Agent Based Modeling and Simulation - Overview and Tools
- 1. Overview and Tools Agent Based Modeling and Simulation By Stathis Grigoropoulos
- 2. Agent Based Modeling and Simulation Importance • A Problem… • Complex Adaptive Systems • CAS Examples • Simulation Agent Based Simulation Definitions • ABMS Characteristics • ABMS Components • Agent Definition • Agent Environments • Agent Interactions • ABMS Examples ABMS Usage Summary – Q & A Agenda End Why? What? When? How? ABMS Software Tools • The Big Two… • NetLogo • RePast
- 3. Problem: Internet Service Provider (ISP) wants to increase the efficiency of the internet service by optimizing packet traffic over the routing network. However, the network looks like this How do you model a Complex Structure? Why? A Problem…
- 4. Answer: Agent Based Paradigm can help analyze and simulate Complex Adaptive Systems (CAS). Why? Complex Adaptive Systems Definition(s) of CAS? • A complex system is one in which there are multiple interactions between many different components • A complex system is a highly structured system, which shows structure with variations… Features of CAS: • Composed by several interacting elements • Nonlinearity • Networked structure • Hierarchical structure • Possibility to evolve and adapt …
- 5. Why? CAS Examples Examples of CAS using ABMS (non exhaustive) • Biology • Virus Spreading • Population Dynamics • Technology • Distributed and Parallel Systems • Wireless and Sensor Systems • Finance & Business • Modeling Markets • Workforce Management • My Msc Thesis
- 6. Simulation execution Dynamics of Target System Modeling and design of a simulator Analysis of results + interpretation (model evaluation leading to explanation or prediction) Target System Model and simulator Collected Data Why? Simulation
- 7. What? ABMS Characteristics • Agent Based Modeling and Simulation (ABMS) is a new approach to modeling systems comprised of autonomous, interacting Agents. • ABMS is a bottom-up process. • Emergent phenomena from micro-behavior. • Describes both optimization models and investigation of a dynamic process. • ABMS succeeds where centralized planning and optimization models fail.
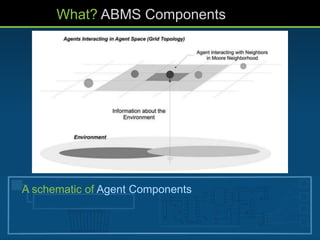
- 8. What? ABMS Components • A set of agents, their attributes and behaviors. • A set of agent relationships and methods of interaction: • An underlying topology of connectedness defines how and with whom agents interact. • The agents’ environment: • Agents interact with their environment in addition to other agents
- 9. What? ABMS Components A schematic of Agent Components
- 10. What? Agent Definition • There is no universal agreement on the precise definition of the term “agent” in the context of ABMS. • We can however provide the main characteristics of an agent: Autonomous: Through agent and environment interaction, agent follows a behavior that relate information with action. Simple rules to Neural Networks. Self-contained: Each agent is unique and modular. One can distinguish whether a part of the model is a part of a specific agent or not. Interacting with other agents: Agents can be social. Interact with other agents through protocols, e.g. movement in space, network connectivity.
- 11. • In addition an agent may be: Adaptive: Able to modify a set of behaviors, adapt based on experience. Goal-Directed: Not necessary maximization. Adapt behavior response to achieve goal. Heterogeneous : Unlike particle simulations, agent intelligence and behavior may vary in the same environment. Equipped with Resources : Resource attributes indicate its current stock of one or more resources, e.g., energy, wealth, information, etc. What? Agent Definition
- 12. What? Agent Definition A typical Agent
- 13. What? Agent Environments Types of Agent Environments
- 14. What? Agent Interactions • Depending on the environment agents interact in a subset topology. • Typically an agent interact with neighbors • For example: • In a Grid, surrounding cells are the neighborhood. • In a network, the first degree connections are neighbors.
- 15. What? ABMS Example Game Of Life: • two-dimensional orthogonal grid • Agents are cells, state dead or alive Rules: • Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbors dies, as if caused by under-population. • Any live cell with two or three live neighbors lives on to the next generation. • Any live cell with more than three live neighbors dies, as if by overcrowding. • Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbors becomes a live cell, as if by reproduction.
- 16. What? ABMS Example Game Of Life Initial and Steady State. At the Steady State patterns are emerging.
- 17. What? ABMS Example Game Of Life Steady State. At the Steady State patterns are emerging.
- 18. What? ABMS Example Preferential Attachment: • The model starts with two nodes connected by an edge. • At each step, a new node is added. A new node picks an existing node to connect to randomly, but with some bias • Node’s chance of being selected is directly proportional to the number of connections it already has.
- 19. When? ABMS Usage • When there are decisions and behaviors that can be well-defined. • When it is important that agents adapt and change their behaviors. • When it is important that agents have a dynamic relationship with other agents, and agent relationships form, change and decay. • When the past is no predictor of the future because the processes of growth and change are dynamic. • When process structural change needs to be an endogenous result of the model, rather than an input to the model.
- 20. How? ABMS Software …Just a few ABMS Software Tools
- 21. NetLogo The Center for Connected Learning (CCL) and Computer-Based Modeling, Northwestern University, USA. Repast Simphony Argonne National Laboratory, Chicago, USA. How? The Big Two… Both Free, Open Source
- 22. • The name NetLogo comes from “Network Logo” and is a functional programming language (Byproduct of Lisp). • Java based Platform (build-in UI and programming interface). • “Turtles” represent the agents and have some state (unique identity, position, and attributes). How? NetLogo
- 23. How? NetLogo NetLogo User and Programming Interface
- 24. • Very popular tool (educational purpose). • Easy-to-use language, great for beginners. • Mature platform, rare bugs to none. • Contains many useful already-made primitives and structures. • Great for prototyping models, deploys web Java applets. • Many example available. • Great documentation, active community. • Can be used for complex models also. • Scalability issues. • Becomes slow when things get complicated. • Lack of Object Oriented style, debugger. How? NetLogo
- 25. How? Repast • Recursive Porous Agent Simulation Toolkit (RePast). • Java based Framework and Library (ships with customized Eclipse IDE). • Initial language used was Java, however seeing the success of NetLogo, ReLogo was introduced.
- 26. How? Repast Repast View and Eclipse Programming Interface
- 27. • Popular tool (social sciences targeted). • Object Oriented and functional for tutoring. • Very good documentation, active community. • Usage of Eclipse. • Mature platform, some bugs. • Lots of examples available. • Includes 3D GIS using GeoTools, Imports NetLogo. • Scalable for complex models. • Learning curve, experience in Java regardless of examples. • No connection of ReLogo and Java. • Not so many primitives and structures available. How? Repast
- 28. • Repast is faster than NetLogo in execution times. • However, you can have a model in NetLogo in few houre, Repast can take weeks (depending on your programming skills). • Although Repast is scalable, what about millions of agents (HPC)? • MASON • RePast C++ HPC • Custom How? Overall
- 29. Summary • Agent Based Modeling and Simulation can model complex non-linear problems. • ABMS elevates system adaptation and learning. • Use agents when autonomous interactions occur. • Prototype with NetLogo, followed by RePast implementation. • Interesting Technology Trends in ABMS: • Software Architecture using Agents rather than Objects. • Distributed Data Mining. • Network Security with Agents.
- 31. References Vizzari, EASSS 2009 - Torino – 3-4/9/2009 Tutorial. CM Macal and MJ North, Tutorial on agent-based modeling and simulation, Journal of Simulation 2010. CM Macal and MJ North, AGENT-BASED MODELING AND SIMULATION, Proceedings of the 2009 Winter Simulation Conference. Paul Davidsson , Agent Based Social Simulation: A Computer Science View, Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation vol. 5, no. 1. Rob Allan, Survey of Agent Based Modelling and Simulation Tools, http://www.grids.ac.uk/Complex/ABMS/ABMS.html#SECTION0003140 00000000000000, visited 31-05-014 .
- 32. NetLogo The Center for Connected Learning (CCL) and Computer-Based Modeling, Northwestern University, USA. Repast Simphony Argonne National Laboratory, Chicago, USA. MASON George Mason University, USA. Multi- Agent Simulator Of Neighborhoods ... or Networks... or something... , The Runner ups…
Editor's Notes
- #7: We might not be able to run all the experiments in the target system