Assignment on Numerical Method C Code
- 1. Assignment on Numerical Methods Assignment topic: C code using numerical methods Course Code: CSE 234 Fall-2014 Submitted To: Md. Jashim Uddin Assistant Professor Dept. of Natural Sciences Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Faculty of Science & Information Technology Submitted by: Name: Syed Ahmed Zaki Name: Fatema Khatun Name: Sumi Basak Name: Priangka Kirtania Name: Afruza Zinnurain ID:131-15-2169 ID:131-15-2372 ID:131-15-2364 ID:131-15-2385 ID:131-15-2345 Sec: B Dept. of CSE,FSIT Date of submission: 12 , December 2014
- 2. Contents: Root Finding Method Page Bisection Method 2 Newton-Raphson Method 4 Interpolation Newton Forward Interpolation 5 Newton Backward Interpolation 7 Lagrange Method 8 Numerical Integration Trapezoidal Rule 10 Simpson’s 1/3 Rule 12 Simpson’s 3/8 Rule 13 Weddle’s Rule 14 Ordinary Differential Equations Euler Method 17 Runge-Kutta 4th order method 18 Linear System Gauss Seidel Method 20 1
- 3. Bisection Method: The Bisection Method is a numerical method for estimating the roots of a polynomial f(x). It is one of the simplest and most reliable but it is not the fastest method. Problem: Here we have to find root for the polynomial x^3+x^2-1 Algorithm: 1. Start 2. Read a1, b1, TOL *Here a1 and b1 are initial guesses TOL is the absolute error or tolerance i.e. the desired degree of accuracy* 3. Compute: f1 = f(a1) and f3 = f(b1) 4. If (f1*f3) > 0, then display initial guesses are wrong and goto step 11 Otherwise continue. 5. root = (a1 + b1)/2 6. If [ (a1 – b1)/root ] < TOL , then display root and goto step 11 * Here [ ] refers to the modulus sign. * or f(root)=0 then display root 7. Else, f2 = f(root) 8. If (f1*f2) < 0, then b1=root 9. Else if (f2*f3)<0 then a1=root 10. else goto step 5 *Now the loop continues with new values.* 11. Stop Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #define f(y) (pow(x,3)+x*x-1); int main() { double a,b,m=-1,x,y; int n=0,k,i; printf("Enter the value of a: "); scanf("%lf",&a); printf("Enter the value of b: "); scanf("%lf",&b); printf("How many itteration you want: "); scanf("%d",&k); printf("n n a b xn=a+b/2 sign of(xn)n"); printf("-------------------------------------------------------------n"); for(i=1;i<=k;i++) { x=(a+b)/2; y=f(x); 2
- 4. 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 if(m==x) { break; } i f(y>=0) { printf(" %d %.5lf %.5lf %.5lf +n",i,a,b,x); b=x; } else if(y<0) { printf(" %d %.5lf %.5lf %.5lf -n",i,a,b,x); a=x; } m=x; } printf("nThe approximation to the root is %.4lf which is upto 4D",b); return 0; } Output: 3
- 5. Newton – Raphson Method: Problem: Here we have to find root for the polynomial x^3-8*x-4 upto 6D(decimal places) Solution in C: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #define f(x) pow(a,3)-8*a-4; #define fd(x) 3*pow(a,2)-8; int main() { double a,b,c,d,h,k,x,y; int i,j,m,n; printf("Enter the value of xn: "); scanf("%lf",&a); printf("Enter itteration number: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf(" xn f(x) f'(x) hn=-f(x)/f'(xn) xn+1=xn+hn"); printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------n"); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { x=f(a); y=fd(x); h=-(x/y); k=h+a; printf(" %.7lf %.7lf %.7lf %.7lf %.7lfn",a,x,y,h,k); a=k; } printf("nThe approximation to the root is %.6lf which is upto 6D",k); return 0; } 4
- 6. Output: Newton Forward Interpolation: Problem: The population of a town is given below as thousands Year : 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population : 46 66 81 93 101 Find the population of 1895 ? Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #include<stdlib.h> main() { float x[20],y[20],f,s,h,d,p; int j,i,n; printf("enter the value of n :"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("enter the elements of x:"); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("n%f",&x[i]); } printf("enter the elements of y:"); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { 5
- 7. 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 scanf("n%f",&y[i]); } h=x[2]-x[1]; printf("Enter the value of f(to findout value):"); scanf("%f",&f); s=(f-x[1])/h; p=1; d=y[1]; for(i=1;i<=(n-1);i++) { for(j=1;j<=(n-i);j++) { y[j]=y[j+1]-y[j]; } p=p*(s-i+1)/i; d=d+p*y[1]; } printf("For the value of x=%6.5f THe value is %6.5f",f,d); getch(); } Output: 6
- 8. Newton Backward Interpolation: Problem: The population of a town is given below as thousands Year : 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population : 46 66 81 93 101 Find the population of 1895 ? Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #include<stdlib.h> main() { float x[20],y[20],f,s,d,h,p; int j,i,k,n; printf("enter the value of the elements :"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("enter the value of x:n"); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%f",&x[i]); } printf("enter the value of y:n"); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%f",&y[i]); } h=x[2]-x[1]; printf("enter the searching point f:"); scanf("%f",&f); s=(f-x[n])/h; d=y[n]; p=1; for(i=n,k=1;i>=1,k<n;i--,k++) { for(j=n;j>=1;j--) { y[j]=y[j]-y[j-1]; } p=p*(s+k-1)/k; d=d+p*y[n]; } printf("for f=%f ,ans is=%f",f,d); getch(); } 7
- 9. Output: Lagrange Method: Problem: The population of a town is given below as thousands Year : 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population : 46 66 81 93 101 Find the population of 1895 ? Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { float x[10],y[10],temp=1,f[10],sum,p; int i,n,j,k=0,c; printf("nhow many record you will be enter: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("nnenter the value of x%d: ",i); scanf("%f",&x[i]); printf("nnenter the value of f(x%d): ",i); scanf("%f",&y[i]); } printf("nnEnter X for finding f(x): "); scanf("%f",&p); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { temp = 1; 8
- 10. 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 k = i; for(j=0;j<n;j++) { if(k==j) { continue; } else { temp = temp * ((p-x[j])/(x[k]-x[j])); } } f[i]=y[i]*temp; } for(i=0;i<n;i++) { sum = sum + f[i]; } printf("nn f(%.1f) = %f ",p,sum); getch(); } 9
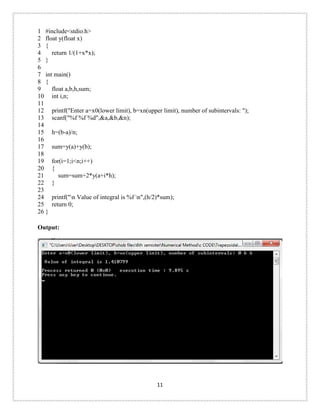
- 11. Output: Trapezoidal Rule: Problem: Here we have to find integration for the (1/1+x*x)dx with lower limit =0 to upper limit = 6 Algorithm: Step 1: input a,b,number of interval n Step 2:h=(b-a)/n Step 3:sum=f(a)+f(b) Step 4:If n=1,2,3,……i Then , sum=sum+2*y(a+i*h) Step 5:Display output=sum *h/2 Code: 10
- 12. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include<stdio.h> float y(float x) { return 1/(1+x*x); } int main() { float a,b,h,sum; int i,n; printf("Enter a=x0(lower limit), b=xn(upper limit), number of subintervals: "); scanf("%f %f %d",&a,&b,&n); h=(b-a)/n; sum=y(a)+y(b); for(i=1;i<n;i++) { sum=sum+2*y(a+i*h); } printf("n Value of integral is %f n",(h/2)*sum); return 0; } Output: 11
- 13. Simpson’s 1/3 rule: Problem: Here we have to find integration for the (1/1+x*x)dx with lower limit =0 to upper limit = 6 Algorithm: Step 1: input a,b,number of interval n Step 2:h=(b-a)/n Step 3:sum=f(a)+f(b)+4*f(a+h) Step 4:sum=sum+4*f(a+i*h)+2*f(a+(i-1)*h) Step 5:Display output=sum * h/3 Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include<stdio.h> float y(float x){ return 1/(1+x*x); } int main(){ float a,b,h,sum; int i,n; printf("Enter a=x0(lower limit), b=xn(upper limit), number of subintervals: "); scanf("%f%f%d",&a,&b,&n); h = (b - a)/n; sum = y(a)+y(b)+4*y(a+h); for(i = 3; i<=n-1; i=i+2){ sum=sum+4*y(a+i*h) + 2*y(a+(i-1)*h); } printf("n Value of integral is %fn",(h/3)*sum); return 0; } 12
- 14. Output: Simpson’s 3/8 rule: Problem: Here we have to find integration for the (1/1+x*x)dx with lower limit =0 to upper limit = 6 Algorithm: Step 1: input a,b,number of interval n Step 2:h=(b-a)/n Step 3:sum=f(a)+f(b) Step 4:If n is odd Then , sum=sum+2*y(a+i*h) Step 5: else, When n I s even Then, Sum = sum+3*y(a+i*h) Step 6:Display output=sum *3* h/8 Code: 1 2 3 4 5 #include<stdio.h> float y(float x){ return 1/(1+x*x); //function of which integration is to be calculated } int main(){ 13
- 15. 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 float a,b,h,sum; int i,n,j; sum=0; printf("Enter a=x0(lower limit), b=xn(upper limit), number of subintervals: "); scanf("%f%f%d",&a,&b,&n); h = (b-a)/n; sum = y(a)+y(b); for(i=1;i<n;i++) { if(i%3==0){ sum=sum+2*y(a+i*h); } else{ sum=sum+3*y(a+i*h); } } printf("Value of integral is %fn", (3*h/8)*sum); } Output: Weddle’s Rule: Problem: Here we have to find integration for the (1/1+x*x)dx with lower limit =0 to upper limit = 6 Algorithm: Step 1: input a,b,number of interval n Step 2:h=(b-a)/n Step 3:If(n%6==0) 14
- 16. Then , sum=sum+((3*h/10)*(y(a)+y(a+2*h)+5*y(a+h)+6*y(a+3*h)+y(a+4*h)+5*y(a+5*h)+y(a+6*h))) ; a=a+6*h and Weddle’s rule is applicable then go to step 6 Step 4: else, Weddle’s rule is not applicable Step 5:Display output Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include<stdio.h> float y(float x){ return 1/(1+x*x); //function of which integration is to be calculated } int main(){ float a,b,h,sum; int i,n,m; printf("Enter a=x0(lower limit), b=xn(upper limit), number of subintervals: "); scanf("%f%f%d",&a,&b,&n); h = (b-a)/n; sum=0; if(n%6==0){ sum=sum+((3*h/10)*(y(a)+y(a+2*h)+5*y(a+h)+6*=a+6*h; printf("Value of integral is %fn", sum); } else{ printf("Sorry ! Weddle rule is not applicable"); } } 15
- 17. Output: Euler Method: Problem: Here we have to find dy/dx=x+y where y(0)=1 at the point x=0.05 and x=0.10 taking h=0.05 Algorithm: 1. Start 2. Define function 3. Get the values of x0, y0, h and xn *Here x0 and y0 are the initial conditions h is the interval xn is the required value 4. n = (xn – x0)/h + 1 5. Start loop from i=1 to n 6. y = y0 + h*f(x0,y0) x = x + h 7. Print values of y0 and x0 8. Check if x < xn If yes, assign x0 = x and y0 = y If no, goto 9. 9. End loop i 10. Stop 16
- 18. Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include<stdio.h> float fun(float x,float y) { float f; f=x+y; return f; } main() { float a,b,x,y,h,t,k; printf("nEnter x0,y0,h,xn: "); scanf("%f%f%f%f",&a,&b,&h,&t); x=a; y=b; printf("n xt yn"); while(x<=t) { k=h*fun(x,y); y=y+k; x=x+h; printf("%0.3ft %0.3fn",x,y); } } Output: 17
- 19. Runge-Kutta 4th order method: Problem: Here we have to find y(0,2) and y(0,4), Given dy/dx=1+y^2 where y=0 when x=0 Algorithm: Step 1: input x0,y0,h,last point n Step 2:m1=f(xi,yi) Step 3:m2=f(xi+h/2,yi+m1h/2) Step 4:m3=f(xi+h/2,yi+m2h/2) Step 5:m4=f(xi+h,yi+m3h) Step 6:yi+1=yi+(m1+2m2+2m3+m4/6)h Step 5:Display output Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include<stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include<conio.h> #define F(x,y) 1 + (y)*(y) void main() { double y0,x0,y1,n,h,f,k1,k2,k3,k4; system("cls"); printf("nEnter the value of x0: "); scanf("%lf",&x0); printf("nEnter the value of y0: "); scanf("%lf",&y0); printf("nEnter the value of h: "); scanf("%lf",&h); printf("nEnter the value of last point: "); scanf("%lf",&n); for(; x0<n; x0=x0+h) { f=F(x0,y0); k1 = h * f; f = F(x0+h/2,y0+k1/2); k2 = h * f; f = F(x0+h/2,y0+k2/2); k3 = h * f; f = F(x0+h/2,y0+k2/2); k4 = h * f; 18
- 20. 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 y1 = y0 + ( k1 + 2*k2 + 2*k3 + k4)/6; printf("nn k1 = %.4lf ",k1); printf("nn k2 = %.4lf ",k2); printf("nn k3 = %.4lf ",k3); printf("nn k4 = %.4lf ",k4); printf("nn y(%.4lf) = %.3lf ",x0+h,y1); y0=y1; } getch(); } Output: Gauss Seidel Method Problem: Solve the following systems using gauss seidel method 5×1-x2-x3-x4=-4 -x1+10×2-x3-x4=12 -x1-x2+5×3-x4=8 -x1-x2-x3+10×4=34 Code: 1 2 3 #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> 19
- 21. 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #define acc 0.0001 #define X1(x2,x3,x4) ((x2 + x3 + x4 -4)/5) #define X2(x1,x3,x4) ((x1 + x3 + x4 +12)/10) #define X3(x1,x2,x4) ((x1 + x2 + x4 +8)/5) #define X4(x1,x2,x3) ((x1 + x2 + x3 +34)/10) void main() { double x1=0,x2=0,x3=0,x4=0,y1,y2,y3,y4; int i=0; system("cls"); printf("n______________________________________________________________n"); printf("n x1tt x2tt x3tt x4n"); printf("n______________________________________________________________n"); printf("n%ft%ft%ft%f",x1,x2,x3,x4); do { y1=X1(x2,x3,x4); y2=X2(x1,x3,x4); y3=X3(x1,x2,x4); y4=X4(x1,x2,x3); if(fabs(y1-x1)<acc && fabs(y2-x2)<acc && fabs(y3-x3)<acc &&fabs(y4-x4) ) { printf("n_____________________________________________________________n"); printf("nnx1 = %.3lf",y1); printf("nnx2 = %.3lf",y2); printf("nnx3 = %.3lf",y3); printf("nnx4= %.3lf",y4); i = 1; } e lse { x1 = y1; x2 = y2; x3 = y3; x4 = y4; printf("n%ft%ft%ft%f",x1,x2,x3,x4); } }while(i != 1); getch(); } 20
- 22. Output: 21



![Bisection Method: The Bisection Method is a numerical method for estimating the roots of a polynomial f(x). It is one of the simplest and most reliable but it is not the fastest method.
Problem: Here we have to find root for the polynomial x^3+x^2-1
Algorithm:
1. Start
2. Read a1, b1, TOL *Here a1 and b1 are initial guesses TOL is the absolute error or tolerance i.e. the desired degree of accuracy*
3. Compute: f1 = f(a1) and f3 = f(b1)
4. If (f1*f3) > 0, then display initial guesses are wrong and goto step 11 Otherwise continue.
5. root = (a1 + b1)/2
6. If [ (a1 – b1)/root ] < TOL , then display root and goto step 11 * Here [ ] refers to the modulus sign. * or f(root)=0 then display root
7. Else, f2 = f(root)
8. If (f1*f2) < 0, then b1=root
9. Else if (f2*f3)<0 then a1=root
10. else goto step 5 *Now the loop continues with new values.*
11. Stop
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#define f(y) (pow(x,3)+x*x-1);
int main()
{
double a,b,m=-1,x,y;
int n=0,k,i;
printf("Enter the value of a: ");
scanf("%lf",&a);
printf("Enter the value of b: ");
scanf("%lf",&b);
printf("How many itteration you want: ");
scanf("%d",&k);
printf("n n a b xn=a+b/2 sign of(xn)n");
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------n");
for(i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
x=(a+b)/2;
y=f(x);
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-141213041833-conversion-gate02/85/Assignment-on-Numerical-Method-C-Code-3-320.jpg)


![Output:
Newton Forward Interpolation: Problem: The population of a town is given below as thousands Year : 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population : 46 66 81 93 101
Find the population of 1895 ?
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
main()
{
float x[20],y[20],f,s,h,d,p;
int j,i,n;
printf("enter the value of n :");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("enter the elements of x:");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("n%f",&x[i]);
}
printf("enter the elements of y:");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-141213041833-conversion-gate02/85/Assignment-on-Numerical-Method-C-Code-6-320.jpg)
![18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
scanf("n%f",&y[i]);
}
h=x[2]-x[1];
printf("Enter the value of f(to findout value):");
scanf("%f",&f);
s=(f-x[1])/h;
p=1;
d=y[1];
for(i=1;i<=(n-1);i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=(n-i);j++)
{
y[j]=y[j+1]-y[j];
}
p=p*(s-i+1)/i;
d=d+p*y[1];
}
printf("For the value of x=%6.5f THe value is %6.5f",f,d);
getch();
}
Output:
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-141213041833-conversion-gate02/85/Assignment-on-Numerical-Method-C-Code-7-320.jpg)
![Newton Backward Interpolation: Problem: The population of a town is given below as thousands Year : 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population : 46 66 81 93 101
Find the population of 1895 ?
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
main()
{
float x[20],y[20],f,s,d,h,p;
int j,i,k,n;
printf("enter the value of the elements :");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("enter the value of x:n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%f",&x[i]);
}
printf("enter the value of y:n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%f",&y[i]);
}
h=x[2]-x[1];
printf("enter the searching point f:");
scanf("%f",&f);
s=(f-x[n])/h;
d=y[n];
p=1;
for(i=n,k=1;i>=1,k<n;i--,k++)
{
for(j=n;j>=1;j--)
{
y[j]=y[j]-y[j-1];
}
p=p*(s+k-1)/k;
d=d+p*y[n];
}
printf("for f=%f ,ans is=%f",f,d);
getch();
}
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-141213041833-conversion-gate02/85/Assignment-on-Numerical-Method-C-Code-8-320.jpg)
![Output:
Lagrange Method: Problem: The population of a town is given below as thousands Year : 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population : 46 66 81 93 101
Find the population of 1895 ?
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
float x[10],y[10],temp=1,f[10],sum,p;
int i,n,j,k=0,c;
printf("nhow many record you will be enter: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("nnenter the value of x%d: ",i);
scanf("%f",&x[i]);
printf("nnenter the value of f(x%d): ",i);
scanf("%f",&y[i]);
}
printf("nnEnter X for finding f(x): ");
scanf("%f",&p);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
temp = 1;
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-141213041833-conversion-gate02/85/Assignment-on-Numerical-Method-C-Code-9-320.jpg)
![23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
k = i;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(k==j)
{
continue;
}
else
{
temp = temp * ((p-x[j])/(x[k]-x[j]));
}
}
f[i]=y[i]*temp;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sum = sum + f[i];
}
printf("nn f(%.1f) = %f ",p,sum);
getch();
}
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-141213041833-conversion-gate02/85/Assignment-on-Numerical-Method-C-Code-10-320.jpg)