Bluetooth and Raspberry Pi
- 1. Bluetooth and Raspberry Pi Damien Magoni University of Bordeaux 2017/10/12 Version 3
- 2. Attribution • The material contained inside is intended for teaching. • This document is licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA license. • All figures and text borrowed from external sources retain the rights of their respective owners. 2
- 3. Table of Contents 1. Bluetooth architecture and operation 2. Bluetooth profiles 3. Bluetooth transport protocols 4. Configuration of Bluetooth on Raspberry Pi 5. Programming with the Bluetooth API on Raspbian 3
- 5. What is Bluetooth? • Bluetooth is a low-power wireless connectivity technology used to stream audio, transfer data and broadcast information between devices • Two forms/flavors of Bluetooth technology • Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate (BR/EDR) • Low Energy (LE) • Both systems include device discovery, connection establishment and connection mechanisms 5
- 6. Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate (BR/EDR) • Bluetooth BR/EDR enables continuous connections • Point-to-point (P2P) network topology, one-to-one (1:1) device communications • Bluetooth BR/EDR audio streaming (e.g., wireless speakers, headsets, hands-free in car systems) • Basic Rate system includes optional Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) and Alternate Media access control and Physical layer (AMP) extensions • Synchronous and asynchronous connections • 721.2 kb/s for BR, 2.1 Mb/s for EDR, up to 54 Mb/s with the 802.11 AMP 6
- 7. BR/EDR Operation • BR/EDR radio PHY layer operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz • Frequency hopping transceiver to combat interference and fading • BR uses a binary frequency modulation to minimize transceiver complexity • 1 Msymbole/s -> 1Mb/s or with EDR 2 or 3Mb/s • A physical radio channel is shared by a group of devices that are synchronized to a common clock and frequency hopping pattern • One master device provides the synchronization reference • All other slave devices are synchronized to the master’s clock and frequency hopping pattern • Such a group of synchronized devices form a piconet 7
- 8. Time Slots • The physical channel is sub-divided into time units known as slots • Data is transmitted between Bluetooth devices in packets that are positioned in these slots • Up to 5 consecutive slots may be allocated to a single packet • Frequency hopping may take place between the transmission or reception of packets • Bluetooth provides the effect of full duplex transmission through the use of a Time-Division Duplex (TDD) scheme 8
- 9. Channels and Links Hierarchy • The upwards hierarchy of channels and links • physical channel, physical link, logical transport, logical link and L2CAP channel • Within a physical channel, physical links providing bidirectional packet transport are formed between each slave and the master • Physical links are not formed directly between the slaves • The physical link is used as a transport for one or more logical links that support unicast synchronous and asynchronous traffic, and broadcast traffic • Traffic on logical links is multiplexed onto the physical link by occupying slots assigned by a scheduling function in the resource manager 9
- 10. Link Manager Protocol (LMP) • Control protocol for the baseband and radio physical layers which is carried over logical links in addition to user data • Devices active in a piconet have a default asynchronous connection- oriented logical transport, known as ACL logical transport • The primary ACL logical transport is created whenever a device joins a piconet • LMP signaling is carried on the primary ACL and active slave broadcast logical transports 10
- 11. Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) • Above the baseband layer the L2CAP layer provides a channel-based abstraction to applications and services • It carries out segmentation and reassembly of application data and multiplexing and de-multiplexing of multiple channels over a shared logical link • Application data submitted to the L2CAP protocol may be carried on any logical link that supports the L2CAP protocol • L2CAP has a protocol control channel that is carried over the default ACL logical transport 11
- 12. L2CAP Architectural Blocks • Connection-oriented and connectionless data services to upper layer protocols • Permits higher level protocols and applications to transmit and receive data packets up to 64 kB • L2CAP layer provides logical channels, named L2CAP channels, which are multiplexed over one or more logical links • Permits per-channel flow control and retransmission 12
- 13. Low Energy (LE) • Bluetooth LE enables short-burst wireless connections • LE system requires lower current consumption, lower complexity and lower cost than BR/EDR • LE system has lower duty cycles and is designed for use cases and applications with lower data rates 13
- 14. Low Energy Network Topologies • Bluetooth LE uses multiple network topologies • Point-to-point (P2P) topology for one-to-one device communications: data transfers, connected devices • (e.g., fitness trackers and health monitors) • Broadcast topology for one-to-many device communications: localized information sharing, beacon solutions • (e.g., point-of-interest (PoI) information, item and way-finding services) • Mesh topology for many-to-many (m:m) device communications: large-scale device networks • (e.g., building automation, sensor network, asset tracking) 14
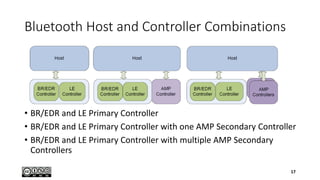
- 15. Host and Controllers • The Bluetooth core system consists of a Host and one or more Controllers • A Host is a logical entity defined as all of the layers below the non- core profiles and above the Host Controller Interface (HCI) • A Controller is a logical entity defined as all of the layers below HCI • Two types of Controllers are defined in this version of the Core Specification • Primary Controllers • Secondary Controllers 15
- 16. Controllers • An implementation of the Bluetooth Core has only one Primary Controller which may be • a BR/EDR Controller including the Radio, Baseband, Link Manager and optionally HCI • an LE Controller including the LE PHY, Link Layer and optionally HCI • a combined BR/EDR Controller portion and LE Controller portion into a single Controller • A Bluetooth core system may additionally have one or more Secondary Controllers • an Alternate MAC/PHY (AMP) Controller including an 802.11 PAL (Protocol Adaptation Layer), 802.11 MAC and PHY, and optionally HCI 16
- 17. Bluetooth Host and Controller Combinations • BR/EDR and LE Primary Controller • BR/EDR and LE Primary Controller with one AMP Secondary Controller • BR/EDR and LE Primary Controller with multiple AMP Secondary Controllers 17
- 19. Profile Specifications • Define possible applications and specify general behaviors that Bluetooth devices use to communicate with other Bluetooth devices • Define what kind of data a Bluetooth module is transmitting • The device’s application determines which profiles it must support • hands-free capabilities, heart rate sensors, alerts, etc. 19
- 20. Profile Compatibility • For two Bluetooth devices to be compatible, they must support the same profiles • Profiles describing the same use case behaviors, are different for BR/EDR and LE implementations • Compatibility between BR/EDR and LE implementations requires a dual-mode controller on at least one device • For BR/EDR, a wide range of adopted profiles describe many different, commonly used types of applications or use cases for devices • For LE, developers can use a comprehensive set of adopted profiles, or they can use Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) to create new profiles • This flexibility helps support innovative new applications that maintain interoperability with other Bluetooth devices 20
- 21. Traditional Profile Specifications • Bluetooth profiles typically contain information such as dependencies on other profiles and suggested user interface formats • For BR/EDR, the profile will also specify the particular options and parameters at each layer of the Bluetooth protocol stack • this may include an outline of the required service record • There are 27 adopted traditional profile specifications 21
- 22. Interesting Profiles for Data Transfer • FTP: File Transfer Profile • GOEP: Generic Object Exchange Profile • MAP: Message Access Profile • OPP: Object Push Profile • SPP: Serial Port Profile • GAP: Generic Access Profile • Etc. 22
- 23. File Transfer Profile (FTP) • A device can • browse an object store (file system) of another device • transfer objects (files and folders copy) to/from another device • manipulate objects (files and folders) on another device (deleting objects, creating new folders) 23
- 24. FTP Stack • SDP is the Bluetooth service discovery protocol • OBEX is the Bluetooth adaptation of the IrDA Object Exchange Protocol 24
- 25. FTP Roles • The Client device initiates the operation, which pushes and pulls objects to and from the Server or instructs the Server to perform actions on objects on the Server • The Client shall be able to interpret the OBEX Folder Listing format and may display this information for the user • The Server device is the target remote device that provides an object exchange server and folder browsing capability using the OBEX Folder Listing format 25
- 26. Generic Object Exchange Profile (GOEP) • GEOP provides object exchange capabilities • Usage models can be Synchronization, File Transfer, Object Push, etc. 26
- 27. GOEP Fundamentals • Before a Server is used with a Client for the first time, a bonding procedure including the pairing may be performed • This procedure must be supported, but its usage is dependent on the application profiles • In addition to the link level bonding, an OBEX initialization procedure may be performed before the Client can use the Server for the first time • The application profiles using GOEP must specify whether this procedure must be supported to provide the required security level. • Security can be provided by authenticating the other party upon connection establishment, and by encrypting all user data on the link level • The authentication and encryption must be supported by the devices; but whether they are used depends on the application profile using GOEP. • Link and channel establishments must be done according to the procedures defined in the Generic Access Profile • There are no fixed master/slave roles • This profile does not require any lower power mode to be used 27
- 28. OBEX Protocol Operations • Application profiles using GOEP must specify which operations must be supported to provide the functionality defined in the application profiles • The OBEX specification does not define how long a client should wait for a response to an OBEX request • Implementations which do not provide a user interface for canceling an OBEX operation should wait a reasonable period between a request and response before automatically canceling the operation (i.e., 30 seconds or more) 28
- 29. Establishment of OBEX Connection • For the object exchange, the OBEX connection can be made with or without OBEX authentication • All application profiles using GOEP must support an OBEX session without authentication as shown here • Connect 0x80 (table 5.2) • Response 0xA0 (table 5.3) 29
- 30. Pushing / Pulling Data to Server • The data object(s) is pushed to the Server using the PUT operation of the OBEX protocol • The data object(s) is pulled from the Server using the GET operation of the OBEX protocol • For each case, the data can be sent in one or more OBEX packets 30
- 31. Serial Port Profile (SPP) • The Serial Port Profile defines protocols and procedures used by devices using Bluetooth for RS232 (or similar) serial cable emulation • For legacy applications using Bluetooth as a cable replacement, through a virtual serial port abstraction • which in itself is operating system- dependent 31
- 32. SPP Stack • Applications on both sides are legacy applications, able to communicate over a serial cable (which in this case is emulated) • Non-legacy applications wishing to perform serial communications over Bluetooth must also adhere to the behavior specified in this profile • This ensures that all combinations of legacy and non-legacy applications remain interoperable at the Bluetooth level 32
- 33. SPP Roles • Device A (DevA) takes initiative to form a connection to another device • DevA is the Initiator according to GAP • Device B (DevB) waits for another device to take initiative to connect • DevB is the Acceptor according to GAP • The order of connection (from DevA to DevB) is independent of the order in which the legacy applications are started • For mapping the Serial Port profile to the conventional serial port architecture, both DevA and DevB can be either a Data Circuit Endpoint (DCE) or a Data Terminal Endpoint (DTE) • RFCOMM protocol is independent of DTE-DCE or DTE-DTE relationships 33
- 34. SPP Fundamentals • Use of security features such as authorization, authentication and encryption is optional • Support for authentication and encryption is mandatory, such that the device can take part in the corresponding procedures if requested from a peer device • Bonding is not used in this profile, and thus is optional • Service discovery procedures have to be performed to set up an emulated serial cable connection • There are no fixed master slave roles • RFCOMM is used to transport the user data, modem control signals and configuration commands 34
- 35. GATT Specifications • Generic Attributes (GATT) services are collections of characteristics and relationships to other services that encapsulate the behavior of a part of a device • This also includes hierarchy of services, characteristics and attributes used in the attribute server • A GATT profile describes a use case, roles, and general behaviors based on the GATT functionality • enable innovation while maintaining interoperability with other Bluetooth devices 35
- 36. GATT Overview • GATT defines a hierarchical data structure that is exposed to connected Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) devices • GATT is built on top of the Attribute Protocol (ATT), which uses GATT data to define how two LE devices send and receive standard messages • GATT defines procedures and formats of services and their characteristics, including discovering, reading, writing, notifying and indicating characteristics 36
- 37. GATT Profile Hierarchy • The top level of the hierarchy is a profile, which is composed of one or more services necessary to fulfill a use case • A service is composed of characteristics or references to other services • A characteristic consists of a type (represented by a UUID), a value, a set of properties indicating the operations the characteristic supports and a set of permissions relating to security • It may also include one or more descriptors—metadata or configuration flags relating to the owning characteristic 37
- 38. GATT Client and Server Roles • GATT defines client and server roles • GATT procedures can be considered to be split into three basic types • Discovery procedures • Client-initiated procedures • Server-initiated procedures • The GATT server stores the data transported over the ATT and accepts ATT requests, commands and confirmations from the GATT client • The GATT server sends responses to requests and sends indications and notifications asynchronously to the GATT client when specified events occur on the GATT server • GATT also specifies the format of data contained on the GATT server 38
- 40. Protocol Specifications • Protocol specifications define the protocols that govern communication among devices on Bluetooth networks 40 Protocol Specification Version Date Adopted AVCTP A/V Control Transport 1.4 24 July 2012 AVDTP A/V Distribution Transport 1.3 24 July 2012 BNEP Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol 1.0 20 February 2003 IrDA IrDA Interoperability 2.0 26 August 2010 MCAP Multi-Channel Adaptation Protocol 1.0 26 June 2008 RFCOMM RFCOMM 1.2 06 November 2012
- 41. Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol (BNEP) • Encapsulates packets from various networking protocols • Those protocols are transported over L2CAP • The Bluetooth Personal Area Networking (PAN) profile describes how BNEP shall be used to provide networking capabilities for Bluetooth devices 41
- 42. BNEP Assumptions • Implemented using connection oriented L2CAP channels • Bluetooth is considered to be a data link layer transmission media • L2CAP is considered to be the Bluetooth Data MAC layer • Specifies a minimum L2CAP MTU of 1691 bytes • IEEE802.3 rules of network connectivity and topology shall be applied to Bluetooth in a manner consistent with IEEE 802.3 media • The Bluetooth BD_ADDR address space is administered by the IEEE, and is assigned from the Ethernet address space • It is possible to build a Bluetooth network access point as a bridge between Bluetooth devices and an Ethernet network 42
- 43. Byte and Bit Ordering • Multiple-byte fields are written from MSB on the left to LSB on the right • Multiple-byte fields in the BNEP header are in standard network byte order (big endian) • more significant bytes (byte 0 is the most significant byte) being transferred before less significant bytes (low-order) • Multiple-bit fields are written msb left to lsb right 43
- 44. BNEP for Transporting an Ethernet Payload • BNEP removes and replaces the Ethernet Header with the BNEP Header • Both the BNEP Header and the Ethernet Payload is encapsulated by L2CAP • Maximum payload that BNEP shall accept from the higher layer is equal to the negotiated L2CAP MTU (minimum value: 1691), minus 191 bytes (or 187 bytes if IEEE 802.1Q) reserved for BNEP headers 44
- 45. Sending an Ethernet Frame • The BNEP_GENERAL_ETHERNET (0x00) packet type header is used to carry Ethernet frames to and from Bluetooth networks • Example frame sent from a device with 48 bit IEEE address of 00:AA:00:55:44:33 to a 48 bit Bluetooth address of 00:30:B7:45:67:89 45
- 46. Sending an IP Packet between Bluetooth Master and Slave • The BNEP_COMPRESSED_ETHERNET (0x02) packet type header is used to carry packets to and from devices that are directly connected at L2CAP level (have a valid L2CAP channel for BNEP) • It may be used when two Bluetooth devices are exchanging packets, in which the source @ is set to the local device’s @ which is the source device sending the packet and destination @ is set to the other device’s @ which is the final destination for the packet • Devices do not need to include the source or destination @s because they are neighbors 46
- 47. RFCOMM Protocol • Provides emulation of serial ports over the L2CAP protocol • Based on a subset of the ETSI standard GSM 07.10 • Supports up to 60 simultaneous connections between two devices • Binary numbers are ordered/sent from left to right from least significant bit (lsb) to most significant bit (msb) 47
- 48. Service Overview • RFCOMM can emulate the nine circuits of RS-232 (ITU-T V.24) serial ports • Built-in scheme for null modem emulation • If a baud rate is set for a particular port through the RFCOMM service interface, that will not affect the actual data throughput in RFCOMM (no artificial rate limitation or pacing) • If either device is a type 2 device (relays data onto other media), or if data pacing is done above the RFCOMM service interface in either or both ends, actual throughput will reflect the baud rate setting 48
- 49. RS-232 Control Signals • Serial port emulation includes transfer of the state of the non- data circuits • RFCOMM supports emulation of multiple serial ports between two devices and emulation of serial ports between multiple devices 49
- 50. Control Signals • For the transfer of the states of the non-data circuits, GSM 07.10 does not distinguish between DTE and DCE devices 50
- 51. Null Modem Emulation • RS-232 control signals are sent as a number of DTE/DCE independent signals which creates an implicit null modem when two devices of the same kind are connected together • The cable-wiring scheme of the null modem created when two DTE are connected via RFCOMM works in most cases 51
- 52. Device Type • Type 1 devices are communication endpoints such as computers and printers • Type 2 devices are those that are part of the communication segment such as modems • In the protocol, no distinction is made between type 1 and type 2: the information transferred between two RFCOMM entities has been defined to support both types of devices • some information is only needed by type 2 devices while other information is intended to be used by both • Since the device is not aware of the type of the other device, each shall pass on all available information specified by the protocol 52
- 53. Direct/Network Connection • RFCOMM is intended to cover applications that make use of the serial ports of the devices in which they reside • In the simple configuration, the communication segment is a Bluetooth link from one device to another (direct connect) • Where the communication segment is another network, Bluetooth is used for the path between the device and a network connection device like a modem • RFCOMM is only concerned with the connection between the devices in the direct connect case, or between the device and a modem in the network case 53
- 54. GSM 07.10 Frame Types Supported in RFCOMM 54
- 56. Flow Control • L2CAP may employ either the Link Controller stop and go flow control mechanism or the L2CAP per-channel flow control mechanism • The flow control mechanism between the L2CAP and RFCOMM layers is implementation-specific • Wired Serial ports use 1) software flow control using characters such as XON/XOFF 2) flow control using RTS/CTS or DTR/DSR circuits • These methods may be used by both sides of a wired link, or may be used only in one direction • The GSM 07.10 protocol provides two flow control mechanisms • The GSM 07.10 protocol contains flow control commands that operate on the aggregate data flow between two RFCOMM entities; i.e. all DLCIs are affected • The Modem Status command is the flow control mechanism that operates on individual DLCI • It is mandatory to support these GSM 07.10-styles of flow control, in order to maintain backward compatibility with earlier Bluetooth versions 56
- 57. Configuration of Bluetooth on Raspberry Pi Part 4
- 58. Bluetooth Installation • Update and get the packages sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get install bluetooth bluez bluez-utils blueman python-gobject python-gobject-2 • Start the GUI desktop startx 58
- 59. Bluetooth Configuration • Check bluetooth status sudo systemctl status bluetooth • Disable SAP in the configuration file /lib/systemd/system/bluetooth.service ExecStart=/usr/lib/bluetooth/bluetoothd --noplugin=sap • Restart $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ service bluetooth restart • The command line control tool is bluetoothctl • Use list and show options, use man if needed 59
- 60. Bluetooth Connection • Switch your Bluetooth device on and activate pairing mode • Typically involves holding down a button or key, see device’s documentation • With the device in pairing mode, click the Bluetooth icon on the Raspbian taskbar (near the clock at the right edge of the screen) • Click on Add Device to launch the Add New Device menu • Find your chosen device in the list, and then click Pair • The Pi will launch the pairing procedure (differs from device to device), follow onscreen instructions to pair the two devices together 60
- 61. Programming with the Bluetooth API on Raspbian Part 5
- 62. Development Tools • Bluez is the official Linux Bluetooth protocol stack • It includes a kernel module, libraries and utilities • Information is here http://www.bluez.org/ • Source code can be found here http://www.bluez.org/development/git/ • For C programming apt-get install libbluetooth-dev 62
- 64. Bluez Capabilities • Current protocols: HCI, L2CAP, SDP, RFCOMM, OBEX, BNEP, etc. • Current profiles: GAP, SDAP, SPP, GOEP, DUN, LAN, PUSH, SYNC, FTP, PAN, etc. • Full source code is available under the GPL • Socket based interfaces • Simple API for special HCI or SDP tasks • Access to all Bluetooth host layers 64
- 65. Python Development Libraries • The PyBluez library https://github.com/karulis/pybluez • It can be downloaded at the Python Package Index https://pypi.python.org/pypi/PyBluez/0.22 • The LightBlue library https://pypi.python.org/pypi/lightblue/0.2 • The PyOBEX library https://pypi.python.org/pypi/PyOBEX/0.10 65
- 66. Python 3 Socket Library • Since version 3.3, Bluetooth is integrated into the sockets API https://docs.python.org/3.3/library/socket.html • Write your classic C/S program • AF_BLUETOOTH supports the following protocols and address formats • BTPROTO_L2CAP accepts (bdaddr, psm) where bdaddr is the Bluetooth address as a string and psm is an integer. • BTPROTO_RFCOMM accepts (bdaddr, channel) where bdaddr is the Bluetooth address as a string and channel is an integer. • BTPROTO_HCI accepts (device_id,) where device_id is either an integer or a string with the Bluetooth address of the interface • BTPROTO_SCO accepts bdaddr where bdaddr is a bytes object containing the Bluetooth address in a string format. (ex. b'12:23:34:45:56:67') 66

























































































































![[HIFLUX] Lok Fitting&Valve Catalog 2025 (Eng)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lokfittingen-250528072439-8696f1c6-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






![[HIFLUX] High Pressure Tube Support Catalog 2025](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/tubesupporten-250529073613-16c22974-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)











