ASP.NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat.pdf
- 1. Top 50 ASP.NET Core Interview Questions and Answers for 2024 ASP.NET Core Interview Questions & Answers for Beginners 1. Explain ASP.NET Core ASP.NET Core Top 50 Most Important Interview Questions: An Overview Are you someone eager to learn Microsoft technologies? Do you want to explore the building blocks of Microsoft Applications? If so, ASP.NET Core is a compulsory web application framework to be learned. Along with learning the technology, one must also be aware of the technical questions being asked in the interviews. With this aspect in mind, we have come up with the commonly asked ASP. NET Core interview questions in this ASP.NET Core tutorial. This can be referred by both, freshers and professionals. ASP.NET Core is a modern, open-source web framework for building cross-platform web apps and APIs. It's lightweight, modular, and runs on Windows, Linux, and macOS. It unifies MVC and Web API into a single model, making it flexible for web, mobile backends, and even IoT applications. It's backed by Microsoft and the .NET community, offering strong tooling, extensive documentation, and a vibrant ecosystem.
- 2. 2. Explain the key differences between ASP.NET Core and ASP.NET. Key differences between ASP.NET Core and ASP.NET Feature Platform Microsoft Support Framework Size Performance Architecture Model-View-Controller (MVC) Configuration Open Source ASP.NET Core Cross-platform macOS) Modular and lightweight Generally faster and more efficient Built on .NET Core runtime ASP.NET (Windows, Linux,Windows only Larger and more complex Potentially slower due to larger size Built on full .NET Framework Integrated with Web API in a unifiedSeparate MVC framework and Web API framework More flexible and streamlined Yes Complex and XML-based configuration Primarily closed-source, with some open- source components Fully supported by Microsoft Limited support for older ASP.NET versions
- 3. Suitable for Modern web apps, cloud deployments, microservices Legacy applications, deployments Windows-specific The Startup class in ASP.NET Core is your application's control center, controlling its setup and behavior. It defines how your app interacts with databases, middleware, and external services through the ConfigureServices and Configure methods. It also enables dependency injection for modularity and testability. 4. Explain Dependency Injection. 3. Describe the role of the Startup class.
- 4. Training Name ASP.NET Core Training ASP.NET Core Certification Training Training Mode Live Training Live Training Cross-platform: Develop for Windows, macOS, Linux, & various architectures. Get Free Demo!! Book a FREE Live Demo! Book a FREE Live Demo! Dependency injection is a design pattern that allows you to inject dependencies (objects) into your code at runtime. In ASP.NET Core, the built-in DI container manages the creation and lifetime of these dependencies. This means your code doesn't need to create or manage them directly, leading to looser coupling and more testable code. 5. What are the benefits of ASP.NET Core? Upskill for Higher Salary with ASP.NET Core Programming Courses
- 5. Feature Purpose Use Case Execution app.Run vs. app.Use in ASP.NET Core Middleware Configuration Lightweight & performant: Blazing fast execution & minimal resource footprint. Unified APIs: Build web UIs & APIs with a consistent, flexible approach. Modular & testable: Easy to customize & test, promoting code maintainability. Cloud-friendly: Integrates seamlessly with cloud platforms like Azure. Blazingly fast: Optimized for modern web frameworks & APIs. Open-source & community-driven: Access to vast resources & ongoing development. app.Run Adds a terminal middleware delegate to the pipeline. app.Use Adds a non-terminal middleware delegate to the pipeline. Processes the request and passes it to the next middleware in the pipeline. Suitable for complex applications requiring multiple processing steps. Processes the request and ends the pipeline. Suitable for simple applications with no further processing needed. The ASP.NET Core request processing pipeline, also called the "middleware pipeline," is a series of modular components called "middleware" that handle an incoming HTTP request in sequence.Each middleware performs a specific task before passing the request to the next one, like authentication, logging, or routing. 6. Explain the request processing pipeline in ASP.NET Core. 7. Differentiate between app.Run and app.Use in middleware configuration.
- 6. Result Example Flexibility Testability Can be challenging to test due to its terminal nature. app.Run(async context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!")); Sends the response directly to the client. context => await app.UseAuthentication(); app.UseAuthorization(); Modifies the request context and passes it to the next middleware. More flexible, and allows chaining multiple middleware components. Limited, only handles the request directly. Easier to test in isolation as it is part of a larger pipeline. In ASP.NET Core, a Request delegate is a function that processes and handles an incoming HTTP request.It's the core building block of the request processing pipeline, which is essentially a series of middleware components that handle the request one after the other. ASP.NET Core config lives in key-value pairs across sources like files (appsettings.json) and environment. Providers like JSON or environment vars read these pairs and build a unified view. Access values by key using IConfiguration to control app behavior without hardcoding. In ASP.NET Core, the Host plays a crucial role in managing the application's lifecycle and providing resources for its execution. It's essentially the container that houses your application and orchestrates its startup, execution, and shutdown. Responsibilities of the Host are: Configuration: Reads and parses application settings and environment variables. Dependency Injection (DI): Creates and manages the lifetime of dependencies needed by your application. Logging: Configures and manages logging infrastructure for your application. Lifetime Management: Starts, runs, and stops your application gracefully. Hosting Environment: Provides information about the environment your application runs in (e.g., development, production). Web Server Integration: Manages the web server (e.g., Kestrel) used to serve your application. Hosted Services: Enables background tasks to run alongside your application. 9. Describe the Host in ASP.NET Core. 8. What is a Request delegate and how is it used? 10. Explain how Configuration works in ASP.NET Core and reading values from the appsettings.json file.
- 7. Example: Reading Values from appsettings.json: ASP.NET Core doesn't serve static files like images, HTML, or CSS by default. Instead, it relies on the UseStaticFiles middleware to handle this task. You configure this middleware to point to your static file folder, typically wwwroot. Then, the middleware intercepts requests for these files and delivers them directly to the client, bypassing the entire ASP.NET Core pipeline. Once the configuration is built, you can access values from appsettings.json using the IConfiguration interface injected in your classes or accessed through the Host.Configuration property. You can retrieve values by their key using methods like GetValue<T>("key"), where T is the expected type of the value. 11. How does ASP.NET Core handle static file serving? public class MyController : Controller { private readonly IConfiguration _configuration; public MyController(IConfiguration configuration) { } _configuration = configuration; public IActionResult Index() { } } string connectionString = _configuration.GetValue<string>("ConnectionStrings:Default"); // Use the connection string to access your database... return View();
- 8. This keeps things fast and efficient. Additionally, you can control caching and authorization for static files to further optimize your application. In ASP.NET Core, Session and State Management refers to techniques for storing and maintaining data across multiple user requests. This data can be user-specific (like shopping cart items) or application-wide (like configuration settings). Session state uses cookies to track users, while other options like cache or database can hold global state. Choosing the right approach depends on the type and persistence needs of your data. Docker containers offer a perfect match for the agility and flexibility of ASP.NET Core applications. It's a powerful combination for building and deploying modern web applications. Here's why: Lightweight and portable Scalability and isolation Microservices architecture Simplified deployment In ASP.NET Core, model binding is a powerful feature that bridges the gap between user input and your application logic. It automatically maps data from an HTTP request (like forms, query strings, or JSON bodies) to C# model objects used in your controller actions. This simplifies development by removing the need for manual data parsing and validation. 14. Describe Model Binding in ASP.NET Core. 12. Explain Session and State Management options in ASP.NET Core. 13. Can ASP.NET Core applications be run in Docker containers? Explain. 15. Explain Model Validation and how to perform custom validation logic.
- 9. Here are some ways to perform custom validation logic in ASP.NET Core: Using IValidatableObject: Inside the Validate method, you can perform your custom checks and add ValidationResult objects to the errors list. These results are then used to display error messages to the user. Creating custom validation attributes: You can inherit from the ValidationAttribute class and implement your custom logic in the IsValid method. This allows you to define reusable validation rules that can be applied to multiple model properties. Using validation libraries: Libraries like Fluent Validation provide an intuitive syntax for defining validation rules and error messages. You can create validation classes specific to your models and integrate them with the framework's validation system. Model validation ensures that data submitted to your application meets certain criteria before being processed.It's crucial for maintaining data integrity and preventing invalid or incomplete data from entering your system.ASP.NET Core provides built-in features and libraries for model validation, but you can also implement custom logic for specific scenarios. ASP.NET Core MVC architecture is based on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern, cleanly separating concerns in your web application. Models represent data, Views handle presentation, and Controllers manage the interaction between them. Models are the building blocks, Views are the blueprints, and Controllers are the construction crew, working together to create a beautiful and functional web experience. This separation improves code maintainability, testability, and scalability, making your applications well- organized and flexible. Performing custom validation logic: 16. Explain the ASP.NET Core MVC architecture. 17. Explain the components (Model, View, Controller) of ASP.NET Core MVC.
- 10. The components of ASP.NET Core MVC are as follows: In ASP.NET Core MVC, routing acts like a map, directing incoming URLs to the right controller action. In ASP.NET Core MVC development, ViewModels play a crucial role in separating data and presentation concerns. They act as a bridge between your domain models (entities representing business data) and the views (user interface). ViewModels are custom classes specifically designed to represent the data required by a particular view. Unlike domain models, they are not directly tied to the database or business logic. They are lightweight and hold only the data relevant to that specific view, often combining information from multiple domain models or adding formatting or calculations for display purposes. Models: Represent the data and logic of your application. They define the entities and their relationships, encapsulate business rules, and handle data access. Model classes typically interact with databases or other data sources. Views: Responsible for presenting the user interface. They use technologies like HTML, CSS, and Razor to render the data received from the models in a visually appealing way. Views do not know the application logic and only focus on presentation. Controllers: Act as the entry point for user interaction and orchestrate the flow of the application. They receive user requests, process them using the models, and ultimately choose which view to render. Controllers interact with both models and views, but never directly with the user interface. 19. Explain how routing works in ASP.NET Core MVC applications. 18. Describe the concept of view models in ASP.NET Core MVC development.
- 11. Dependency Injection (DI) addresses several key problems in ASP.NET Core, leading to a more robust and maintainable application: Tight Coupling. It uses two key ingredients: route templates that define possible URL patterns and middleware that scan requests against those patterns. When a match is found, the corresponding controller action is invoked, handling the request and generating a response. Attribute-based routing is a powerful feature in ASP.NET Core MVC that allows you to define the routes for your web application directly on your controller classes and action methods using Route attributes.This approach offers several advantages over convention-based routing, providing more control and flexibility over the URIs your application exposes. 21. What problems does Dependency Injection solve in ASP.NET Core? 20. Explain the concept of Attribute-based routing in ASP.NET Core MVC. ASP.NET Core Interview Questions and Answers for Intermediate
- 12. Code Rigidity. Testing Difficulties. Maintainability Challenges. 1. Transient Lifetime: A new instance of the service is created every time it's injected. 2. Scoped Lifetime: A single instance of the service is created per request scope (e.g., per HTTP request). 3. Singleton Lifetime: A single instance of the service is created for the entire lifetime of the application. In ASP.NET Core, service lifetimes define how long a particular instance of a service will be managed by the dependency injection (DI) container.Choosing the right lifetime for your services is crucial for optimizing performance, managing resources, and preventing memory leaks. Here are the three primary service lifetimes: 23. Explain the concept of Middleware. 22. Describe the different Service Lifetimes in ASP.NET Core.
- 13. Intercepts HTTP requests and responses Processes requests in a configurable pipeline Offers built-in features like authentication, logging, and compression Allows custom middleware for specific application needs Extends functionality without modifying the core framework In ASP.NET Core, middleware is a powerful and flexible concept for processing incoming HTTP requests and generating responses. It essentially acts like a pipeline of components, where each component performs a specific task on the request or response before passing it to the next one. Middleware is essentially software code that gets plugged into the ASP.NET Core application pipeline. Each middleware component is a class that implements the IMiddleware interface. Each component gets executed sequentially on every HTTP request and response. The Options Pattern is a design pattern used in ASP.NET Core to manage and load configuration settings from various sources, primarily the appsettings.json file. It works by: Defining strongly typed classes: You create classes with properties representing your configuration settings. This provides type safety and better code readability. 24. What is the role of middleware in ASP.NET Core? 25. What is the Options Pattern and how is it used in ASP.NET Core configuration?
- 14. .NET Core's logging system is a flexible tool for recording application events. It uses the ILogger interface and ILoggerFactory to generate and manage logs. You can send logs to various destinations like consoles, files, and databases. Different log levels like Information and Error control message severity. The system integrates with dependency injection and web frameworks, making it easy to configure and use throughout your application. Tools: Consider using tools like dotnet CLI or deployment platforms like Azure DevOps to manage environment-specific configuration and deployment processes. Code isolation: Separate code specific to different environments (e.g., database connection strings) into different assemblies or modules. Secret management: Use secure methods like Azure Key Vault to store sensitive information like passwords or API keys, ensuring they are not exposed in configuration files. Binding configuration: You use the IOptions<TOptions> interface to bind the corresponding section of the configuration file to your options class. Dependency Injection: You register the IOptions<TOptions> service in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. This allows your code to access the configuration data throughout the application. ASP.NET Core's logging system uses structured messages and flexible configuration. It offers pre-built providers like console and debug, but you can extend it with custom sinks like databases or third-party tools. Managing multiple environments in ASP.NET Core is crucial for a smooth development and deployment process. Here's how to configure and manage them effectively: Environment Variable: This is the most common method. Set an environment variable like ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT to values like Development, Staging, or Production. Your code can then react to this variable to adjust settings. Multiple appsettings.json files: Create separate appsettings.json files for each environment, named appsettings.Development.json, appsettings.Staging.json, etc. Your application can then read the specific file based on the environment variable. Other sources: You can also use other configuration sources like Azure Key Vault, command-line arguments, or custom providers. 27. Explain the Logging system in .NET Core and ASP.NET Core. Logging system in .NET Core: 26. How to configure and manage multiple environments in ASP.NET Core applications? Configuration: Managing Environments: Logging system in ASP.NET Core:
- 15. Dependency injection provides ILogger instances for code to log application events, errors, and performance details, helping you troubleshoot and monitor your web app effectively. Routing in ASP.NET Core acts like a map, directing incoming requests to the right destination. It matches the URL path against predefined templates in two main ways: convention-based (like "/Products/{id}" for product details) and attribute-based (using [Route] annotations on controllers). These routes can be named for easier navigation and URL generation. Convention-based routing kicks in first, followed by attribute-based, ensuring flexibility and control. This dynamic system lets you build clean, intuitive URLs for your users. There are two main ways to define routes in ASP.NET Core: 1. Convention-Based Routing It creates routes based on a series of conventions representing all the possible routes in your system. Convention-based is defined in the Startup.cs file. 28. Describe how Routing works in ASP.NET Core and its different types. Convention-Based Routing Configuration & Mapping
- 16. 2. Attribute Routing It creates routes based on attributes placed on the controller or action level. Attribute routing provides us more control over the URL generation patterns which helps us in SEO.
- 17. Attribute Routing Tokens One of the cool things about ASP.NET Core routing is its flexibility as compared to ASP.NET MVC5 routing since it provides tokens for [area], [controller], and [action]. These tokens get replaced by their values in the route table.
- 18. 30. How to implement custom model binding in ASP.NET Core. Following are the steps to implement custom model binding in ASP.NET Core: 29. Explain strategies for handling errors and exceptions in ASP.NET Core applications. Error and exception handling are crucial for building robust and reliable ASP.NET Core applications. Here are some key strategies to consider: 31. How to write custom ASP.NET Core middleware for specific functionalities? 1. Create a custom model binder class implementing IModeBinder. 2. Override BindModelAsync to handle your specific model binding logic. 3. Access request data (form, query string, etc.) using the provided context. 4. Parse and map data to your custom model properties. 5. Register your binder in ConfigureServices using AddMvcOptions. . Specify the model type and binder type in controller actions or Razor Pages. Middleware: Global error handling with specific responses, logging, and custom error pages. Try/Catch: Localized error handling for specific scenarios and resource cleanup. Exception Filters: Intercept and handle exceptions before reaching the middleware. Descriptive Errors: Throw specific exceptions with clear messages for better debugging. Logging: Capture all exceptions for analysis and later troubleshooting.
- 19. OWIN, or Open Web Interface for .NET, is a standardized interface that sits between web applications written in .NET and the web servers that host them.It acts as a decoupling layer, allowing different frameworks and servers to work together seamlessly. Accessing ASP.NET Core APIs from a class library involves two key steps: 1. Target the ASP.NET Core Shared Framework: This ensures your library shares the same base framework as an ASP.NET Core application, allowing seamless API usage. 2. Reference relevant NuGet packages: For specific ASP.NET Core functionalities, install the corresponding NuGet packages within your class library project. This grants access to specific API components you need. To create custom ASP.NET Core middleware, you need two key things: a class implementing IMiddleware or an extension method. The class constructor takes a RequestDelegate which defines your next step in the request pipeline. In the Invoke method, access the HttpContext to perform your desired functionality. Remember to call _next(httpContext) to continue processing the request. You can then modify the request/response objects, and log information, or even short-circuit the pipeline. This opens up endless possibilities for custom tasks like authentication, logging, or request manipulation in your ASP.NET Core application. A Change Token in ASP.NET Core is a lightweight, efficient mechanism for detecting changes to a resource or piece of data. It's like a mini-observer that sits on your data and silently waits for any modifications. When something changes, the token raises an event, notifying you to take appropriate action. In ASP.NET Core, there are two main ways to access the HttpContext object: 1. Dependency Injection: This is the preferred approach. Inject the IHttpContextAccessor service into your class through the constructor. Then, use _httpContextAccessor.HttpContext to access the current request context. 2. Direct Access: In controllers and Razor Pages, you can directly access HttpContext as a property. However, this is less flexible and tightly couples your code to the request context. 33. What is a Change Token in ASP.NET Core development? 32. Explain how to access the HttpContext object within an ASP.NET Core application. 35. Explain the Open Web Interface for .NET (OWIN) and its relationship to ASP.NET Core. 34. How can ASP.NET Core APIs be used and accessed from a class library project? Relationship with ASP.NET Core:
- 20. In ASP.NET Core, the application model acts as a blueprint for your MVC app. It's built by the framework of scanning your controllers, actions, filters, and routes. This internal map lets ASP.NET understand your app's structure and handle requests efficiently. Think of it like a detailed backstage map that helps the actors (controllers and viewers) perform their roles smoothly. While you don't directly interact with it much, the application model plays a crucial role in making your ASP.NET Core apps function as intended. ASP.NET Core offers two main caching strategies: response caching and distributed caching. Response caching leverages HTTP headers like "Cache-Control" to store static content like images or frequently accessed data in the browser or server memory, reducing server load and improving response The URL Rewriting Middleware in ASP.NET Core is a powerful tool for manipulating incoming request URLs based on predefined rules. It allows you to decouple the physical location of your resources from their public URLs, creating a more flexible and maintainable application.Now, let's talk about some real-world applications of the URL Rewriting Middleware: SEO-friendly URLs: Rewrite long, parameter-heavy URLs into shorter, keyword-rich ones to improve search engine ranking and user experience. Migrating content: Seamlessly transitions users to new content locations without breaking existing links by rewriting old URLs to point to new ones. Vanity URLs: Create custom URLs for specific marketing campaigns or promotional offers. URL normalization: Ensure consistent URL formats throughout your application by rewriting variations like upper/lowercase or trailing slashes. Legacy compatibility: Maintain compatibility with older applications that expect specific URL structures by rewriting newer URLs to match them. Hosting foundation: ASP.NET Core itself is built on top of OWIN, meaning it adheres to the OWIN interface for communication with web servers. Middleware integration: ASP.NET Core middleware, which adds functionality like authentication and logging, is built as OWIN middleware components, allowing them to be easily plugged into any OWIN-compliant server. Hosting flexibility: ASP.NET Core applications can be hosted on various OWIN-compliant servers like IIS, Kestrel (ASP.NET Core's built-in server), and self-hosted environments. ASP.NET Core Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced 36. Describe the URL Rewriting Middleware in ASP.NET Core and its applications. 37. Explain the concept of the application model in ASP.NET Core development. 38. Describe Caching or Response Caching strategies in ASP.NET Core.
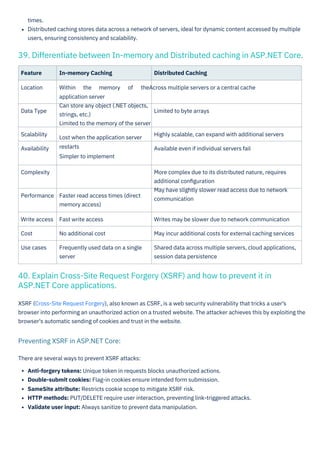
- 21. There are several ways to prevent XSRF attacks: Anti-forgery tokens: Unique token in requests blocks unauthorized actions. Double-submit cookies: Flag-in cookies ensure intended form submission. SameSite attribute: Restricts cookie scope to mitigate XSRF risk. HTTP methods: PUT/DELETE require user interaction, preventing link-triggered attacks. Validate user input: Always sanitize to prevent data manipulation. times. Distributed caching stores data across a network of servers, ideal for dynamic content accessed by multiple users, ensuring consistency and scalability. Feature In-memory Caching Distributed Caching Location Within the memory of theAcross multiple servers or a central cache application server Can store any object (.NET objects, strings, etc.) Limited to the memory of the server Lost when the application server restarts Simpler to implement Data Type Limited to byte arrays Scalability Availability Highly scalable, can expand with additional servers Available even if individual servers fail Complexity More complex due to its distributed nature, requires additional configuration May have slightly slower read access due to network communication Performance Faster read access times (direct memory access) Write access Cost Use cases Fast write access No additional cost Frequently used data on a single server Writes may be slower due to network communication May incur additional costs for external caching services Shared data across multiple servers, cloud applications, session data persistence XSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery), also known as CSRF, is a web security vulnerability that tricks a user's browser into performing an unauthorized action on a trusted website. The attacker achieves this by exploiting the browser's automatic sending of cookies and trust in the website. 40. Explain Cross-Site Request Forgery (XSRF) and how to prevent it in ASP.NET Core applications. 39. Differentiate between In-memory and Distributed caching in ASP.NET Core. Preventing XSRF in ASP.NET Core:
- 22. 44. How does ASP.NET Core support Dependency Injection for views? 43. Explain how Dependency Injection is implemented for controllers in ASP.NET Core MVC. 41. Describe strategies for protecting your ASP.NET Core applications from Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks. Following are the strategies for protecting your ASP.NET Core applications from Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks: 45. Describe the approach to unit testing controllers in ASP.NET Core MVC applications. 42. Explain how to enable Cross-Origin Requests (CORS) in ASP.NET Core for API access from different domains. Install Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cors NuGet package. Register CORS middleware in ConfigureServices of Startup.cs. Define CORS policy with allowed origins, methods, and headers. Use the [EnableCors] attribute on controllers or apply globally. Optionally, set exposed response headers for client access. In ASP.NET Core, views can leverage Dependency Injection (DI) through the @inject directive. This directive acts like a property declaration, allowing you to inject services directly into the view. This approach helps keep controllers focused on logic and views focused on presentation, promoting the separation of concerns. While injecting complex dependencies into views isn't recommended, it's useful for scenarios like populating UI elements with dynamic data retrieved from services specific to the view. Unit testing ASP.NET Core MVC controllers involves isolating the controller's logic from dependencies like databases and focusing on its core functionality. You achieve this by mocking external services and injecting them into the controller. In ASP.NET Core MVC, controllers request their dependencies (like data access or service classes) explicitly through their constructors. This dependency injection happens via a built-in Inversion of Control (IoC) container. The container manages the creation and lifetime of these dependencies, injecting them into the controllers when needed. This keeps controllers loose-coupled, testable, and easily adaptable to changes. Simply put, controllers tell the container what they need, and the container provides it automatically. Validate and sanitize all user input. Escape HTML in output to prevent script injection. Use Content Security Policy (CSP) to restrict executable content. Leverage anti-XSS libraries and frameworks. Regularly update dependencies and perform security audits.
- 23. Compile-time type checking. Improved tooling support. Reduced runtime errors. Cleaner and more readable code. Improved maintainability. Improve performance: By caching frequently accessed content, reducing server workload. Boost scalability: Serve cached content faster to handle higher traffic. Simplify caching: Declarative approach within Razor views, avoiding complex caching code. Fine-grained control: Configure duration, vary-by factors, and cache invalidation. Integrates seamlessly: Works with existing ASP.NET Core caching infrastructure. A built-in Razor Tag Helper for caching content within Razor views, using the internal ASP.NET Core cache. In ASP.NET Core MVC, a strongly typed view is a view that's explicitly associated with a specific data type or model class. This means the view is aware of the model's properties and methods, offering several benefits compared to "dynamic" views. In ASP.NET Core MVC, validation follows the DRY principle through built-in data annotations and model binding. Data annotations like Required and StringLength decorate model properties, defining validation rules without repeating code. Model binding automatically applies these annotations during data submission, catching errors and displaying user-friendly messages before controller actions execute. Partial views are reusable Razor components in ASP.NET Core MVC applications. They're essentially mini-views, built as .cshtml files but without the @page directive (used in Razor Pages). Instead, they're incorporated into other views to render specific sections of the UI. The test follows the "Arrange-Act-Assert" pattern: set up the mock dependencies, invoke the controller action, and verify that the expected results (e.g., returned data, view model, status code) are generated. This approach ensures your controller logic works as intended, independent of external influences. 49. Explain Partial Views and their use cases in ASP.NET Core MVC. 46. What is the Cache Tag Helper in ASP.NET Core MVC and its purpose? 48. Describe strongly typed views and their benefits in ASP.NET Core MVC. 47. Explain how validation works in ASP.NET Core MVC and how it follows the DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principle. Purpose: Benefits of strongly typed views: HTML to PDF
- 24. Use Cases for Partial Views: Authorization and Access Control Mechanisms: Identity and Authentication. Roles and Claims. Authorization Policies. Middleware. Best Practices for Secure Implementation: Principle of Least Privilege. Avoid Hardcoded Credentials. Validate Inputs. Use HTTPS. Implement CSRF Protection. Regularly Update Libraries and Frameworks. Perform Security Audits. ASP.NET Core offers several features and best practices to handle authorization and access control, ensuring secure and controlled access to your application's resources. Navigation menus: Render a common navigation menu across multiple pages using a single partial view. Product lists: Display dynamic product listings on different pages by dynamically loading the partial view with different product data. Comments sections: Implement a reusable comment section component across various blog posts or ar ticles. Modals and popups: Create reusable modals or popup windows for different functionalities. Form sections: Break down complex forms into smaller, reusable sections for better organization and validation. This detailed guide covers everything from fundamental principles and frameworks to sophisticated functionalities and security measures. Master these questions and demonstrate your skills to potential employers, making a memorable impression. Remember that practice makes perfect, so start coding and acing your interview! If you're looking for a career in ASP.NET, consider enrolling in our ASP.NET Certification Course to get your hands on a comprehensive guide that will give expertise in this field. Q1. How do I Prepare for an ASP.NET Core Interview? 50. How does ASP.NET Core handle security concerns like authorization and access control, and what are some best practices for implementing them effectively in real-world applications? Summary FAQs
- 25. Resources like official documentation, online tutorials, blogs, coding challenge platforms might be helpful for you to prepare for your ASP.NET Core Interview. When you are answering ASP.NET Core Interview Questions, try to be more concise, clear with your responses and be confident while you speak. You can showcase your ASP.NET Core projects by emphasizing on the problems you solved, what technologies and frameworks you used, your role in the said project. To prepare for an ASP.NET Core Interview, have proper understanding of its concepts like MVC architecture, middleware, dependency injection and authentication mechanisms and practice as much coding as you can. Q2. How do I showcase ASP.NET Core Projects in an Interview? Q3. What are Some Resources for ASP.NET Core Interview Preparation? Q4. What are Some Tips for Answering ASP.NET Core Interview Questions?














![Dependency injection provides ILogger instances for code to log application events, errors, and performance
details, helping you troubleshoot and monitor your web app effectively.
Routing in ASP.NET Core acts like a map, directing incoming requests to the right destination.
It matches the URL path against predefined templates in two main ways: convention-based (like
"/Products/{id}" for product details) and attribute-based (using [Route] annotations on controllers).
These routes can be named for easier navigation and URL generation.
Convention-based routing kicks in first, followed by attribute-based, ensuring flexibility and control.
This dynamic system lets you build clean, intuitive URLs for your users.
There are two main ways to define routes in ASP.NET Core:
1. Convention-Based Routing
It creates routes based on a series of conventions representing all the possible routes in your system.
Convention-based is defined in the Startup.cs file.
28. Describe how Routing works in ASP.NET Core and its different types.
Convention-Based Routing Configuration & Mapping](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-240715121828-9a858c26/85/ASP-NET-Core-Interview-Questions-PDF-By-ScholarHat-pdf-15-320.jpg)

![Attribute Routing Tokens
One of the cool things about ASP.NET Core routing is its flexibility as compared to ASP.NET MVC5 routing
since it provides tokens for [area], [controller], and [action]. These tokens get replaced by their values in the
route table.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-240715121828-9a858c26/85/ASP-NET-Core-Interview-Questions-PDF-By-ScholarHat-pdf-17-320.jpg)



![44. How does ASP.NET Core support Dependency Injection for views?
43. Explain how Dependency Injection is implemented for controllers in
ASP.NET Core MVC.
41. Describe strategies for protecting your ASP.NET Core applications from
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
Following are the strategies for protecting your ASP.NET Core applications from Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
attacks:
45. Describe the approach to unit testing controllers in ASP.NET Core MVC
applications.
42. Explain how to enable Cross-Origin Requests (CORS) in ASP.NET Core for
API access from different domains.
Install Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cors NuGet package.
Register CORS middleware in ConfigureServices of Startup.cs.
Define CORS policy with allowed origins, methods, and headers.
Use the [EnableCors] attribute on controllers or apply globally.
Optionally, set exposed response headers for client access.
In ASP.NET Core, views can leverage Dependency Injection (DI) through the @inject directive.
This directive acts like a property declaration, allowing you to inject services directly into the view.
This approach helps keep controllers focused on logic and views focused on presentation, promoting the
separation of concerns.
While injecting complex dependencies into views isn't recommended, it's useful for scenarios like populating
UI elements with dynamic data retrieved from services specific to the view.
Unit testing ASP.NET Core MVC controllers involves isolating the controller's logic from dependencies like
databases and focusing on its core functionality.
You achieve this by mocking external services and injecting them into the controller.
In ASP.NET Core MVC, controllers request their dependencies (like data access or service classes) explicitly
through their constructors.
This dependency injection happens via a built-in Inversion of Control (IoC) container.
The container manages the creation and lifetime of these dependencies, injecting them into the controllers
when needed.
This keeps controllers loose-coupled, testable, and easily adaptable to changes.
Simply put, controllers tell the container what they need, and the container provides it automatically.
Validate and sanitize all user input.
Escape HTML in output to prevent script injection.
Use Content Security Policy (CSP) to restrict executable content.
Leverage anti-XSS libraries and frameworks.
Regularly update dependencies and perform security audits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-240715121828-9a858c26/85/ASP-NET-Core-Interview-Questions-PDF-By-ScholarHat-pdf-22-320.jpg)


