node].Count; i++)
if (_dfsNumber[_connectedNodes[node][i].node] == -1)
DFS(_connectedNodes[node][i].node, node, _connectedNodes[node][i].cost, dfsN
umber + 1);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-40-320.jpg)
![Solution
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string input = Console.ReadLine(); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
input = Console.ReadLine();
int n = Convert.ToInt32(input); string[] inputs = input.Split(' ');
_connectedNodes = new List<Edge>[n + 1]; int x = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[0]);
_dfsNumber = new int[n + 1]; int y = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[1]);
_parent = new int[n + 1][]; int z = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[2]);
_maxCost = new int[n + 1][];
_connectedNodes[x].Add(new Edge {
node = y, cost = z });
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) _connectedNodes[y].Add(new Edge {
{ node = x, cost = z });
_dfsNumber[i] = -1; }
_parent[i] = new int[18];
DFS(1, -1, 0, 1);
_maxCost[i] = new int[18];
_connectedNodes[i] = new List<Edge>();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-41-320.jpg)
![Solution
for (int j = 1; ; j++)
{
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (_parent[i][j - 1] != -1 && _parent[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1] != -1)
{
_parent[i][j] = _parent[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
_maxCost[i][j] = _maxCost[i][j - 1];
if (_maxCost[i][j] < _maxCost[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1])
_maxCost[i][j] = _maxCost[_parent[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
flag = true;
}
else
_parent[i][j] = -1;
}
if (!flag)break;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-42-320.jpg)
![Solution
input = Console.ReadLine();
int q = Convert.ToInt32(input);
for (int q1 = 1; q1 <= q; q1++)
{
input = Console.ReadLine();
string[] inputs = input.Split(' ');
int x = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[0]);
int y = Convert.ToInt32(inputs[1]);
int max = 0;
if (_dfsNumber[x] > _dfsNumber[y])
{
int z = x;
x = y;
y = z;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-43-320.jpg)
![Solution
while (_dfsNumber[x] != _dfsNumber[y])
{
for (int i = 0; ; i++)
{
if (_parent[y][i] == -1 || _dfsNumber[_parent[y][i]] <
_dfsNumber[x])
{
y = _parent[y][i - 1];
break;
}
else
{
if (_maxCost[y][i] > max)
max = _maxCost[y][i];
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-44-320.jpg)
![Solution
while (x != y)
{ else
for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++) {
{ if (_maxCost[x][i] > max)
if (_parent[x][i] == _parent[y][i])
{
max = _maxCost[x][i];
if (i == 0) if (_maxCost[y][i] > max)
{ max = _maxCost[y][i];
if (_maxCost[x][i] > max) }
max = _maxCost[x][i]; }
if (_maxCost[y][i] > max)
max = _maxCost[y][i];
}
x = _parent[x][i]; Console.WriteLine(max);
y = _parent[y][i]; }
} }
else
{
x = _parent[x][i - 1];
y = _parent[y][i - 1];
}
break;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanceddatastructure-121217105139-phpapp02/85/Advanced-data-structure-45-320.jpg)












































































































