agile with scrum methodology
- 2. Presented by:- K.Rahul Reddy Ch.Avinash Reddy T.Uday Kiran
- 3. Topics that are covered:- Different SDLC. Waterfall methodology advantages and disadvantages. Agile with scrum framework Roles, Process and Benefits. Requirements and analysis Structure of 3-tier architecture and its layers.
- 4. Topics that are covered:- model view controller(MVC). Technical design document(TDD). Code re-use, code convention, code comments, unit testing Testing phase which includes QA and QC. source control.
- 5. Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC):- A software development life cycle is a series of steps or phases that are performed to develop a software project.
- 6. Different Software development life cycles(SDLC):- Waterfall model Agile-scrum model Spiral model Rapid application model V-model Etc…
- 8. Advantages :- A waterfall model is easy to follow. Quality is given higher priority than time and cost. Documentation is done at every stage of a waterfall model allowing team to understand what has been done. The stages cannot be jumped or bypass.
- 9. Disadvantages :- It can be implemented for any size project but mostly preferable to small projects. Requirement must be gathered in the beginning and there won’t be any change. The stakeholder may not be completely satisfied. Its difficult to estimate time and cost.
- 11. Why agile is mostly used? The highest priority is to satisfy the customer. It saves time, money and it involves stakeholders through the project. The change in requirements is possible during the project. Deliver working software frequently.
- 13. Agile with scrum methodology:- Scrum is an framework in agile that is basically used in software development for better results. Self-organization small teams manage their own workload. They organize themselves around clear goals and constraints.
- 14. Note:- Teams goals are your goals you must commit to them. There is no individual failure-the team fails ! There is no individual success-the team succeed !
- 16. Product Owner:- The person responsible for maintaining the Product Backlog by representing the interests of the stakeholders. Scrum Master:- The person responsible for the Scrum process, who arranges daily meetings, tracks the backlog of work to be done. Development Team:- A cross-functional group of people responsible for delivering potentially shippable increments of Product at the end of every Sprint.
- 18. Sprint:- It is a span of 2-4 weeks to finish a part of project. Product backlog:- The product backlog is an priority ordered list of requirements. Sprint planning meeting:- The scrum master plans the sprints and gives the tasks to the teams. Sprint backlogs:- The list of tasks that are to be completed during the sprint.
- 19. Stand up meeting:- In this meet the team reports about – What they did? What they are going to do? Impediments meeting:- They will discuss about new technique or any problem in the sprint. Retrospective meeting:- It is held after every sprint, what went well and what went wrong.
- 20. Requirements:-
- 22. Development phase:- Every developer develops the project using a 3-tier architecture in their projects. In this architecture the software is divided into three layers they are- 1. User Interface Layer(UI) 2. Business Logic Layer(BLL) 3. Data Access Layer(DAL) Through this logic, data and user interface are divided into three division.
- 23. Structure Of 3-Tier Architecture:-
- 24. Use:- if any change need to be done then we can modify a particular structure without disturbing the other structure. Example :- If the replace Sql server database with oracle database then we need to change only data layer.
- 25. How this layers work:- UI Layer:- It deals with the user interface and interaction. Presentation layer is your UI Layer. You can design your interface for you application using our own control (i.e web, windows or mobile).
- 26. Business Logic Layer:- Application layer or Business Layer is the middle or Bridge layer. In this layer we can write logics of the program or any validation code. This layer communicates with presentation layer and database layer.
- 27. Data Access layer:- This layer makes a connection to the database layer. In this layer we can write queries or database connection. It communicates only with the Business layer.
- 28. Advantages of using 3 tier architecture:- It makes the logical separation between business layer, presentation layer and database layer. It helps to maintain and understand large project and complex project. Database Security can be provided at application layer.
- 29. Why to use 3 tier architecture in projects:- If a new developer joins you for the same project then it becomes very difficult to make him/her understand about the code. It becomes very difficult to find any specific part of project code. Our database server is not secured because database server code is directly written in the page level.
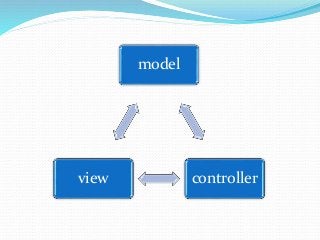
- 30. Model view controller(MVC):- Model:- It handles the logic for the application (i.e model objects retrieves stored data from the database). View:- It handles the display part for the application. Controller:- This part handles the user interactions (typically read from the view, control user input and input data to the model)
- 31. example:- It is a framework for building web application. Consider a web application:- The model represents the application core(in case of list of database). The view displays the data(the database records). The controller handles the input(to the database).
- 33. Technical Design Document(TDD):- This TDD is prepared by team in the presence of all team members. It consists of- o Class diagram o Database diagram o Controls added and modified o Code level changes. This document is studied clearly by every team member before starting of the project.
- 34. Code Re-use:- Code reuse is the practice of using the same segment of code in multiple applications. Reusing code saves programming time, which reduces costs. Code reuse is promoted through API Frameworks Libraries.
- 35. Coding conventions:- This are the rules to be followed when we are writing a code. There are some rules in using private and public variables. camel case-Car Performance. Adding space after use of binary operators ==,&&.
- 36. Coding comments:- Comments are like describing a part of code what it does. It is important to use comments while programming. When a coder replaces with a new coder, the new coder must easily understand the code.
- 37. Unit test:- This test is done at the end of the program. It is basically done by the coder to check whether the code runs properly or not. After checking the code, if it runs properly then the code is sent to testing phase.
- 38. Testing Phase In testing phase it’s basically done two methods . 1. Manual 2. Automation. In manual testing he check the working application manually by observing each and every option in the project. Using automation we need to write a program in which we can test a particular option many times.
- 39. In automation various tools are used like selenium, QTP etc. Automation method is best technique because we can save a lot of time.
- 40. Quality assurance(QA):- QA is a planned and systematic set of activities necessary to provide adequate confidence that products and services will conform to specified requirements and meet user needs. It is process oriented. Defect prevention based.
- 41. Quality control:- Quality control is the process by which product quality is compared with applicable standards and the action taken when non conformance is detected. It is product oriented. Defect detection based.
- 42. Tester must have the knowledge of all the requirement's of the project and he must know the tools used in the project. There are many types of testing - Black box testing:- In this testing simply the input is given and checks for the output. White box testing- This testing includes the code checking at every stage.
- 43. Source control:- It is to maintain the source code in the central server. By this any coder can access the code. We can even keep a track on history of modifications. Comparison of different versions can be done so that we will have an idea of where the code has been modified.