Ad
Basic Compute Memory and data base Concepts.ppt
- 1. 1 Session : Chapter – Computer Basics Topic : Memory COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS
- 2. 2 CONTENTS Introduction • RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM • Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk • Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 3. 3
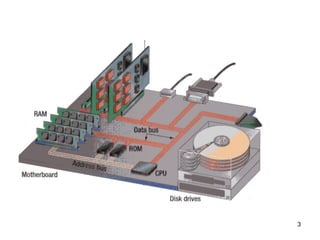
- 4. 4 Memory
- 5. 5 1. Introduction • Memory Devices (RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM) • Storage Devices (Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk .Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs)
- 6. 6
- 7. 7 Characteristics of Storage Devices • Speed • Volatility • Access method • Portability • Cost and capacity
- 8. 8 Basic Units Of Measurement • Bit Binary digit Smallest unit of measurement Two possible values 0 1 on off OR •Byte •8 bits
- 9. 9 Small Units Of Measurement (Processor And Memory Speed) Millisecond (ms) – a thousandth of a second (1/1,000 = 10-3 ) Microsecond (μs) - a millionth of a second (1/1,000,000 = 10-6 ) Nanosecond (ns) – a billionth of a second (1/1,000,000,000 = 10-9 )
- 10. 10 Large Units Of Measurement (Memory, Storage) • Note: powers of two are used because computer memory and storage are based on the basic unit (bit). • Kilobyte (KB) – a thousand bytes (1,024 = 210 ) • Megabyte (MB) - a million (1,048,576 = 220 )
- 11. 11 Large Units Of Measurement (Memory, Storage) • Gigabyte (GB) – a billion (1,073,741,824 = 230 ) –~ A complete set of encyclopedias requires about 700 MB of storage –~ 30 minutes of video (1/4 of the information stored on a typical DVD)
- 12. 12 Large Units Of Measurement (Memory, Storage) • Terabyte (TB) – a trillion (1,099,511,627,776 = 240 ) – ~ 20 million four-drawer filing cabinets full of text – ~ 200 DVD’s of information
- 13. 13 CONTENTS • Introduction • RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM • Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk • Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 14. 14 • Memory Devices – Memory: Is one or more sets of chips that store data/program instructions, either temporarily or permanently . – It is critical processing component in any computer – PCs use several different types 2. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM
- 15. 15 RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM • Memory Devices – Two most important are • RAM(Random Access Memory) • ROM(Read-only Memory) – They work in different ways and perform distinct functions – CPU Registers – Cache Memory
- 16. 16 RAM • RAM is packaged as a chip. • Basic storage unit is a cell (one bit per cell). • Multiple RAM chips form a memory. • Random Access Memory Volatile Used for temporary storage Typical ranges 256 MB - 4 GB • Random Access means direct access to any part of memory
- 17. 17 Nonvolatile Memories(ROM) • DRAM and SRAM are volatile memories –Lose information if powered off. • Nonvolatile memories retain value even if powered off. –Generic name is read-only memory (ROM). –Misleading because some ROMs can be read and modified.
- 18. 18 Nonvolatile Memories(ROM) • Types of ROMs – Programmable ROM (PROM) – Eraseable programmable ROM (EPROM) – Electrically eraseable PROM (EEPROM) – Flash memory (used in portable digital devices) • Firmware (Program instruction used frequently) – Program stored in a ROM • Boot time code, BIOS (basic input/output system) • graphics cards, disk controllers.
- 19. 19 Memory
- 20. 20 3. Storage Vs. Memory Memory (e.g., RAM) •Keep the information for a shorter period of time (usually volatile) •Faster •More expensive
- 21. 21 3. Storage Vs. Memory Storage (e.g., Hard disk) • The information is retained longer (non-volatile) • Slower • Cheaper
- 22. 22 CONTENTS • Introduction • RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM • Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk • Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 23. 23 Categories Of Storage • Magnetic – Floppy disks – Zip disks – Hard drives • Optical – CD-ROM – DVD • Solid state storage devices – USB Key (a very common form of solid state storage)
- 24. 24 Magnetic Storage • Exploits duality of magnetism and electricity – Converts electrical signals into magnetic charges – Captures magnetic charge on a storage medium – Later regenerates electrical current from stored magnetic charge • Polarity of magnetic charge represents bit values zero and one
- 26. 26 Magnetic Disk • Flat, circular platter with metallic coating that is rotated beneath read/write heads • Random access device; read/write head can be moved to any location on the platter • Hard disks and floppy disks • Cost performance leader for general- purpose on-line secondary storage
- 27. 27 1. Magnetic Drives: Storage Capacities •Floppy disks –~ 1 MB •Hard drives –~80 – 500 GB (TB is possible but very rare)
- 28. 28 Floppy Disks A floppy disk is a portable, inexpensive storage medium that consists of a thin, circular, flexible plastic disk with a magnetic coating enclosed in a square-shaped plastic shell.
- 29. 29 Structure Of Floppy Disks • Initially Floppy disks were 8-inches wide, they then shrank to 5.25 inches, and today the most widely used folly disks are 3.5 inches wide and can typically store 1.44 megabytes of data. • A folly disk is a magnetic disk, which means that it used magnetic patterns to store data. • Data in floppy disks can be read from and written to. • Formatting is the process of preparing a disk for reading and writing. • A track is a narrow recording band that forms a full circle on the surface of the disk.
- 30. 30 Hard Disks • Another form of auxiliary storage is a hard disk. A hard disk consists of one or more rigid metal plates coated with a metal oxide material that allows data to be magnetically recorded on the surface of the platters. • The hard disk platters spin at a high rate of speed, typically 5400 to 7200 revolutions per minute (RPM). • Storage capacities of hard disks for personal computers range from 10 GB to 120 GB (one billion bytes are called a gigabyte).
- 31. 31 sectors each track is divided into pie- shaped wedges cluster two or more sectors combined tracks data is recorded in concentric circular bands
- 32. 32 Optical Mass Storage Devices • Store bit values as variations in light reflection • Higher areal density & longer data life than magnetic storage • Standardized and relatively inexpensive • Uses: read-only storage with low performance requirements, applications with high capacity requirements & where portability in a standardized format is needed
- 33. 33 2. Optical Drives •CD's (Compact Disk) ~ 700 MB storage –CD-ROM (read only) –CD-R: (record) to a CD –CD-RW: can write and erase CD to reuse it (re- writable) •DVD(Digital Video Disk)
- 34. 34 Compact Discs (CD) • A compact disk (CD), also called an optical disc, is a flat round, portable storage medium that is usually 4.75 inch in diameter. • A CD-ROM (read only memory), is a compact disc that used the same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music. In addition it can contain other types of data such as text, graphics, and video. • The capacity of a CD-ROM is 650 MB of data.
- 35. 35 DVD-ROM – Over 4 GB storage (varies with format) – DVD- ROM (read only) – Many recordable formats (e.g., DVD-R, DVD-RW; ..) – Are more highly compact than a CD. – Special laser is needed to read them DVD (Digital Video Disk)
- 36. 36 Blu-ray Technology • Name Derived from the blue-violet laser used to read and write data. – Developed by the Blu-ray Disc Association with more than 180 members. • Dell • Sony • LG
- 37. 37 Blu-ray Technology Cont. • Data capacity – Because Blu-ray uses a blue laser(405 nanometers) instead of a red laser(650 nanometers) this allows the data tracks on the disc to be very compact. – This allows for more than twice as small pits as on a DVD.
- 38. 38 Blu-ray Technology Cont. • BD-ROM (read-only) - for pre-recorded content • BD-R (recordable) - for PC data storage • BD-RW (rewritable) - for PC data storage • BD-RE (rewritable) - for HDTV recording Formats
- 39. 39 Summary • Introduction • RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM • Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk • Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 40. 40 Thank You