autoencoder-190813144108.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes220 views
- Autoencoders are unsupervised artificial neural networks useful for dimensionality reduction and clustering of unlabeled data. They compress the input into a latent-space representation and then reconstruct the output from this representation. - Deep autoencoders, also known as stacked autoencoders, can learn hierarchical representations of the data by stacking multiple autoencoders together. The features learned by one autoencoder are used as the input for the next autoencoder in the stack. - Variational autoencoders use probabilistic encoding and decoding to model the data distribution and can generate new samples from this distribution. They have been used for tasks like image generation, data manipulation, and unsupervised learning.
1 of 27
Download to read offline
























Ad
Recommended
Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine Learning



Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine LearningFrancesco Casalegno ▸ Machine Learning / Deep Learning models require to set the value of many hyperparameters
▸ Common examples: regularization coefficients, dropout rate, or number of neurons per layer in a Neural Network
▸ Instead of relying on some "expert advice", this presentation shows how to automatically find optimal hyperparameters
▸ Exhaustive Search, Monte Carlo Search, Bayesian Optimization, and Evolutionary Algorithms are explained with concrete examples
Learning to Rank with Neural Networks



Learning to Rank with Neural NetworksBhaskar Mitra Tutorial presented at ACM SIGIR/SIGKDD Africa Summer School on Machine Learning for Data Mining and Search (AFIRM 2020) conference in Cape Town, South Africa.
알기쉬운 Variational autoencoder



알기쉬운 Variational autoencoder홍배 김 동경대 Sho Tatsuno 군이 작성한 Variational autoencoder 설명자료를 부분 수정 번역한 자료로 작동원리를 쉽게 이해할 수 있습니다.
Flow based generative models



Flow based generative models수철 박 NICE: Non-linear Independent Components Estimation
Laurent Dinh, David Krueger, Yoshua Bengio. 2014.
Density estimation using Real NVP
Laurent Dinh, Jascha Sohl-Dickstein, Samy Bengio. 2017.
Glow: Generative Flow with Invertible 1x1 Convolutions
Diederik P. Kingma, Prafulla Dhariwal. 2018.
논문 리뷰 자료
1시간만에 GAN(Generative Adversarial Network) 완전 정복하기



1시간만에 GAN(Generative Adversarial Network) 완전 정복하기NAVER Engineering 발표자: 최윤제(고려대 석사과정)
최윤제 (Yunjey Choi)는 고려대학교에서 컴퓨터공학을 전공하였으며, 현재는 석사과정으로 Machine Learning을 공부하고 있는 학생이다. 코딩을 좋아하며 이해한 것을 다른 사람들에게 공유하는 것을 좋아한다. 1년 간 TensorFlow를 사용하여 Deep Learning을 공부하였고 현재는 PyTorch를 사용하여 Generative Adversarial Network를 공부하고 있다. TensorFlow로 여러 논문들을 구현, PyTorch Tutorial을 만들어 Github에 공개한 이력을 갖고 있다.
개요:
Generative Adversarial Network(GAN)은 2014년 Ian Goodfellow에 의해 처음으로 제안되었으며, 적대적 학습을 통해 실제 데이터의 분포를 추정하는 생성 모델입니다. 최근 들어 GAN은 가장 인기있는 연구 분야로 떠오르고 있고 하루에도 수 많은 관련 논문들이 쏟아져 나오고 있습니다.
수 없이 쏟아져 나오고 있는 GAN 논문들을 다 읽기가 힘드신가요? 괜찮습니다. 기본적인 GAN만 완벽하게 이해한다면 새로 나오는 논문들도 쉽게 이해할 수 있습니다.
이번 발표를 통해 제가 GAN에 대해 알고 있는 모든 것들을 전달해드리고자 합니다. GAN을 아예 모르시는 분들, GAN에 대한 이론적인 내용이 궁금하셨던 분들, GAN을 어떻게 활용할 수 있을지 궁금하셨던 분들이 발표를 들으면 좋을 것 같습니다.
발표영상: https://youtu.be/odpjk7_tGY0
Support Vector Machine without tears



Support Vector Machine without tearsAnkit Sharma This document provides an overview of support vector machines (SVMs), including their basic concepts, formulations, and applications. SVMs are supervised learning models that analyze data, recognize patterns, and are used for classification and regression. The document explains key SVM properties, the concept of finding an optimal hyperplane for classification, soft margin SVMs, dual formulations, kernel methods, and how SVMs can be used for tasks beyond binary classification like regression, anomaly detection, and clustering.
Hyperparameter Tuning



Hyperparameter TuningJon Lederman The document discusses hyperparameters and hyperparameter tuning in deep learning models. It defines hyperparameters as parameters that govern how the model parameters (weights and biases) are determined during training, in contrast to model parameters which are learned from the training data. Important hyperparameters include the learning rate, number of layers and units, and activation functions. The goal of training is for the model to perform optimally on unseen test data. Model selection, such as through cross-validation, is used to select the optimal hyperparameters. Training, validation, and test sets are also discussed, with the validation set used for model selection and the test set providing an unbiased evaluation of the fully trained model.
Deep Neural Methods for Retrieval



Deep Neural Methods for RetrievalBhaskar Mitra Deep neural methods have recently demonstrated significant performance improvements in several IR tasks. In this lecture, we will present a brief overview of deep models for ranking and retrieval.
This is a follow-up lecture to "Neural Learning to Rank" (https://www.slideshare.net/BhaskarMitra3/neural-learning-to-rank-231759858)
Regularization in deep learning



Regularization in deep learningKien Le Presentation in Vietnam Japan AI Community in 2019-05-26.
The presentation summarizes what I've learned about Regularization in Deep Learning.
Disclaimer: The presentation is given in a community event, so it wasn't thoroughly reviewed or revised.
Variational Autoencoder Tutorial 



Variational Autoencoder Tutorial Hojin Yang The document provides an introduction to variational autoencoders (VAE). It discusses how VAEs can be used to learn the underlying distribution of data by introducing a latent variable z that follows a prior distribution like a standard normal. The document outlines two approaches - explicitly modeling the data distribution p(x), or using the latent variable z. It suggests using z and assuming the conditional distribution p(x|z) is a Gaussian with mean determined by a neural network gθ(z). The goal is to maximize the likelihood of the dataset by optimizing the evidence lower bound objective.
Variational Autoencoder



Variational AutoencoderMark Chang Youtube:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLeeHDpwX2Kj55He_jfPojKrZf22HVjAZY
Paper review of "Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes"
Densely Connected Convolutional Networks



Densely Connected Convolutional NetworksHosein Mohebbi This document describes DenseNets, a type of convolutional neural network architecture. DenseNets connect each layer to every other layer in a feed-forward fashion to encourage feature reuse and consolidate feature maps early in the network. This architecture improves information and gradient flow. The document outlines key DenseNet concepts like collective knowledge, compression layers, and growth rate. It also provides results comparing DenseNets to ResNet on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet datasets.
Feature selection



Feature selectionDong Guo This document summarizes a machine learning workshop on feature selection. It discusses typical feature selection methods like single feature evaluation using metrics like mutual information and Gini indexing. It also covers subset selection techniques like sequential forward selection and sequential backward selection. Examples are provided showing how feature selection improves performance for logistic regression on large datasets with more features than samples. The document outlines the workshop agenda and provides details on when and why feature selection is important for machine learning models.
3 tier data warehouse



3 tier data warehouseJ M This document provides an overview of the 3-tier data warehouse architecture. It discusses the three tiers: the bottom tier contains the data warehouse server which fetches relevant data from various data sources and loads it into the data warehouse using backend tools for extraction, cleaning, transformation and loading. The bottom tier also contains the data marts and metadata repository. The middle tier contains the OLAP server which presents multidimensional data to users from the data warehouse and data marts. The top tier contains the front-end tools like query, reporting and analysis tools that allow users to access and analyze the data.
Classification in data mining 



Classification in data mining Sulman Ahmed This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques
Wasserstein GAN 수학 이해하기 I



Wasserstein GAN 수학 이해하기 ISungbin Lim 이 슬라이드는 Martin Arjovsky, Soumith Chintala, Léon Bottou 의 Wasserstein GAN (https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07875v2) 논문 중 Example 1 을 해설하는 자료입니다
Faster R-CNN - PR012



Faster R-CNN - PR012Jinwon Lee Faster R-CNN improves object detection by introducing a Region Proposal Network (RPN) that shares full-image convolutional features with the detection network, thus enabling nearly cost-free region proposals. The RPN slides over feature maps and predicts object bounds and objectness at each position. During training, anchors are assigned positive or negative labels based on Intersection over Union with ground truth boxes. Faster R-CNN runs the RPN in parallel with Fast R-CNN for detection, end-to-end in a single network and stage. This achieves state-of-the-art object detection speed and accuracy while eliminating computationally expensive selective search for proposals.
Visualizaing and understanding convolutional networks



Visualizaing and understanding convolutional networksSungminYou Paper review presentation of "Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks.“(ECCV 2014, Zeiler et al.)
Introduction of Xgboost



Introduction of Xgboostmichiaki ito XGBoost is a machine learning algorithm based on boosting decision trees. It builds decision trees sequentially to optimize a specified loss function. At each step, it fits a decision tree to the residuals of the previous tree to minimize the loss. It uses regularization to control overfitting by penalizing complex trees with many leaves and high weights. To determine the best split at each node, it calculates the loss reduction from splitting the node versus keeping it whole. The split that maximizes loss reduction is selected.
[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...Deep Learning JP 2018/08/03
Deep Learning JP:
http://deeplearning.jp/seminar-2/
Graph Analytics for big data



Graph Analytics for big dataSigmoid -Graph Analytics Frameworks & Trends
-Graph Databases & Trends
-IBM System G
-IBM Graph Store
-IBM System G & Graph Store in Bluemix
딥러닝의 기본



딥러닝의 기본deepseaswjh < 딥러닝의 기본 >
- 딥러닝의 역사
- 머신러닝 수행 과정
- 신경망이 동작 방식
- 신경망의 학습 방법
- 케라스 사용법
< 인공지능 개발자 모임 >
- http://aidev.co.kr/
XGBoost: the algorithm that wins every competition



XGBoost: the algorithm that wins every competitionJaroslaw Szymczak meet.ml #1 - Applied Big Data and Machine Learning
Poznań Data Science Meetup
Poznań Univeristy of Technology; April 28th, 2016
[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기JungHyun Hong 뉴런, perceptron, cnn, r-cnn, fast r-cnn, faster r-cnn 및
backpropagation, activation function, batch normalization, cost function, optimizer 등 전반적인 딥뉴럴 네트워크에 대한 지식을 다루고 있습니다.
mail : [email protected]
blog : gomguard.tistory.com
【DL輪読会】Perceiver io a general architecture for structured inputs & outputs 



【DL輪読会】Perceiver io a general architecture for structured inputs & outputs Deep Learning JP 2021/09/17
Deep Learning JP:
http://deeplearning.jp/seminar-2/
Vgg



VggheedaeKwon This document discusses very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. It describes network configurations that use 3x3 convolutional filters with max pooling layers and fully connected layers. The networks have 11 or 19 weight layers and use 1x1 convolutional filters to introduce nonlinearity. Classification experiments on ImageNet data with over 1 million training images achieve top-1 and top-5 error rates.
Deep Visual Understanding from Deep Learning by Prof. Jitendra Malik



Deep Visual Understanding from Deep Learning by Prof. Jitendra MalikThe Hive In this The Hive Think Tank talk, Prof. Jitendra Malik talks about Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer Vision, past, present and future.
autoencoder-190813145130.pdf



autoencoder-190813145130.pdfSameer Gulshan This document discusses various types of autoencoders, including stacked autoencoders, denoising autoencoders, sparse autoencoders, and variational autoencoders. Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that learn efficient data encodings in order to reconstruct input data. They can be used for tasks like dimensionality reduction, feature learning, and generating new data samples. Variational autoencoders additionally use probabilistic encodings and decoders to learn latent space representations of input data.
Autoencoder



AutoencoderMehrnaz Faraz 1. Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that are useful for dimensionality reduction and clustering. They learn an efficient coding of the input in an unsupervised manner.
2. Deep autoencoders, also known as stacked autoencoders, are autoencoders with multiple hidden layers that can learn hierarchical representations of the data. They are trained layer-by-layer to learn increasingly higher level features.
3. Variational autoencoders are a type of autoencoder that are probabilistic models, with the encoder output being the parameters of an assumed distribution such as Gaussian. They can generate new samples from the learned distribution.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Deep Neural Methods for Retrieval



Deep Neural Methods for RetrievalBhaskar Mitra Deep neural methods have recently demonstrated significant performance improvements in several IR tasks. In this lecture, we will present a brief overview of deep models for ranking and retrieval.
This is a follow-up lecture to "Neural Learning to Rank" (https://www.slideshare.net/BhaskarMitra3/neural-learning-to-rank-231759858)
Regularization in deep learning



Regularization in deep learningKien Le Presentation in Vietnam Japan AI Community in 2019-05-26.
The presentation summarizes what I've learned about Regularization in Deep Learning.
Disclaimer: The presentation is given in a community event, so it wasn't thoroughly reviewed or revised.
Variational Autoencoder Tutorial 



Variational Autoencoder Tutorial Hojin Yang The document provides an introduction to variational autoencoders (VAE). It discusses how VAEs can be used to learn the underlying distribution of data by introducing a latent variable z that follows a prior distribution like a standard normal. The document outlines two approaches - explicitly modeling the data distribution p(x), or using the latent variable z. It suggests using z and assuming the conditional distribution p(x|z) is a Gaussian with mean determined by a neural network gθ(z). The goal is to maximize the likelihood of the dataset by optimizing the evidence lower bound objective.
Variational Autoencoder



Variational AutoencoderMark Chang Youtube:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLeeHDpwX2Kj55He_jfPojKrZf22HVjAZY
Paper review of "Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes"
Densely Connected Convolutional Networks



Densely Connected Convolutional NetworksHosein Mohebbi This document describes DenseNets, a type of convolutional neural network architecture. DenseNets connect each layer to every other layer in a feed-forward fashion to encourage feature reuse and consolidate feature maps early in the network. This architecture improves information and gradient flow. The document outlines key DenseNet concepts like collective knowledge, compression layers, and growth rate. It also provides results comparing DenseNets to ResNet on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet datasets.
Feature selection



Feature selectionDong Guo This document summarizes a machine learning workshop on feature selection. It discusses typical feature selection methods like single feature evaluation using metrics like mutual information and Gini indexing. It also covers subset selection techniques like sequential forward selection and sequential backward selection. Examples are provided showing how feature selection improves performance for logistic regression on large datasets with more features than samples. The document outlines the workshop agenda and provides details on when and why feature selection is important for machine learning models.
3 tier data warehouse



3 tier data warehouseJ M This document provides an overview of the 3-tier data warehouse architecture. It discusses the three tiers: the bottom tier contains the data warehouse server which fetches relevant data from various data sources and loads it into the data warehouse using backend tools for extraction, cleaning, transformation and loading. The bottom tier also contains the data marts and metadata repository. The middle tier contains the OLAP server which presents multidimensional data to users from the data warehouse and data marts. The top tier contains the front-end tools like query, reporting and analysis tools that allow users to access and analyze the data.
Classification in data mining 



Classification in data mining Sulman Ahmed This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques.This course is all about the data mining that how we get the optimized results. it included with all types and how we use these techniques
Wasserstein GAN 수학 이해하기 I



Wasserstein GAN 수학 이해하기 ISungbin Lim 이 슬라이드는 Martin Arjovsky, Soumith Chintala, Léon Bottou 의 Wasserstein GAN (https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07875v2) 논문 중 Example 1 을 해설하는 자료입니다
Faster R-CNN - PR012



Faster R-CNN - PR012Jinwon Lee Faster R-CNN improves object detection by introducing a Region Proposal Network (RPN) that shares full-image convolutional features with the detection network, thus enabling nearly cost-free region proposals. The RPN slides over feature maps and predicts object bounds and objectness at each position. During training, anchors are assigned positive or negative labels based on Intersection over Union with ground truth boxes. Faster R-CNN runs the RPN in parallel with Fast R-CNN for detection, end-to-end in a single network and stage. This achieves state-of-the-art object detection speed and accuracy while eliminating computationally expensive selective search for proposals.
Visualizaing and understanding convolutional networks



Visualizaing and understanding convolutional networksSungminYou Paper review presentation of "Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks.“(ECCV 2014, Zeiler et al.)
Introduction of Xgboost



Introduction of Xgboostmichiaki ito XGBoost is a machine learning algorithm based on boosting decision trees. It builds decision trees sequentially to optimize a specified loss function. At each step, it fits a decision tree to the residuals of the previous tree to minimize the loss. It uses regularization to control overfitting by penalizing complex trees with many leaves and high weights. To determine the best split at each node, it calculates the loss reduction from splitting the node versus keeping it whole. The split that maximizes loss reduction is selected.
[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zero-shot-gcn-180803004516-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[DL輪読会]Zero-shot Recognition via Semantic Embeddings and Knowledge Graphs (CV...Deep Learning JP 2018/08/03
Deep Learning JP:
http://deeplearning.jp/seminar-2/
Graph Analytics for big data



Graph Analytics for big dataSigmoid -Graph Analytics Frameworks & Trends
-Graph Databases & Trends
-IBM System G
-IBM Graph Store
-IBM System G & Graph Store in Bluemix
딥러닝의 기본



딥러닝의 기본deepseaswjh < 딥러닝의 기본 >
- 딥러닝의 역사
- 머신러닝 수행 과정
- 신경망이 동작 방식
- 신경망의 학습 방법
- 케라스 사용법
< 인공지능 개발자 모임 >
- http://aidev.co.kr/
XGBoost: the algorithm that wins every competition



XGBoost: the algorithm that wins every competitionJaroslaw Szymczak meet.ml #1 - Applied Big Data and Machine Learning
Poznań Data Science Meetup
Poznań Univeristy of Technology; April 28th, 2016
[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/part1mlp2cnn-slidesharev-180308015531-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[GomGuard] 뉴런부터 YOLO 까지 - 딥러닝 전반에 대한 이야기JungHyun Hong 뉴런, perceptron, cnn, r-cnn, fast r-cnn, faster r-cnn 및
backpropagation, activation function, batch normalization, cost function, optimizer 등 전반적인 딥뉴럴 네트워크에 대한 지식을 다루고 있습니다.
mail : [email protected]
blog : gomguard.tistory.com
【DL輪読会】Perceiver io a general architecture for structured inputs & outputs 



【DL輪読会】Perceiver io a general architecture for structured inputs & outputs Deep Learning JP 2021/09/17
Deep Learning JP:
http://deeplearning.jp/seminar-2/
Vgg



VggheedaeKwon This document discusses very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. It describes network configurations that use 3x3 convolutional filters with max pooling layers and fully connected layers. The networks have 11 or 19 weight layers and use 1x1 convolutional filters to introduce nonlinearity. Classification experiments on ImageNet data with over 1 million training images achieve top-1 and top-5 error rates.
Deep Visual Understanding from Deep Learning by Prof. Jitendra Malik



Deep Visual Understanding from Deep Learning by Prof. Jitendra MalikThe Hive In this The Hive Think Tank talk, Prof. Jitendra Malik talks about Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer Vision, past, present and future.
Similar to autoencoder-190813144108.pptx (20)
autoencoder-190813145130.pdf



autoencoder-190813145130.pdfSameer Gulshan This document discusses various types of autoencoders, including stacked autoencoders, denoising autoencoders, sparse autoencoders, and variational autoencoders. Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that learn efficient data encodings in order to reconstruct input data. They can be used for tasks like dimensionality reduction, feature learning, and generating new data samples. Variational autoencoders additionally use probabilistic encodings and decoders to learn latent space representations of input data.
Autoencoder



AutoencoderMehrnaz Faraz 1. Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that are useful for dimensionality reduction and clustering. They learn an efficient coding of the input in an unsupervised manner.
2. Deep autoencoders, also known as stacked autoencoders, are autoencoders with multiple hidden layers that can learn hierarchical representations of the data. They are trained layer-by-layer to learn increasingly higher level features.
3. Variational autoencoders are a type of autoencoder that are probabilistic models, with the encoder output being the parameters of an assumed distribution such as Gaussian. They can generate new samples from the learned distribution.
Autoencoders in Deep Learning



Autoencoders in Deep Learningmilad abbasi 1. Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that are useful for dimensionality reduction and clustering. They compress the input into a latent-space representation then reconstruct the output from this representation.
2. Deep autoencoders stack multiple autoencoder layers to learn hierarchical representations of the data. Each layer is trained sequentially.
3. Variational autoencoders use probabilistic encoders and decoders to learn a Gaussian latent space. They can generate new samples from the learned data distribution.
Explanation of Autoencoder to Variontal Auto Encoder



Explanation of Autoencoder to Variontal Auto Encoderseshathirid Autoencoder to Variontal Auto Encoder notes
A Comprehensive Overview of Encoder and Decoder Architectures in Deep Learnin...



A Comprehensive Overview of Encoder and Decoder Architectures in Deep Learnin...ShubhamMittal569818 The encoder-decoder architecture is a fundamental framework in deep learning, commonly used in tasks such as sequence-to-sequence modeling, machine translation, and image generation. The encoder processes the input data into a compact representation, capturing essential features, while the decoder reconstructs the output from this encoded representation. This structure enables efficient learning of complex transformations and is widely applied in natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and generative models.
Autoencoders in Computer Vision: A Deep Learning Approach for Image Denoising...



Autoencoders in Computer Vision: A Deep Learning Approach for Image Denoising...ShubhamMittal569818 Autoencoders are neural networks used for unsupervised learning, designed to encode input data into a lower-dimensional latent representation and then reconstruct it back with minimal loss. They consist of an encoder that compresses the input and a decoder that reconstructs it. In computer vision, autoencoders are widely used for image denoising, anomaly detection, dimensionality reduction, and feature extraction. Variants like denoising autoencoders (DAEs), variational autoencoders (VAEs), and convolutional autoencoders (CAEs) enhance their capabilities for different tasks.
Introduction to Autoencoders: Types and Applications



Introduction to Autoencoders: Types and ApplicationsAmr Rashed Introduction to Autoencoders: Types and Applications
UNIT-4.pptx



UNIT-4.pptxNiharikaThakur32 - Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that are used for dimensionality reduction and feature extraction. They compress the input into a latent-space representation and then reconstruct the output from this representation.
- The architecture of an autoencoder consists of an encoder that compresses the input into a latent space, a decoder that reconstructs the output from the latent space, and a reconstruction loss that is minimized during training.
- There are different types of autoencoders like undercomplete, convolutional, sparse, denoising, contractive, stacked, and deep autoencoders that apply additional constraints or have more complex architectures. Autoencoders can be used for tasks like image compression, anomaly detection, and feature learning.
UNIT-4.pdf



UNIT-4.pdfNiharikaThakur32 - Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that compress input data into a latent space representation and then reconstruct the output from this representation. They aim to copy their input to their output with minimal loss of information.
- Autoencoders consist of an encoder that compresses the input into a latent space and a decoder that decompresses this latent space back into the original input space. The network is trained to minimize the reconstruction loss between the input and output.
- Autoencoders are commonly used for dimensionality reduction, feature extraction, denoising images, and generating new data similar to the training data distribution.
UNIT-4.pdf



UNIT-4.pdfNiharikaThakur32 - Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that compress input data into a latent space representation and then reconstruct the output from this representation. They aim to copy their input to their output with minimal loss of information.
- Autoencoders consist of an encoder that compresses the input into a latent space and a decoder that decompresses this latent space back into the original input space. The network is trained to minimize the reconstruction loss between the input and output.
- Autoencoders are commonly used for dimensionality reduction, feature extraction, denoising images, and generating new data similar to the training data distribution.
Lec16 - Autoencoders.pptx



Lec16 - Autoencoders.pptxSameer Gulshan Autoencoders are unsupervised neural networks that are trained to reconstruct their input. They compress the input into a latent space encoding and then decode the encoding to reconstruct the original input. Variations include denoising autoencoders, which are trained to reconstruct clean inputs from corrupted versions, and sparse autoencoders, which add regularization to activations to learn a sparse code. Contractive autoencoders add a penalty to make the hidden units invariant to small changes in input.
Foundations: Artificial Neural Networks



Foundations: Artificial Neural Networksananth Artificial Neural Networks have been very successfully used in several machine learning applications. They are often the building blocks when building deep learning systems. We discuss the hypothesis, training with backpropagation, update methods, regularization techniques.
InfoGAN and Generative Adversarial Networks



InfoGAN and Generative Adversarial NetworksZak Jost An introductory look at Generative Adversarial Networks generally and the InfoGAN implementation specifically.
Autoencoders



AutoencodersCloudxLab An autoencoder is an artificial neural network that is trained to copy its input to its output. It consists of an encoder that compresses the input into a lower-dimensional latent-space encoding, and a decoder that reconstructs the output from this encoding. Autoencoders are useful for dimensionality reduction, feature learning, and generative modeling. When constrained by limiting the latent space or adding noise, autoencoders are forced to learn efficient representations of the input data. For example, a linear autoencoder trained with mean squared error performs principal component analysis.
Variational Autoencoders For Image Generation



Variational Autoencoders For Image GenerationJason Anderson Meetup: https://www.meetup.com/Cognitive-Computing-Enthusiasts/events/260580395/
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fnULFOyNZn8
Blog: http://www.compthree.com/blog/autoencoder/
Code: https://github.com/compthree/variational-autoencoder
An autoencoder is a machine learning algorithm that represents unlabeled high-dimensional data as points in a low-dimensional space. A variational autoencoder (VAE) is an autoencoder that represents unlabeled high-dimensional data as low-dimensional probability distributions. In addition to data compression, the randomness of the VAE algorithm gives it a second powerful feature: the ability to generate new data similar to its training data. For example, a VAE trained on images of faces can generate a compelling image of a new "fake" face. It can also map new features onto input data, such as glasses or a mustache onto the image of a face that initially lacks these features. In this talk, we will survey VAE model designs that use deep learning, and we will implement a basic VAE in TensorFlow. We will also demonstrate the encoding and generative capabilities of VAEs and discuss their industry applications.
Autoencoder



AutoencoderWataru Hirota This document discusses autoencoders, which are unsupervised neural networks that learn efficient data encodings. It describes typical autoencoder architectures, including stacked autoencoders, and different types such as denoising autoencoders, sparse autoencoders, and variational autoencoders. It also covers visualizing learned features, unsupervised pretraining, and implementations with TensorFlow.
AUTO ENCODERS (Deep Learning fundamentals)



AUTO ENCODERS (Deep Learning fundamentals)aayanshsingh0401 Deep Learning fundamental. Helps in understanding Auto Encoders
Ad
More from kiran814572 (6)
seminar ppt blue eyes.pptx



seminar ppt blue eyes.pptxkiran814572 The document summarizes a seminar on "Blue Eyes Technology". Blue Eyes Technology uses sensors and devices to understand human emotions and behavior. It can sense a user's mood through factors like eye movement, pressure, temperature and heartbeat. This is used to develop smarter devices with emotional intelligence. Some applications of this technology include smart cameras, video games, military, power stations and more. The seminar covered various technologies used like Emotion Mouse, MAGIC pointing, speech recognition and more. It discussed the objectives, needs, advantages and future scope of Blue Eyes Technology.
dokumen.tips_mind-reading-computer-ppt.pptx



dokumen.tips_mind-reading-computer-ppt.pptxkiran814572 The document discusses mind reading technology that uses facial expression analysis and functional near-infrared spectroscopy to infer people's mental states. A team at the University of Cambridge developed a system that tracks 24 facial feature points in real time to identify expressions correlated with mental states like interest or engagement. The technology has potential applications in human-computer interaction, monitoring human interactions, and detecting driver states but also risks privacy breaches or misuse if not properly safeguarded. Researchers at Tufts University are developing a system using head-mounted sensors to detect brain activity and allow computer responses based on the user's mind.
brainchips-170420163645.pptx



brainchips-170420163645.pptxkiran814572 The presentation discusses the evolution and future of brain chips. It describes how brain chips can be implanted on the brain's surface or cortex to enhance memory, help paralyzed patients, and serve military purposes. The Braingate technology allows brain signals to be transmitted to a computer to control devices like a cursor. While brain chips offer benefits, challenges remain around the interface between biology and technology and reducing chip size. The technology may someday help paralyzed individuals control prosthetics with just their thoughts.
gan-190318135433 (1).pptx



gan-190318135433 (1).pptxkiran814572 This document provides an overview of generative adversarial networks (GANs). It explains that GANs were introduced in 2014 and consist of two neural networks, a generator and discriminator, that compete against each other. The generator produces synthetic data to fool the discriminator, while the discriminator learns to distinguish real from synthetic data. As they train, the generator improves at mimicking real data distribution. The document outlines GAN training procedures and provides examples of GAN applications, including image generation, text-to-image synthesis, and face aging.
VIOLENCE.pptx



VIOLENCE.pptxkiran814572 This document discusses violence and ways to deal with it. It defines violence and describes different types including physical, psychological, domestic, economic, gender-based, and verbal violence. It outlines factors that can influence violence at the individual, family, and social/community levels. The effects of violence and its impact on victims, children, and communities are described. The cycle of violence and ways to raise awareness, prevent violence, and deal with its effects through actions by parents/families, communities, and schools are presented.
Cognitive-approaches-to-learning-powerpoint.ppt



Cognitive-approaches-to-learning-powerpoint.pptkiran814572 The document provides an overview of cognitivist learning theories, including those proposed by Piaget, Vygotsky, and Bruner. Some key points of cognitivism are that learning is an internal process of associating new information with prior knowledge, and that learning involves input, processing, and output of information. Piaget's theory proposed that children progress through distinct stages of cognitive development. Vygotsky emphasized the social aspects of learning and proposed the zone of proximal development. Bruner viewed learning as an active process where learners construct new understandings based on previous knowledge.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungen



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungenpanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-und-verwaltung-von-multiuser-umgebungen/
HCL Nomad Web wird als die nächste Generation des HCL Notes-Clients gefeiert und bietet zahlreiche Vorteile, wie die Beseitigung des Bedarfs an Paketierung, Verteilung und Installation. Nomad Web-Client-Updates werden “automatisch” im Hintergrund installiert, was den administrativen Aufwand im Vergleich zu traditionellen HCL Notes-Clients erheblich reduziert. Allerdings stellt die Fehlerbehebung in Nomad Web im Vergleich zum Notes-Client einzigartige Herausforderungen dar.
Begleiten Sie Christoph und Marc, während sie demonstrieren, wie der Fehlerbehebungsprozess in HCL Nomad Web vereinfacht werden kann, um eine reibungslose und effiziente Benutzererfahrung zu gewährleisten.
In diesem Webinar werden wir effektive Strategien zur Diagnose und Lösung häufiger Probleme in HCL Nomad Web untersuchen, einschließlich
- Zugriff auf die Konsole
- Auffinden und Interpretieren von Protokolldateien
- Zugriff auf den Datenordner im Cache des Browsers (unter Verwendung von OPFS)
- Verständnis der Unterschiede zwischen Einzel- und Mehrbenutzerszenarien
- Nutzung der Client Clocking-Funktion
tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdf



tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdffjgm517 descaripcion detallada del avance de las tecnologias en mesopotamia, egipto, roma y grecia.
TrsLabs - Fintech Product & Business Consulting



TrsLabs - Fintech Product & Business ConsultingTrs Labs Hybrid Growth Mandate Model with TrsLabs
Strategic Investments, Inorganic Growth, Business Model Pivoting are critical activities that business don't do/change everyday. In cases like this, it may benefit your business to choose a temporary external consultant.
An unbiased plan driven by clearcut deliverables, market dynamics and without the influence of your internal office equations empower business leaders to make right choices.
Getting things done within a budget within a timeframe is key to Growing Business - No matter whether you are a start-up or a big company
Talk to us & Unlock the competitive advantage
AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global Trends



AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global TrendsInData Labs In this infographic, we explore how businesses can implement effective governance frameworks to address AI data privacy. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective strategies that ensure compliance, safeguard customer trust, and leverage AI responsibly. Equip yourself with insights that can drive informed decision-making and position your organization for success in the future of data privacy.
This infographic contains:
-AI and data privacy: Key findings
-Statistics on AI data privacy in the today’s world
-Tips on how to overcome data privacy challenges
-Benefits of AI data security investments.
Keep up-to-date on how AI is reshaping privacy standards and what this entails for both individuals and organizations.
Special Meetup Edition - TDX Bengaluru Meetup #52.pptx



Special Meetup Edition - TDX Bengaluru Meetup #52.pptxshyamraj55 We’re bringing the TDX energy to our community with 2 power-packed sessions:
🛠️ Workshop: MuleSoft for Agentforce
Explore the new version of our hands-on workshop featuring the latest Topic Center and API Catalog updates.
📄 Talk: Power Up Document Processing
Dive into smart automation with MuleSoft IDP, NLP, and Einstein AI for intelligent document workflows.
Linux Professional Institute LPIC-1 Exam.pdf



Linux Professional Institute LPIC-1 Exam.pdfRHCSA Guru Introduction to LPIC-1 Exam - overview, exam details, price and job opportunities
Heap, Types of Heap, Insertion and Deletion



Heap, Types of Heap, Insertion and DeletionJaydeep Kale This pdf will explain what is heap, its type, insertion and deletion in heap and Heap sort
Mobile App Development Company in Saudi Arabia



Mobile App Development Company in Saudi ArabiaSteve Jonas EmizenTech is a globally recognized software development company, proudly serving businesses since 2013. With over 11+ years of industry experience and a team of 200+ skilled professionals, we have successfully delivered 1200+ projects across various sectors. As a leading Mobile App Development Company In Saudi Arabia we offer end-to-end solutions for iOS, Android, and cross-platform applications. Our apps are known for their user-friendly interfaces, scalability, high performance, and strong security features. We tailor each mobile application to meet the unique needs of different industries, ensuring a seamless user experience. EmizenTech is committed to turning your vision into a powerful digital product that drives growth, innovation, and long-term success in the competitive mobile landscape of Saudi Arabia.
Noah Loul Shares 5 Steps to Implement AI Agents for Maximum Business Efficien...



Noah Loul Shares 5 Steps to Implement AI Agents for Maximum Business Efficien...Noah Loul Artificial intelligence is changing how businesses operate. Companies are using AI agents to automate tasks, reduce time spent on repetitive work, and focus more on high-value activities. Noah Loul, an AI strategist and entrepreneur, has helped dozens of companies streamline their operations using smart automation. He believes AI agents aren't just tools—they're workers that take on repeatable tasks so your human team can focus on what matters. If you want to reduce time waste and increase output, AI agents are the next move.
#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025



#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, transcript, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered Manufacturing



Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered ManufacturingAndrew Leo From predictive maintenance to robotic automation, AI is driving the future of manufacturing. But without high-quality annotated data, even the smartest models fall short.
Discover how data annotation services are powering accuracy, safety, and efficiency in AI-driven manufacturing systems.
Precision in data labeling = Precision on the production floor.
Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptx



Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptxJon Hansen Procurement Insights integrated Historic Procurement Industry Archives, serves as a powerful complement — not a competitor — to other procurement industry firms. It fills critical gaps in depth, agility, and contextual insight that most traditional analyst and association models overlook.
Learn more about this value- driven proprietary service offering here.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in Business



Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in BusinessDr. Tathagat Varma My talk for the Indian School of Business (ISB) Emerging Leaders Program Cohort 9. In this talk, I discussed key issues around adoption of GenAI in business - benefits, opportunities and limitations. I also discussed how my research on Theory of Cognitive Chasms helps address some of these issues
The Evolution of Meme Coins A New Era for Digital Currency ppt.pdf



The Evolution of Meme Coins A New Era for Digital Currency ppt.pdfAbi john Analyze the growth of meme coins from mere online jokes to potential assets in the digital economy. Explore the community, culture, and utility as they elevate themselves to a new era in cryptocurrency.
Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdf



Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdfSoftware Company Explore the benefits and features of advanced logistics management software for businesses in Riyadh. This guide delves into the latest technologies, from real-time tracking and route optimization to warehouse management and inventory control, helping businesses streamline their logistics operations and reduce costs. Learn how implementing the right software solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a competitive edge in the growing logistics sector of Riyadh.
Massive Power Outage Hits Spain, Portugal, and France: Causes, Impact, and On...



Massive Power Outage Hits Spain, Portugal, and France: Causes, Impact, and On...Aqusag Technologies In late April 2025, a significant portion of Europe, particularly Spain, Portugal, and parts of southern France, experienced widespread, rolling power outages that continue to affect millions of residents, businesses, and infrastructure systems.
autoencoder-190813144108.pptx
- 1. Auto Encoders In the name of God Mehrnaz Faraz Faculty of Electrical Engineering K. N. Toosi University of Technology Milad Abbasi Faculty of Electrical Engineering Sharif University of Technology 1
- 2. Auto Encoders • An unsupervised deep learning algorithm • Are artificial neural networks • Useful for dimensionality reduction and clustering Unlabeled data 𝑧 = 𝑠 𝑤𝑥 + 𝑏 𝑥 ^= 𝑠 𝑤′z + 𝑏′ 𝑥 ^is 𝑥’s reconstruction 𝑧 is some latent representation or code and 𝑠 is a non-linearity such as the sigmoid 𝑧 𝑥 ^ 𝑥 2 Encoder Decoder
- 3. Auto Encoders • Simple structure: 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒙˜𝟏 𝒙˜𝟑 𝒙˜𝟐 Input Reconstructed Output Hidden Encoder 3 Decoder
- 4. Undercomplete AE • Hidden layer is Undercomplete if smaller than the input layer – Compresses the input – Hidden nodes will be Good features for the training 𝑥 ^ 𝑤′ 𝑧 𝑤 𝑥 4
- 5. Overcomplete AE • Hidden layer is Overcomplete if greater than the input layer – No compression in hidden layer. – Each hidden unit could copy a different input component. 𝑥 ^ 𝑤′ 𝑧 𝑤 𝑥 5
- 6. Deep Auto Encoders • Deep Auto Encoders (DAE) • Stacked Auto Encoders (SAE) 6
- 7. Training Deep Auto Encoder • First layer: 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟒 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒙^𝟏 𝒙^𝟒 𝒙^𝟑 𝒙^𝟐 𝒂𝟑 𝒂𝟐 𝒂𝟏 Encoder Decoder 7
- 8. Training Deep Auto Encoder • Features of first layer: 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟒 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒂𝟑 𝒂𝟐 𝒂𝟏 𝑎1 𝑎2 𝑎3 8
- 9. Training Deep Auto Encoder • Second layer: 𝒂𝟑 𝒂𝟐 𝒂𝟏 𝒂^𝟏 𝒂^𝟑 𝒂^𝟐 𝒃𝟐 𝒃𝟏 9
- 10. Training Deep Auto Encoder • Features of second layer: 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟒 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒂𝟑 𝒂𝟐 𝒂𝟏 𝒃𝟐 𝒃𝟏 𝑏1 𝑏2 10
- 11. Using Deep Auto Encoder 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒂𝟑 𝒂𝟐 • Feature extraction • Dimensionality reduction • Classification 𝒙𝟏 𝒂𝟏 𝒃𝟐 𝒃𝟏 Inputs Features 𝒙𝟒 Encoder 11
- 12. Using Deep Auto Encoder • Reconstruction 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟒 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒂𝟑 𝒂𝟐 𝒂𝟏 𝒃𝟐 𝒃𝟏 𝒂^𝟏 𝒂^𝟑 𝒂^𝟐 𝒙^𝟒 𝒙^𝟑 𝒙^𝟐 𝒙^𝟏 Encoder Decoder 12
- 13. Using AE • Denoising • Data compression • Unsupervised learning • Manifold learning • Generative model 13
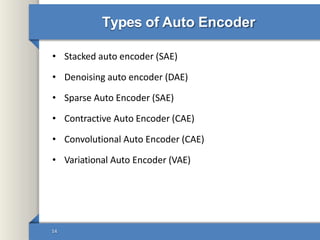
- 14. Types of Auto Encoder • Stacked auto encoder (SAE) • Denoising auto encoder (DAE) • Sparse Auto Encoder (SAE) • Contractive Auto Encoder (CAE) • Convolutional Auto Encoder (CAE) • Variational Auto Encoder (VAE) 14
- 15. Generative Models • Given training data, generate new samples from same distribution – Variational Auto Encoder (VAE) – Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) 15
- 16. Variational Auto Encoder Encoder Decoder Output 𝐱˜ ∅ 𝒒 𝒛|𝒙 𝒑𝜽 𝒙|𝒛 𝒙𝟏 16 𝒙𝟒 Input x 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒙˜𝟏 𝒙˜𝟒 𝒙˜𝟑 𝒙˜𝟐 𝒛𝟏 𝒛𝟐
- 17. Variational Auto Encoder • Use probabilistic encoding and decoding – Encoder: – Decoder: • x: Unknown probability distribution • z: Gaussian probability distribution 𝑞∅ 𝑧|𝑥 𝑝𝜃 𝑥|𝑧 17
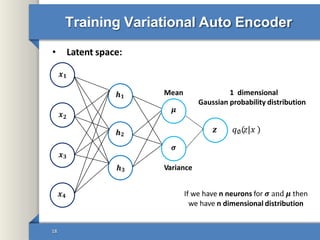
- 18. Training Variational Auto Encoder • Latent space: 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟒 𝒙𝟑 𝒙𝟐 𝒉𝟏 𝒉𝟐 𝒉𝟑 𝝈 𝝁 𝒛 𝑞∅ 𝑧|𝑥 18 Mean Variance 1 dimensional Gaussian probability distribution If we have n neurons for 𝝈 and 𝝁 then we have n dimensional distribution
- 19. Training Variational Auto Encoder • Generating new data: – Example: MNIST Database 𝐱 Encoder Latent space Decoder 19
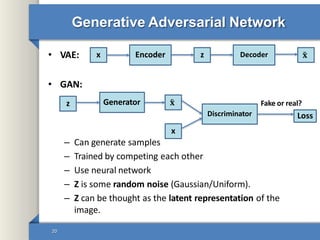
- 20. Generative Adversarial Network • VAE: • GAN: – Can generate samples – Trained by competing each other – Use neural network – Z is some random noise (Gaussian/Uniform). – Z can be thought as the latent representation of the image. x Decoder 𝐱 ˜ z Encoder z Generator 𝐱 ˜ x Discriminator Fake or real? 20 Loss
- 21. GAN’s Architecture Discriminator Generated fake samples Fine tune training Latent space Noise Is D correct? Generator • Overview: Real samples
- 22. Using GAN • Image generation: 22
- 23. Using GAN • Data manipulation: 23
- 24. Denoising Auto Encoder • Add noise to its input, and train it to recover this original. 24
- 25. Denoising Auto Encoder Input Output Hidden 3 Hidden 2 Hidden 1 + Noise Input Output Hidden 3 Hidden 2 Hidden 1 Dropout 25 Randomly switched input Gaussian noise
- 26. Sparse Auto Encoder • Reduce the number of active neurons in the coding layer. – Add sparsity loss into the cost function. • Sparsity loss: – Kullback-Leibler(KL) divergence is commonly used. 26
- 27. Sparse Auto Encoder j j j ˆ KL ̂ log 1 log 1 1 ̂ Jsparse w,b J w,b KL ̂j j1 27







