Ad
Arrays in Java Programming Language slides
- 1. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Chapter 7 - Arrays Outline 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Arrays 7.3 Declaring and Creating Arrays 7.4 Examples Using Arrays 7.5 References and Reference Parameters 7.6 Passing Arrays to Methods 7.7 Sorting Arrays 7.8 Searching Arrays: Linear Search and Binary Search 7.9 Multidimensional Arrays
- 2. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 7.1 Introduction • Arrays – Data structures – Related data items of same type – Remain same size once created • Fixed-length entity
- 3. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 7.2 Arrays • Array – Group of variables (elements, components) • Have same type • Elements can be primitives or objects (including other arrays) – Java arrays are objects – Arrays are 0-based (first subscript is 0)
- 4. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 4 Fig. 7.1 A 12-element array. Name of array (note that all elements of this array have the same name, c) Index (or subscript) of the element in array c c[ 0 ] c[ 1 ] c[ 2 ] c[ 3 ] c[ 4 ] c[ 5 ] c[ 6 ] c[ 7 ] c[ 8 ] c[ 9 ] c[ 10 ] c[ 11 ] -45 6 0 72 1543 -89 0 62 -3 1 6453 78
- 5. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 5 7.2 Arrays (cont.) • Index – Also called subscript – Position number in square brackets – Must be positive integer or integer expression a = 5; b = 6; c[ a + b ] += 2; • Adds 2 to c[ 11 ]
- 6. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6 7.2 Arrays (cont.) • Examine array c – c is the array name – c.length accesses array c’s length (12) – c has 12 elements ( c[0], c[1], … c[11] ) • The value of c[0] is –45
- 7. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 7 7.3 Declaring and Creating Arrays • Declaring and Creating arrays – Arrays are objects that occupy memory – Created dynamically with keyword new int c[] = new int[ 12 ]; – Equivalent to int c[]; // declare array variable c = new int[ 12 ]; // create array • We can create arrays of objects too String b[] = new String[ 100 ]; – Each array element has a default – zero (primitives), false (boolean), null (objects)
- 8. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 8 7.4 Examples Using Arrays • Creating and initializing an array – Declare array – Create array – Initialize array elements
- 9. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 9 InitArray.java Line 9 Declare array as an array of ints Line 11 Create 10 ints for array; each int is initialized to 0 by default Line 16 array.length returns length of array Line 17 array[counter] returns int associated with index in array 1 // Fig. 7.2: InitArray.java 2 // Creating an array. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class InitArray { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 int array[]; // declare reference to an array 10 11 array = new int[ 10 ]; // create array 12 13 String output = "IndextValuen"; 14 15 // append each array element's value to String output 16 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 17 output += counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "n"; 18 19 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 20 outputArea.setText( output ); 21 22 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea, 23 "Initializing an Array of int Values", 24 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 25 26 System.exit( 0 ); 27 28 } // end main 29 30 } // end class InitArray Declare array as an array of ints Create 10 ints for array; each int is initialized to 0 by default array.length returns length of array array[counter] returns int associated with index in array
- 10. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 10 InitArray.java Each int is initialized to 0 by default Each int is initialized to 0 by default
- 11. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 11 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Using an array initializer – Use initializer list • Items enclosed in braces ({}) • Items in list separated by commas int n[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }; – Creates a five-element array – Index values of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 – Do not need keyword new
- 12. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 12 InitArray.java Line 11 Declare array as an array of ints Line 11 Compiler uses initializer list to allocate array 1 // Fig. 7.3: InitArray.java 2 // Initializing an array with a declaration. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class InitArray { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 // array initializer specifies number of elements and 10 // value for each element 11 int array[] = { 32, 27, 64, 18, 95, 14, 90, 70, 60, 37 }; 12 13 String output = "IndextValuen"; 14 15 // append each array element's value to String output 16 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 17 output += counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "n"; 18 19 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 20 outputArea.setText( output ); 21 22 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea, 23 "Initializing an Array with a Declaration", 24 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 25 26 System.exit( 0 ); 27 28 } // end main 29 30 } // end class InitArray Declare array as an array of ints Compiler uses initializer list to allocate array
- 13. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 13 InitArray.java Each array element corresponds to element in initializer list Each array element corresponds to element in initializer list
- 14. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 14 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Calculating the value to store in each array element – Initialize elements of 10-element array to even integers
- 15. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 15 InitArray.java Line 10 Declare array as an array of ints Line 12 Create 10 ints for array Line 16 Use array index to assign array value 1 // Fig. 7.4: InitArray.java 2 // Initialize array with the even integers from 2 to 20. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class InitArray { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 final int ARRAY_LENGTH = 10; // constant 10 int array[]; // reference to int array 11 12 array = new int[ ARRAY_LENGTH ]; // create array 13 14 // calculate value for each array element 15 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 16 array[ counter ] = 2 + 2 * counter; 17 18 String output = "IndextValuen"; 19 20 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 21 output += counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "n"; 22 23 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 24 outputArea.setText( output ); 25 Declare array as an array of ints Create 10 ints for array Use array index to assign array value
- 16. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 16 InitArray.java 26 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea, 27 "Initializing to Even Numbers from 2 to 20", 28 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 29 30 System.exit( 0 ); 31 32 } // end main 33 34 } // end class InitArray
- 17. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 17 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Summing the elements of an array – Array elements can represent a series of values • We can sum these values
- 18. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 18 SumArray.java Line 9 Declare array with initializer list Lines 13-14 Sum all array values 1 // Fig. 7.5: SumArray.java 2 // Total the values of the elements of an array. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class SumArray { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; 10 int total = 0; 11 12 // add each element's value to total 13 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 14 total += array[ counter ]; 15 16 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, 17 "Total of array elements: " + total, 18 "Sum the Elements of an Array", 19 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 20 21 System.exit( 0 ); 22 23 } // end main 24 25 } // end class SumArray Declare array with initializer list Sum all array values
- 19. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 19 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Using histograms to display array data graphically – Histogram • Plot each numeric value as bar of asterisks (*)
- 20. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 20 Histogram.java Line 9 Declare array with initializer list Line 19 For each array element, print associated number of asterisks 1 // Fig. 7.6: Histogram.java 2 // Histogram printing program. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class Histogram { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 int array[] = { 19, 3, 15, 7, 11, 9, 13, 5, 17, 1 }; 10 11 String output = "ElementtValuetHistogram"; 12 13 // for each array element, output a bar in histogram 14 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) { 15 output += "n" + counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "t"; 16 17 // print bar of asterisks 18 for ( int stars = 0; stars < array[ counter ]; stars++ ) 19 output += "*"; 20 21 } // end outer for 22 23 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 24 outputArea.setText( output ); 25 Declare array with initializer list For each array element, print associated number of asterisks
- 21. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 21 Histogram.java 26 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea, 27 "Histogram Printing Program", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 28 29 System.exit( 0 ); 30 31 } // end main 32 33 } // end class Histogram
- 22. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 22 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Using the elements of an array as counters – Use a series of counter variables to summarize data
- 23. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 23 RollDie.java Line 9 Declare frequency as array of 7 ints Lines 12-13 Generate 6000 random integers in range 1-6 Line 13 Increment frequency values at index associated with random number 1 // Fig. 7.7: RollDie.java 2 // Roll a six-sided die 6000 times. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class RollDie { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 int frequency[] = new int[ 7 ]; 10 11 // roll die 6000 times; use die value as frequency index 12 for ( int roll = 1; roll <= 6000; roll++ ) 13 ++frequency[ 1 + ( int ) ( Math.random() * 6 ) ]; 14 15 String output = "FacetFrequency"; 16 17 // append frequencies to String output 18 for ( int face = 1; face < frequency.length; face++ ) 19 output += "n" + face + "t" + frequency[ face ]; 20 21 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 22 outputArea.setText( output ); 23 24 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea, 25 "Rolling a Die 6000 Times", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 26 27 System.exit( 0 ); 28 29 } // end main 30 31 } // end class RollDie Declare frequency as array of 7 ints Generate 6000 random integers in range 1-6 Increment frequency values at index associated with random number
- 24. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 24 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Using arrays to analyze survey results – 40 students rate the quality of food • 1-10 Rating scale: 1 means awful, 10 means excellent – Place 40 responses in array of integers – Summarize results
- 25. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 25 StudentPoll.jav a Lines 9-11 Declare responses as array to store 40 responses Line 12 Declare frequency as array of 11 int and ignore the first element Lines 16-17 For each response, increment frequency values at index associated with that response 1 // Fig. 7.8: StudentPoll.java 2 // Student poll program. 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 public class StudentPoll { 6 7 public static void main( String args[] ) 8 { 9 int responses[] = { 1, 2, 6, 4, 8, 5, 9, 7, 8, 10, 1, 6, 3, 8, 6, 10 10, 3, 8, 2, 7, 6, 5, 7, 6, 8, 6, 7, 5, 6, 6, 5, 6, 7, 5, 6, 11 4, 8, 6, 8, 10 }; 12 int frequency[] = new int[ 11 ]; 13 14 // for each answer, select responses element and use that value 15 // as frequency index to determine element to increment 16 for ( int answer = 0; answer < responses.length; answer++ ) 17 ++frequency[ responses[ answer ] ]; 18 19 String output = "RatingtFrequencyn"; 20 21 // append frequencies to String output 22 for ( int rating = 1; rating < frequency.length; rating++ ) 23 output += rating + "t" + frequency[ rating ] + "n"; 24 25 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 26 outputArea.setText( output ); 27 Declare responses as array to store 40 responses Declare frequency as array of 11 int and ignore the first element For each response, increment frequency values at index associated with that response
- 26. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 26 StudentPoll.jav a 28 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea, 29 "Student Poll Program", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 30 31 System.exit( 0 ); 32 33 } // end main 34 35 } // end class StudentPoll
- 27. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 27 7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.) • Some additional points – When looping through an array • Index should never go below 0 • Index should be less than total number of array elements – When invalid array reference occurs • Java generates ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException – Chapter 15 discusses exception handling
- 28. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 28 7.5 References and Reference Parameters • Two ways to pass arguments to methods – Pass-by-value • Copy of argument’s value is passed to called method • In Java, every primitive is pass-by-value – Pass-by-reference • Caller gives called method direct access to caller’s data • Called method can manipulate this data • Improved performance over pass-by-value • In Java, every object is pass-by-reference – In Java, arrays are objects • Therefore, arrays are passed to methods by reference – Unlike other languages, Java does not make these choice of the programmer
- 29. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 29 7.6 Passing Arrays to Methods • To pass array argument to a method – Specify array name without brackets • Array hourlyTemperatures is declared as int hourlyTemperatures[] = new int[ 24 ]; • The method call modifyArray( hourlyTemperatures ); • Passes array hourlyTemperatures to method modifyArray • Be careful! This allows array elements to be modified by the method!!
- 30. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 30 PassArray.java Line 15 Declare 5-int array with initializer list Line 24 Pass array by reference to method modifyArray 1 // Fig. 7.9: PassArray.java 2 // Passing arrays and individual array elements to methods. 3 import java.awt.Container; 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 public class PassArray extends JApplet { 7 8 // initialize applet 9 public void init() 10 { 11 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 12 Container container = getContentPane(); 13 container.add( outputArea ); 14 15 int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; 16 17 String output = "Effects of passing entire array by reference:n" + 18 "The values of the original array are:n"; 19 20 // append original array elements to String output 21 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 22 output += " " + array[ counter ]; 23 24 modifyArray( array ); // array passed by reference 25 26 output += "nnThe values of the modified array are:n"; 27 Declare 5-int array with initializer list Pass array by reference to method modifyArray
- 31. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 31 PassArray.java Line 35 Pass array[3] by value to method modifyElement Lines 43-47 Method modifyArray manipulates the array directly Lines 50-53 Method modifyElement manipulates a primitive’s copy Lines 52 The original primitive is left unmodified 28 // append modified array elements to String output 29 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 30 output += " " + array[ counter ]; 31 32 output += "nnEffects of passing array element by value:n" + 33 "array[3] before modifyElement: " + array[ 3 ]; 34 35 modifyElement( array[ 3 ] ); // attempt to modify array[ 3 ] 36 37 output += "narray[3] after modifyElement: " + array[ 3 ]; 38 outputArea.setText( output ); 39 40 } // end method init 41 42 // multiply each element of an array by 2 43 public void modifyArray( int array2[] ) 44 { 45 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array2.length; counter++ ) 46 array2[ counter ] *= 2; 47 } 48 49 // multiply argument by 2 50 public void modifyElement( int element ) 51 { 52 element *= 2; 53 } 54 55 } // end class PassArray Pass array[3] by value to method modifyElement Method modifyArray manipulates the array directly Method modifyElement manipulates a primitive’s copy The original primitive is left unmodified
- 32. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 32 PassArray.java The object passed-by-reference is modified The primitive passed-by-value is unmodified
- 33. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 33 7.7 Sorting Arrays • Sorting data – Attracted intense research in Computer Science field – Bubble sort • Smaller values “bubble” their way to top of array • Larger values “sink” to bottom of array • Use nested loops to make several passes through array – Each pass compares successive pairs of elements • Pairs are left alone if increasing order (or equal) • Pairs are swapped if decreasing order – Other sorts (interchange sort, quick sort, merge sort) are more efficient
- 34. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 34 BubbleSort.java Line 15 Declare 10-int array with initializer list Line 23 Pass array by reference to method bubbleSort to sort array 1 // Fig. 7.10: BubbleSort.java 2 // Sort an array's values into ascending order. 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 public class BubbleSort extends JApplet { 7 8 // initialize applet 9 public void init() 10 { 11 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea(); 12 Container container = getContentPane(); 13 container.add( outputArea ); 14 15 int array[] = { 2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 12, 89, 68, 45, 37 }; 16 17 String output = "Data items in original ordern"; 18 19 // append original array values to String output 20 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 21 output += " " + array[ counter ]; 22 23 bubbleSort( array ); // sort array 24 25 output += "nnData items in ascending ordern"; 26 Declare 10-int array with initializer list Pass array by reference to method bubbleSort to sort array
- 35. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 35 BubbleSort.java Line 36 Method bubbleSort receives array reference as parameter Lines 39-53 Use loop and nested loop to make passes through array Lines 48-49 If pairs are in decreasing order, invoke method swap to swap pairs 27 // append sorted array values to String output 28 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 29 output += " " + array[ counter ]; 30 31 outputArea.setText( output ); 32 33 } // end method init 34 35 // sort elements of array with bubble sort 36 public void bubbleSort( int array2[] ) 37 { 38 // loop to control number of passes 39 for ( int pass = 1; pass < array2.length; pass++ ) { 40 41 // loop to control number of comparisons 42 for ( int element = 0; 43 element < array2.length - 1; 44 element++ ) { 45 46 // compare side-by-side elements and swap them if 47 // first element is greater than second element 48 if ( array2[ element ] > array2[ element + 1 ] ) 49 swap( array2, element, element + 1 ); 50 51 } // end loop to control comparisons 52 53 } // end loop to control passes 54 55 } // end method bubbleSort Method bubbleSort receives array reference as parameter Use loop and nested loop to make passes through array If pairs are in decreasing order, invoke method swap to swap pairs
- 36. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 36 BubbleSort.java Lines 58-65 Method swap swaps two values in array reference 56 57 // swap two elements of an array 58 public void swap( int array3[], int first, int second ) 59 { 60 int hold; // temporary holding area for swap 61 62 hold = array3[ first ]; 63 array3[ first ] = array3[ second ]; 64 array3[ second ] = hold; 65 } 66 67 } // end class BubbleSort Method swap swaps two values in array reference
- 37. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 37 7.8 Searching Arrays: Linear Search and Binary Search • Searching – Finding elements in large amounts of data • Determine whether array contains value matching key value – Linear searching – Binary searching
- 38. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 38 7.8 Searching Arrays: Linear Search and Binary Search (Cont.) • Linear search – Compare each array element with search key • If search key found, return element index • If search key not found, return –1 (invalid index) – Works best for small or unsorted arrays – Inefficient for larger arrays
- 39. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 39 LinearSearch.ja va Line 11 Declare array of ints 1 // Fig. 7.11: LinearSearch.java 2 // Linear search of an array. 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.awt.event.*; 5 import javax.swing.*; 6 7 public class LinearSearch extends JApplet implements ActionListener { 8 9 JLabel enterLabel, resultLabel; 10 JTextField enterField, resultField; 11 int array[]; 12 13 // set up applet's GUI 14 public void init() 15 { 16 // get content pane and set its layout to FlowLayout 17 Container container = getContentPane(); 18 container.setLayout( new FlowLayout() ); 19 20 // set up JLabel and JTextField for user input 21 enterLabel = new JLabel( "Enter integer search key" ); 22 container.add( enterLabel ); 23 24 enterField = new JTextField( 10 ); 25 container.add( enterField ); 26 27 // register this applet as enterField's action listener 28 enterField.addActionListener( this ); 29 Declare array of ints
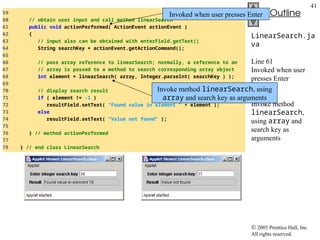
- 40. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 40 LinearSearch.ja va Lines 39-42 Allocate 100 ints for array and populate array with even ints Line 50 Loop through array Lines 53-54 If array element at index matches search key, return index 30 // set up JLabel and JTextField for displaying results 31 resultLabel = new JLabel( "Result" ); 32 container.add( resultLabel ); 33 34 resultField = new JTextField( 20 ); 35 resultField.setEditable( false ); 36 container.add( resultField ); 37 38 // create array and populate with even integers 0 to 198 39 array = new int[ 100 ]; 40 41 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 42 array[ counter ] = 2 * counter; 43 44 } // end method init 45 46 // search array for specified key value 47 public int linearSearch( int array2[], int key ) 48 { 49 // loop through array elements 50 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array2.length; counter++ ) 51 52 // if array element equals key value, return location 53 if ( array2[ counter ] == key ) 54 return counter; 55 56 return -1; // key not found 57 58 } // end method linearSearch Create 100 ints for array and populate array with even ints Loop through array If array element at index matches search key, return index
- 41. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 41 LinearSearch.ja va Line 61 Invoked when user presses Enter Line 68 Invoke method linearSearch, using array and search key as arguments 59 60 // obtain user input and call method linearSearch 61 public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent actionEvent ) 62 { 63 // input also can be obtained with enterField.getText() 64 String searchKey = actionEvent.getActionCommand(); 65 66 // pass array reference to linearSearch; normally, a reference to an 67 // array is passed to a method to search corresponding array object 68 int element = linearSearch( array, Integer.parseInt( searchKey ) ); 69 70 // display search result 71 if ( element != -1 ) 72 resultField.setText( "Found value in element " + element ); 73 else 74 resultField.setText( "Value not found" ); 75 76 } // method actionPerformed 77 78 } // end class LinearSearch Invoked when user presses Enter Invoke method linearSearch, using array and search key as arguments
- 42. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 42 7.8 Searching Arrays: Linear Search and Binary Search (Cont.) • Binary search – Efficient for large, sorted arrays – Eliminates half of the elements in search through each pass • Compare middle array element to search key – If element equals key • Return array index – If element is less than key • Repeat search on first half of array – If element is greater then key • Repeat search on second half of array – Continue search until • element equals search key (success) • Search contains one element not equal to key (failure)
- 43. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 43 BinarySearch.ja va Line 14 Declare array of ints 1 // Fig. 7.12: BinarySearch.java 2 // Binary search of an array. 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.awt.event.*; 5 import java.text.*; 6 7 import javax.swing.*; 8 9 public class BinarySearch extends JApplet implements ActionListener { 10 JLabel enterLabel, resultLabel; 11 JTextField enterField, resultField; 12 JTextArea output; 13 14 int array[]; 15 String display = ""; 16 17 // set up applet's GUI 18 public void init() 19 { 20 // get content pane and set its layout to FlowLayout 21 Container container = getContentPane(); 22 container.setLayout( new FlowLayout() ); 23 24 // set up JLabel and JTextField for user input 25 enterLabel = new JLabel( "Enter integer search key" ); 26 container.add( enterLabel ); 27 28 enterField = new JTextField( 10 ); 29 container.add( enterField ); 30 Declare array of ints
- 44. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 44 BinarySearch.ja va Lines 48-51 Allocate 15 ints for array and populate array with even ints Line 56 Invoked when user presses Enter 31 // register this applet as enterField's action listener 32 enterField.addActionListener( this ); 33 34 // set up JLabel and JTextField for displaying results 35 resultLabel = new JLabel( "Result" ); 36 container.add( resultLabel ); 37 38 resultField = new JTextField( 20 ); 39 resultField.setEditable( false ); 40 container.add( resultField ); 41 42 // set up JTextArea for displaying comparison data 43 output = new JTextArea( 6, 60 ); 44 output.setFont( new Font( "Monospaced", Font.PLAIN, 12 ) ); 45 container.add( output ); 46 47 // create array and fill with even integers 0 to 28 48 array = new int[ 15 ]; 49 50 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) 51 array[ counter ] = 2 * counter; 52 53 } // end method init 54 55 // obtain user input and call method binarySearch 56 public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent actionEvent ) 57 { 58 // input also can be obtained with enterField.getText() 59 String searchKey = actionEvent.getActionCommand(); 60 Allocate 15 ints for array and populate array with even ints Invoked when user presses Enter
- 45. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 45 BinarySearch.ja va Line 65 Invoke method binarySearch, using array and search key as arguments 61 // initialize display string for new search 62 display = "Portions of array searchedn"; 63 64 // perform binary search 65 int element = binarySearch( array, Integer.parseInt( searchKey ) ); 66 67 output.setText( display ); 68 69 // display search result 70 if ( element != -1 ) 71 resultField.setText( "Found value in element " + element ); 72 else 73 resultField.setText( "Value not found" ); 74 75 } // end method actionPerformed 76 77 // method to perform binary search of an array 78 public int binarySearch( int array2[], int key ) 79 { 80 int low = 0; // low element index 81 int high = array2.length - 1; // high element index 82 int middle; // middle element index 83 84 // loop until low index is greater than high index 85 while ( low <= high ) { 86 middle = ( low + high ) / 2; // determine middle index 87 88 // display subset of array elements used in this 89 // iteration of binary search loop 90 buildOutput( array2, low, middle, high ); Invoke method binarySearch, using array and search key as arguments
- 46. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 46 BinarySearch.ja va Lines 93-94 If search key matches middle array element, return element index Lines 97-98 If search key is less than middle array element, repeat search on first array half Lines 101-102 If search key is greater than middle array element, repeat search on second array half Lines 112-137 Method build- Output displays array contents being searched 91 92 // if key matches middle element, return middle location 93 if ( key == array[ middle ] ) 94 return middle; 95 96 // if key less than middle element, set new high element 97 else if ( key < array[ middle ] ) 98 high = middle - 1; 99 100 // key greater than middle element, set new low element 101 else 102 low = middle + 1; 103 104 } // end while 105 106 return -1; // key not found 107 108 } // end method binarySearch 109 110 // build row of output showing subset of array elements 111 // currently being processed 112 void buildOutput( int array3[], int low, int middle, int high ) 113 { 114 // create 2-digit integer number format 115 DecimalFormat twoDigits = new DecimalFormat( "00" ); 116 If search key matches middle array element, return element index If search key is greater than middle array element, repeat search on second array half If search key is less than middle array element, repeat search on first array half Method buildOutput displays array contents being searched
- 47. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 47 BinarySearch.ja va Line 128 Display an asterisk next to middle element 117 // loop through array elements 118 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array3.length; counter++ ) { 119 120 // if counter outside current array subset, append 121 // padding spaces to String display 122 if ( counter < low || counter > high ) 123 display += " "; 124 125 // if middle element, append element to String display 126 // followed by asterisk (*) to indicate middle element 127 else if ( counter == middle ) 128 display += twoDigits.format( array3[ counter ] ) + "* "; 129 130 else // append element to String display 131 display += twoDigits.format( array3[ counter ] ) + " "; 132 133 } // end for 134 135 display += "n"; 136 137 } // end method buildOutput 138 139 } // end class BinarySearch Display an asterisk next to middle element
- 48. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 48 BinarySearch.ja va
- 49. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 49 7.9 Multidimensional Arrays • Multidimensional arrays – Tables with rows and columns • Two-dimensional array • Declaring two-dimensional array b[2][2] int b[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } }; – 1 and 2 initialize b[0][0] and b[0][1] – 3 and 4 initialize b[1][0] and b[1][1] int b[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4, 5 } }; – row 0 contains elements 1 and 2 – row 1 contains elements 3, 4 and 5 – “ragged” array
- 50. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 50 7.9 Multidimensional Arrays (Cont.) • Creating multidimensional arrays – Can be allocated dynamically • 3-by-4 array int b[][]; b = new int[ 3 ][ 4 ]; • Rows can have different number of columns int b[][]; b = new int[ 2 ][ ]; // allocate rows b[ 0 ] = new int[ 5 ]; // allocate row 0 b[ 1 ] = new int[ 3 ]; // allocate row 1
- 51. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 51 Fig. 7.13 Two-dimensional array with three rows and four columns. a[ 1 ][ 0 ] a[ 1 ][ 1 ] a[ 1 ][ 2 ] a[ 1 ][ 3 ] Row 0 Row 1 Row 2 Column 0 Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Row index Array name Column index a[ 0 ][ 0 ] a[ 0 ][ 1 ] a[ 0 ][ 2 ] a[ 0 ][ 3 ] a[ 2 ][ 0 ] a[ 2 ][ 1 ] a[ 2 ][ 2 ] a[ 2 ][ 3 ]
- 52. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 52 InitArray.java Line 16 Declare array1 with six initializers in two sublists Line 17 Declare array2 with six initializers in three sublists 1 // Fig. 7.14: InitArray.java 2 // Initializing two-dimensional arrays. 3 import java.awt.Container; 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 public class InitArray extends JApplet { 7 JTextArea outputArea; 8 9 // set up GUI and initialize applet 10 public void init() 11 { 12 outputArea = new JTextArea(); 13 Container container = getContentPane(); 14 container.add( outputArea ); 15 16 int array1[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } }; 17 int array2[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } }; 18 19 outputArea.setText( "Values in array1 by row aren" ); 20 buildOutput( array1 ); 21 22 outputArea.append( "nValues in array2 by row aren" ); 23 buildOutput( array2 ); 24 25 } // end method init 26 Declare array1 with six initializers in two sublists Declare array2 with six initializers in three sublists
- 53. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 53 InitArray.java Line 34 array[row].leng th returns number of columns associated with row subscript Line 35 Use double-bracket notation to access two- dimensional array values 27 // append rows and columns of an array to outputArea 28 public void buildOutput( int array[][] ) 29 { 30 // loop through array's rows 31 for ( int row = 0; row < array.length; row++ ) { 32 33 // loop through columns of current row 34 for ( int column = 0; column < array[ row ].length; column++ ) 35 outputArea.append( array[ row ][ column ] + " " ); 36 37 outputArea.append( "n" ); 38 } 39 40 } // end method buildOutput 41 42 } // end class InitArray Use double-bracket notation to access two-dimensional array values array[row].length returns number of columns associated with row subscript
- 54. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 54 DoubleArray.jav a Lines 7-9 Declare grades as 3- by-4 array Lines 7-9 Each row represents a student; each column represents an exam grade 1 // Fig. 7.15: DoubleArray.java 2 // Two-dimensional array example. 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 public class DoubleArray extends JApplet { 7 int grades[][] = { { 77, 68, 86, 73 }, 8 { 96, 87, 89, 81 }, 9 { 70, 90, 86, 81 } }; 10 11 int students, exams; 12 String output; 13 JTextArea outputArea; 14 15 // initialize fields 16 public void init() 17 { 18 students = grades.length; // number of students 19 exams = grades[ 0 ].length; // number of exams 20 21 // create JTextArea and attach to applet 22 outputArea = new JTextArea(); 23 Container container = getContentPane(); 24 container.add( outputArea ); 25 Declare grades as 3-by-4 array Each row represents a student; each column represents an exam grade
- 55. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 55 DoubleArray.jav a Lines 31-32 Determine minimum and maximum for all student Lines 35-37 Determine average for each student 26 // build output string 27 output = "The array is:n"; 28 buildString(); 29 30 // call methods minimum and maximum 31 output += "nnLowest grade: " + minimum() + 32 "nHighest grade: " + maximum() + "n"; 33 34 // call method average to calculate each student's average 35 for ( int counter = 0; counter < students; counter++ ) 36 output += "nAverage for student " + counter + " is " + 37 average( grades[ counter ] ); // pass one row of array grades 38 39 // change outputArea's display font 40 outputArea.setFont( new Font( "Monospaced", Font.PLAIN, 12 ) ); 41 42 // place output string in outputArea 43 outputArea.setText( output ); 44 45 } // end method init 46 47 // find minimum grade 48 public int minimum() 49 { 50 // assume first element of grades array is smallest 51 int lowGrade = grades[ 0 ][ 0 ]; 52 Determine average for each student Determine minimum and maximum for all student
- 56. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 56 DoubleArray.jav a Lines 54-61 Use a nested loop to search for lowest grade in series Lines 74-81 Use a nested loop to search for highest grade in series 53 // loop through rows of grades array 54 for ( int row = 0; row < students; row++ ) 55 56 // loop through columns of current row 57 for ( int column = 0; column < exams; column++ ) 58 59 // if grade is less than lowGrade, assign it to lowGrade 60 if ( grades[ row ][ column ] < lowGrade ) 61 lowGrade = grades[ row ][ column ]; 62 63 return lowGrade; // return lowest grade 64 65 } // end method minimum 66 67 // find maximum grade 68 public int maximum() 69 { 70 // assume first element of grades array is largest 71 int highGrade = grades[ 0 ][ 0 ]; 72 73 // loop through rows of grades array 74 for ( int row = 0; row < students; row++ ) 75 76 // loop through columns of current row 77 for ( int column = 0; column < exams; column++ ) 78 79 // if grade is greater than highGrade, assign it to highGrade 80 if ( grades[ row ][ column ] > highGrade ) 81 highGrade = grades[ row ][ column ]; Use a nested loop to search for lowest grade in series Use a nested loop to search for highest grade in series
- 57. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 57 DoubleArray.jav a Line 88 Method average takes array of student test results as parameter Lines 93-94 Calculate sum of array elements Line 97 Divide by number of elements to get average 82 83 return highGrade; // return highest grade 84 85 } // end method maximum 86 87 // determine average grade for particular student (or set of grades) 88 public double average( int setOfGrades[] ) 89 { 90 int total = 0; // initialize total 91 92 // sum grades for one student 93 for ( int count = 0; count < setOfGrades.length; count++ ) 94 total += setOfGrades[ count ]; 95 96 // return average of grades 97 return ( double ) total / setOfGrades.length; 98 99 } // end method average 100 101 // build output string 102 public void buildString() 103 { 104 output += " "; // used to align column heads 105 106 // create column heads 107 for ( int counter = 0; counter < exams; counter++ ) 108 output += "[" + counter + "] "; Method average takes array of student test results as parameter Calculate sum of array elements Divide by number of elements to get average
- 58. 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Outline 58 DoubleArray.jav a 109 110 // create rows/columns of text representing array grades 111 for ( int row = 0; row < students; row++ ) { 112 output += "ngrades[" + row + "] "; 113 114 for ( int column = 0; column < exams; column++ ) 115 output += grades[ row ][ column ] + " "; 116 } 117 118 } // end method buildString 119 120 } // end class DoubleArray



![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
4
Fig. 7.1 A 12-element array.
Name of array
(note that all
elements of this
array have the
same name, c)
Index (or subscript) of
the element in array c
c[ 0 ]
c[ 1 ]
c[ 2 ]
c[ 3 ]
c[ 4 ]
c[ 5 ]
c[ 6 ]
c[ 7 ]
c[ 8 ]
c[ 9 ]
c[ 10 ]
c[ 11 ]
-45
6
0
72
1543
-89
0
62
-3
1
6453
78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-4-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
5
7.2 Arrays (cont.)
• Index
– Also called subscript
– Position number in square brackets
– Must be positive integer or integer expression
a = 5;
b = 6;
c[ a + b ] += 2;
• Adds 2 to c[ 11 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-5-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
6
7.2 Arrays (cont.)
• Examine array c
– c is the array name
– c.length accesses array c’s length (12)
– c has 12 elements ( c[0], c[1], … c[11] )
• The value of c[0] is –45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-6-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
7
7.3 Declaring and Creating Arrays
• Declaring and Creating arrays
– Arrays are objects that occupy memory
– Created dynamically with keyword new
int c[] = new int[ 12 ];
– Equivalent to
int c[]; // declare array variable
c = new int[ 12 ]; // create array
• We can create arrays of objects too
String b[] = new String[ 100 ];
– Each array element has a default – zero (primitives), false
(boolean), null (objects)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-7-320.jpg)

![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
9
InitArray.java
Line 9
Declare array as an
array of ints
Line 11
Create 10 ints for
array; each int is
initialized to 0 by
default
Line 16
array.length
returns length of
array
Line 17
array[counter]
returns int associated
with index in array
1 // Fig. 7.2: InitArray.java
2 // Creating an array.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class InitArray {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 int array[]; // declare reference to an array
10
11 array = new int[ 10 ]; // create array
12
13 String output = "IndextValuen";
14
15 // append each array element's value to String output
16 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
17 output += counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "n";
18
19 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
20 outputArea.setText( output );
21
22 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea,
23 "Initializing an Array of int Values",
24 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
25
26 System.exit( 0 );
27
28 } // end main
29
30 } // end class InitArray
Declare array as an
array of ints
Create 10 ints for array; each
int is initialized to 0 by default
array.length returns
length of array
array[counter] returns int
associated with index in array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-9-320.jpg)

![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
11
7.4 Examples Using Arrays (Cont.)
• Using an array initializer
– Use initializer list
• Items enclosed in braces ({})
• Items in list separated by commas
int n[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
– Creates a five-element array
– Index values of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
– Do not need keyword new](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-11-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
12
InitArray.java
Line 11
Declare array as an
array of ints
Line 11
Compiler uses
initializer list to
allocate array
1 // Fig. 7.3: InitArray.java
2 // Initializing an array with a declaration.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class InitArray {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 // array initializer specifies number of elements and
10 // value for each element
11 int array[] = { 32, 27, 64, 18, 95, 14, 90, 70, 60, 37 };
12
13 String output = "IndextValuen";
14
15 // append each array element's value to String output
16 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
17 output += counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "n";
18
19 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
20 outputArea.setText( output );
21
22 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea,
23 "Initializing an Array with a Declaration",
24 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
25
26 System.exit( 0 );
27
28 } // end main
29
30 } // end class InitArray
Declare array as an
array of ints
Compiler uses initializer list
to allocate array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-12-320.jpg)


![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
15
InitArray.java
Line 10
Declare array as an
array of ints
Line 12
Create 10 ints for
array
Line 16
Use array index to
assign array value
1 // Fig. 7.4: InitArray.java
2 // Initialize array with the even integers from 2 to 20.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class InitArray {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 final int ARRAY_LENGTH = 10; // constant
10 int array[]; // reference to int array
11
12 array = new int[ ARRAY_LENGTH ]; // create array
13
14 // calculate value for each array element
15 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
16 array[ counter ] = 2 + 2 * counter;
17
18 String output = "IndextValuen";
19
20 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
21 output += counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "n";
22
23 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
24 outputArea.setText( output );
25
Declare array as an
array of ints
Create 10 ints for array
Use array index to
assign array value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-15-320.jpg)


![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
18
SumArray.java
Line 9
Declare array with
initializer list
Lines 13-14
Sum all array values
1 // Fig. 7.5: SumArray.java
2 // Total the values of the elements of an array.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class SumArray {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
10 int total = 0;
11
12 // add each element's value to total
13 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
14 total += array[ counter ];
15
16 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null,
17 "Total of array elements: " + total,
18 "Sum the Elements of an Array",
19 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
20
21 System.exit( 0 );
22
23 } // end main
24
25 } // end class SumArray
Declare array with
initializer list
Sum all array values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-18-320.jpg)

![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
20
Histogram.java
Line 9
Declare array with
initializer list
Line 19
For each array
element, print
associated number of
asterisks
1 // Fig. 7.6: Histogram.java
2 // Histogram printing program.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class Histogram {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 int array[] = { 19, 3, 15, 7, 11, 9, 13, 5, 17, 1 };
10
11 String output = "ElementtValuetHistogram";
12
13 // for each array element, output a bar in histogram
14 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ ) {
15 output += "n" + counter + "t" + array[ counter ] + "t";
16
17 // print bar of asterisks
18 for ( int stars = 0; stars < array[ counter ]; stars++ )
19 output += "*";
20
21 } // end outer for
22
23 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
24 outputArea.setText( output );
25
Declare array with
initializer list
For each array element, print
associated number of asterisks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-20-320.jpg)


![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
23
RollDie.java
Line 9
Declare frequency
as array of 7 ints
Lines 12-13
Generate 6000
random integers in
range 1-6
Line 13
Increment
frequency values at
index associated with
random number
1 // Fig. 7.7: RollDie.java
2 // Roll a six-sided die 6000 times.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class RollDie {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 int frequency[] = new int[ 7 ];
10
11 // roll die 6000 times; use die value as frequency index
12 for ( int roll = 1; roll <= 6000; roll++ )
13 ++frequency[ 1 + ( int ) ( Math.random() * 6 ) ];
14
15 String output = "FacetFrequency";
16
17 // append frequencies to String output
18 for ( int face = 1; face < frequency.length; face++ )
19 output += "n" + face + "t" + frequency[ face ];
20
21 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
22 outputArea.setText( output );
23
24 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea,
25 "Rolling a Die 6000 Times", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
26
27 System.exit( 0 );
28
29 } // end main
30
31 } // end class RollDie
Declare frequency as
array of 7 ints
Generate 6000 random
integers in range 1-6
Increment frequency values at
index associated with random number](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-23-320.jpg)

![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
25
StudentPoll.jav
a
Lines 9-11
Declare responses
as array to store 40
responses
Line 12
Declare frequency
as array of 11 int
and ignore the first
element
Lines 16-17
For each response,
increment
frequency values at
index associated with
that response
1 // Fig. 7.8: StudentPoll.java
2 // Student poll program.
3 import javax.swing.*;
4
5 public class StudentPoll {
6
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 int responses[] = { 1, 2, 6, 4, 8, 5, 9, 7, 8, 10, 1, 6, 3, 8, 6,
10 10, 3, 8, 2, 7, 6, 5, 7, 6, 8, 6, 7, 5, 6, 6, 5, 6, 7, 5, 6,
11 4, 8, 6, 8, 10 };
12 int frequency[] = new int[ 11 ];
13
14 // for each answer, select responses element and use that value
15 // as frequency index to determine element to increment
16 for ( int answer = 0; answer < responses.length; answer++ )
17 ++frequency[ responses[ answer ] ];
18
19 String output = "RatingtFrequencyn";
20
21 // append frequencies to String output
22 for ( int rating = 1; rating < frequency.length; rating++ )
23 output += rating + "t" + frequency[ rating ] + "n";
24
25 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
26 outputArea.setText( output );
27
Declare responses as
array to store 40 responses
Declare frequency as array of 11
int and ignore the first element
For each response, increment
frequency values at index
associated with that response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-25-320.jpg)



![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
29
7.6 Passing Arrays to Methods
• To pass array argument to a method
– Specify array name without brackets
• Array hourlyTemperatures is declared as
int hourlyTemperatures[] =
new int[ 24 ];
• The method call
modifyArray( hourlyTemperatures );
• Passes array hourlyTemperatures to method
modifyArray
• Be careful! This allows array elements to be modified by the
method!!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-29-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
30
PassArray.java
Line 15
Declare 5-int
array with initializer
list
Line 24
Pass array by
reference to method
modifyArray
1 // Fig. 7.9: PassArray.java
2 // Passing arrays and individual array elements to methods.
3 import java.awt.Container;
4 import javax.swing.*;
5
6 public class PassArray extends JApplet {
7
8 // initialize applet
9 public void init()
10 {
11 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
12 Container container = getContentPane();
13 container.add( outputArea );
14
15 int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
16
17 String output = "Effects of passing entire array by reference:n" +
18 "The values of the original array are:n";
19
20 // append original array elements to String output
21 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
22 output += " " + array[ counter ];
23
24 modifyArray( array ); // array passed by reference
25
26 output += "nnThe values of the modified array are:n";
27
Declare 5-int array
with initializer list
Pass array by reference to
method modifyArray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-30-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
31
PassArray.java
Line 35
Pass array[3] by
value to method
modifyElement
Lines 43-47
Method
modifyArray
manipulates the array
directly
Lines 50-53
Method
modifyElement
manipulates a
primitive’s copy
Lines 52
The original primitive
is left unmodified
28 // append modified array elements to String output
29 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
30 output += " " + array[ counter ];
31
32 output += "nnEffects of passing array element by value:n" +
33 "array[3] before modifyElement: " + array[ 3 ];
34
35 modifyElement( array[ 3 ] ); // attempt to modify array[ 3 ]
36
37 output += "narray[3] after modifyElement: " + array[ 3 ];
38 outputArea.setText( output );
39
40 } // end method init
41
42 // multiply each element of an array by 2
43 public void modifyArray( int array2[] )
44 {
45 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array2.length; counter++ )
46 array2[ counter ] *= 2;
47 }
48
49 // multiply argument by 2
50 public void modifyElement( int element )
51 {
52 element *= 2;
53 }
54
55 } // end class PassArray
Pass array[3] by value to
method modifyElement
Method modifyArray
manipulates the array directly
Method modifyElement
manipulates a primitive’s copy
The original primitive is left unmodified](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-31-320.jpg)


![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
34
BubbleSort.java
Line 15
Declare 10-int
array with initializer
list
Line 23
Pass array by
reference to method
bubbleSort to sort
array
1 // Fig. 7.10: BubbleSort.java
2 // Sort an array's values into ascending order.
3 import java.awt.*;
4 import javax.swing.*;
5
6 public class BubbleSort extends JApplet {
7
8 // initialize applet
9 public void init()
10 {
11 JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea();
12 Container container = getContentPane();
13 container.add( outputArea );
14
15 int array[] = { 2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 12, 89, 68, 45, 37 };
16
17 String output = "Data items in original ordern";
18
19 // append original array values to String output
20 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
21 output += " " + array[ counter ];
22
23 bubbleSort( array ); // sort array
24
25 output += "nnData items in ascending ordern";
26
Declare 10-int array
with initializer list
Pass array by reference to method
bubbleSort to sort array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-34-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
35
BubbleSort.java
Line 36
Method
bubbleSort
receives array
reference as parameter
Lines 39-53
Use loop and nested
loop to make passes
through array
Lines 48-49
If pairs are in
decreasing order,
invoke method swap
to swap pairs
27 // append sorted array values to String output
28 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
29 output += " " + array[ counter ];
30
31 outputArea.setText( output );
32
33 } // end method init
34
35 // sort elements of array with bubble sort
36 public void bubbleSort( int array2[] )
37 {
38 // loop to control number of passes
39 for ( int pass = 1; pass < array2.length; pass++ ) {
40
41 // loop to control number of comparisons
42 for ( int element = 0;
43 element < array2.length - 1;
44 element++ ) {
45
46 // compare side-by-side elements and swap them if
47 // first element is greater than second element
48 if ( array2[ element ] > array2[ element + 1 ] )
49 swap( array2, element, element + 1 );
50
51 } // end loop to control comparisons
52
53 } // end loop to control passes
54
55 } // end method bubbleSort
Method bubbleSort receives
array reference as parameter
Use loop and nested loop to make
passes through array
If pairs are in decreasing order,
invoke method swap to swap pairs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-35-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
36
BubbleSort.java
Lines 58-65
Method swap swaps
two values in array
reference
56
57 // swap two elements of an array
58 public void swap( int array3[], int first, int second )
59 {
60 int hold; // temporary holding area for swap
61
62 hold = array3[ first ];
63 array3[ first ] = array3[ second ];
64 array3[ second ] = hold;
65 }
66
67 } // end class BubbleSort
Method swap swaps two
values in array reference](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-36-320.jpg)


![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
39
LinearSearch.ja
va
Line 11
Declare array of
ints
1 // Fig. 7.11: LinearSearch.java
2 // Linear search of an array.
3 import java.awt.*;
4 import java.awt.event.*;
5 import javax.swing.*;
6
7 public class LinearSearch extends JApplet implements ActionListener {
8
9 JLabel enterLabel, resultLabel;
10 JTextField enterField, resultField;
11 int array[];
12
13 // set up applet's GUI
14 public void init()
15 {
16 // get content pane and set its layout to FlowLayout
17 Container container = getContentPane();
18 container.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
19
20 // set up JLabel and JTextField for user input
21 enterLabel = new JLabel( "Enter integer search key" );
22 container.add( enterLabel );
23
24 enterField = new JTextField( 10 );
25 container.add( enterField );
26
27 // register this applet as enterField's action listener
28 enterField.addActionListener( this );
29
Declare array of ints](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-39-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
40
LinearSearch.ja
va
Lines 39-42
Allocate 100 ints
for array and
populate array with
even ints
Line 50
Loop through array
Lines 53-54
If array element at
index matches search
key, return index
30 // set up JLabel and JTextField for displaying results
31 resultLabel = new JLabel( "Result" );
32 container.add( resultLabel );
33
34 resultField = new JTextField( 20 );
35 resultField.setEditable( false );
36 container.add( resultField );
37
38 // create array and populate with even integers 0 to 198
39 array = new int[ 100 ];
40
41 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
42 array[ counter ] = 2 * counter;
43
44 } // end method init
45
46 // search array for specified key value
47 public int linearSearch( int array2[], int key )
48 {
49 // loop through array elements
50 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array2.length; counter++ )
51
52 // if array element equals key value, return location
53 if ( array2[ counter ] == key )
54 return counter;
55
56 return -1; // key not found
57
58 } // end method linearSearch
Create 100 ints for array and
populate array with even ints
Loop through array
If array element at index matches
search key, return index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-40-320.jpg)

![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
43
BinarySearch.ja
va
Line 14
Declare array of
ints
1 // Fig. 7.12: BinarySearch.java
2 // Binary search of an array.
3 import java.awt.*;
4 import java.awt.event.*;
5 import java.text.*;
6
7 import javax.swing.*;
8
9 public class BinarySearch extends JApplet implements ActionListener {
10 JLabel enterLabel, resultLabel;
11 JTextField enterField, resultField;
12 JTextArea output;
13
14 int array[];
15 String display = "";
16
17 // set up applet's GUI
18 public void init()
19 {
20 // get content pane and set its layout to FlowLayout
21 Container container = getContentPane();
22 container.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
23
24 // set up JLabel and JTextField for user input
25 enterLabel = new JLabel( "Enter integer search key" );
26 container.add( enterLabel );
27
28 enterField = new JTextField( 10 );
29 container.add( enterField );
30
Declare array of ints](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-43-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
44
BinarySearch.ja
va
Lines 48-51
Allocate 15 ints for
array and populate
array with even
ints
Line 56
Invoked when user
presses Enter
31 // register this applet as enterField's action listener
32 enterField.addActionListener( this );
33
34 // set up JLabel and JTextField for displaying results
35 resultLabel = new JLabel( "Result" );
36 container.add( resultLabel );
37
38 resultField = new JTextField( 20 );
39 resultField.setEditable( false );
40 container.add( resultField );
41
42 // set up JTextArea for displaying comparison data
43 output = new JTextArea( 6, 60 );
44 output.setFont( new Font( "Monospaced", Font.PLAIN, 12 ) );
45 container.add( output );
46
47 // create array and fill with even integers 0 to 28
48 array = new int[ 15 ];
49
50 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array.length; counter++ )
51 array[ counter ] = 2 * counter;
52
53 } // end method init
54
55 // obtain user input and call method binarySearch
56 public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent actionEvent )
57 {
58 // input also can be obtained with enterField.getText()
59 String searchKey = actionEvent.getActionCommand();
60
Allocate 15 ints for array and
populate array with even ints
Invoked when user presses Enter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-44-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
45
BinarySearch.ja
va
Line 65
Invoke method
binarySearch,
using array and
search key as
arguments
61 // initialize display string for new search
62 display = "Portions of array searchedn";
63
64 // perform binary search
65 int element = binarySearch( array, Integer.parseInt( searchKey ) );
66
67 output.setText( display );
68
69 // display search result
70 if ( element != -1 )
71 resultField.setText( "Found value in element " + element );
72 else
73 resultField.setText( "Value not found" );
74
75 } // end method actionPerformed
76
77 // method to perform binary search of an array
78 public int binarySearch( int array2[], int key )
79 {
80 int low = 0; // low element index
81 int high = array2.length - 1; // high element index
82 int middle; // middle element index
83
84 // loop until low index is greater than high index
85 while ( low <= high ) {
86 middle = ( low + high ) / 2; // determine middle index
87
88 // display subset of array elements used in this
89 // iteration of binary search loop
90 buildOutput( array2, low, middle, high );
Invoke method binarySearch, using
array and search key as arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-45-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
46
BinarySearch.ja
va
Lines 93-94
If search key matches
middle array
element, return
element index
Lines 97-98
If search key is less
than middle array
element, repeat search
on first array half
Lines 101-102
If search key is greater
than middle array
element, repeat search
on second array half
Lines 112-137
Method build-
Output displays
array contents being
searched
91
92 // if key matches middle element, return middle location
93 if ( key == array[ middle ] )
94 return middle;
95
96 // if key less than middle element, set new high element
97 else if ( key < array[ middle ] )
98 high = middle - 1;
99
100 // key greater than middle element, set new low element
101 else
102 low = middle + 1;
103
104 } // end while
105
106 return -1; // key not found
107
108 } // end method binarySearch
109
110 // build row of output showing subset of array elements
111 // currently being processed
112 void buildOutput( int array3[], int low, int middle, int high )
113 {
114 // create 2-digit integer number format
115 DecimalFormat twoDigits = new DecimalFormat( "00" );
116
If search key matches middle array
element, return element index
If search key is greater than middle array
element, repeat search on second array half
If search key is less than middle array
element, repeat search on first array half
Method buildOutput displays
array contents being searched](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-46-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
47
BinarySearch.ja
va
Line 128
Display an asterisk
next to middle element
117 // loop through array elements
118 for ( int counter = 0; counter < array3.length; counter++ ) {
119
120 // if counter outside current array subset, append
121 // padding spaces to String display
122 if ( counter < low || counter > high )
123 display += " ";
124
125 // if middle element, append element to String display
126 // followed by asterisk (*) to indicate middle element
127 else if ( counter == middle )
128 display += twoDigits.format( array3[ counter ] ) + "* ";
129
130 else // append element to String display
131 display += twoDigits.format( array3[ counter ] ) + " ";
132
133 } // end for
134
135 display += "n";
136
137 } // end method buildOutput
138
139 } // end class BinarySearch
Display an asterisk next to middle element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-47-320.jpg)

![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
49
7.9 Multidimensional Arrays
• Multidimensional arrays
– Tables with rows and columns
• Two-dimensional array
• Declaring two-dimensional array b[2][2]
int b[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
– 1 and 2 initialize b[0][0] and b[0][1]
– 3 and 4 initialize b[1][0] and b[1][1]
int b[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4, 5 } };
– row 0 contains elements 1 and 2
– row 1 contains elements 3, 4 and 5
– “ragged” array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-49-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
50
7.9 Multidimensional Arrays (Cont.)
• Creating multidimensional arrays
– Can be allocated dynamically
• 3-by-4 array
int b[][];
b = new int[ 3 ][ 4 ];
• Rows can have different number of columns
int b[][];
b = new int[ 2 ][ ]; // allocate rows
b[ 0 ] = new int[ 5 ]; // allocate row 0
b[ 1 ] = new int[ 3 ]; // allocate row 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-50-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
51
Fig. 7.13 Two-dimensional array with three rows and four columns.
a[ 1 ][ 0 ] a[ 1 ][ 1 ] a[ 1 ][ 2 ] a[ 1 ][ 3 ]
Row 0
Row 1
Row 2
Column 0 Column 1 Column 2 Column 3
Row index
Array name
Column index
a[ 0 ][ 0 ] a[ 0 ][ 1 ] a[ 0 ][ 2 ] a[ 0 ][ 3 ]
a[ 2 ][ 0 ] a[ 2 ][ 1 ] a[ 2 ][ 2 ] a[ 2 ][ 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-51-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
52
InitArray.java
Line 16
Declare array1 with
six initializers in two
sublists
Line 17
Declare array2 with
six initializers in three
sublists
1 // Fig. 7.14: InitArray.java
2 // Initializing two-dimensional arrays.
3 import java.awt.Container;
4 import javax.swing.*;
5
6 public class InitArray extends JApplet {
7 JTextArea outputArea;
8
9 // set up GUI and initialize applet
10 public void init()
11 {
12 outputArea = new JTextArea();
13 Container container = getContentPane();
14 container.add( outputArea );
15
16 int array1[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
17 int array2[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
18
19 outputArea.setText( "Values in array1 by row aren" );
20 buildOutput( array1 );
21
22 outputArea.append( "nValues in array2 by row aren" );
23 buildOutput( array2 );
24
25 } // end method init
26
Declare array1 with six
initializers in two sublists
Declare array2 with six
initializers in three sublists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-52-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
53
InitArray.java
Line 34
array[row].leng
th returns number of
columns associated
with row subscript
Line 35
Use double-bracket
notation to access two-
dimensional array
values
27 // append rows and columns of an array to outputArea
28 public void buildOutput( int array[][] )
29 {
30 // loop through array's rows
31 for ( int row = 0; row < array.length; row++ ) {
32
33 // loop through columns of current row
34 for ( int column = 0; column < array[ row ].length; column++ )
35 outputArea.append( array[ row ][ column ] + " " );
36
37 outputArea.append( "n" );
38 }
39
40 } // end method buildOutput
41
42 } // end class InitArray
Use double-bracket notation to access
two-dimensional array values
array[row].length returns number
of columns associated with row subscript](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-53-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
54
DoubleArray.jav
a
Lines 7-9
Declare grades as 3-
by-4 array
Lines 7-9
Each row represents a
student; each column
represents an exam
grade
1 // Fig. 7.15: DoubleArray.java
2 // Two-dimensional array example.
3 import java.awt.*;
4 import javax.swing.*;
5
6 public class DoubleArray extends JApplet {
7 int grades[][] = { { 77, 68, 86, 73 },
8 { 96, 87, 89, 81 },
9 { 70, 90, 86, 81 } };
10
11 int students, exams;
12 String output;
13 JTextArea outputArea;
14
15 // initialize fields
16 public void init()
17 {
18 students = grades.length; // number of students
19 exams = grades[ 0 ].length; // number of exams
20
21 // create JTextArea and attach to applet
22 outputArea = new JTextArea();
23 Container container = getContentPane();
24 container.add( outputArea );
25
Declare grades as 3-by-4 array
Each row represents a student; each
column represents an exam grade](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-54-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
55
DoubleArray.jav
a
Lines 31-32
Determine minimum
and maximum for all
student
Lines 35-37
Determine average for
each student
26 // build output string
27 output = "The array is:n";
28 buildString();
29
30 // call methods minimum and maximum
31 output += "nnLowest grade: " + minimum() +
32 "nHighest grade: " + maximum() + "n";
33
34 // call method average to calculate each student's average
35 for ( int counter = 0; counter < students; counter++ )
36 output += "nAverage for student " + counter + " is " +
37 average( grades[ counter ] ); // pass one row of array grades
38
39 // change outputArea's display font
40 outputArea.setFont( new Font( "Monospaced", Font.PLAIN, 12 ) );
41
42 // place output string in outputArea
43 outputArea.setText( output );
44
45 } // end method init
46
47 // find minimum grade
48 public int minimum()
49 {
50 // assume first element of grades array is smallest
51 int lowGrade = grades[ 0 ][ 0 ];
52
Determine average
for each student
Determine minimum and
maximum for all student](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-55-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
56
DoubleArray.jav
a
Lines 54-61
Use a nested loop to
search for lowest
grade in series
Lines 74-81
Use a nested loop to
search for highest
grade in series
53 // loop through rows of grades array
54 for ( int row = 0; row < students; row++ )
55
56 // loop through columns of current row
57 for ( int column = 0; column < exams; column++ )
58
59 // if grade is less than lowGrade, assign it to lowGrade
60 if ( grades[ row ][ column ] < lowGrade )
61 lowGrade = grades[ row ][ column ];
62
63 return lowGrade; // return lowest grade
64
65 } // end method minimum
66
67 // find maximum grade
68 public int maximum()
69 {
70 // assume first element of grades array is largest
71 int highGrade = grades[ 0 ][ 0 ];
72
73 // loop through rows of grades array
74 for ( int row = 0; row < students; row++ )
75
76 // loop through columns of current row
77 for ( int column = 0; column < exams; column++ )
78
79 // if grade is greater than highGrade, assign it to highGrade
80 if ( grades[ row ][ column ] > highGrade )
81 highGrade = grades[ row ][ column ];
Use a nested loop to search
for lowest grade in series
Use a nested loop to search
for highest grade in series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-56-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
57
DoubleArray.jav
a
Line 88
Method average
takes array of student
test results as
parameter
Lines 93-94
Calculate sum of array
elements
Line 97
Divide by number of
elements to get
average
82
83 return highGrade; // return highest grade
84
85 } // end method maximum
86
87 // determine average grade for particular student (or set of grades)
88 public double average( int setOfGrades[] )
89 {
90 int total = 0; // initialize total
91
92 // sum grades for one student
93 for ( int count = 0; count < setOfGrades.length; count++ )
94 total += setOfGrades[ count ];
95
96 // return average of grades
97 return ( double ) total / setOfGrades.length;
98
99 } // end method average
100
101 // build output string
102 public void buildString()
103 {
104 output += " "; // used to align column heads
105
106 // create column heads
107 for ( int counter = 0; counter < exams; counter++ )
108 output += "[" + counter + "] ";
Method average takes array of
student test results as parameter
Calculate sum of array elements
Divide by number of
elements to get average](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-57-320.jpg)
![ 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Outline
58
DoubleArray.jav
a
109
110 // create rows/columns of text representing array grades
111 for ( int row = 0; row < students; row++ ) {
112 output += "ngrades[" + row + "] ";
113
114 for ( int column = 0; column < exams; column++ )
115 output += grades[ row ][ column ] + " ";
116 }
117
118 } // end method buildString
119
120 } // end class DoubleArray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-240826093201-da231e65/85/Arrays-in-Java-Programming-Language-slides-58-320.jpg)






















































