Approximate Dynamic Programming: A New Paradigm for Process Control & Optimization
5 likes982 views
1. Approximate dynamic programming (ADP) is a computationally feasible approach for handling large-scale and uncertain systems like process industries more effectively than conventional tools. 2. ADP works by approximating the optimal "scores" or value functions for every system state and action offline through simulations, rather than computing them exactly. This allows for manageable online computation. 3. By handling uncertainties through simulations during offline learning, ADP can provide improved policies for decision making under uncertainty compared to approaches that ignore uncertainties.
1 of 24




![Regulatory Control LC LC FC FC Feed Keep flow rates, levels, .. @ specified values Decisions: Valve opening [sec] Uncertainties: Valve dynamics, resolutions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approximate-dynamic-programming-a-new-paradigm-for-process-control-optimization-7511/85/Approximate-Dynamic-Programming-A-New-Paradigm-for-Process-Control-Optimization-5-320.jpg)









![Simulations X = [s 1 , s 2 , s 3 , s 4 , s 5 , z 1 , z 2 , z 3 , z 4 , z 5 , L 1 , L 2 , t] Which task is performed? Result of the most recent task Duration 230 billion points Simulations (150000) 1. High Success Probability Task First 2. Short Duration Task First 3. High Reward Project First Sampled X 3.7 x 10 5 probabilistic description](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approximate-dynamic-programming-a-new-paradigm-for-process-control-optimization-7511/85/Approximate-Dynamic-Programming-A-New-Paradigm-for-Process-Control-Optimization-19-320.jpg)





Ad
Recommended
Operation management project



Operation management projectAvi Pipada This document discusses the importance of quality in global business. It notes that quality helps firms increase sales and reduce costs in two key ways: through improved sales via factors like reputation, and reduced costs through increased productivity and lower rework costs. The document then outlines several tools for total quality management (TQM), including flowcharts, check sheets, scatter diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, and statistical process control charts. It emphasizes that quality is crucial for a firm's success through maintaining customer loyalty, a strong brand reputation, and the ability to attract and retain good staff.
Sales and operations planning a research synthesis



Sales and operations planning a research synthesisWallace Almeida Despite the growing body of literature on sales and operation planning (S&OP), efforts to synthesise the overall state of the art of research in this area are limited. Within this context, this paper provides a systematic review of the literature on S&OP. The purpose of this systematic review is twofold: (i) to integrate the highly dispersed work on S&OP in order to identify and analyse S&OP as a business process and (ii) to assemble quantitative evidence of its impact on the performance of the firm. A literature search framework is proposed, with 271 papers reviewed and classified. The framework embraces S&OP context information, inputs and goals, structure and processes, outcomes, and results. The major expected outcome in most papers was a cross-functional integration of plans, although few studies report on the integration of finance plans into S&OP. Despite the existence of common process descriptors and definitions of S&OP, there is a lack of unifying frameworks for maturity models, measurement of S&OP, and constructs related to the firm's performance. The need for additional scientifically sound survey or case study research on S&OP is emphasised. This paper contributes to a better understanding of S&OP's role as a determinant of firm's performance in the supply chain
Project management- Operation Management



Project management- Operation ManagementVikram Singh This document discusses project management group no. 5 and provides an overview of key project management concepts. It defines a project as a temporary endeavor to create a unique product or service. Project management is described as applying knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet requirements. The document outlines the project management process, which includes integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, and other components. It also discusses the project life cycle and constraints of time, cost, scope, and quality.
Process & Capacity 2



Process & Capacity 2knksmart The document discusses different process strategies including process-focused, product-focused, and repetitive-focused strategies. It provides examples of each strategy and discusses their relative advantages and disadvantages. Key factors in selecting a process strategy include volume, variety, and the level of customization required. The document also covers topics like capacity planning, breakeven analysis, and techniques for improving process efficiency.
Strategic Facility Planning PowerPoint Presentation Slides



Strategic Facility Planning PowerPoint Presentation SlidesSlideTeam Download our professional PPT comprising extensively researched content and professional design layouts. Don t waste hours fiddling with PowerPoint toolbars and finding professional PowerPoint templates. This complete Strategic Facility Planning Powerpoint Presentation Slides saves hours of your time. Comprising a total of twenty one slides, the PowerPoint presentation is a visual masterpiece with professional PPT templates, data-driven graphs, charts and tables, a beautiful theme, impressive slide designs, icons, imagery and more. It is fully editable so that you can make changes to colors, data and fonts if you need to. Just enter your text in the placeholders provided and rock the meeting or conference you are presenting at.
Aligning It And Business Strategy PowerPoint Presentation Slides 



Aligning It And Business Strategy PowerPoint Presentation Slides SlideTeam Presenting this set of slides with name - Aligning It And Business Strategy Powerpoint Presentation Slides. This PPT deck displays twentyone slides with in depth research. Our topic oriented Aligning It And Business Strategy Powerpoint Presentation Slides presentation deck is a helpful tool to plan, prepare, document and analyse the topic with a clear approach. We provide a ready to use deck with all sorts of relevant topics subtopics templates, charts and graphs, overviews, analysis templates. Outline all the important aspects without any hassle. It showcases of all kind of editable templates infographs for an inclusive and comprehensive Aligning It And Business Strategy Powerpoint Presentation Slides presentation. Professionals, managers, individual and team involved in any company organization from any field can use them as per requirement.
A Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy



A Roadmap To World Class Forecasting AccuracyPresident Stephen Crane Consulting, LLC A case study on how to implement a world class forecasting process to achieve world class forecast accuracy performance
Resource Planning PowerPoint Presentation Slides



Resource Planning PowerPoint Presentation SlidesSlideTeam Presenting this set of slides with name - Resource Planning Powerpoint Presentation Slides. Our topic specific Resource Planning Powerpoint Presentation Slides presentation deck contains twenty six slides to formulate the topic with a sound understanding. This PPT deck is what you can bank upon. With diverse and professional slides at your side, worry the least for a powerpack presentation. A range of editable and ready to use slides with all sorts of relevant charts and graphs, overviews, topics subtopics templates, and analysis templates makes it all the more worth. This deck displays creative and professional looking slides of all sorts. Whether you are a member of an assigned team or a designated official on the look out for impacting slides, it caters to every professional field.
Process planning SMED and VSM: Single minute exchange of die and Value stream...



Process planning SMED and VSM: Single minute exchange of die and Value stream...Yatinkumar Patel in this presentation, two methods are described which is a very useful tool for process planning and production scheduling.
also, there are examples of this methods are well described.
Capacity Planning and Modelling



Capacity Planning and ModellingAnthony Dehnashi The document discusses capacity planning, which is determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands while meeting service level agreements. It outlines the overall capacity planning process, including identifying SLAs, analyzing current baseline capacity, forecasting future capacity needs, and adding capacity through lead, lag, or match strategies. The key steps discussed are identifying SLAs, analyzing current capacity, workload forecasting, performance modeling, and adding capacity as needed through a match strategy. Various capacity planning models and considerations are also mentioned.
Capacity Planning



Capacity PlanningMOHD ARISH The document discusses capacity planning, which involves determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demand. It covers determining current and future capacity needs, identifying options to modify capacity, and addressing imbalances between demand and capacity. Short-term adjustments and long-term responses are discussed. Models like present value analysis, aggregate planning, and decision trees can be useful for capacity planning. Economies of scale and concepts like efficiency and utilization are also summarized.
How to Do Capacity Planning



How to Do Capacity PlanningTeamQuest Corporation The document discusses how to perform capacity planning in three steps:
1. Determine service level requirements by defining workloads, units of work, and expected service levels.
2. Analyze current capacity by measuring service levels, resource usage, and workload impacts to identify constraints.
3. Plan for the future by forecasting changes and ensuring sufficient capacity through configuration changes.
Real-world examples are provided using a scheduling application and TeamQuest performance tools.
Capacity and availability management (CMMI SVC 1.3 PA) Explained



Capacity and availability management (CMMI SVC 1.3 PA) ExplainedVishnuvarthanan Moorthy The document discusses capacity and availability management in IT and ITES services. It defines capacity as the maximum amount of service or requests a system can handle, and availability as the degree to which a service is accessible when needed. An example is provided of a call center whose capacity needs to increase to meet growing demand from clients. Good practices for capacity and availability management include periodically predicting demand, planning capacity to meet it, ensuring capacity is provided as planned, and studying the overall system performance.
Material requirements planning in a demand driven world 2



Material requirements planning in a demand driven world 2jackson_bowie The document discusses Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and its limitations in today's volatile supply chain environments. It introduces Demand Driven MRP (DDMRP) as a new approach with 5 components: 1) strategic inventory positioning, 2) establishing buffer profiles and levels, 3) dynamic adjustments, 4) demand driven planning, and 5) visible and collaborative execution. DDMRP aims to dampen variability, compress lead times, and better leverage working capital by positioning inventory and pulling materials based on demand rather than pushing materials through the supply chain.
5. capacity planning.



5. capacity planning.Akash Bakshi The document discusses different types of capacities for production facilities: designed/rated capacity is the maximum output achievable under ideal conditions; planned capacity accounts for expected downtime and is lower than designed capacity; demonstrated capacity is the actual average output achieved over time, which may differ from planned capacity due to factors like product mix, machine health, and quality issues. Load refers to the scheduled or actual work released for production, whereas capacity is the maximum output a facility can produce.
Lean Manufacturing Exam Questions Mar 2011



Lean Manufacturing Exam Questions Mar 2011ExerciseLeanLLC The document appears to be a Lean Manufacturing exam that tests knowledge of key Lean concepts and tools through multiple choice and short answer questions. It covers topics like value stream mapping, takt time, 5S, mistake proofing, 8D problem solving, statistical process control, total productive maintenance, Kanban systems, and waste elimination. The exam is designed to evaluate understanding of Lean principles and their application across various manufacturing processes and environments.
Process Strategy



Process StrategyTuhin Parves This presentation discusses different process strategies including process-focused, repetitive-focused, and product-focused strategies. It provides examples of each strategy and compares their advantages and disadvantages. A process-focused strategy uses general purpose equipment for low volume, high variety products. Repetitive-focused strategies organize facilities by modules for high volume standardized products. Product-focused strategies use specialized equipment for high volume, low variety production. Mass customization blurs the distinctions by enabling high volume, high variety production. The presentation also discusses production technologies, process redesign, and environmentally friendly processes.
LinggamResume2015M



LinggamResume2015MLinggam Narayanasamy Linggam Narayanasamy is seeking a management position with over 20 years of experience in manufacturing. He currently works as a Material Program Manager at Intel Products Malaysia, where he is responsible for program management, inventory management, and ensuring material readiness. Previously he worked as a Manufacturing Shift Manager and Production Superintendent at Intel, leading teams and improving quality, yield rates, and reducing costs. He has a Master's in Business Administration and Bachelor's degree, and is highly motivated with strong communication, problem solving, and organizational skills.
Capacity Planning



Capacity PlanningPam Cudal This document discusses capacity planning and identifies key aspects of evaluating capacity requirements and plans. It describes measuring customer demand through forecasts and measuring current organizational capacity levels. It then evaluates three approaches to capacity planning: level capacity which fixes capacity at a constant level; chase demand which adjusts capacity to match fluctuating demand; and demand management which attempts to adjust demand to meet available capacity through strategies like varying price, marketing efforts, or an appointment system.
Pgbm03 MBA OPERATION MANAGEMENT session 06 planning and managing capacity



Pgbm03 MBA OPERATION MANAGEMENT session 06 planning and managing capacityAquamarine Emerald Planning involves deciding what activities should take place, when they should take place, and what resources should be allocated. Control involves understanding what is actually happening and deciding if there are deviations from the plan, then changing resources if needed. Planning looks further into the future using aggregated data, while control has a shorter time horizon and uses more detailed data. Capacity is the maximum output possible and can be measured in units per time period. Effective capacity is the achievable output rate which is usually lower than design capacity.
Six Sigma & Process Capability



Six Sigma & Process CapabilityEric Blumenfeld Six sigma aims to reduce defects and conform to customer specifications. To make sure that each project adheres to customer specifications Adev Research assists your organization focus on process improvements and variation reduction.
Process Capability[1]![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Process Capability[1]ahmad bassiouny This document provides an overview of process capability, which measures how likely a product is to meet design specifications. It discusses common process capability measurements like Cp and Cpk. An example is given of a car company where only 3.4 out of 1,000,000 cars produced were defective, demonstrating an effective process capability. The document stresses that understanding basic process capability concepts is important before delving into more complex calculations and metrics. Maintaining a capable process is key to minimizing defects and optimizing profit.
Strategic capacity planning for products and services



Strategic capacity planning for products and servicesgerlyn bonus This document discusses strategic capacity planning for products and services. It defines key capacity planning terms like design capacity, effective capacity, and actual output. It discusses factors that determine effective capacity such as facilities, products, processes, human factors, and external factors. The document outlines the capacity planning process, including estimating future capacity needs, evaluating existing capacity, identifying alternatives, and implementing solutions. It also discusses challenges in planning service capacity and tools for analysis like cost-volume analysis and financial analysis.
Capacity planning 



Capacity planning Abdullah Shahid Capacity planning is the process of determining a company's production capacity needed to meet changing demands. It involves determining the type, amount, and timing of capacity required. Key decisions include selecting the appropriate level and flexibility of facilities while maintaining balance. The process includes estimating future needs, evaluating existing capacity, identifying alternatives, analyzing costs, assessing qualitative factors, selecting an alternative, and monitoring results. Efficiency and utilization are measured by comparing actual output to effective and design capacities. Economies and diseconomies of scale affect costs based on output levels. Cost-volume analysis examines the relationships between costs, revenues, and profits at different volumes.
Chap006



Chap006Cheska Custodio The document discusses process selection and facility layout. It explains that process selection refers to how production will be organized and has implications for capacity planning, layout, equipment, and work systems. The main types of process selection are job shop, batch, repetitive/assembly, and continuous production. Effective facility layout depends on the type of process selection and aims to minimize transportation costs and distances. Key considerations for layout include production workflows, distances, costs, budgets, and utilities.
Project Risk Management



Project Risk ManagementIFAD International Fund for Agricultural Development The document discusses project risk management. It defines risk as the uncertainty of an action or activity that may impact project objectives. Project risk management is a systematic process used to identify, assess, and respond to risks to minimize negative impacts. The key steps in the risk management cycle are risk identification, assessment, prioritization, response, monitoring, and reporting. Risks should be regularly updated and communicated.
Capacity Management



Capacity ManagementYash Vardhan Lohia The document discusses various concepts related to capacity management. It defines capacity and explains strategic capacity planning. It discusses different time horizons for capacity planning - long range, intermediate range, and short range. It explains concepts like capacity utilization, best operating level, economies and diseconomies of scale. It also covers learning curves, types of learning, decision trees, and considerations for capacity analysis and determining capacity requirements. Finally, it discusses some key differences for capacity planning for services compared to manufacturing.
Cost reduction strategies



Cost reduction strategiesDr. Lutfi Apiliogullari This document outlines strategies for cost reduction and an Industry 4.0 roadmap. It discusses operational excellence through techniques like Lean, Agile, and Six Sigma to improve productivity, quality, and efficiency. It also covers strategic sourcing best practices like selecting suppliers analytically rather than heuristically and adopting just-in-time purchasing. The document outlines production strategies for different product types and a hybrid model. It discusses operational efficiency methods including total productive maintenance (TPM), total quality management (TQM), standards, and skills development. Finally, it proposes a multi-phase roadmap to Industry 4.0 through standards, integration, advanced technologies, and change management.
C2 Acetylene Hydrogenation



C2 Acetylene HydrogenationGerard B. Hawkins Acetylene Hydrogenation - Consultancy
Ethylene Plant Flowsheets
Placement of Acetylene Hydrogenation Reactor
Cracker Feedstock / Product Variability
Acetylene Reactor Feeds
Reasons for Acetylene Removal
Reacting Components and Conditions
Reactor Operation and Reacting Components
Reactor Design
Selectivity vs. Temperature and Ethane Formation
Effect of CO
Poisons
Green Oil
Turndown
H/D Ratio and Pressure Drop
Thermocouple Placement
Start-up
Problems During Start-up
Shut Down
Regeneration
Catalyst Experience, Problems and Other Information
Front End / Tail End Comparison
A Multiple-Shooting Differential Dynamic Programming Algorithm



A Multiple-Shooting Differential Dynamic Programming AlgorithmEtienne Pellegrini Presentation given at the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting in San Antonio, TX, on 2/6/17. Paper available here: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315444784_A_Multiple-Shooting_Differential_Dynamic_Programming_Algorithm
Multiple-shooting benefits a wide variety of optimal control algorithms, by alleviating large sensitivities present in highly nonlinear problems, improving robustness to initial guesses, and increasing the potential for a parallel implementation. In this work, the multiple shooting approach is embedded for the first time in the formulation of a differential dynamic programming algorithm. The necessary theoretical developments are presented for a DDP algorithm based on augmented Lagrangian techniques, using an outer loop to update the Lagrange multipliers, and an inner loop to optimize the controls of independent legs and select the multiple-shooting initial conditions. Numerical results are shown for several optimal control problems, including the low-thrust orbit transfer problem.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Process planning SMED and VSM: Single minute exchange of die and Value stream...



Process planning SMED and VSM: Single minute exchange of die and Value stream...Yatinkumar Patel in this presentation, two methods are described which is a very useful tool for process planning and production scheduling.
also, there are examples of this methods are well described.
Capacity Planning and Modelling



Capacity Planning and ModellingAnthony Dehnashi The document discusses capacity planning, which is determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands while meeting service level agreements. It outlines the overall capacity planning process, including identifying SLAs, analyzing current baseline capacity, forecasting future capacity needs, and adding capacity through lead, lag, or match strategies. The key steps discussed are identifying SLAs, analyzing current capacity, workload forecasting, performance modeling, and adding capacity as needed through a match strategy. Various capacity planning models and considerations are also mentioned.
Capacity Planning



Capacity PlanningMOHD ARISH The document discusses capacity planning, which involves determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demand. It covers determining current and future capacity needs, identifying options to modify capacity, and addressing imbalances between demand and capacity. Short-term adjustments and long-term responses are discussed. Models like present value analysis, aggregate planning, and decision trees can be useful for capacity planning. Economies of scale and concepts like efficiency and utilization are also summarized.
How to Do Capacity Planning



How to Do Capacity PlanningTeamQuest Corporation The document discusses how to perform capacity planning in three steps:
1. Determine service level requirements by defining workloads, units of work, and expected service levels.
2. Analyze current capacity by measuring service levels, resource usage, and workload impacts to identify constraints.
3. Plan for the future by forecasting changes and ensuring sufficient capacity through configuration changes.
Real-world examples are provided using a scheduling application and TeamQuest performance tools.
Capacity and availability management (CMMI SVC 1.3 PA) Explained



Capacity and availability management (CMMI SVC 1.3 PA) ExplainedVishnuvarthanan Moorthy The document discusses capacity and availability management in IT and ITES services. It defines capacity as the maximum amount of service or requests a system can handle, and availability as the degree to which a service is accessible when needed. An example is provided of a call center whose capacity needs to increase to meet growing demand from clients. Good practices for capacity and availability management include periodically predicting demand, planning capacity to meet it, ensuring capacity is provided as planned, and studying the overall system performance.
Material requirements planning in a demand driven world 2



Material requirements planning in a demand driven world 2jackson_bowie The document discusses Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and its limitations in today's volatile supply chain environments. It introduces Demand Driven MRP (DDMRP) as a new approach with 5 components: 1) strategic inventory positioning, 2) establishing buffer profiles and levels, 3) dynamic adjustments, 4) demand driven planning, and 5) visible and collaborative execution. DDMRP aims to dampen variability, compress lead times, and better leverage working capital by positioning inventory and pulling materials based on demand rather than pushing materials through the supply chain.
5. capacity planning.



5. capacity planning.Akash Bakshi The document discusses different types of capacities for production facilities: designed/rated capacity is the maximum output achievable under ideal conditions; planned capacity accounts for expected downtime and is lower than designed capacity; demonstrated capacity is the actual average output achieved over time, which may differ from planned capacity due to factors like product mix, machine health, and quality issues. Load refers to the scheduled or actual work released for production, whereas capacity is the maximum output a facility can produce.
Lean Manufacturing Exam Questions Mar 2011



Lean Manufacturing Exam Questions Mar 2011ExerciseLeanLLC The document appears to be a Lean Manufacturing exam that tests knowledge of key Lean concepts and tools through multiple choice and short answer questions. It covers topics like value stream mapping, takt time, 5S, mistake proofing, 8D problem solving, statistical process control, total productive maintenance, Kanban systems, and waste elimination. The exam is designed to evaluate understanding of Lean principles and their application across various manufacturing processes and environments.
Process Strategy



Process StrategyTuhin Parves This presentation discusses different process strategies including process-focused, repetitive-focused, and product-focused strategies. It provides examples of each strategy and compares their advantages and disadvantages. A process-focused strategy uses general purpose equipment for low volume, high variety products. Repetitive-focused strategies organize facilities by modules for high volume standardized products. Product-focused strategies use specialized equipment for high volume, low variety production. Mass customization blurs the distinctions by enabling high volume, high variety production. The presentation also discusses production technologies, process redesign, and environmentally friendly processes.
LinggamResume2015M



LinggamResume2015MLinggam Narayanasamy Linggam Narayanasamy is seeking a management position with over 20 years of experience in manufacturing. He currently works as a Material Program Manager at Intel Products Malaysia, where he is responsible for program management, inventory management, and ensuring material readiness. Previously he worked as a Manufacturing Shift Manager and Production Superintendent at Intel, leading teams and improving quality, yield rates, and reducing costs. He has a Master's in Business Administration and Bachelor's degree, and is highly motivated with strong communication, problem solving, and organizational skills.
Capacity Planning



Capacity PlanningPam Cudal This document discusses capacity planning and identifies key aspects of evaluating capacity requirements and plans. It describes measuring customer demand through forecasts and measuring current organizational capacity levels. It then evaluates three approaches to capacity planning: level capacity which fixes capacity at a constant level; chase demand which adjusts capacity to match fluctuating demand; and demand management which attempts to adjust demand to meet available capacity through strategies like varying price, marketing efforts, or an appointment system.
Pgbm03 MBA OPERATION MANAGEMENT session 06 planning and managing capacity



Pgbm03 MBA OPERATION MANAGEMENT session 06 planning and managing capacityAquamarine Emerald Planning involves deciding what activities should take place, when they should take place, and what resources should be allocated. Control involves understanding what is actually happening and deciding if there are deviations from the plan, then changing resources if needed. Planning looks further into the future using aggregated data, while control has a shorter time horizon and uses more detailed data. Capacity is the maximum output possible and can be measured in units per time period. Effective capacity is the achievable output rate which is usually lower than design capacity.
Six Sigma & Process Capability



Six Sigma & Process CapabilityEric Blumenfeld Six sigma aims to reduce defects and conform to customer specifications. To make sure that each project adheres to customer specifications Adev Research assists your organization focus on process improvements and variation reduction.
Process Capability[1]![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Process Capability[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/processcapability1-1226090261326164-9-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Process Capability[1]ahmad bassiouny This document provides an overview of process capability, which measures how likely a product is to meet design specifications. It discusses common process capability measurements like Cp and Cpk. An example is given of a car company where only 3.4 out of 1,000,000 cars produced were defective, demonstrating an effective process capability. The document stresses that understanding basic process capability concepts is important before delving into more complex calculations and metrics. Maintaining a capable process is key to minimizing defects and optimizing profit.
Strategic capacity planning for products and services



Strategic capacity planning for products and servicesgerlyn bonus This document discusses strategic capacity planning for products and services. It defines key capacity planning terms like design capacity, effective capacity, and actual output. It discusses factors that determine effective capacity such as facilities, products, processes, human factors, and external factors. The document outlines the capacity planning process, including estimating future capacity needs, evaluating existing capacity, identifying alternatives, and implementing solutions. It also discusses challenges in planning service capacity and tools for analysis like cost-volume analysis and financial analysis.
Capacity planning 



Capacity planning Abdullah Shahid Capacity planning is the process of determining a company's production capacity needed to meet changing demands. It involves determining the type, amount, and timing of capacity required. Key decisions include selecting the appropriate level and flexibility of facilities while maintaining balance. The process includes estimating future needs, evaluating existing capacity, identifying alternatives, analyzing costs, assessing qualitative factors, selecting an alternative, and monitoring results. Efficiency and utilization are measured by comparing actual output to effective and design capacities. Economies and diseconomies of scale affect costs based on output levels. Cost-volume analysis examines the relationships between costs, revenues, and profits at different volumes.
Chap006



Chap006Cheska Custodio The document discusses process selection and facility layout. It explains that process selection refers to how production will be organized and has implications for capacity planning, layout, equipment, and work systems. The main types of process selection are job shop, batch, repetitive/assembly, and continuous production. Effective facility layout depends on the type of process selection and aims to minimize transportation costs and distances. Key considerations for layout include production workflows, distances, costs, budgets, and utilities.
Project Risk Management



Project Risk ManagementIFAD International Fund for Agricultural Development The document discusses project risk management. It defines risk as the uncertainty of an action or activity that may impact project objectives. Project risk management is a systematic process used to identify, assess, and respond to risks to minimize negative impacts. The key steps in the risk management cycle are risk identification, assessment, prioritization, response, monitoring, and reporting. Risks should be regularly updated and communicated.
Capacity Management



Capacity ManagementYash Vardhan Lohia The document discusses various concepts related to capacity management. It defines capacity and explains strategic capacity planning. It discusses different time horizons for capacity planning - long range, intermediate range, and short range. It explains concepts like capacity utilization, best operating level, economies and diseconomies of scale. It also covers learning curves, types of learning, decision trees, and considerations for capacity analysis and determining capacity requirements. Finally, it discusses some key differences for capacity planning for services compared to manufacturing.
Cost reduction strategies



Cost reduction strategiesDr. Lutfi Apiliogullari This document outlines strategies for cost reduction and an Industry 4.0 roadmap. It discusses operational excellence through techniques like Lean, Agile, and Six Sigma to improve productivity, quality, and efficiency. It also covers strategic sourcing best practices like selecting suppliers analytically rather than heuristically and adopting just-in-time purchasing. The document outlines production strategies for different product types and a hybrid model. It discusses operational efficiency methods including total productive maintenance (TPM), total quality management (TQM), standards, and skills development. Finally, it proposes a multi-phase roadmap to Industry 4.0 through standards, integration, advanced technologies, and change management.
Viewers also liked (12)
C2 Acetylene Hydrogenation



C2 Acetylene HydrogenationGerard B. Hawkins Acetylene Hydrogenation - Consultancy
Ethylene Plant Flowsheets
Placement of Acetylene Hydrogenation Reactor
Cracker Feedstock / Product Variability
Acetylene Reactor Feeds
Reasons for Acetylene Removal
Reacting Components and Conditions
Reactor Operation and Reacting Components
Reactor Design
Selectivity vs. Temperature and Ethane Formation
Effect of CO
Poisons
Green Oil
Turndown
H/D Ratio and Pressure Drop
Thermocouple Placement
Start-up
Problems During Start-up
Shut Down
Regeneration
Catalyst Experience, Problems and Other Information
Front End / Tail End Comparison
A Multiple-Shooting Differential Dynamic Programming Algorithm



A Multiple-Shooting Differential Dynamic Programming AlgorithmEtienne Pellegrini Presentation given at the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting in San Antonio, TX, on 2/6/17. Paper available here: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315444784_A_Multiple-Shooting_Differential_Dynamic_Programming_Algorithm
Multiple-shooting benefits a wide variety of optimal control algorithms, by alleviating large sensitivities present in highly nonlinear problems, improving robustness to initial guesses, and increasing the potential for a parallel implementation. In this work, the multiple shooting approach is embedded for the first time in the formulation of a differential dynamic programming algorithm. The necessary theoretical developments are presented for a DDP algorithm based on augmented Lagrangian techniques, using an outer loop to update the Lagrange multipliers, and an inner loop to optimize the controls of independent legs and select the multiple-shooting initial conditions. Numerical results are shown for several optimal control problems, including the low-thrust orbit transfer problem.
Elements of dynamic programming



Elements of dynamic programmingTafhim Islam An introductory project showing how to identify if a DP solution to a problem exists. It also discusses the essential parts of DP solutions briefly.
Dynamic Programming



Dynamic Programmingcontact2kazi This document discusses dynamic programming techniques for solving optimization problems that can be divided into stages. It provides examples of using dynamic programming to find the shortest path from New York to Los Angeles, solve an inventory problem of determining optimal airplane production schedules, and allocate study time across courses to maximize grade points. Dynamic programming works by breaking problems into stages, finding optimal solutions for later stages, and then using these to recursively determine the optimal solutions for earlier stages working backwards.
Dynamic programming - fundamentals review



Dynamic programming - fundamentals reviewElifTech Dynamic Programming is an algorithmic paradigm that solves a given complex problem by breaking it into subproblems and stores the results of subproblems to avoid computing the same results again.
Dynamic programming class 16



Dynamic programming class 16Kumar Dynamic programming is an algorithm design technique that solves problems by breaking them down into smaller overlapping subproblems and storing the results of already solved subproblems, rather than recomputing them. It is applicable to problems exhibiting optimal substructure and overlapping subproblems. The key steps are to define the optimal substructure, recursively define the optimal solution value, compute values bottom-up, and optionally reconstruct the optimal solution. Common examples that can be solved with dynamic programming include knapsack, shortest paths, matrix chain multiplication, and longest common subsequence.
Dynamic Programming - Part 1



Dynamic Programming - Part 1Amrinder Arora This document discusses dynamic programming techniques. It covers matrix chain multiplication and all pairs shortest paths problems. Dynamic programming involves breaking down problems into overlapping subproblems and storing the results of already solved subproblems to avoid recomputing them. It has four main steps - defining a mathematical notation for subproblems, proving optimal substructure, deriving a recurrence relation, and developing an algorithm using the relation.
5.3 dynamic programming 03



5.3 dynamic programming 03Krish_ver2 Dynamic programming is an algorithm design paradigm that can be applied to problems exhibiting optimal substructure and overlapping subproblems. It works by breaking down a problem into subproblems and storing the results of already solved subproblems, rather than recomputing them multiple times. This allows for an efficient bottom-up approach. Examples where dynamic programming can be applied include the matrix chain multiplication problem, the 0-1 knapsack problem, and finding the longest common subsequence between two strings.
Dynamic pgmming



Dynamic pgmmingDr. C.V. Suresh Babu This document provides an overview of dynamic programming. It begins by explaining that dynamic programming is a technique for solving optimization problems by breaking them down into overlapping subproblems and storing the results of solved subproblems in a table to avoid recomputing them. It then provides examples of problems that can be solved using dynamic programming, including Fibonacci numbers, binomial coefficients, shortest paths, and optimal binary search trees. The key aspects of dynamic programming algorithms, including defining subproblems and combining their solutions, are also outlined.
Dynamic programming



Dynamic programmingShakil Ahmed The document discusses dynamic programming and provides examples of problems that can be solved using dynamic programming including unidirectional traveling salesman problem, coin change, longest common subsequence, and longest increasing subsequence. Source code is presented for solving these problems using dynamic programming including dynamic programming tables, tracing optimal solutions, and time complexity analysis. Various online judges are listed that contain sample problems relating to these dynamic programming techniques.
Dynamic Programming



Dynamic ProgrammingSahil Kumar it contains the detail information about Dynamic programming, Knapsack problem, Forward / backward knapsack, Optimal Binary Search Tree (OBST), Traveling sales person problem(TSP) using dynamic programming
Dynamic Programming



Dynamic Programmingparamalways Dynamic programming is a recursive optimization technique used to solve problems with interrelated decisions. It breaks the problem down into sequential steps, where each step builds on the solutions to previous steps. The optimal solution is determined by working through each step in order. Dynamic programming has advantages like computational savings over complete enumeration and providing insight into problem nature. However, it also has disadvantages like requiring more expertise, lacking general algorithms, and facing dimensionality problems for applications with multiple states.
Ad
Similar to Approximate Dynamic Programming: A New Paradigm for Process Control & Optimization (20)
Industrial plant optimization in reduced dimensional spaces



Industrial plant optimization in reduced dimensional spacesCapstone This document summarizes an industrial plant optimization lecture given in Toronto. It discusses the history of optimization in oil refining from early adoption in the 1950s to modern real-time optimization (RTO). RTO aims to capture opportunities from changing plant conditions by modeling the plant with engineering equations and optimizing the model in parallel with plant operation. While RTO provides benefits, reconciling measurements, non-linear constraints, and operator acceptance present technical and behavioral challenges. New approaches using projection methods to model plants from historical operating data in reduced dimensional spaces are discussed as alternatives to traditional modeling that may better represent operator preferences and familiarity.
Lean six sigma executive overview (case study) templates



Lean six sigma executive overview (case study) templatesSteven Bonacorsi This case study describes a project to improve the average speed to answer calls at a retail business. The project team analyzed call data, identified root causes such as call type and time of day, and implemented cross-training and staffing changes. These improvements reduced customer downtime costs by $150,000 annually and increased the process sigma level. Key tools used in the project included data collection, analysis of call times, and control charts to monitor ongoing performance.
CH1.ppt



CH1.pptFathiShokry The document outlines the policies, course objectives, and schedule for CHE 536 Engineering Optimization taught by Prof. Shi-Shang Jang at National Tsing Hua University. The class will meet every Thursday from 2-5pm in room 221 of the Chemical Engineering building. The course aims to teach problem formulation, numerical optimization algorithms, and their applications. Homework is due biweekly and grades are based on homework, a midterm exam, and a term project. Topics include single variable optimization, unconstrained optimization, linear programming, and nonlinear programming.
Quality Management.ppt



Quality Management.pptddelucy Quality management aims to continuously improve processes to meet customer needs and reduce defects. It encompasses tools like statistical process control (SPC), which uses control charts to monitor processes for abnormal variation. Control charts have upper and lower control limits to detect assignable causes of variation. P-charts are used for attributes where outcomes are pass/fail, while X-bar and R-charts are used for variables with sample means and ranges. Capability indices like Cpk indicate if a process can produce within specifications. Continuous improvement requires preventing defects through tools like fishbone diagrams, histograms, and Pareto charts to prioritize issues.
Presentation about Quality Management for beginners



Presentation about Quality Management for beginnersMena Wagdy Presentation about quality management for beginners
1-introduction.ppt



1-introduction.pptParveshKumar17303 This document provides an overview of an Operations Research/Management Science course. It introduces some key OR/MS techniques like linear programming, simplex method, duality theory, PERT-CPM, game theory, decision analysis, Markov chains, queueing theory, inventory theory, forecasting, and simulation. It lists the textbook and references for the course. The grading breakdown and topic outline are also provided. Several applications of each technique are mentioned.
Catapult DOE Case Study



Catapult DOE Case StudyLarry Thompson, MfgT. The document describes a case study involving optimizing a catapult to hit targets within a specified range. A team is tasked with developing a process to reliably hit targets from 5-12 feet away within 6 inches of accuracy. The team conducts experiments to identify key factors (stop pin position, draw back angle, front tension pin) affecting the distance and variation. A full factorial design of experiments is used to determine the relationship between factors and the distance response. The analysis results in an equation to predict distance based on factor settings. Based on minimizing variation, the recommended settings are a stop pin of 2, front tension pin of 2, and a draw back angle that satisfies the equation to hit the 60 inch target distance.
increasing the action gap - new operators for reinforcement learning



increasing the action gap - new operators for reinforcement learningRyo Iwaki The document introduces new operators called consistent Bellman operators for reinforcement learning. These operators aim to increase the "action gap" or difference in value between the optimal action and suboptimal actions at each state. Increasing the action gap makes value function approximation and estimation errors less impactful on the induced greedy policy. The consistent Bellman operator incorporates a notion of local policy consistency to devalue suboptimal actions while preserving optimal values, providing a first-order solution to inconsistencies from function approximation. Experiments showed these operators achieve overwhelming performance on Atari 2600 games and other tasks.
Deep Parameters Tuning for Android Mobile Apps



Deep Parameters Tuning for Android Mobile AppsDavide De Chiara This document discusses using genetic improvement techniques like mutation testing and parameter tuning to optimize non-functional properties like execution time, CPU usage, and memory allocation of Android mobile apps. It presents an approach to expose "deep parameters" through mutation analysis and then optimize apps by evaluating parameter configurations. An empirical study compares the original performance of 6 apps to performance after random parameter tuning and grid search-based tuning, finding the latter approach improved execution time by 13%, CPU time by 23%, and memory allocation by 6%.
D03 15 Deliverable Roadmap



D03 15 Deliverable RoadmapLeanleaders.org This document outlines the steps in a Six Sigma DMAIC process improvement project. It includes defining the problem and critical metrics, measuring current performance, analyzing processes and measurements, improving the processes, and controlling future performance. Key steps are defining critical metrics, establishing baselines, determining root causes, piloting solutions, creating control systems, and finalizing documentation.
D03 15 Deliverable Roadmap



D03 15 Deliverable RoadmapLeanleaders.org This document outlines the steps in a Six Sigma DMAIC process improvement project. It includes defining critical metrics, measuring current performance, analyzing processes, improving processes through pilot tests, and controlling ongoing performance. Key steps are defining customer needs, measuring baseline performance, determining critical factors, piloting solutions, creating control systems, and finalizing documentation.
Control phase lean six sigma tollgate template



Control phase lean six sigma tollgate templateSteven Bonacorsi The document outlines the control phase tools and activities for a Lean Six Sigma project. It includes reviewing project documentation, validating goals and benefits, developing standard operating procedures and controls, implementing and monitoring the solution, confirming attainment of goals, identifying opportunities for replication, and transitioning the project to the process owner. Key metrics are monitored to ensure the process remains in control. Lessons learned are captured to improve future projects.
Control phase lean six sigma tollgate template



Control phase lean six sigma tollgate templateSteven Bonacorsi The document outlines the control phase tools and activities in a Lean Six Sigma project. It includes reviewing project documentation and metrics, developing standard operating procedures and controls, implementing and monitoring the solution, confirming goals are met, identifying opportunities for replication, and transitioning the project to the process owner. Key steps are developing a control plan to monitor processes and respond to variation, updating failure modes and effects analysis, and communicating project results and benefits.
Causal reasoning and Learning Systems



Causal reasoning and Learning SystemsTrieu Nguyen 1. The document discusses causal reasoning and learning systems for online marketplaces like advertising exchanges.
2. It introduces concepts like causal inference, counterfactual measurements, and using historical data to estimate how changes to the system would have affected outcomes.
3. The key challenges are dealing with feedback loops between users, advertisers, and the learning system itself over different time scales, and gaining enough knowledge about the system to reliably estimate these counterfactuals.
Business Process Monitoring and Mining



Business Process Monitoring and MiningMarlon Dumas Lecture delivered at the Second Latin-American Summer School in Business Process Management, Bogota, Colombia, 28 June 2017 - http://ii-las-bpm.uniandes.edu.co/
Quantum Business in Japanese Market



Quantum Business in Japanese MarketYuichiro MInato This document discusses quantum computing business in the Japanese market. It introduces MDR Inc., a Japanese quantum computing startup founded in 2008. MDR develops full-stack quantum computing, from software to hardware, and works with over 20 clients in industries like banking, automotive, materials and more. Some applications discussed include quantum simulation, optimization, and machine learning. The document also provides an overview of the quantum computing developer community and ecosystem in Japan.
Optimization of Continuous Queries in Federated Database and Stream Processin...



Optimization of Continuous Queries in Federated Database and Stream Processin...Zbigniew Jerzak The constantly increasing number of connected devices and sensors results in increasing volume and velocity of sensor-based streaming data. Traditional approaches for processing high velocity sensor data rely on stream processing engines. However, the increasing complexity of continuous queries executed on top of high velocity data has resulted in growing demand for federated systems composed of data stream processing engines and database engines. One of major challenges for such systems is to devise the optimal query execution plan to maximize the throughput of continuous queries.
In this paper we present a general framework for federated database and stream processing systems, and introduce the design and implementation of a cost-based optimizer for optimizing relational continuous queries in such systems. Our optimizer uses characteristics of continuous queries and source data streams to devise an optimal placement for each operator of a continuous query. This fine level of optimization, combined with the estimation of the feasibility of query plans, allows our optimizer to devise query plans which result in 8 times higher throughput as compared to the baseline approach which uses only stream processing engines. Moreover, our experimental results showed that even for simple queries, a hybrid execution plan can result in 4 times and 1.6 times higher throughput than a pure stream processing engine plan and a pure database engine plan, respectively.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Potential Crypto Airdrops – Checklist to Track the Most Promising Airdrops.pdf



Potential Crypto Airdrops – Checklist to Track the Most Promising Airdrops.pdfCoin Gabbar Potential Crypto Airdrops are quickly becoming one of the most exciting ways to earn free cryptocurrency with little to no investment. As blockchain projects look to build traction and reward early supporters, airdrops offer a unique opportunity for users to receive tokens simply by participating in tasks like signing up, holding specific assets, or engaging with a community. With the rapid growth of DeFi, NFTs, and Web3, keeping an eye on Potential Crypto Airdrops can give investors and crypto enthusiasts a significant edge.
This guide is designed to help you identify, evaluate, and claim Potential Crypto Airdrops with confidence. You’ll learn how to differentiate between high-quality projects and risky ones, what criteria to consider before joining an airdrop, and how to avoid scams. Many promising blockchain startups use airdrops as part of their marketing and growth strategies, so spotting these opportunities early can lead to impressive rewards.
Whether you're a beginner or seasoned crypto user, tracking Potential Crypto Airdrops allows you to diversify your holdings, discover new projects, and even profit from emerging tokens. We'll walk you through reliable sources to find airdrops, how to safely participate, and tips to increase your chances of being eligible for premium airdrops. With so many new tokens launching in 2025, now is the perfect time to build your airdrop strategy.
Don’t miss out—stay informed, stay safe, and stay ahead in the crypto game by following the latest Potential Crypto Airdrops today!
Analysis of Waste Recycling Companies.pptx



Analysis of Waste Recycling Companies.pptxManikaGoyal13 This presentation aims to analyse the various waste recycling companies in India. It is a potential booming sector.
Currently I have analysed a single company, Gravita India.
Silver One May 2025 Corporate Presentation



Silver One May 2025 Corporate PresentationAdnet Communications Silver One May 2025 Corporate Presentation
Trusted Forex Broker Reviews for Smarter Trading



Trusted Forex Broker Reviews for Smarter TradingBroker Reviewfx Make informed trading decisions with our honest and comprehensive forex broker reviews. We evaluate top brokers based on key factors like trading platforms, account types, spreads, leverage, customer support, and regulatory compliance. Whether you're a new trader or a seasoned professional, our reviews help you compare and choose the most reliable forex brokers in the market. Stay ahead with updated insights and avoid hidden risks. Start your forex journey with a broker you can trust—explore our reviews today.
Top Dividend Paying Stocks in India 2025



Top Dividend Paying Stocks in India 2025Amit Finowings Discover the best dividend paying stocks in India for 2025. Explore high-yield stocks that offer steady returns and long-term wealth creation for investors.
How To Recover Stolen Funds From Online Trading Investment Scam



How To Recover Stolen Funds From Online Trading Investment Scamraymondwilliam1022 Through Hoffman Law Recovery, Bitcoin scam victims can retrieve their money. I recommend Hoffman Law Recovery to anyone who has fallen victim to a scam and has been looking for methods and techniques to recover their lost cryptocurrency or wallets. Hoffman Law Recovery is a reliable cryptocurrency recovery firm that assists victims in recovering their stolen cryptocurrency and offers secure solutions to protect your wallets from online scammers. I must admit that I was deeply melancholy and had given up on life until these experts could restore my $23,400 to my wallet. If you've lost your cryptocurrency and you are helpless about it, contact Hoffman Law Recovery to get your money back. One key aspect that makes Hoffman Law Recovery stand out is its focus on providing secure solutions to protect wallets from online scammers. It's not just about recovering lost funds; it's also about preventing future incidents and ensuring that clients' digital assets are safeguarded against potential threats. This proactive approach demonstrates their commitment to the long-term financial security of their clients. Furthermore, for individuals who have lost their cryptocurrency and are feeling helpless, reaching out to Hoffman Law Recovery could be a turning point in their situation. The reassurance that they are legitimate for seeking help and recovering lost funds can provide much-needed relief and a sense of empowerment. Hoffman Law Recovery as a reliable cryptocurrency recovery firm is certainly well-founded. Their ability to assist scam victims in recovering stolen cryptocurrency, their focus on providing secure solutions, and their commitment to supporting clients through challenging situations make them a valuable resource for individuals navigating the complex world of digital currencies. If you or someone you know has fallen victim to a cryptocurrency scam, contacting Hoffman Law Recovery could be the first step towards reclaiming lost funds and regaining peace of mind.
Website: https://hoffmannlawintl.sbs/
Mail: [email protected]
Text /Call +12364990548
Money Matters_ Transforming Your Financial Relationship.pdf



Money Matters_ Transforming Your Financial Relationship.pdfpckhetal Introduction
In the tapestry of our lives, few threads are as pervasive and influential as money. It shapes our daily decisions, defines our aspirations, and ultimately, plays a pivotal role in our sense of security and freedom. Yet, for many of us, our relationship with money is often fraught with challenges—be it managing debts, navigating financial uncertainties, or struggling to achieve our desired level of financial independence.
“Money Matters: Transforming Your Financial Relationship” is more than just a guide to managing finances; it is a transformative journey towards mastering the art of financial well-being and empowerment. This eBook is designed to empower you with the knowledge, tools, and mindset necessary to not only understand but also reshape your financial landscape. Whether you’re starting your financial journey or seeking to elevate your current approach, this eBook offers practical strategies, insightful perspectives, and actionable steps to help you achieve lasting financial success.
Through these pages, you will explore the fundamental principles of financial literacy, uncover the hidden influences shaping your financial decisions, and learn proven strategies to overcome challenges and build wealth. Each chapter is crafted to guide you through essential aspects of personal finance, from assessing your current financial situation to setting clear goals, mastering budgeting, and investing wisely. Moreover, you’ll delve into the mindset shifts necessary to cultivate financial abundance and resilience, ensuring that your journey towards financial transformation is not just effective but also sustainable.
Financial empowerment is not merely about numbers on a balance sheet; it’s about reclaiming control over your financial destiny, creating opportunities for yourself and your loved ones, and ultimately, living a life of greater freedom and fulfillment. I invite you to embark on this transformative journey with an open mind and a commitment to taking actionable steps towards a brighter financial future.
Let “Money Matters: Transforming Your Financial Relationship” be your guide as you embark on a journey towards financial empowerment and mastery. Together, let’s unlock the secrets to financial well-being and embark on a path towards realizing your true financial potential.
More Details Visit Official website page here :- www.digiwininfotech.com
The Role of Storytelling in Legal Communication (www.kiu.ac.ug)



The Role of Storytelling in Legal Communication (www.kiu.ac.ug)publication11 Storytelling is a powerful tool in legal communication, serving as a means of making complex legal
arguments more comprehensible and persuasive. This paper investigates how storytelling enhances
advocacy by engaging the emotions and empathy of judges, jurors, and other legal audiences. It delves
into the significance of narrative techniques in trial proceedings, legal writing, and negotiation,
examining how storytelling can simplify intricate legal matters while maintaining accuracy and ethical
integrity. The study further discusses strategies for integrating storytelling into legal practice,
emphasizing the selection of appropriate narratives and their impact on legal decision-making. Through
case studies and theoretical analysis, this paper highlights how effective storytelling contributes to
successful legal advocacy while addressing the ethical considerations surrounding its use.
Truxton Capital: Middle Market Quarterly Review - April 2025



Truxton Capital: Middle Market Quarterly Review - April 2025truxtontrust An overview of the middle market from the perspectives of Truxton Capital Advisors in Q1 of 2025.
Strategic Resources May 2025 Corporate Presentation



Strategic Resources May 2025 Corporate PresentationAdnet Communications Strategic Resources May 2025 Corporate Presentation
Approximate Dynamic Programming: A New Paradigm for Process Control & Optimization
- 1. Approximate Dynamic Programming Jong Min Lee Chemical and Materials Engineering University of Alberta A New Paradigm for Process Control & Optimization
- 2. How does a process industry run? Feedstock Purchase Plant / Unit Operation Inventory Control Supply Chain Management
- 3. What decisions do we make in process industries? Regulatory Control Real Time Optimizer Production Planning Strategic Planning Customer Plant Scheduling Advaced Process Control $ $ $ $ sec min ~ day week ~ month month ~ year
- 4. Ethylene Plant Furnaces Primary Fractionator Quench Tower Charge Gas Compressor Chilling Demethanizer Deethanizer Ethylene Fractionator Debutanizer Propylene Fractionator Depropanizer Fuel Oil Hydrogen Methane Ethylene Ethane Propylene Propane B - B Gasoline Light H-C Naphtha Feedstock
- 5. Regulatory Control LC LC FC FC Feed Keep flow rates, levels, .. @ specified values Decisions: Valve opening [sec] Uncertainties: Valve dynamics, resolutions
- 6. Scheduling and Planning Demands Inventories Ethylene Plant Feedstock Market Blending Daily ~ Monthly Maximize CSL and Profit Decisions: Purchase / Blending / Unit Maintenance / Inventories / Distributions Uncertainties: Market Prices / Raw Mat. Properties / Unit Failures / Demands… ? ? ? ? ETY PPY ETA BBP GSL
- 7. All the decision-making problems are fundamentally SAME We are concerned with future performance Future Time Profit
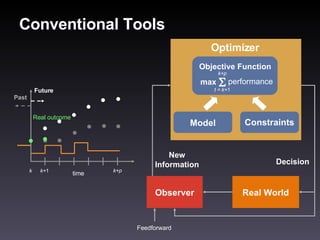
- 8. Conventional Tools Observer Decision Feedforward New Information Real outcome Optimizer Model Constraints Objective Function max t = k+ 1 k+p performance Real World Future Past k k+ 1 k+p time
- 9. What are the issues of conventional tools? 1. They ignore UNCERTAINTIES. - Can yield wrong decisions 2. They put too much efforts ONLINE. - Can be late for timely decision
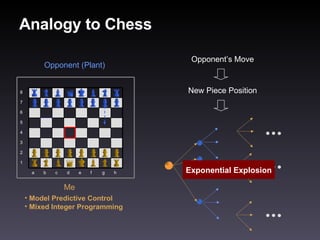
- 10. Analogy to Chess Me Opponent (Plant) Model Predictive Control Mixed Integer Programming h g f e d c b a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Opponent’s Move New Piece Position Exponential Explosion
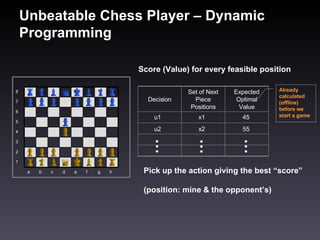
- 11. Unbeatable Chess Player – Dynamic Programming Score (Value) for every feasible position Pick up the action giving the best “score” (position: mine & the opponent’s) Already calculated (offline) before we start a game h g f e d c b a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Expected Optimal Value Set of Next Piece Positions Decision u1 x1 45 u2 x2 55
- 12. How do we find the “scores”? Discretization of entire state & action space INFEASIBLE = J ( x ) min u ( x , u ) J ( x ’ ) + E x 1 x 2 x 3 u 1 u 2 u 3
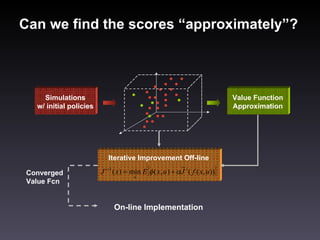
- 13. Can we find the scores “approximately”? Converged Value Fcn On-line Implementation Simulations w/ initial policies Value Function Approximation Iterative Improvement Off-line
- 14. Advantages of Approximate Dynamic Programming Manageable online computation Applicable to practical systems Stochastic systems as well as deterministic system All about simulation! Improved policy
- 15. Key to Success of ADP Store – Search – Averaging e.g.) nearest neighbor Convergence of Off-line Learning
- 16. Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling J. Choi, et al. Computers and Chemical Engineering , 28 (2004)
- 17. Drug Discovery / Development Discovery Development Market Drug 1 Drug 2 Drug n Phase 1 Phase 2 a/b Phase 3 Submission & Approval 0.5 – 2 yrs 1 – 2 yrs 1.5 – 3.5 yrs 2.5 – 4 yrs 0.5 – 2 yrs $2-4 MM $1-3 MM $5-25 MM $50-250 MM $5-20 MM Pre-clinical Development R&D takes 6.5 – 13.5 years 60 – 300 million $
- 18. Problem Complexity I 1 I 2 P 1 I 3 I 4 P 2 I 5 I 6 I 7 P 3 I 8 I 9 I 10 P 4 I 11 I 12 P 5 Drug 1 Drug 2 Drug 3 Drug 4 Drug 5 Success/Failure, Duration, Cost 1.2 x 10 9 scenarios 5 3 6 6 5 3 7 4 5 4 6 3 3 8 4 3 5
- 19. Simulations X = [s 1 , s 2 , s 3 , s 4 , s 5 , z 1 , z 2 , z 3 , z 4 , z 5 , L 1 , L 2 , t] Which task is performed? Result of the most recent task Duration 230 billion points Simulations (150000) 1. High Success Probability Task First 2. Short Duration Task First 3. High Reward Project First Sampled X 3.7 x 10 5 probabilistic description
- 20. ADP improved on the starting policies 10000 realizations 0 4000 8000 12000 H1 H2 H3 ADP
- 22. If you ignore uncertainties… y(k+1) = y(k) + b u(k) + e(k+1) parameter change noise enters
- 23. ADP “actively” handles uncertainties Output & Input Parameter Estimate & Variance Active probing at t=t b ( 10 ) : t e =15 Decrease of parameter uncertainty t=10: parameter changes, t=15: exogenous noise enters
- 24. Summary ADP is a computationally feasible approach to large-scale and uncertain systems and provides an improved solution “ ”












