An Agent-Based Approach to Evaluating the Effect of Dynamic Age Changes on Community Acceptance of Mining Projects
- 1. An Agent-Based Approach to Evaluating the Effect of Dynamic Age Changes on Community Acceptance of Mining Projects 1 Mark K. Boateng, PhD Student, Department of Mining & Nuclear Engineering Missouri S&T, Rolla, MO Dr. Kwame Awuah-Offei, Associate Professor, Department of Mining & Nuclear Engineering Missouri S&T, Rolla, MO
- 2. Presentation Outline Background Methodology Validation Case Study Conclusions & Future Work 2
- 3. Background 3 Why Local Communities Opposing Mining? General Causes: Social and cultural change Economic change Socio Environmental change The process of change (Davis & Franks, 2011)
- 4. Background 4 Effects of Local Community Conflicts on Mining Based on 64 Studied Cases: (Davis & Franks, 2011)
- 5. Background Literature 5 (IFC, 2007) : Stakeholder Engagement Principle (Que & Awuah-Offei , 2014): Framework for Mining Community Consultations (ICMM , 2012): Community Development Toolkit (Thomson & Boutilier , 2011): Social License to Operate (Ivanova and Rolfe , 2011): Assessing Development Options in Mining Community Using Stated Preference Techniques The existing work done by other researchers have focused more on static and qualitative approach to evaluating community acceptance of mining project
- 6. Background Literature (Work done by Ivanova & Rolfe) 6Source: (Ivanova and Rolfe, 2011) R Results of the Survey: 43% of the respondent preferred Option A 32% of the respondent chose Option B 25% of the respondent selected Option C
- 7. Motivation Lack of community acceptance leads to cost of mining. The local community’s degree of acceptance is a complicated function of demographics and mine characteristics over time (Ivanova & Rolfe, 2011; Que & Awuah-Offei, 2014) A challenge to quantify community support has been a concern (Davis & Franks, 2011). Mine engineers and managers need the tools to understand the inter-relationship between project & dynamic community acceptance 7 Exploration & permitting Development Exploitation Closure & reclamation
- 8. Objectives To present an agent-based model (ABM) framework for estimating local community acceptance of mining project. Using the ABM framework to evaluate dynamic local community acceptance of a mining project as a function of demographic factors such as age The hypothesis for this study is to quantitatively predict dynamic community acceptance of a mining project using Agent-Based Model 8
- 9. Methodology Agent Based Model (ABM) Elements of Agent-Based Model: Agents are computational entities that make decisions based on their relationship with other agents and environment Agent’s environment: Agents interact with their environment, defined by a set of common variables Agents are autonomous: Being capable of making independent decisions • Utility function vs. agent state 9 Age Agent Interactions with Other Agents Agent Interactions with the Environment Agent Attributes: Static: name, gender… Dynamic: memory, resources Methods: Behaviors Behaviors that modify behaviors Update rules for dynamic attributes (Macal & North, 2010)
- 10. Odds Ratio = > 1: means an agent accepts the option (proposal) Odds Ratio < 1: means an agent does not accept the option (proposal) Modeling Community Acceptance of Mining Project Using ABM Agent: Individuals in the community older than 18 Environment: variables to describe the status quo and proposed action Agent’s Autonomy: Utility function based on discrete choice modeling Odds Ratio = 10 1 1 exp n n p b o m i i j ji j i j x x a a
- 11. Flowchart The agent-based modeling of dynamic local community acceptance built in MATLAB 7.7 (2012). 11
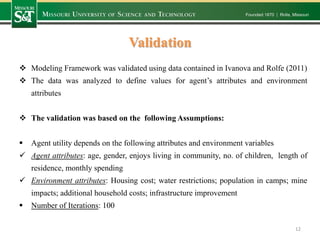
- 12. Validation Modeling Framework was validated using data contained in Ivanova and Rolfe (2011) The data was analyzed to define values for agent’s attributes and environment attributes The validation was based on the following Assumptions: Agent utility depends on the following attributes and environment variables Agent attributes: age, gender, enjoys living in community, no. of children, length of residence, monthly spending Environment attributes: Housing cost; water restrictions; population in camps; mine impacts; additional household costs; infrastructure improvement Number of Iterations: 100 12
- 13. Validation Input Data- (Agent Attributes) Agent’s Attributes Coefficient, 𝛃 Median Age (years) 0.037 *** 38 Gender 1.24 *** 0.5 Enjoy Living in the community (years) 0.21* 0.5 Number of Children 0.26*** 2 Length of Residence (years) -0.10 * 5 Monthly Spending ($) -0.01** 2200 13 Source: (Ivanova and Rolfe ,2011)
- 14. Validation Input Data –(Environment Attributes) Environment Attributes Option A Option B Option C Coefficient 𝛃 Base case 𝑋 𝑏 Proposal 𝑋 𝑝 Base case 𝑋 𝑏 Proposal 𝑋 𝑝 Basecase 𝑋 𝑏 Proposal 𝑋 𝑝 Housing Pricing 2 2 2 2 2 1 0.284 ** Water Restrictions 1 1 1 2 1 3 0.218* Population in Camps 2 2 2 3 2 2 1.583** Buffer for mine impacts 1 1 1 2 1 2 0.248** Additional household cost 0 0 0 250 0 1000 0.001*** Infrastructure Improvement 2 2 2 2 2 2 0.025*** 14
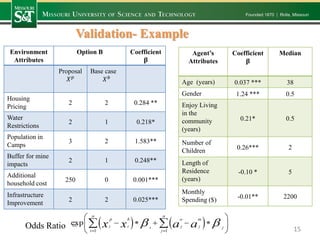
- 15. Validation- Example Environment Attributes Option B Coefficient 𝛃 Proposal 𝑋 𝑝 Base case 𝑋 𝑏 Housing Pricing 2 2 0.284 ** Water Restrictions 2 1 0.218* Population in Camps 3 2 1.583** Buffer for mine impacts 2 1 0.248** Additional household cost 250 0 0.001*** Infrastructure Improvement 2 2 0.025*** 15Odds Ratio = Agent’s Attributes Coefficient 𝛃 Median Age (years) 0.037 *** 38 Gender 1.24 *** 0.5 Enjoy Living in the community (years) 0.21* 0.5 Number of Children 0.26*** 2 Length of Residence (years) -0.10 * 5 Monthly Spending ($) -0.01** 2200
- 16. Results and Discussion (Framework) 16 Results of the Survey: 43% of the respondent preferred Option A 32% of the respondent chose Option B 25% of the respondent selected Option C
- 17. Results & Discussion(Framework) The model appears to perform well when only demographic factors play a role Model confirms Option B is preferred to Option C Option A (status quo) is preferred to Option C Model appears to validate the utility function obtained by Ivanova & Rolf ‘s work (Ivanova & Rolf, 2011) using odds ratio 17
- 18. Case Study This was carried out using already built modeling framework. The evaluation was achieved by varying birth rate, mortality rate and length of residence The results were compared to option A results (status quo) 18
- 19. Input Data Birth and mortality rates were increased and decreased by 10% Increasing the percentage of new entrants (>5years) by 10% Increasing the percentage of new entrants (>5years) by 20% 19
- 21. Results and Discussion 21 The results show that over the five years, there is only a marginal change in support, decreasing from 46 to 44%. There is very slight change in support as the birth and death rates are increased. Increasing the number of new entrants reduces the level of support more than the other two factors.
- 22. Conclusions & Future Work An agent based model (ABM) framework for estimating local community acceptance of mining has been successfully demonstrated This study indicates that age and associated demographics on their own do not significantly affect the acceptance of mining project in the model This work has successfully used odds ratio to model utility function It is therefore recommended that future work will incorporate mine characteristics and environmental aspects that change over time It is expected that this work would assist investors and stakeholders to understand drivers of community acceptance early in project planning and design 22
- 23. 23













































![[HIFLUX] Lok Fitting&Valve Catalog 2025 (Eng)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lokfittingen-250528072439-8696f1c6-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)









