Basic concepts of Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)
- 2. MUSCLE TESTING Muscle testing is the evaluation of contractile units, including muscles and tendons, and their ability to generate forces.
- 4. Forms of muscle testing include manual strength testing, functional tests, and dynamometry.
- 5. MANUAL MUSCLE TESTING An evaluation system for diagnosis of disease or dysfunction of the musculo- skeletal and nervous systems Manual muscle test (MMT) is a procedure for the evaluation of strength of individual muscle or muscles group, based upon the effective performance of a movement in relation to the forces of gravity or Manual Resistance through the available Range of motion (ROM).
- 6. MANUAL MUSCLE TESTING MMT is the most vital part of motor assessment performed in Medical Examination. Manual Muscle Testing(MMT) is a method diagnostic evaluation used by physical therapists, chiropractors, physiological researchers and others concerned with establishing effective treatment and tracking progress throughout a specific regimen.
- 7. HISTORY First developed by Swedish physiotherapists (1860-1880) from the Royal Central Institute of Gymnastics, Sweden. Dr. George H. Taylor (MD) from USA learned the Swedish medical gymnastics (kinesiology) and wrote the very first American book about it in 1860 - "Exposition of the Swedish Movement Cure" (New York, 1860)
- 8. The very first, still documented, Manual Muscle Test was made by the well-known Swedish physiotherapist and kinesiologist Henrik Kellgren. He was the grandfather of James Cyriax, who founded what is called Orthopedic Medicine.
- 9. This is the earliest preserved image of a manual muscle test, anywhere in the world.
- 10. FROM SWEDEN TO UNITED STATES Manual Muscle Testing was later further developed by the physiotherapist Wilhelmine G Wright and orthopedic surgeon Robert W Lovett at Harvard University in Boston, in the early 1910s Manual muscle testing was developed in response to the need to assess muscle strength losses during the polio outbreaking.
- 11. DEVELOPERS OF MMT Modern Manual Muscle Testing pioneers: (1930- 1940) Henry Kendall & Florence Kendall Lucille Daniels & Catherine Worthingham
- 12. MMT was further developed by chiropractor George Goodheart and chiropractor Alan Beardall in the 1960s and 1970s. The chiropractor Alan Beardall did single- handed develop more manual muscle tests than anyone else in the world.
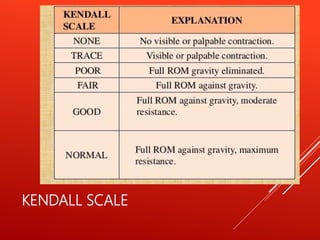
- 13. KENDALL SCALE
- 17. DESCRIPTION OF MODIFIED MRC SCALE
- 18. THE COMPARISON
- 19. CRITERIA FOR EFFECTIVE MUSCLE TESTING Gonella pointed out that three criteria must be met to ensure the success of any muscle testing method: 1) testing must be skillfully administered, 2) The method must allow for the collection of definitive data, and 3) the method must have the facility for controlled, repeated application. (Guffey T, Burton B: A critical look at muscle testing. Clin Mgmt 1991 ;11 :15-19.)
- 20. APPROACHES OF MMT Kendall and McCreary method The Daniels and Worthingham method Tests individual muscle’s action. (Specific muscle action) Tests specific muscle group activity in particular joint motion. (Specific muscle group motion ) Requires more specific knowledge about particular muscle(i.e., Anatomy, Kinesiology etc.,) Relatively easy Ex: Tendon injuries, Muscle rupture etc Ex: Spinal Cord Injuries, Myopathies, Neuromuscular conditions etc Zimny N, Kirk C. A comparison of methods of manual muscle testing. Clin Mgmt 1987;7:6-11.
- 22. MMT CLINICAL VARIATION Individual muscle MMT – ex. tendon transfer. Gross MMT – ex Major muscles only as in case of Amputation. Myotomal MMT – ex Neck or back pain with neurological deficit/ SCI.
- 23. PURPOSES OF MMT • Diagnostic • Examine the improvement or deterioration of a patient’s status over time • Predictive or prognostic tool • Determine the extent of strength loss • Outcome measures in clinical research • Determine the need for compensatory measures or assistive devices • Helps in the formulation of the treatment plan • Evaluates the effectiveness of treatment
- 24. WHY MMT IS PERFORMED To get some answers such as:- Is a particular muscle is normal? Is it weak? (How much weak) Is it strong enough? (How much strong) Is it weak on both the side (bilateral symmetrical)? Is it weak only on one side (Unilateral)? Is proximal muscles are weaker than the proximal one? Is there any particular pattern of muscle weakness?
- 25. PRINCIPLES OF MMT Position Stabilization Demonstration Application of Grades Application of Resistance Checking normal strength Objectivity Documentation
- 26. POSITIONING Patient is positioned Eliminated or Against gravity. (Patient depend upon testing on muscle or muscles group). Do not change patient position repeatedly. The patient should be as free as possible from discomfort or pain for the duration of each test. It may be necessary to allow some patients to move or be positioned differently between tests. Patient position should be carefully organized so that position changes in a test sequence are minimized. The patient' s position must permit adequate stabilization of the part or parts being tested by virtue of body weight or with help provided by the examiner.
- 27. JOINT POSITIONING The joint position is also changed depend upon their performance. Distal part of the joint is moved. Place the joint in Antigravity position- Grade 3 Place the joint in Horizontal position – Grade 2
- 28. POSITIONING
- 29. STABILIZATION Patient could stabilizes our self during performed Antigravity position. The hand placement of the therapist is important. HAND PLACEMENT: I. PROXIMAL HAND – At Origin of muscle & proximal joint giving stabilization. II. DISTAL HAND – Distally offering resistance or Assistance depend upon performance.
- 30. STABILISATION
- 31. DEMONSTRATION Demonstrate the desired movement. Therapist demonstrate the application of movement or performance to the patient.
- 32. APPLICATIONS OF GRADES Always start with GRADE 3. Based on the response, plan accordingly
- 33. MMT FLOW CHART
- 34. APPLICATIONS OF RESISTANCE Resistance is applied slowly & gradually. Increasing or decreasing manual resistance. Increasing length of weight arm. Apply presence opposite to the line of pull (Grade 4,5) Apply force distally. It varies between the persons. Use long lever to applied resistance whenever it possible.
- 35. METHODS FOR PERFORMIMG MMT Break testing is when resistance is applied to the body part at the end of the available range of motion. It's called the break test because when a therapist provides resistance the objective for the patient is to not allow the therapist to "break" the muscle hold. Active Resistance testing/Make Test is when resistance is applied through the body part through the available range of motion. This type of manual muscle testing requires skill and experience and is not the recommended practice.
- 36. BREAK TEST VS MAKE TEST
- 37. CHECKING NORMAL STRENGTH Therapist to check the strength of the muscle normal side first.
- 38. OBJECTIVITY Therapist ability to palpate and observe the tendon or muscle response in very weak muscles.
- 39. DOCUMENTATION Examiners complete testing documentation or Record first. This will help for next step of treatment applications. And help for checking improvement of treatment.
- 40. MATERIALS NEEDED FOR DOCUMENTATION Muscle test documentation forms Pen, pencil, or computer terminal Pillows, towels, pads, and wedges for positioning Sheets or other draping linen Goniometer Interpreter (if needed) Assistance for turning, moving, or stabilizing the patient
- 43. DIAGNOSIS
- 44. CONTRAINDICATIONS OF MMT: (ABSOLUTE/RELATIVE) Spastic Cerebral Palsy Cardio vascular disease / Brain injury Dislocated/ unhealed fracture Myositis ossifications Parkinson’s disease Pain Inflammation /(inflammatory disease in muscles and or joints) Severe cardiac & respiratory disease . Subluxation joint Hemophelia Osteoporosis
- 45. PRECAUTIONS Relative contraindications Do not harm (Be gentle) Respect pain Examiner know the available ROM. Follow the principles of procedure Take care of patient comfort Record accurately. Extra care taken to giving Resisted Exercise. Newly united fracture Bony ankylosis Hematoma If patients take muscle relaxers and or pain medications Prolonged immobilization Abdomen surgery or hernia
- 46. LIMITATION OF MMT UMN LESIONS : Spastic muscle have poor control from higher centers thus its better to go for voluntary control assessment rather than MMT. PRESENCE OF PAIN & SWELLING: Pain and swelling increases the intra articular tension causing irritation of joint and can affect the MMT result, thus in case always mention about presence of pain along with Grade. TYPES OF CONTRACTION : MMT gives idea about Quality of concentric contraction only. (Not Eccentric which is more functional).
- 47. LIMITATION OF MMT UNDERSTANDING OF COMMANDS: Paediatric Age group < 5 years IQ STRENGTH Vs ENDURANCE: MMT give knowledge about only the strength and not endurane Subjectivity (patient) HOOVERS sign
- 48. TO GET STANDARDIZED RESULTS Proper training and education Knowledge base of anatomy, physiology and neurology of muscle function Follow precise testing protocol Practice, Practice, Practice A skill developed and maintained with number of cases
- 49. MMT IN CHILDREN The following are suggested commands for manual muscle testing in pediatric patients. I’m going to see how strong you are. When I tell you hold and don’t let me push you, you try really, really hard not to let me move you. You need to be strong like a tree or a power ranger Ex: Biceps brachii: Bend your elbow, now don’t let me pull your arm down. Hold it hard and don’t let me pull it out.
- 50. ACTIVE MOVEMENT SCALE/ TORONTO MUSCLE GRADING SYSTEM (SCALE FOR CHILDREN)
- 51. SCALE FOR MEASURING HAND MUSCLES For evaluating the strength of the intrinsic hand muscles, a small modification to the standard MRC grading has been made so that grade 3 indicates ‘full active range of motion’ as compared to ‘movement against gravity’ Brandsma JW, Schreuders TA (2001)
- 52. MODIFIED MMT INSTRUMENTED MUSCLE TESTING
- 54. MYOMETER
- 56. PINCH METER
- 57. STRAIN GAUGE
- 61. FUNCTIONAL MUSCLE TESTING Functional muscle testing allows for the assessment of muscles to perform components of, or entire, tasks related to daily activities. Categories of functional muscle testing include the following: Single leg squat, Gower’s Sign, Intrinsic plus hand, balance, excursion, lunge, step-up, step- down, jump and hop tests.
- 62. THANK YOU