Automatic Metadata Generation Charles Duncan
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes516 views
Slides by Charles Duncan summarising the findings of the automatic metadata generation use cases project, see http://www.intrallect.com/wiki/index.php/AMG-UC
1 of 12
Download to read offline
![Findings of the Automatic Metadata Generation Use Cases project Charles Duncan [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/automaticmetadatagenerationcharlesduncan-091130113652-phpapp02/85/Automatic-Metadata-Generation-Charles-Duncan-1-320.jpg)










Recommended
The Reach of Crossref metadata - Crossref LIVE South Africa



The Reach of Crossref metadata - Crossref LIVE South AfricaCrossref Vanessa Fairhurst talks about the reach of Crossref metadata and what it is used for at Crossref LIVE local events in Pretoria and Cape Town. 17th and 19th April 2018.
New product developments - Jennifer Lin - London LIVE 2017



New product developments - Jennifer Lin - London LIVE 2017Crossref The document discusses rethinking metadata to better connect scholarly works and enable transparency. It proposes three key areas: 1) Adding a new "Reviews" content type to link peer review assets like reports and responses. 2) Developing event data standards to aggregate metadata about publications and establish trust. 3) Citing data and software to provide proper credit and facilitate reproducibility. The goal is to improve infrastructure for scholarly discussion by making provenance, context and peer review processes more open and linked over time.
Introduction to Crossref: History, Mission, Members



Introduction to Crossref: History, Mission, MembersCrossref This document provides an agenda and overview for an introduction to Crossref meeting. The agenda includes sessions on Crossref history and mission, DOIs and metadata, content on multiple sites, text and data mining, and administrative matters. Background information is given on Crossref's founding in 2000 with 12 publishers, current staff and governance structure, over 5500 publisher members representing over 85 million scholarly works, and services used by publishers, libraries, and other organizations. Growth statistics are shown and upcoming initiatives like linked clinical trials and a new website are highlighted.
Crossref Metadata and Metadata Services



Crossref Metadata and Metadata ServicesCrossref Presentation on how to access Crossref metadata and how tools and services are using it. From Crossref LIVE in Brazil, Dec 2016.
New Initiatives - Geoffrey Bilder - London LIVE 2017



New Initiatives - Geoffrey Bilder - London LIVE 2017Crossref Presentation by Geoffrey Bilder at Crossref London LIVE, 26th September 2017. New initiatives at Crossref including organisational and grant identifiers.
Exploration of a Data Landscape using a Collaborative Linked Data Framework.



Exploration of a Data Landscape using a Collaborative Linked Data Framework.Laurent Alquier The document discusses using a collaborative linked data framework to explore a data landscape. It describes how the framework helps scientists access and integrate disparate data sources to answer translational research questions. Key components of the framework include a semantic wiki for cataloging data sources, linking data concepts, querying across sources, and visualizing relationships between sources. The goal is to provide scientists with flexible tools to discover and leverage relevant data without needing expertise in data management.
Managing plagiarism: Similarity Check



Managing plagiarism: Similarity CheckCrossref - CrossCheck has rebranded to Crossref Similarity Check to provide clearer messaging and reduce confusion.
- The service checks documents against over 53 million papers from over 1200 publishers, as well as 105 million items from other sources and over 60 billion web pages.
- Over 1200 Crossref publishers and over 100 Brazilian publishers are using the service, with increasing usage in countries like Japan, South Korea, and Turkey.
- Publishers are looking to identify issues like poor references, self-plagiarism, unattributed use of others' works, and submitting others' works as their own through the similarity checking service.
Who is using your metadata - Ginny Hendricks



Who is using your metadata - Ginny HendricksCrossref The document discusses how Crossref metadata helps researchers find and track information. Crossref collects metadata like titles, authors, and references from publishers and makes it available via APIs and tools. Many organizations use this metadata for search, discovery, author profiling, and funding tracking. Crossref is working to expand the metadata to include items like funder IDs, licenses, and ORCID IDs. This additional metadata would help tools like collaborative writing platforms and open data repositories that integrate Crossref data.
Multiple Resolution and handling content available in multiple places



Multiple Resolution and handling content available in multiple placesCrossref The document discusses how Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) can be used to provide more context and connections between related scholarly works beyond just linking to an article. It describes how multiple resolution allows a DOI to resolve to multiple locations of the same content. Relations allow DOIs to link to other related works like cited articles, prior versions, or referenced data. The document advocates including these relationship connections in metadata to provide more context and allow systems to understand the connections between scholarly outputs.
Cited-by Linking 



Cited-by Linking Crossref This document discusses strategies for participating in Crossref's Cited-By linking service, which allows members to see references from other publications that cite their own journal articles. It outlines three ways for members to deposit reference lists with their article metadata to Crossref, and three strategies for retrieving cited-by data - periodically downloading new data and updating pages; downloading data once and enabling alerts; or retrieving data on-the-fly when users view cited-by results. The document provides examples of HTTP requests members can make to Crossref to deposit references and retrieve cited-by data using these different strategies.
Introduction to DataCite - Martin Fenner



Introduction to DataCite - Martin FennerCrossref Introduction to DataCite including members, collaborations, advocacy and future plans. Presented at Crossref LIVE Seoul, 12 June 2017.
RDAP 15: “This is just for me”: Researchers on their data documentation pract...



RDAP 15: “This is just for me”: Researchers on their data documentation pract...ASIS&T This document summarizes a panel discussion on researchers' data documentation practices. It finds that metadata is often not sufficient because data itself is messy and domain-specific. Researchers in different disciplines like chemistry, ecology, computer science, microbiology, and earth sciences approach documentation differently based on norms and needs within their fields. For example, chemists use numbering systems and documentation protocols while microbiologists emphasize keeping detailed lab notebooks. The document concludes more interviews are needed to better understand disciplinary practices and tailor library services accordingly.
Using Funding Data



Using Funding DataCrossref The document discusses Crossref funding data, which standardizes funder names using the Open Funder Registry. It allows publishers to deposit funding metadata and enables large-scale analysis and reporting of funding data to funders. More information can be found on Crossref's website and API.
Introduction to Crossref, Seoul - Ed Pentz



Introduction to Crossref, Seoul - Ed PentzCrossref The document provides an agenda for a Crossref event taking place in Seoul, South Korea. It includes sessions on Crossref as a global infrastructure partner, registering content to enable connections, how Korean research is found through Crossref metadata, additional Crossref services, community initiatives, and guest sessions on ORCID and DataCite. There will also be discussions on supporting Korean research globally, additional Crossref member services, and data sharing policies. The event aims to showcase how Crossref can help Korean research have global reach and visibility.
Text and Data Mining



Text and Data MiningCrossref Presentation on how Crossref's REST API can be used to get the full text of publisher content for the purpose of TDM. From Crossref LIVE in Brazil, Dec 2016.
Working with ROR as a Crossref member: what you need to know



Working with ROR as a Crossref member: what you need to knowCrossref Webinar focusing on the importance of ROR and how to implement that as a Crossref member.
Covers:
What is ROR?
Why is Crossref supporting ROR?
Publisher use cases for ROR (from Hindawi)
How to become a ROR adopter
Discussion/Q&A
A recording of the presentation is available on the Crossref YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D9Mtqb64OEk
Data Repositories Impact



Data Repositories ImpactMerce Crosas Presentation at the meeting on Measuring the Impact of Digital repositories (https://www.nitrd.gov/nitrdgroups/index.php?title=DigitalRepositories).
Federated Search Falls Short



Federated Search Falls Shortslknight The document summarizes an evaluation of a federated search implementation at Booth Library, Eastern Illinois University. Key findings from analyzing search logs and user statistics over multiple years include: (1) users had significantly more searches and views of full records in native databases compared to the federated search, (2) databases interpreted search queries differently which impacted relevancy of results, (3) proper staffing, training, and statistics tracking are needed for a federated search to be effective. The evaluation highlights the reality that expectations often do not match actual user behaviors and search capabilities.
Annotating research resources with rrid’s



Annotating research resources with rrid’sMaryann Martone The document discusses annotating research resources with Resource Identification Initiative (RRID) identifiers to uniquely and consistently identify key resources like antibodies, software, and genetically modified animals across publications. It notes that currently researchers do not provide enough information to conclusively identify resources, making it difficult to determine what other studies used a particular resource. The RRID pilot project aims to have authors provide standard identifiers for resources to make them machine-readable, publicly accessible, and uniform. The document also covers annotating retrospective literature by attempting to assign RRIDs to resources based on descriptions and searching the RRID portal.
TAIR ICAR 2010 Presentation



TAIR ICAR 2010 PresentationPhoenix Bioinformatics How to make your published data more findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable (and how to make your data more visible in TAIR)
RDAP 15: Beyond Metadata: Leveraging the “README” to support disciplinary Doc...



RDAP 15: Beyond Metadata: Leveraging the “README” to support disciplinary Doc...ASIS&T Research Data Access and Preservation Summit, 2015
Minneapolis, MN
April 22-23, 2015
Part of “Beyond metadata: Supporting non-standardized documentation to facilitate data reuse”
Gaining credit for sharing research data: Viewpoints on Data Publishing



Gaining credit for sharing research data: Viewpoints on Data PublishingVarsha Khodiyar Presentation given at the Viewpoints on Data Publishing workshop, University of Southampton, 21st September 2015
8. Reach of Crossref metadata and who is using it



8. Reach of Crossref metadata and who is using itCrossref Crossref provides metadata for scholarly publications including titles, authors, references, abstracts, licenses, and links to related resources. This metadata helps make research more discoverable, reproducible, and assessable by linking publications to funding sources, versions, data, and more. Crossref's metadata APIs allow users to access and integrate this information into tools and services to unlock its value for mining and analyzing research outputs.
The OI Project - Geoffrey Bilder



The OI Project - Geoffrey BilderCrossref An update on the genesis of the Organisational Identifier (OI) Project and plans for implementation. Presented by Geoffrey Bilder at Crossref LIVE Seoul, 12 June 2017.
Registering content to enable connections - Rachael Lammey



Registering content to enable connections - Rachael LammeyCrossref Introduction to content registration and what Crossref metadata lets you do. Presented at Crossref LIVE Seoul, 12 June 2017.
Global reach of Crossref metadata - Rachael Lammey - London LIVE 2017



Global reach of Crossref metadata - Rachael Lammey - London LIVE 2017Crossref Presentation by Rachael Lammey on the global reach of Crossref metadata at Crossref's London LIVE event, 26th September 2017.
The DATS model: datasets descriptions for data discovery in DataMed



The DATS model: datasets descriptions for data discovery in DataMedAlejandra Gonzalez-Beltran Presentation at the Smart Descriptions & Smarter Vocabularies (SDSVoc) meeting in Amsterdam, 30th Nov-1st Dec 2016.
UKSG webinar - Introduction to Text-Mining Research Papers with Petr Knoth an...



UKSG webinar - Introduction to Text-Mining Research Papers with Petr Knoth an...UKSG: connecting the knowledge community This webinar will explain what text-mining is and why it is important to text-mine research papers. We will consider real-world use-cases and applications and discuss barriers to wider adoption of text-mining.
We will also provide practical advice on how to start text-mining research papers, such as where to obtain data, how to access relevant APIs and highlight some of the tools that are available.
MIDESS



MIDESSJISC CETIS The MIDESS Project explored sharing digital content like images between university repositories. It tested standards like OAI-PMH and METS for exchanging metadata and objects. While these standards allow some interoperability, repositories implemented them differently, preventing full sharing. The project highlighted ongoing issues around information architecture, repository functionality for multimedia, and integrating repositories into broader systems.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Multiple Resolution and handling content available in multiple places



Multiple Resolution and handling content available in multiple placesCrossref The document discusses how Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) can be used to provide more context and connections between related scholarly works beyond just linking to an article. It describes how multiple resolution allows a DOI to resolve to multiple locations of the same content. Relations allow DOIs to link to other related works like cited articles, prior versions, or referenced data. The document advocates including these relationship connections in metadata to provide more context and allow systems to understand the connections between scholarly outputs.
Cited-by Linking 



Cited-by Linking Crossref This document discusses strategies for participating in Crossref's Cited-By linking service, which allows members to see references from other publications that cite their own journal articles. It outlines three ways for members to deposit reference lists with their article metadata to Crossref, and three strategies for retrieving cited-by data - periodically downloading new data and updating pages; downloading data once and enabling alerts; or retrieving data on-the-fly when users view cited-by results. The document provides examples of HTTP requests members can make to Crossref to deposit references and retrieve cited-by data using these different strategies.
Introduction to DataCite - Martin Fenner



Introduction to DataCite - Martin FennerCrossref Introduction to DataCite including members, collaborations, advocacy and future plans. Presented at Crossref LIVE Seoul, 12 June 2017.
RDAP 15: “This is just for me”: Researchers on their data documentation pract...



RDAP 15: “This is just for me”: Researchers on their data documentation pract...ASIS&T This document summarizes a panel discussion on researchers' data documentation practices. It finds that metadata is often not sufficient because data itself is messy and domain-specific. Researchers in different disciplines like chemistry, ecology, computer science, microbiology, and earth sciences approach documentation differently based on norms and needs within their fields. For example, chemists use numbering systems and documentation protocols while microbiologists emphasize keeping detailed lab notebooks. The document concludes more interviews are needed to better understand disciplinary practices and tailor library services accordingly.
Using Funding Data



Using Funding DataCrossref The document discusses Crossref funding data, which standardizes funder names using the Open Funder Registry. It allows publishers to deposit funding metadata and enables large-scale analysis and reporting of funding data to funders. More information can be found on Crossref's website and API.
Introduction to Crossref, Seoul - Ed Pentz



Introduction to Crossref, Seoul - Ed PentzCrossref The document provides an agenda for a Crossref event taking place in Seoul, South Korea. It includes sessions on Crossref as a global infrastructure partner, registering content to enable connections, how Korean research is found through Crossref metadata, additional Crossref services, community initiatives, and guest sessions on ORCID and DataCite. There will also be discussions on supporting Korean research globally, additional Crossref member services, and data sharing policies. The event aims to showcase how Crossref can help Korean research have global reach and visibility.
Text and Data Mining



Text and Data MiningCrossref Presentation on how Crossref's REST API can be used to get the full text of publisher content for the purpose of TDM. From Crossref LIVE in Brazil, Dec 2016.
Working with ROR as a Crossref member: what you need to know



Working with ROR as a Crossref member: what you need to knowCrossref Webinar focusing on the importance of ROR and how to implement that as a Crossref member.
Covers:
What is ROR?
Why is Crossref supporting ROR?
Publisher use cases for ROR (from Hindawi)
How to become a ROR adopter
Discussion/Q&A
A recording of the presentation is available on the Crossref YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D9Mtqb64OEk
Data Repositories Impact



Data Repositories ImpactMerce Crosas Presentation at the meeting on Measuring the Impact of Digital repositories (https://www.nitrd.gov/nitrdgroups/index.php?title=DigitalRepositories).
Federated Search Falls Short



Federated Search Falls Shortslknight The document summarizes an evaluation of a federated search implementation at Booth Library, Eastern Illinois University. Key findings from analyzing search logs and user statistics over multiple years include: (1) users had significantly more searches and views of full records in native databases compared to the federated search, (2) databases interpreted search queries differently which impacted relevancy of results, (3) proper staffing, training, and statistics tracking are needed for a federated search to be effective. The evaluation highlights the reality that expectations often do not match actual user behaviors and search capabilities.
Annotating research resources with rrid’s



Annotating research resources with rrid’sMaryann Martone The document discusses annotating research resources with Resource Identification Initiative (RRID) identifiers to uniquely and consistently identify key resources like antibodies, software, and genetically modified animals across publications. It notes that currently researchers do not provide enough information to conclusively identify resources, making it difficult to determine what other studies used a particular resource. The RRID pilot project aims to have authors provide standard identifiers for resources to make them machine-readable, publicly accessible, and uniform. The document also covers annotating retrospective literature by attempting to assign RRIDs to resources based on descriptions and searching the RRID portal.
TAIR ICAR 2010 Presentation



TAIR ICAR 2010 PresentationPhoenix Bioinformatics How to make your published data more findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable (and how to make your data more visible in TAIR)
RDAP 15: Beyond Metadata: Leveraging the “README” to support disciplinary Doc...



RDAP 15: Beyond Metadata: Leveraging the “README” to support disciplinary Doc...ASIS&T Research Data Access and Preservation Summit, 2015
Minneapolis, MN
April 22-23, 2015
Part of “Beyond metadata: Supporting non-standardized documentation to facilitate data reuse”
Gaining credit for sharing research data: Viewpoints on Data Publishing



Gaining credit for sharing research data: Viewpoints on Data PublishingVarsha Khodiyar Presentation given at the Viewpoints on Data Publishing workshop, University of Southampton, 21st September 2015
8. Reach of Crossref metadata and who is using it



8. Reach of Crossref metadata and who is using itCrossref Crossref provides metadata for scholarly publications including titles, authors, references, abstracts, licenses, and links to related resources. This metadata helps make research more discoverable, reproducible, and assessable by linking publications to funding sources, versions, data, and more. Crossref's metadata APIs allow users to access and integrate this information into tools and services to unlock its value for mining and analyzing research outputs.
The OI Project - Geoffrey Bilder



The OI Project - Geoffrey BilderCrossref An update on the genesis of the Organisational Identifier (OI) Project and plans for implementation. Presented by Geoffrey Bilder at Crossref LIVE Seoul, 12 June 2017.
Registering content to enable connections - Rachael Lammey



Registering content to enable connections - Rachael LammeyCrossref Introduction to content registration and what Crossref metadata lets you do. Presented at Crossref LIVE Seoul, 12 June 2017.
Global reach of Crossref metadata - Rachael Lammey - London LIVE 2017



Global reach of Crossref metadata - Rachael Lammey - London LIVE 2017Crossref Presentation by Rachael Lammey on the global reach of Crossref metadata at Crossref's London LIVE event, 26th September 2017.
The DATS model: datasets descriptions for data discovery in DataMed



The DATS model: datasets descriptions for data discovery in DataMedAlejandra Gonzalez-Beltran Presentation at the Smart Descriptions & Smarter Vocabularies (SDSVoc) meeting in Amsterdam, 30th Nov-1st Dec 2016.
UKSG webinar - Introduction to Text-Mining Research Papers with Petr Knoth an...



UKSG webinar - Introduction to Text-Mining Research Papers with Petr Knoth an...UKSG: connecting the knowledge community This webinar will explain what text-mining is and why it is important to text-mine research papers. We will consider real-world use-cases and applications and discuss barriers to wider adoption of text-mining.
We will also provide practical advice on how to start text-mining research papers, such as where to obtain data, how to access relevant APIs and highlight some of the tools that are available.
UKSG webinar - Introduction to Text-Mining Research Papers with Petr Knoth an...



UKSG webinar - Introduction to Text-Mining Research Papers with Petr Knoth an...UKSG: connecting the knowledge community
Viewers also liked (16)
MIDESS



MIDESSJISC CETIS The MIDESS Project explored sharing digital content like images between university repositories. It tested standards like OAI-PMH and METS for exchanging metadata and objects. While these standards allow some interoperability, repositories implemented them differently, preventing full sharing. The project highlighted ongoing issues around information architecture, repository functionality for multimedia, and integrating repositories into broader systems.
Espero Que Te Guste



Espero Que Te Gusteluces Este poema corto expresa los sentimientos intensos de amor y deseo de un hablante hacia otra persona, disculpándose por mirarla y besarla con la mirada a pesar de que sus sentimientos lo delatan, y deseando vivir apasionadamente siguiendo sus instintos y amándola sin restricciones.
Sword Slides Cetissig 120208 Public



Sword Slides Cetissig 120208 PublicJISC CETIS 1) The document discusses an implementation of the SWORD standard for depositing content into repositories using Intrallect's intraLibrary software.
2) It describes Intrallect building a desktop deposit tool for intraLibrary that allows dragging and dropping of files and metadata into a repository.
3) The SWORD desktop deposit tool supports features like drag and drop uploading of any file type, bulk deposit, and configuration of collection deposit location. It also allows for workflows after publication like metadata augmentation and quality checking.
Becta Vms



Becta VmsJISC CETIS Presentation on Becta Vocabulary management systems by Mike Taylor at the CETIS MDR SIG meeting on 2008-02-12
Introduction



IntroductionJISC CETIS The document summarizes an agenda for a workshop discussing strategies for resource description and discovery without heavy metadata. The agenda includes presentations on automatic metadata generation, linked open courseware, and search engine optimization lessons from an open educational resources project. Attendees will then break into groups to discuss experiences with and future plans for automatic metadata, search engine optimization, social tagging, semantic web approaches, or other topics. The goal is to ensure open educational resources can be coherently organized and managed as a national collection to meet institutional objectives and target key audiences.
MrCute



MrCuteJISC CETIS MR CUTE is a Moodle plugin that adds repository functionality, allowing users to upload, tag, and search for educational resources. It builds on an existing IMS repository to enhance Moodle's repository browsing capabilities. Key new features include the ability to upload content, tag resources with keywords to aid searching, and package content using IMS standards. The plugin aims to facilitate easier discovery and sharing of educational resources among Moodle users.
Making your content visible - Russell Stannard



Making your content visible - Russell StannardJISC CETIS The document discusses the use of open educational resources (OER) to market multimedia courses at the University of Westminster. It details the growth of a website called MMTV that provides lecture videos and notes from the courses. A survey found that while the site was not a primary factor for most students in choosing the program, it was seen as important in providing information about the courses and influenced some students' decisions. As more content was added to the site, more students cited it as a key factor or as having impacted their decision. The OER resources may be helping to increase enrollment numbers in the programs.
Dc Ed Use Case Session Cetismdrsig 120208



Dc Ed Use Case Session Cetismdrsig 120208JISC CETIS Presentation by Sarah Currier and Lara Whitelaw on DC Ed use cases at the CETIS MDR SIG meeting on 2008-02-12
Protecting Your Investment In L&D Initiatives



Protecting Your Investment In L&D InitiativesPeople Coaching Works Bhd This is a corporate presentation that explains why investments in learning & development produce low returns and what we do to help managers to become better leaders.
Building Leaders The Coaching Way



Building Leaders The Coaching WayPeople Coaching Works Bhd A brief introduction of the key success factors of People Coaching Works. More success factors to come.
ASTRO FOR BANKING INSTITUTIONS



ASTRO FOR BANKING INSTITUTIONSPeople Coaching Works Bhd This document summarizes the Achieving Substantial Targets through Results Orientation (ASTRO) program, a gamified leadership development program for banking institutions. The 2-day program uses group exercises, videos, and simulated work projects to help participants recognize which results to focus on, find necessary resources, and consistently achieve demanding targets. Participants can expect to gain insights into results orientation, learn from high achievers, and create an action plan to apply lessons at work. The program is unique in its focus on work relevance, accountability, and learning transfer to ensure participants improve individual and team performance.
Similar to Automatic Metadata Generation Charles Duncan (20)
Inteligent Catalogue Final



Inteligent Catalogue Finalguestcaef1d To appreciate the paradigm shift involved in the next generation search systems one needs to look back at the traditional approach to resource discovery and compare to the new trends. Here I focus on three aspects:
• Databases versus search engines
• Federated versus integrated search
• Integrated versus modular architecture.
Using metadata repositories with search



Using metadata repositories with searchJean Graef The document discusses metadata repositories and their role in search and discovery. It provides examples of metadata repositories like library card catalogs and bibliographic databases. It describes how metadata repositories store metadata separately from content in order to standardize, share, and search metadata more easily. Commercial metadata repository products are also discussed, including their features and pricing.
Rscd 2017 bo f data lifecycle data skills for libs



Rscd 2017 bo f data lifecycle data skills for libsSusanMRob This document discusses the data skills required of librarians and presents a matrix of factors that influence these skills, including the librarian's role, the data lifecycle services provided by the library, and the research intensity of the institution. It notes the wide range of possible data-related skills and acknowledges that no individual can master all of them, emphasizing the need for librarians to work as a team with complementary skills. The document also examines questions around how librarians can become more involved in data science and what their future roles may be in supporting data-intensive research.
How search engines work Anand Saini



How search engines work Anand SainiDr,Saini Anand The document discusses various aspects of search engines and information retrieval systems. It covers topics like how search engines work, indexing content, query processing, relevance ranking, displaying search results and improving search quality. Some key points include how search engines convert information needs to queries, index content ahead of time, match query terms to indexed words, use relevance algorithms to sort results, and factors that influence search quality like content coverage, query clarity and system failures.
Tovek Presentation by Livio Costantini



Tovek Presentation by Livio Costantinimaxfalc Livio Costantini Tovek presented on tools for accessing unstructured information including Tovek Tools, an enterprise search engine and analytical system. The presentation covered basic information retrieval concepts, the Verity Query Language, and Topic Trees which allow searching for concepts through a predefined hierarchical structure defined by subject experts. Topic Trees address the semantic ambiguity of text by establishing relationships between keywords and providing rules for evaluating documents.
Semantic Search using RDF Metadata (SemTech 2005)



Semantic Search using RDF Metadata (SemTech 2005)Bradley Allen The document summarizes a presentation about using RDF metadata for semantic search. It discusses problems with current enterprise search, and how semantic search using RDF can address these by unifying access to content and data, providing context, and capturing intellectual contributions to searches. The presentation provides examples of semantic search applications using RDF, and describes a case study of using RDF to provide faceted navigation of conference proceedings metadata.
Semantic Search Tutorial at SemTech 2012 



Semantic Search Tutorial at SemTech 2012 Thanh Tran This document provides an overview of a seminar on semantic search. It introduces the speakers, Peter Mika and Tran Duc Thanh, and outlines the agenda which includes introductions to semantic web data using the RDF data model, crawling and indexing RDF data, query processing, ranking results, and evaluating semantic search. It discusses why semantic search is needed to address queries that are not well solved by traditional search and provides examples. It also describes combining document retrieval with data retrieval from structured sources and how semantic search systems can incorporate different models and techniques.
Haystacks slides



Haystacks slidesTed Sullivan his talk will feature some of my recent research into the alternative uses for Solr facets and facet metadata. I will develop the idea that facets can be used to discover similarities between items and attributes in a search index, and show some interesting applications of this idea. A common takeaway is that using facets and facet metadata in non-conventional ways enables the semantic context of a query to be automatically tuned. This has important implications for user-centric and semantically focused relevance.
Reflected Intelligence: Lucene/Solr as a self-learning data system



Reflected Intelligence: Lucene/Solr as a self-learning data systemTrey Grainger What if your search engine could automatically tune its own domain-specific relevancy model? What if it could learn the important phrases and topics within your domain, automatically identify alternate spellings (synonyms, acronyms, and related phrases) and disambiguate multiple meanings of those phrases, learn the conceptual relationships embedded within your documents, and even use machine-learned ranking to discover the relative importance of different features and then automatically optimize its own ranking algorithms for your domain?
In this presentation, you’ll learn you how to do just that - to evolving Lucene/Solr implementations into self-learning data systems which are able to accept user queries, deliver relevance-ranked results, and automatically learn from your users’ subsequent interactions to continually deliver a more relevant experience for each keyword, category, and group of users.
Such a self-learning system leverages reflected intelligence to consistently improve its understanding of the content (documents and queries), the context of specific users, and the relevance signals present in the collective feedback from every prior user interaction with the system. Come learn how to move beyond manual relevancy tuning and toward a closed-loop system leveraging both the embedded meaning within your content and the wisdom of the crowds to automatically generate search relevancy algorithms optimized for your domain.
Tdm information retrieval



Tdm information retrievalKU Leuven Information retrieval (IR) is the process of searching for and retrieving relevant documents from a large collection based on a user's query. Key aspects of IR include:
- Representing documents and queries in a way that allows measuring their similarity, such as the vector space model.
- Ranking retrieved documents by relevance to the query using factors like term frequency and inverse document frequency.
- Allowing for similarity-based retrieval where documents similar to a given document are retrieved.
Using Search Analytics to Diagnose What’s Ailing your Information Architecture



Using Search Analytics to Diagnose What’s Ailing your Information ArchitectureLouis Rosenfeld Presented by Lou Rosenfeld and Rich Wiggins at the 2007 ASIS&T IA Summit, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, March 24, 2007.
Information retrieval is the process of accessing data resources. Usually doc...



Information retrieval is the process of accessing data resources. Usually doc...NALESVPMEngg Information retrieval is the process of accessing data resources. Usually documents or other unstructured data for the purpose of sharing knowledge.
DM110 - Week 10 - Semantic Web / Web 3.0



DM110 - Week 10 - Semantic Web / Web 3.0John Breslin DM110 Emerging Web Media / Huston Film School, National University of Ireland, Galway / 13th March 2007
Semantic Search tutorial at SemTech 2012



Semantic Search tutorial at SemTech 2012Peter Mika This document provides an introduction to a semantic search tutorial given by Peter Mika and Tran Duc Thanh. The agenda covers semantic web data, including the RDF data model and publishing RDF data. It also covers query processing, ranking, result presentation, evaluation, and a question period. The document discusses why semantic search is needed to address poorly solved queries and enable novel search tasks using structured data and background knowledge.
Applications of Semantic Technology in the Real World Today



Applications of Semantic Technology in the Real World TodayAmit Sheth Amit Sheth, "Applications of Semantic Technology in the Real World Today," talk given at Semantic Technology Conference, San Jose, CA, March 2005.
This talk reviews real-world applications mainly deployed in financial services industry developed over Semagix Freedom platform described in http://knoesis.org/library/resource.php?id=810 . Technology is based on this patent: "Semantic web and its applications in browsing, searching, profiling, personalization and advertising", http://knoesis.org/library/resource.php?id=843 .
Amit Sheth founded Taalee in 1999, which merged with Voquette in 2002, and then with Semagix in 2004.
Humanidades digitales por Ryan Shaw (University of North Carolina at Chapel H...



Humanidades digitales por Ryan Shaw (University of North Carolina at Chapel H...innovatics This document discusses managing working research notes for documentary editing projects. It describes the challenges with current tools for organizing editorial research and introduces the Editors' Notes system for addressing these challenges. The system allows editors to store, link, and publish research notes. It also discusses experiments with using linked data and future efforts to better integrate structured data and leverage linked open data.
Reflected Intelligence - Lucene/Solr as a self-learning data system: Presente...



Reflected Intelligence - Lucene/Solr as a self-learning data system: Presente...Lucidworks Trey Grainger gave a presentation about using Lucene/Solr as a self-learning data system through the concept of "reflected intelligence". The presentation covered topics like basic keyword search, taxonomies/entity extraction, query intent, and relevancy tuning. It proposed that by leveraging previous user data and interactions, new data and interactions could be better interpreted to continuously improve the system.
NetIKX Semantic Search Presentation



NetIKX Semantic Search Presentationurvics The slides discuss the research agenda for search of the semantic web and current available search tools. The slides were prepared for an audience of information
Week12



Week12Esha Meher The document discusses text mining and provides examples. It defines text mining as the extraction of implicit knowledge from large amounts of textual data. It discusses applications such as marketing, industry research, and job seeking. Key text mining methods covered include information retrieval, information extraction, web mining, and clustering. The document outlines the text mining process and discusses text characteristics, learning methods such as classification and clustering, and evaluation metrics. Examples are provided to illustrate classification using decision trees and k-nearest neighbors on structured and unstructured text data.
MetadataTheory: Introduction to Metadata (5th of 10)



MetadataTheory: Introduction to Metadata (5th of 10)Nikos Palavitsinis, PhD This document provides an overview of metadata, including:
1) Definitions of metadata from various sources, describing it as data that describes other data or information resources.
2) The main types of metadata - descriptive, processing, administrative, and semantic. Descriptive metadata retrieves information, processing metadata processes information, and administrative metadata manages information.
3) How metadata can be created automatically by tools or manually by people. Metadata schemes provide a formal structure to identify a discipline's knowledge and link it to information resources.
Recently uploaded (20)
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 817 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 97 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 817 (As of 05/3/2025)
• Texas: 688 (+20)(62% of these cases are in Gaines County).
• New Mexico: 67 (+1 )(92.4% of the cases are from Eddy County)
• Oklahoma: 16 (+1)
• Kansas: 46 (32% of the cases are from Gray County)
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 97 (+2)
• Texas: 89 (+2) - This is 13.02% of all TX cases.
• New Mexico: 7 - This is 10.6% of all NM cases.
• Kansas: 1 - This is 2.7% of all KS cases.
DEATHS: 3
• Texas: 2 – This is 0.31% of all cases
• New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.54% of all cases
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 967 (Confirmed and suspected):
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD (As of 4/2/2025)
• Mexico – 865 (+58)
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 844 (+58) cases, 3 hospitalizations, 1 fatality
• Canada: 1531 (+270) (This reflects Ontario's Outbreak, which began 11/24)
‒Ontario, Canada – 1243 (+223) cases, 84 hospitalizations.
• Europe: 6,814
World war-1(Causes & impacts at a glance) PPT by Simanchala Sarab(BABed,sem-4...



World war-1(Causes & impacts at a glance) PPT by Simanchala Sarab(BABed,sem-4...larencebapu132 This is short and accurate description of World war-1 (1914-18)
It can give you the perfect factual conceptual clarity on the great war
Regards Simanchala Sarab
Student of BABed(ITEP, Secondary stage)in History at Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar Punjab 🙏🙏
apa-style-referencing-visual-guide-2025.pdf



apa-style-referencing-visual-guide-2025.pdfIshika Ghosh Title: A Quick and Illustrated Guide to APA Style Referencing (7th Edition)
This visual and beginner-friendly guide simplifies the APA referencing style (7th edition) for academic writing. Designed especially for commerce students and research beginners, it includes:
✅ Real examples from original research papers
✅ Color-coded diagrams for clarity
✅ Key rules for in-text citation and reference list formatting
✅ Free citation tools like Mendeley & Zotero explained
Whether you're writing a college assignment, dissertation, or academic article, this guide will help you cite your sources correctly, confidently, and consistent.
Created by: Prof. Ishika Ghosh,
Faculty.
📩 For queries or feedback: [email protected]
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan. This chapter provides an in-depth overview of the viscosity of macromolecules, an essential concept in biophysics and medical sciences, especially in understanding fluid behavior like blood flow in the human body.
Key concepts covered include:
✅ Definition and Types of Viscosity: Dynamic vs. Kinematic viscosity, cohesion, and adhesion.
⚙️ Methods of Measuring Viscosity:
Rotary Viscometer
Vibrational Viscometer
Falling Object Method
Capillary Viscometer
🌡️ Factors Affecting Viscosity: Temperature, composition, flow rate.
🩺 Clinical Relevance: Impact of blood viscosity in cardiovascular health.
🌊 Fluid Dynamics: Laminar vs. turbulent flow, Reynolds number.
🔬 Extension Techniques:
Chromatography (adsorption, partition, TLC, etc.)
Electrophoresis (protein/DNA separation)
Sedimentation and Centrifugation methods.
To study Digestive system of insect.pptx



To study Digestive system of insect.pptxArshad Shaikh Education is one thing no one can take away from you.”
Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdf



Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdfSandeep Swamy Exploring Substances:
Acidic, Basic, and
Neutral
Welcome to the fascinating world of acids and bases! Join siblings Ashwin and
Keerthi as they explore the colorful world of substances at their school's
National Science Day fair. Their adventure begins with a mysterious white paper
that reveals hidden messages when sprayed with a special liquid.
In this presentation, we'll discover how different substances can be classified as
acidic, basic, or neutral. We'll explore natural indicators like litmus, red rose
extract, and turmeric that help us identify these substances through color
changes. We'll also learn about neutralization reactions and their applications in
our daily lives.
by sandeep swamy
Quality Contril Analysis of Containers.pdf



Quality Contril Analysis of Containers.pdfDr. Bindiya Chauhan Quality control test for containers, rubber closures and secondary packing materials.
Presentation on Tourism Product Development By Md Shaifullar Rabbi



Presentation on Tourism Product Development By Md Shaifullar RabbiMd Shaifullar Rabbi Presentation on Tourism Product Development By Md Shaifullar Rabbi, Assistant Manager- SABRE Bangladesh.
GDGLSPGCOER - Git and GitHub Workshop.pptx



GDGLSPGCOER - Git and GitHub Workshop.pptxazeenhodekar This presentation covers the fundamentals of Git and version control in a practical, beginner-friendly way. Learn key commands, the Git data model, commit workflows, and how to collaborate effectively using Git — all explained with visuals, examples, and relatable humor.
Odoo Inventory Rules and Routes v17 - Odoo Slides



Odoo Inventory Rules and Routes v17 - Odoo SlidesCeline George Odoo's inventory management system is highly flexible and powerful, allowing businesses to efficiently manage their stock operations through the use of Rules and Routes.
Social Problem-Unemployment .pptx notes for Physiotherapy Students



Social Problem-Unemployment .pptx notes for Physiotherapy StudentsDrNidhiAgarwal Unemployment is a major social problem, by which not only rural population have suffered but also urban population are suffered while they are literate having good qualification.The evil consequences like poverty, frustration, revolution
result in crimes and social disorganization. Therefore, it is
necessary that all efforts be made to have maximum.
employment facilities. The Government of India has already
announced that the question of payment of unemployment
allowance cannot be considered in India
To study the nervous system of insect.pptx



To study the nervous system of insect.pptxArshad Shaikh The *nervous system of insects* is a complex network of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells that process and transmit information. Here's an overview:
Structure
1. *Brain*: The insect brain is a complex structure that processes sensory information, controls behavior, and integrates information.
2. *Ventral nerve cord*: A chain of ganglia (nerve clusters) that runs along the insect's body, controlling movement and sensory processing.
3. *Peripheral nervous system*: Nerves that connect the central nervous system to sensory organs and muscles.
Functions
1. *Sensory processing*: Insects can detect and respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
2. *Motor control*: The nervous system controls movement, including walking, flying, and feeding.
3. *Behavioral responThe *nervous system of insects* is a complex network of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells that process and transmit information. Here's an overview:
Structure
1. *Brain*: The insect brain is a complex structure that processes sensory information, controls behavior, and integrates information.
2. *Ventral nerve cord*: A chain of ganglia (nerve clusters) that runs along the insect's body, controlling movement and sensory processing.
3. *Peripheral nervous system*: Nerves that connect the central nervous system to sensory organs and muscles.
Functions
1. *Sensory processing*: Insects can detect and respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
2. *Motor control*: The nervous system controls movement, including walking, flying, and feeding.
3. *Behavioral responses*: Insects can exhibit complex behaviors, such as mating, foraging, and social interactions.
Characteristics
1. *Decentralized*: Insect nervous systems have some autonomy in different body parts.
2. *Specialized*: Different parts of the nervous system are specialized for specific functions.
3. *Efficient*: Insect nervous systems are highly efficient, allowing for rapid processing and response to stimuli.
The insect nervous system is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation, enabling insects to thrive in diverse environments.
The insect nervous system is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation, enabling insects to thrive
UNIT 3 NATIONAL HEALTH PROGRAMMEE. SOCIAL AND PREVENTIVE PHARMACY



UNIT 3 NATIONAL HEALTH PROGRAMMEE. SOCIAL AND PREVENTIVE PHARMACYDR.PRISCILLA MARY J NATIONAL HEALTH PROGRAMMEE
Niamh Lucey, Mary Dunne. Health Sciences Libraries Group (LAI). Lighting the ...



Niamh Lucey, Mary Dunne. Health Sciences Libraries Group (LAI). Lighting the ...Library Association of Ireland
CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - Worksheet



CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - WorksheetSritoma Majumder Introduction
All the materials around us are made up of elements. These elements can be broadly divided into two major groups:
Metals
Non-Metals
Each group has its own unique physical and chemical properties. Let's understand them one by one.
Physical Properties
1. Appearance
Metals: Shiny (lustrous). Example: gold, silver, copper.
Non-metals: Dull appearance (except iodine, which is shiny).
2. Hardness
Metals: Generally hard. Example: iron.
Non-metals: Usually soft (except diamond, a form of carbon, which is very hard).
3. State
Metals: Mostly solids at room temperature (except mercury, which is a liquid).
Non-metals: Can be solids, liquids, or gases. Example: oxygen (gas), bromine (liquid), sulphur (solid).
4. Malleability
Metals: Can be hammered into thin sheets (malleable).
Non-metals: Not malleable. They break when hammered (brittle).
5. Ductility
Metals: Can be drawn into wires (ductile).
Non-metals: Not ductile.
6. Conductivity
Metals: Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Non-metals: Poor conductors (except graphite, which is a good conductor).
7. Sonorous Nature
Metals: Produce a ringing sound when struck.
Non-metals: Do not produce sound.
Chemical Properties
1. Reaction with Oxygen
Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides.
These metal oxides are usually basic.
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides.
These oxides are usually acidic.
2. Reaction with Water
Metals:
Some react vigorously (e.g., sodium).
Some react slowly (e.g., iron).
Some do not react at all (e.g., gold, silver).
Non-metals: Generally do not react with water.
3. Reaction with Acids
Metals react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
Non-metals: Do not react with acids.
4. Reaction with Bases
Some non-metals react with bases to form salts, but this is rare.
Metals generally do not react with bases directly (except amphoteric metals like aluminum and zinc).
Displacement Reaction
More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their salt solutions.
Uses of Metals
Iron: Making machines, tools, and buildings.
Aluminum: Used in aircraft, utensils.
Copper: Electrical wires.
Gold and Silver: Jewelry.
Zinc: Coating iron to prevent rusting (galvanization).
Uses of Non-Metals
Oxygen: Breathing.
Nitrogen: Fertilizers.
Chlorine: Water purification.
Carbon: Fuel (coal), steel-making (coke).
Iodine: Medicines.
Alloys
An alloy is a mixture of metals or a metal with a non-metal.
Alloys have improved properties like strength, resistance to rusting.
How to Set warnings for invoicing specific customers in odoo



How to Set warnings for invoicing specific customers in odooCeline George Odoo 16 offers a powerful platform for managing sales documents and invoicing efficiently. One of its standout features is the ability to set warnings and block messages for specific customers during the invoicing process.
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan.
Niamh Lucey, Mary Dunne. Health Sciences Libraries Group (LAI). Lighting the ...



Niamh Lucey, Mary Dunne. Health Sciences Libraries Group (LAI). Lighting the ...Library Association of Ireland
Automatic Metadata Generation Charles Duncan
- 1. Findings of the Automatic Metadata Generation Use Cases project Charles Duncan [email_address]
- 2. Find and Seek Hide and Seek?
- 3. What is metadata? Anything that aids the discovery and discrimination of resources known unknowns unknown unknowns too many results ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
- 4. Purposes of metadata Discovery (known unknowns) Discrimination (too many results) Recommendation (unknown unknowns)
- 6. Closer to reality Just-in-case Metadata Generation Other Information Archives Other Information Arc hives Other Information Archives Metadata Use Information Archive Deposit Discovery Metadata Generation Discrimination Recommendation Metadata Generation Just-in-time
- 7. In-case v. In-time Could require unreasonable processing times for a real-time service Allows great flexibility for new applications Just-in-time May create and store metadata which might never be used Efficient if metadata is created once and used many times Just-in-case Against For
- 8. Use case - student Student on history course gets reading list from VLE. Selects an article and is offered, additional information about geographic locations and historical characters mention in the article, list of other articles by same author that have the same highly ranked keywords, other articles that commonly appear on reading lists with this article and books borrowed by students of similar profile with matched keywords.
- 9. Use case - depositor Researcher submits a paper for deposit in a repository. The PDF is analysed and keywords and classification suggested. File type and size are detected. Author and journal names are detected and checked and disambiguated against authoritative source. Page numbers and date of publication extracted. All these metadata fields completed automatically. Depositor puts paper into two “collections”. All references are identified and related to this paper.
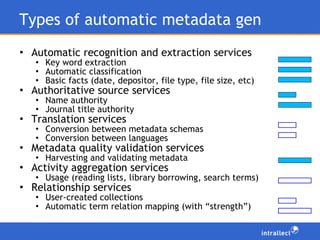
- 10. Types of automatic metadata gen Automatic recognition and extraction services Key word extraction Automatic classification Basic facts (date, depositor, file type, file size, etc) Authoritative source services Name authority Journal title authority Translation services Conversion between metadata schemas Conversion between languages Metadata quality validation services Harvesting and validating metadata Activity aggregation services Usage (reading lists, library borrowing, search terms) Relationship services User-created collections Automatic term relation mapping (with “strength”)
- 11. Types of automatic metadata gen Relationship services Activity aggregation services Metadata quality validation services Translation services Authoritative source services Automatic recognition and extraction services Just-in-time Just-in-case
- 12. Reports Synthesis Report (Use Cases) Guidance Report (Tools) Recommendations Report (JISC only) Specialist reports Subject metadata Name metadata Geospatial metadata Factual metadata Bibliographic metadata Usage metadata File format metadata Integrating automatic metadata services http://www.intrallect.com/index.php/intrallect/knowledge_base/research_projects/automatic_metadata_generation_use_cases
Editor's Notes
- #3: “ open”





![Photos Superb[1].Pps Dd](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/photos-superb1pps-dd-1202917176227320-2-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)



