C programming session5
2 likes2,336 views
The document discusses various aspects of functions in C programming including: 1. How function calls work by copying parameters, performing calculations, and returning values. 2. The components of a function definition including name, parameters, return type, and body. 3. Function prototypes and declarations. 4. Differences between passing single values vs arrays to functions. 5. Memory layout of a C program including text, data, heap, and stack segments.
1 of 38
Downloaded 492 times











![Lab:Calculate the Minimum Value of any
Given Array
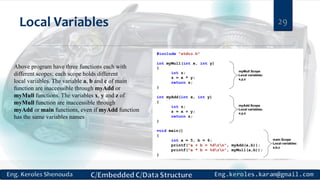
int calcMin(int values[], int n) ;
12
Important: calcMin function takes two parameters an array and (int) value containing
the array size. Know that function could not expect the given array size, you must supply
it by yourself.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-session5-171018113655/85/C-programming-session5-12-320.jpg)

![Finding a Name in a Set of Names
int findName(char names[][14], int n, char name[]);
14
void main()
{
char name[14];
char names[5][14] = {"Alaa", "Osama", "Mamdouh",
"Samy", "Hossain"};
puts("Enter your first name:");
gets(name);
if(findName(names, 5, name)==1)
puts("Welcome");
else
puts("Goodby");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-session5-171018113655/85/C-programming-session5-14-320.jpg)











![Data segment
There are two sub section of this segment called initialized & uninitialized
data segment
Initialized data:- It contains both static and global data that are initialized
with non-zero values.
This segment can be further classified into read-only area and read-write area.
For example : The global string defined by char string[ ] = “hello world” and a statement
like int count=1 outside the main (i.e. global) would be stored in initialized read-write
area. And a global statement like const int A=3 makes the variable ‘A’ read-only and to
be stored in initialized read-only area.
Uninitialized data (bss segment):- Uninitialized data segment is also called BSS segment.
BSS stands for ‘Block Started by Symbol’ named after an ancient assembler operator.
Uninitialized data segment contains all global and static variables that are initialized to zero
or do not have explicit initialization in source code.
For example : The global variable declared as int A would be stored in uninitialized data
segment. A statement like static int X=0 will also stored in this segment cause it
initialized with zero.
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-session5-171018113655/85/C-programming-session5-26-320.jpg)











Ad
Recommended
C programming first_session



C programming first_sessionKeroles karam khalil This document provides an introduction to C programming and discusses reasons for using C over assembly language or other languages. It notes that C provides portability across architectures while retaining much of the control of assembly. It also discusses that C allows for memory allocation and dynamic memory management. The document then covers setting up the C development environment with MinGW or Cygwin compilers and Eclipse IDE. It provides an example of writing a basic "Hello World" C program, building, running and debugging it. Finally, it outlines the GCC compilation process.
C programming session6



C programming session6Keroles karam khalil The document discusses various C preprocessor directives and their usage. It provides examples of how to use #define, #include, #ifdef, #ifndef, #if, #else, #endif, #undef, and #pragma directives in C code. It also discusses macro definitions and how they allow text replacement before compilation. Conditional compilation directives like #ifdef allow including or excluding blocks of code based on conditions. The #pragma directive is implementation specific and examples show how to use #pragma startup and #pragma exit to define functions to run before and after main.
Automotive embedded systems part5 v2



Automotive embedded systems part5 v2Keroles karam khalil The document discusses the AUTOSAR standard, which was developed by automotive manufacturers to help manage the increasing complexity of automotive software systems. AUTOSAR aims to standardize software architecture to improve quality, enable reuse of components across manufacturers, and make application software independent of hardware. It establishes a layered architecture and specifies interfaces to facilitate collaboration and reuse in automotive development. The document provides an overview of the AUTOSAR standard and design process.
Automotive embedded systems part4 v1



Automotive embedded systems part4 v1Keroles karam khalil The document discusses various concepts related to the OSEK operating system including conformance classes, hook routines, shared resources, and mutual exclusion. Specifically, it covers:
1) OSEK defines 4 conformance classes to support systems with different capacities and demands.
2) Hook routines allow user-defined functions to be called at specific points during OS operation, such as startup, shutdown, before/after tasks.
3) Shared resources must be accessed exclusively to prevent data corruption, and mutual exclusion techniques like mutexes and semaphores are used to serialize access.
EMBEDDED C



EMBEDDED CKeroles karam khalil This document discusses how to write embedded C code from scratch without using an IDE. It explains that you need a cross toolchain, Makefile, linker script, startup assembly code, and C code files. It then discusses the requirements for C startup, including initializing the stack, global variables (.data, .bss, .rodata sections), and jumping to the main function. It emphasizes that the linker script is important for section placement in memory. Finally, it outlines the key parts of the startup code: exception vectors, copying .data to RAM, zeroing .bss, setting up the stack pointer, and branching to main.
Automotive embedded systems part3 v1



Automotive embedded systems part3 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses OSEK/VDX operating systems and concepts related to extended tasks, events, interrupts, counters, and alarms. It begins by explaining extended tasks which can wait for events. It then covers the different states an extended task can be in and how events work through event masks and signaling/waiting services. The document discusses two categories of interrupts in OSEK/VDX and how ISR2 interrupts can make system calls. Finally, it describes how counters track hardware ticks and alarms can be used to perform actions periodically by connecting alarms to counters.
Automotive embedded systems part5 v1



Automotive embedded systems part5 v1Keroles karam khalil The document provides an overview of the AUTOSAR standard and its objectives. AUTOSAR (AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) is a standardized software architecture developed by automotive manufacturers to address the increasing complexity of automotive ECU systems. The key goals of AUTOSAR include improving software quality, reusability of functions across manufacturers, and making application software independent of hardware. The document outlines the layered AUTOSAR architecture and the four main steps to developing software using the AUTOSAR standard: input descriptions, system configuration, ECU configuration, and generation of software executables.
Microcontroller part 1



Microcontroller part 1Keroles karam khalil This document provides an index and overview of topics to be covered in a course on embedded systems. The index lists subjects like computer system components, microprocessors, memory, I/O, and microcontrollers. Diagrams are included to illustrate the basic structure of a computer system and a microprocessor. The document promotes sharing code in a GitHub repository and discusses differences between microcontrollers, microprocessors, and system on a chip (SOC) devices.
C programming session7



C programming session7Keroles karam khalil This document discusses various C programming concepts including macros vs functions, ANSI C standards, constants, structures, unions, enums, storage classes like automatic, external, static, and register variables, and references for further reading. It provides examples to illustrate key differences between macros and functions, declaring and initializing constants, defining and using nested structures, unions that allow storing different data types in the same variable, and static and extern storage class specifiers.
C programming part2



C programming part2Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses the features of C including that it is simple, versatile, supports separate compilation of functions, and can be used for systems programming. It also covers C data types like integers, floating-point numbers, and how they are represented. Additional topics include variable names, comments, input/output functions like printf() and scanf(), and conventions for writing readable C code. The document serves as an introduction to key concepts in C programming.
Automotive embedded systems part1 v1



Automotive embedded systems part1 v1Keroles karam khalil The document discusses various topics related to embedded systems and real-time operating systems (RTOS), including:
1) It explains the differences between bare-metal applications, which run directly on hardware without an OS, and OS applications, which run on top of an operating system.
2) It describes some key characteristics and services provided by RTOS kernels, such as deterministic behavior and task scheduling.
3) It discusses different types of real-time systems, including soft and hard real-time, and explains the importance of meeting timing deadlines in real-time systems.
Automotive embedded systems part6 v1



Automotive embedded systems part6 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses the AUTOSAR application layer. It explains that the application layer provides the system functionality through software components (SWCs) that contain software. The document outlines different types of SWCs and their elements like ports, runnable entities, and events. It also discusses how SWCs communicate internally and across ECUs using the virtual functional bus. The mapping of runnable entities to operating system tasks is mentioned as the topic for the next session.
Automotive embedded systems part2 v1



Automotive embedded systems part2 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses embedded operating systems for automotive applications. It provides an overview of OSEK/VDX, an operating system specification for distributed automotive systems. Key topics covered include OSEK/VDX specifications and goals, the AUTOSAR operating system based on OSEK/VDX, task services in OSEK/VDX like TerminateTask and ActivateTask, and examples of task scheduling and chaining in OSEK/VDX. The document aims to teach about real-time operating systems for automotive embedded systems.
Automotive embedded systems part8 v1



Automotive embedded systems part8 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses Controller Area Network (CAN) which is a vehicle bus standard that allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer. It covers the general characteristics of CAN including its event-driven nature, bus arbitration, message filtering, and the different types of CAN messages including data frames, remote frames, error frames, and overload frames. The document provides detailed explanations and illustrations of the fields that make up CAN data frames.
C programming session8



C programming session8Keroles karam khalil Bit-fields allow access to individual bits within registers or bytes. They define the number of bits allocated to each field within a structure. Pointers store the address of other variables in memory and can be used to access or modify these variables indirectly. Pointer arithmetic allows pointers to be incremented or decremented to access sequential memory locations represented by an array.
C basics quiz part 1_solution



C basics quiz part 1_solutionKeroles karam khalil This document discusses C programming concepts and provides quiz questions and solutions. It covers topics like data type conversions, operator precedence, bitwise operations, and more. Multiple choice questions are presented along with hints and explanations of tricks and techniques. Readers are encouraged to think through the problems and examples to improve their understanding of fundamental C programming principles.
Autosar software component



Autosar software componentFarzad Sadeghi This document provides an overview of software components (SWCs) in AUTOSAR. It defines different types of SWCs including application SWCs, sensoractuator SWCs, parameter SWCs, and others. It describes the purpose and functionality of each SWC type. It also discusses SWC elements like ports, runnables, and implementation.
Autosar Basics hand book_v1



Autosar Basics hand book_v1Keroles karam khalil The document provides guidance on learning about automotive embedded systems through a 10 part series. It recommends first studying parts on real-time operating system basics, OSEK/VDX, AUTOSAR basics, and automotive protocols. Then users should validate their understanding and solve practice questions. The document directs readers to online materials and emphasizes the importance of depth of learning to become professional in the field of embedded systems.
Embedded C programming session10



Embedded C programming session10Keroles karam khalil 1. Embedded C requires compilers to create files that can be downloaded and run on microcontrollers, while C compilers typically generate OS-dependent executables for desktop computers.
2. Embedded systems often have real-time constraints and limited memory/power that are usually not concerns for desktop applications.
3. Programming for embedded systems requires optimally using limited resources and satisfying real-time constraints, which is done using the basic C syntax and function libraries but with an embedded/hardware-oriented mindset.
Linux Kernel Module - For NLKB



Linux Kernel Module - For NLKBshimosawa Kernel modules allow adding and removing functionality from the Linux kernel while it is running. Modules are compiled as ELF binaries with a .ko extension and are loaded and unloaded using commands like insmod, rmmod, and modprobe. Modules can export symbols to be used by other modules and have dependencies on other modules that must be loaded first. The kernel tracks modules and their state using data structures like struct module to manage loading, unloading, and dependencies between modules.
UEFI Spec Version 2.4 Facilitates Secure Update



UEFI Spec Version 2.4 Facilitates Secure Updateinsydesoftware The document discusses new features in UEFI Spec Version 2.4 related to facilitating secure firmware updates. Key points include:
1) UEFI 2.4 defines a new capsule format for delivering firmware management protocol (FMP) updates that allows firmware components to be updated early in the pre-boot process.
2) The capsule format supports delivering multiple driver and image payloads.
3) UEFI 2.4 also defines delivering update capsules to the boot disk and having the firmware process them on restart, as well as leaving a variable with the processing status.
4) These new methods are meant to help securely update firmware in a more automated way compared to previous solutions like using EFI shell.
Microcontroller part 1



Microcontroller part 1Keroles karam khalil Here are the steps to determine the status of the C, H, and Z flags after adding 0x38 and 0x2F:
1. 0x38 + 0x2F = 0x67
2. The addition does not generate a carry, so the C flag remains unset.
3. The addition results in a half carry, so the H flag is set.
4. The result 0x67 is non-zero, so the Z flag is unset.
Therefore, after adding 0x38 and 0x2F, the status flags would be:
C flag = 0
H flag = 1
Z flag = 0
Automative basics v3



Automative basics v3Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of embedded automotive basics and AUTOSAR. It discusses how vehicle functions are currently implemented, introducing AUTOSAR as a standardized automotive software architecture. The document explains AUTOSAR's 4 step methodology for creating an E/E system architecture, including input descriptions, system configuration, ECU configuration, and generation of software executables. It also describes the AUTOSAR layered architecture and provides examples of CAN communication and client-server/sender-receiver interfaces.
Automotive embedded systems part7 v1



Automotive embedded systems part7 v1Keroles karam khalil Controller Area Network (CAN) is a serial communication protocol that is most commonly used in automotive applications. It allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in real-time. CAN uses a multi-master broadcast communication style where nodes can transmit messages at any time and all nodes receive all messages. It uses priority-based arbitration to determine which message is transmitted when two nodes transmit simultaneously. CAN provides efficient, reliable, and economical communication between sensors, actuators and electronic control units in automotive and other embedded systems applications.
Intro to Embedded OS, RTOS and Communication Protocols



Intro to Embedded OS, RTOS and Communication ProtocolsEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd This document provides an introduction to key concepts in embedded systems including embedded system components, requirements, trends, common design metrics, development tools, communication protocols like I2C and SPI, and real-time operating systems (RTOS). It defines embedded systems and how they differ from general purpose systems. It also discusses RTOS features like multitasking, task priority, inter-task communication, and how they help achieve real-time capabilities. Key sections of the RTOS are identified including task management, scheduling, synchronization, and interrupt handling.
Automotive embedded systems part6 v2



Automotive embedded systems part6 v2Keroles karam khalil This document discusses Automotive Embedded Systems and the AUTOSAR Application Layer. It covers topics like use cases in AUTOSAR, AUTOSAR basic software modules, the AUTOSAR system design process, software components, runnables, events, and the internal behavior of software components. Diagrams and examples are provided to illustrate concepts like software component types, the relationship between software components and runnables, event types that can trigger runnables, and how a timing event is defined in XML.
Introduction to Modern U-Boot



Introduction to Modern U-BootGlobalLogic Ukraine U-Boot is an open source bootloader used widely in embedded systems. It initializes hardware and loads the operating system kernel. The document provides an overview of U-Boot from the user and developer perspectives, including its features, build process, file structure, and boot sequence. It also discusses modernizing efforts like adopting the driver model, device tree, and Kbuild configuration system to improve compatibility and support new platforms.
Misra c rules



Misra c ruleskiranyeligati The document contains guidelines for coding in C including follow standards like ISO 9899, use approved escape sequences and data types, declare variables before using, use braces and indentation properly, avoid undefined behaviors like signed integer overflow, and restrict usage of certain functions and headers.
C programming part4



C programming part4Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of advanced data types in C programming, including arrays, strings, and 2D arrays. It discusses how to define and initialize arrays, access array elements, and store and print values in arrays. String data types and common string functions like strcpy, strcmp, and converting between strings and other data types are also covered. The document concludes with references for further reading on controlling program flow and data representation in C.
Notes part3



Notes part3Keroles karam khalil This document discusses advanced data types in C including 1D and 2D arrays, strings which are arrays of characters, and various string handling functions like strcpy, strcat, strlwr, strupr, strlen, strcmp, atoi, and atof. It notes that scanf takes only the first word as input while gets takes all characters until enter is pressed when dealing with string input.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
C programming session7



C programming session7Keroles karam khalil This document discusses various C programming concepts including macros vs functions, ANSI C standards, constants, structures, unions, enums, storage classes like automatic, external, static, and register variables, and references for further reading. It provides examples to illustrate key differences between macros and functions, declaring and initializing constants, defining and using nested structures, unions that allow storing different data types in the same variable, and static and extern storage class specifiers.
C programming part2



C programming part2Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses the features of C including that it is simple, versatile, supports separate compilation of functions, and can be used for systems programming. It also covers C data types like integers, floating-point numbers, and how they are represented. Additional topics include variable names, comments, input/output functions like printf() and scanf(), and conventions for writing readable C code. The document serves as an introduction to key concepts in C programming.
Automotive embedded systems part1 v1



Automotive embedded systems part1 v1Keroles karam khalil The document discusses various topics related to embedded systems and real-time operating systems (RTOS), including:
1) It explains the differences between bare-metal applications, which run directly on hardware without an OS, and OS applications, which run on top of an operating system.
2) It describes some key characteristics and services provided by RTOS kernels, such as deterministic behavior and task scheduling.
3) It discusses different types of real-time systems, including soft and hard real-time, and explains the importance of meeting timing deadlines in real-time systems.
Automotive embedded systems part6 v1



Automotive embedded systems part6 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses the AUTOSAR application layer. It explains that the application layer provides the system functionality through software components (SWCs) that contain software. The document outlines different types of SWCs and their elements like ports, runnable entities, and events. It also discusses how SWCs communicate internally and across ECUs using the virtual functional bus. The mapping of runnable entities to operating system tasks is mentioned as the topic for the next session.
Automotive embedded systems part2 v1



Automotive embedded systems part2 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses embedded operating systems for automotive applications. It provides an overview of OSEK/VDX, an operating system specification for distributed automotive systems. Key topics covered include OSEK/VDX specifications and goals, the AUTOSAR operating system based on OSEK/VDX, task services in OSEK/VDX like TerminateTask and ActivateTask, and examples of task scheduling and chaining in OSEK/VDX. The document aims to teach about real-time operating systems for automotive embedded systems.
Automotive embedded systems part8 v1



Automotive embedded systems part8 v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses Controller Area Network (CAN) which is a vehicle bus standard that allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer. It covers the general characteristics of CAN including its event-driven nature, bus arbitration, message filtering, and the different types of CAN messages including data frames, remote frames, error frames, and overload frames. The document provides detailed explanations and illustrations of the fields that make up CAN data frames.
C programming session8



C programming session8Keroles karam khalil Bit-fields allow access to individual bits within registers or bytes. They define the number of bits allocated to each field within a structure. Pointers store the address of other variables in memory and can be used to access or modify these variables indirectly. Pointer arithmetic allows pointers to be incremented or decremented to access sequential memory locations represented by an array.
C basics quiz part 1_solution



C basics quiz part 1_solutionKeroles karam khalil This document discusses C programming concepts and provides quiz questions and solutions. It covers topics like data type conversions, operator precedence, bitwise operations, and more. Multiple choice questions are presented along with hints and explanations of tricks and techniques. Readers are encouraged to think through the problems and examples to improve their understanding of fundamental C programming principles.
Autosar software component



Autosar software componentFarzad Sadeghi This document provides an overview of software components (SWCs) in AUTOSAR. It defines different types of SWCs including application SWCs, sensoractuator SWCs, parameter SWCs, and others. It describes the purpose and functionality of each SWC type. It also discusses SWC elements like ports, runnables, and implementation.
Autosar Basics hand book_v1



Autosar Basics hand book_v1Keroles karam khalil The document provides guidance on learning about automotive embedded systems through a 10 part series. It recommends first studying parts on real-time operating system basics, OSEK/VDX, AUTOSAR basics, and automotive protocols. Then users should validate their understanding and solve practice questions. The document directs readers to online materials and emphasizes the importance of depth of learning to become professional in the field of embedded systems.
Embedded C programming session10



Embedded C programming session10Keroles karam khalil 1. Embedded C requires compilers to create files that can be downloaded and run on microcontrollers, while C compilers typically generate OS-dependent executables for desktop computers.
2. Embedded systems often have real-time constraints and limited memory/power that are usually not concerns for desktop applications.
3. Programming for embedded systems requires optimally using limited resources and satisfying real-time constraints, which is done using the basic C syntax and function libraries but with an embedded/hardware-oriented mindset.
Linux Kernel Module - For NLKB



Linux Kernel Module - For NLKBshimosawa Kernel modules allow adding and removing functionality from the Linux kernel while it is running. Modules are compiled as ELF binaries with a .ko extension and are loaded and unloaded using commands like insmod, rmmod, and modprobe. Modules can export symbols to be used by other modules and have dependencies on other modules that must be loaded first. The kernel tracks modules and their state using data structures like struct module to manage loading, unloading, and dependencies between modules.
UEFI Spec Version 2.4 Facilitates Secure Update



UEFI Spec Version 2.4 Facilitates Secure Updateinsydesoftware The document discusses new features in UEFI Spec Version 2.4 related to facilitating secure firmware updates. Key points include:
1) UEFI 2.4 defines a new capsule format for delivering firmware management protocol (FMP) updates that allows firmware components to be updated early in the pre-boot process.
2) The capsule format supports delivering multiple driver and image payloads.
3) UEFI 2.4 also defines delivering update capsules to the boot disk and having the firmware process them on restart, as well as leaving a variable with the processing status.
4) These new methods are meant to help securely update firmware in a more automated way compared to previous solutions like using EFI shell.
Microcontroller part 1



Microcontroller part 1Keroles karam khalil Here are the steps to determine the status of the C, H, and Z flags after adding 0x38 and 0x2F:
1. 0x38 + 0x2F = 0x67
2. The addition does not generate a carry, so the C flag remains unset.
3. The addition results in a half carry, so the H flag is set.
4. The result 0x67 is non-zero, so the Z flag is unset.
Therefore, after adding 0x38 and 0x2F, the status flags would be:
C flag = 0
H flag = 1
Z flag = 0
Automative basics v3



Automative basics v3Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of embedded automotive basics and AUTOSAR. It discusses how vehicle functions are currently implemented, introducing AUTOSAR as a standardized automotive software architecture. The document explains AUTOSAR's 4 step methodology for creating an E/E system architecture, including input descriptions, system configuration, ECU configuration, and generation of software executables. It also describes the AUTOSAR layered architecture and provides examples of CAN communication and client-server/sender-receiver interfaces.
Automotive embedded systems part7 v1



Automotive embedded systems part7 v1Keroles karam khalil Controller Area Network (CAN) is a serial communication protocol that is most commonly used in automotive applications. It allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in real-time. CAN uses a multi-master broadcast communication style where nodes can transmit messages at any time and all nodes receive all messages. It uses priority-based arbitration to determine which message is transmitted when two nodes transmit simultaneously. CAN provides efficient, reliable, and economical communication between sensors, actuators and electronic control units in automotive and other embedded systems applications.
Intro to Embedded OS, RTOS and Communication Protocols



Intro to Embedded OS, RTOS and Communication ProtocolsEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd This document provides an introduction to key concepts in embedded systems including embedded system components, requirements, trends, common design metrics, development tools, communication protocols like I2C and SPI, and real-time operating systems (RTOS). It defines embedded systems and how they differ from general purpose systems. It also discusses RTOS features like multitasking, task priority, inter-task communication, and how they help achieve real-time capabilities. Key sections of the RTOS are identified including task management, scheduling, synchronization, and interrupt handling.
Automotive embedded systems part6 v2



Automotive embedded systems part6 v2Keroles karam khalil This document discusses Automotive Embedded Systems and the AUTOSAR Application Layer. It covers topics like use cases in AUTOSAR, AUTOSAR basic software modules, the AUTOSAR system design process, software components, runnables, events, and the internal behavior of software components. Diagrams and examples are provided to illustrate concepts like software component types, the relationship between software components and runnables, event types that can trigger runnables, and how a timing event is defined in XML.
Introduction to Modern U-Boot



Introduction to Modern U-BootGlobalLogic Ukraine U-Boot is an open source bootloader used widely in embedded systems. It initializes hardware and loads the operating system kernel. The document provides an overview of U-Boot from the user and developer perspectives, including its features, build process, file structure, and boot sequence. It also discusses modernizing efforts like adopting the driver model, device tree, and Kbuild configuration system to improve compatibility and support new platforms.
Misra c rules



Misra c ruleskiranyeligati The document contains guidelines for coding in C including follow standards like ISO 9899, use approved escape sequences and data types, declare variables before using, use braces and indentation properly, avoid undefined behaviors like signed integer overflow, and restrict usage of certain functions and headers.
Viewers also liked (20)
C programming part4



C programming part4Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of advanced data types in C programming, including arrays, strings, and 2D arrays. It discusses how to define and initialize arrays, access array elements, and store and print values in arrays. String data types and common string functions like strcpy, strcmp, and converting between strings and other data types are also covered. The document concludes with references for further reading on controlling program flow and data representation in C.
Notes part3



Notes part3Keroles karam khalil This document discusses advanced data types in C including 1D and 2D arrays, strings which are arrays of characters, and various string handling functions like strcpy, strcat, strlwr, strupr, strlen, strcmp, atoi, and atof. It notes that scanf takes only the first word as input while gets takes all characters until enter is pressed when dealing with string input.
Homework 3



Homework 3Keroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Homework 2 solution



Homework 2 solutionKeroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
C programming session7



C programming session7Keroles karam khalil This document discusses various C programming concepts including macros vs functions, ANSI C standards, constants, structures, unions, enums, storage classes like automatic, external, static, and register variables, and references for further reading. It provides examples to illustrate key differences between macros and functions, declaring and initializing constants, defining and using nested structures, unions that allow storing different data types in the same memory location, and static variables that retain their value between function calls.
Microcontroller part 4



Microcontroller part 4Keroles karam khalil Here are the key steps for how SPI works:
1. The master device initiates the data transfer by selecting a slave device using the chip select (CS) line. This brings the slave device online.
2. The master outputs the clock signal (SCLK) which is used by both the master and slave devices to synchronize the data transfer.
3. The master sends data on the MOSI (master out, slave in) line which the slave receives on its SDI pin in sync with the clock.
4. In parallel, the slave sends data on the MISO (master in, slave out) line which the master receives on its SDO pin, also in sync with the clock.
C programming part4



C programming part4Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of advanced data types in C programming, including arrays, strings, and 2D arrays. It discusses how to define and initialize arrays, access array elements, and store and print values in arrays. It also covers string operations like copying, comparing, converting between strings and other data types, and manipulating string case and length. The document concludes with references for further reading on controlling program flow and variable scope in C.
Microcontroller part 2



Microcontroller part 2Keroles karam khalil The document discusses interrupts in embedded systems using the ATmega32 microcontroller as an example. It defines an interrupt as a signal that causes the CPU to stop its current execution and jump to an interrupt service routine (ISR) to handle the interrupt event. It describes the interrupt vector table, which stores the addresses of the ISRs. It outlines the steps taken when an interrupt occurs, which includes saving the program counter, jumping to the ISR, executing the ISR code, and returning where it left off. As an example, it shows code for configuring an external interrupt on pin 16 and the corresponding ISR to toggle an output pin.
C programming first_session



C programming first_sessionKeroles karam khalil This document provides an introduction to C programming and discusses reasons for using C over assembly language or other languages. It notes that C provides portability across architectures while retaining much of the control of assembly. It also discusses that C allows for memory allocation and dynamic memory management. The document then covers setting up the C development environment with MinGW or Cygwin compilers and Eclipse IDE. It provides an example of writing a basic "Hello World" C program, building, running and debugging it. Finally, it outlines the GCC compilation process.
K vector embedded_linux_workshop



K vector embedded_linux_workshopKeroles karam khalil The document discusses embedded Linux and provides an agenda for an embedded Linux workshop. It begins with an introduction to embedded systems, communication engineer fields, and automotive systems. It then discusses embedded Linux, including toolchains, bootloaders, the Linux kernel, and embedded Linux development. Examples are provided for building U-Boot on the Raspberry Pi 2 and running a bare metal application on an Altera Arria10 virtual platform using a cross-compiler toolchain.
C programming session3



C programming session3Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of key concepts in C programming including identifiers, keywords, data types, operators, control statements, and functions for controlling program flow. It discusses identifiers and keywords rules. It also covers basic data types and different operators used in C. The document explains various control statements like if-else, switch case, for, while, do-while loops. It provides examples of using conditional operators and break and continue statements. Finally, it discusses nested loops and references additional resources to learn C programming.
C programming part2



C programming part2Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses various features of C like it being a simple, versatile language that allows for separate compilation of functions. It also covers different data types in C like integer, floating-point, characters, and arrays. Examples are given to illustrate how integers of different sizes like char, short, int, long are represented. The document also discusses floating-point number representation according to the IEEE 754 standard. Finally, it briefly introduces common input/output functions in C like printf() and scanf() and covers coding conventions.
C programming session8



C programming session8Keroles karam khalil Bit-fields allow access to individual bits within registers or bytes. They define the number of bits for a field within a structure. Bit-fields are useful for storing Boolean values or device status encoded in bits. Pointers store the address of another variable in memory. They allow passing data to functions without copying values and enable functions to modify caller's variables. Pointer arithmetic can be used to access elements in an array using pointers.
Microcontroller part 3



Microcontroller part 3Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of embedded systems concepts including pulse width modulation (PWM), servo motors, DC motors, timers, analog to digital converters (ADCs), and different types of ADCs. It discusses how PWM is used to control servo and DC motors. It also explains the different timer modes for microcontrollers and how timers can generate PWM signals. Finally, it summarizes various ADC types including parallel, ramp counter, and successive approximation designs.
Microcontroller part 5



Microcontroller part 5Keroles karam khalil The document discusses timers and provides examples of using timers in normal mode on the ATmega32 microcontroller. It begins with defining what a timer is and how timers can count up, down, or up/down. It then discusses timer modes, infrastructure, and applications including delays, baud rate generation, and waveform generation. The document provides details on the timer registers and modes on the ATmega32, including normal mode. It gives an example of writing a program to wait 14 machine cycles in normal mode using Timer 0 on the ATmega32.
C programming part2



C programming part2Keroles karam khalil This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses the features of C including that it is simple, versatile, supports separate compilation of functions, and can be used for systems programming. It also covers C data types like integers, floating-point numbers, and how they are represented. Additional topics include variable names, comments, input/output functions like printf() and scanf(), and conventions for writing readable C code. The document serves as an introduction to programming in C.
Microcontroller part 2



Microcontroller part 2Keroles karam khalil This document discusses setting up an embedded system development environment for AVR microcontrollers using Eclipse. It provides steps to install AVR-GCC, the AVR toolchain, Eclipse, and the AVR Eclipse plugin. It then demonstrates creating a simple "Hello World" project in Eclipse that toggles LEDs connected to an AVR microcontroller. The document also discusses configuring the PATH and paths in Eclipse to allow projects to build properly.
Microcontroller part 7_v1



Microcontroller part 7_v1Keroles karam khalil This document discusses the Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) communication protocol. It explains that UART is an asynchronous serial communication protocol commonly used for communication between microcontrollers and peripheral devices. It operates by framing data bits with start and stop bits across two or more wires. The document covers UART fundamentals like frame formatting, transmission and reception of data, baud rate calculation, and differences between UART and Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (USART). It also provides block diagrams of the UART module and examples of configuring baud rates on microcontrollers.
Microcontroller part 9_v1



Microcontroller part 9_v1Keroles karam khalil This document provides an in-depth overview of the I2C communication protocol. It begins by defining I2C, its characteristics such as being a multi-master multi-slave synchronous serial communication standard. It then covers I2C electrical characteristics, start/stop conditions, addressing, data transfer process including acknowledgements, and arbitration. The document uses diagrams and examples to illustrate I2C communication including reading and writing data between a master and slave device.
Microcontroller part 3



Microcontroller part 3Keroles karam khalil This document discusses interfacing with LCD displays and 4x4 keypads. It begins by explaining LCD displays, how they work, and the pins used to interface with them. It then provides details on sending commands and characters to the LCD. The document also discusses creating an LCD driver and displaying real-time sensor data. It moves on to explain how 4x4 keypads work using multiplexing to reduce pin usage, with the keys arranged in a 4x4 grid and scanned by activating one row at a time. The document provides guidance on creating a keypad driver to detect and read key presses.
Ad
Similar to C programming session5 (20)
[ITP - Lecture 12] Functions in C/C++![[ITP - Lecture 12] Functions in C/C++](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lecture-17-19functions-171215172258-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[ITP - Lecture 12] Functions in C/C++](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lecture-17-19functions-171215172258-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[ITP - Lecture 12] Functions in C/C++](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lecture-17-19functions-171215172258-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[ITP - Lecture 12] Functions in C/C++](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lecture-17-19functions-171215172258-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[ITP - Lecture 12] Functions in C/C++Muhammad Hammad Waseem Functions allow programmers to structure code into modular, reusable units. A function contains a block of code that is executed when the function is called. Functions take parameters as input and can return a value. The example function "addition" takes two integer parameters, adds them together, and returns the result. The main function calls addition, passing it the values 5 and 3, and stores the returned value 8 in the variable z. Functions help avoid duplicating code and make programs easier to design, understand, and maintain.
Functions and pointers_unit_4



Functions and pointers_unit_4Saranya saran This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what a function is and explains why we use functions. There are two types of functions - predefined and user-defined. User-defined functions have elements like function declaration, definition, and call. Functions can pass parameters by value or reference. The document also discusses recursion, library functions, and provides examples of calculating sine series using functions.
Presentation on Function in C Programming



Presentation on Function in C ProgrammingShuvongkor Barman The document presents information about functions in the C programming language. It discusses what a C function is, the different types of C functions including library functions and user-defined functions. It provides examples of how to declare, define, call and pass arguments to C functions. Key points covered include how functions allow dividing a large program into smaller subprograms, the ability to call functions multiple times, and how functions improve readability, debugging and reusability of code. An example program demonstrates a simple C function that calculates the square of a number.
9. DBMS Experiment Laboratory PresentationPPT



9. DBMS Experiment Laboratory PresentationPPTTheVerse1 Here are the steps to complete the experiments:
1. Create a procedure that outputs a message:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE expert IS
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('I am a PL/SQL expert.');
END;
/
2. Create a function to check for leap year:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION isLeapYear(year IN NUMBER) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS
BEGIN
IF MOD(year,4)=0 THEN
IF MOD(year,100)=0 THEN
IF MOD(year,400)=0 THEN
RETURN 'Leap year';
ELSE
RETURN 'Not leap year';
END IF;
ELSE
RETURN '
Functionincprogram



FunctionincprogramSampath Kumar 1. A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. Functions allow programmers to split a large program into smaller sub-tasks and call them multiple times.
2. There are two main types of functions - library functions provided by the standard library, and user-defined functions created by the programmer.
3. Functions make programs easier to write, read, update and debug by splitting them into smaller, well-defined tasks.
c-Functions power point presentation on c functions



c-Functions power point presentation on c functions10300PEDDIKISHOR c-Functions power point presentation on c functions
Chapter 1. Functions in C++.pdf



Chapter 1. Functions in C++.pdfTeshaleSiyum The document provides an overview of functions in C++. It discusses the basic concepts of functions including declaring, defining, and calling functions. It covers function components like parameters and arguments. It explains passing parameters by value and reference. It also discusses different types of functions like built-in functions, user-defined functions, and functions with default arguments. Additionally, it covers concepts like scope of variables, return statement, recursion, and automatic vs static variables. The document is intended to teach the fundamentals of functions as building blocks of C++ programs.
Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdfTeshaleSiyum The document provides an overview of functions in C++. It discusses the basic concepts of functions including declaring, defining, and calling functions. It covers different types of functions such as built-in functions, user-defined functions, and functions that return values. The key components of a function like the prototype, definition, parameters, arguments, and return statement are explained. It also describes different ways of passing parameters to functions, including call by value and call by reference. Functions allow breaking down programs into smaller, reusable components, making the code more readable, maintainable and reducing errors.
Function in c



Function in cRaj Tandukar The document discusses C programming functions. It provides examples of defining, calling, and using functions to calculate factorials, Fibonacci sequences, HCF and LCM recursively and iteratively. Functions allow breaking programs into smaller, reusable blocks of code. They take in parameters, can return values, and have local scope. Function prototypes declare their interface so they can be called from other code locations.
cp Module4(1)



cp Module4(1)Amarjith C K This document discusses modular programming and functions in C programming. Modular programming involves separating a program's functionality into independent, interchangeable modules. There are advantages to this approach such as improved manageability, reusability, and collaboration between programmers.
The document then discusses functions in C programming. Functions allow programmers to divide a program into reusable modules. There are two types of functions - standard library functions defined in header files, and user-defined functions. User-defined functions have advantages like making programs easier to understand, maintain, and debug. The key parts of a user-defined function are the declaration, definition, and call. Functions can take arguments, return values, and be used recursively. Arrays and 2D arrays
Function 



Function Kathmandu University The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines functions as mini-programs that can take in inputs, execute statements, and return outputs. Functions allow programmers to break large tasks into smaller, reusable parts. The key aspects of functions covered include: defining functions with return types and parameters; calling functions and passing arguments; return values; function prototypes; recursion; and examples of calculating factorials and acceleration using functions.
Function



FunctionRajat Patel This document discusses functions in C language. It defines what a function is, its properties, types of functions, and how to define, declare and call functions. The key points are:
1. A function is a block of code that performs a specific task and can be called from different parts of a program.
2. Functions have a unique name, are independent units that perform tasks without interfering with other code, and can optionally return a value.
3. Functions are declared with a prototype specifying their return type, name and parameters, and defined with the actual code implementation.
Functions in c



Functions in cSunithaVesalpu slide1: the content of functons
slide2: Introduction to function
slide3:function advantages
slide4 -5: types of functions
slide6: elements of user defined functions
11 functions



11 functionsRohit Shrivastava The document discusses functions in C programming. It covers defining and calling functions, passing arguments to functions, return statements, and different types of functions. Some key points include:
- Functions make code modular and reusable. Arguments can be passed by value or reference.
- A function is defined with a return type, name, and parameters. It is called by name with arguments. Return passes data back to the calling function.
- Functions can take arguments and return values, take arguments but not return, return values without arguments, or do neither.
- Arguments are passed right to left in C. Functions can be nested by calling one function from another.
Lecture 4



Lecture 4Mohammed Saleh The document discusses functions in C++. It defines functions as modules that can be called to perform tasks and structure programs. Functions may take arguments as input and return values. Well-defined functions have a prototype specifying argument and return types. The document provides examples of built-in functions like sqrt() as well as user-defined functions. It discusses function syntax, calling and defining functions, and variable scope within and outside of functions.
Detailed concept of function in c programming



Detailed concept of function in c programminganjanasharma77573 Detailed concept of function in c programming
Unit-III.pptx



Unit-III.pptxMehul Desai This document discusses functions in C programming. It begins by explaining why programs should be divided into smaller subprograms or functions for manageability. There are two types of functions: library functions which are pre-defined and cannot be modified, and user-defined functions which are created by the user. Every C program must contain a main() function. Functions allow code reusability and modularity. Parameters are used to pass data between functions. The return statement returns data from a function. Local variables are only accessible within their own function.
Functions struct&union



Functions struct&unionUMA PARAMESWARI There are two ways to initialize a structure:
1. Initialize structure members individually when declaring structure variables:
struct point {
int x;
int y;
} p1 = {1, 2};
2. Initialize an anonymous structure and assign it to a variable:
struct point p2 = {3, 4};
Structures allow grouping of related data types together under one name. They are useful for representing records, objects, and other data aggregates. Structures can contain nested structures as members. Arrays of structures are also possible. Structures provide data abstraction by allowing access to their members using dot operator.
Ad
More from Keroles karam khalil (14)
Quiz 9



Quiz 9Keroles karam khalil The document contains questions and explanations about C programming keywords and concepts like pointers, arrays, structures, unions, and bit manipulation. It provides definitions and examples for keywords like #define, #include, #pragma, #asm, #ifdef, and #endif. It also gives solutions to questions about pointers, counting bits to access specific bits or bytes of memory at a particular address, and explaining differences between array parameters and pointers in function definitions in C.
C programming session10



C programming session10Keroles karam khalil 1. Embedded C requires compilers to create executable files that can be downloaded and run on microcontrollers, while C compilers typically generate code for operating systems on desktop computers.
2. Embedded systems often have real-time constraints and limited memory and other resources that require more optimization, unlike most desktop applications.
3. Programming for embedded systems focuses on optimally using limited resources and satisfying timing requirements using basic C constructs and function libraries.
C programming session9 -



C programming session9 -Keroles karam khalil The document discusses C programming and embedded C programming concepts. It covers the differences between C and embedded C, embedded C constraints, how to make code more readable through commenting and documenting memory mapped devices. It also discusses data structures, stacks, queues, and provides code examples for stack implementation and operations using arrays.
Quiz 10



Quiz 10Keroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Homework 6



Homework 6Keroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Homework 5 solution



Homework 5 solutionKeroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Notes part7



Notes part7Keroles karam khalil An enum is a user-defined type in C that allows a variable to be a set of predefined constants (names that represent integer values). A structure is a collection of variables (also known as members) of different types grouped together under a single name. A union is a data type that allows to store different data types in the same memory location.
Homework 5



Homework 5Keroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Notes part6



Notes part6Keroles karam khalil This 3 sentence document provides information about notes for an embedded systems session six. The document references Eng. Keroles Shenouda and includes a Facebook group link for embedded system KS. It also includes the hashtag #Paragma.
Homework 4 solution



Homework 4 solutionKeroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Notes part5



Notes part5Keroles karam khalil This document discusses different ways that functions can access arguments in C programming including pass by value which copies the argument's value and pass by reference which copies the argument's address, allowing changes to the parameter to affect the argument. It also mentions static and global memory, local variables stored on the stack, dynamic memory allocation, and recursion in functions.
Homework 4



Homework 4Keroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Homework 3 solution



Homework 3 solutionKeroles karam khalil https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/learning-cembedded-c-step-by-step-from-scratch-keroles-karam/
Session 5-exersice



Session 5-exersiceKeroles karam khalil The document contains 10 questions related to C programming concepts like arrays, strings, and multi-dimensional arrays. It also provides sample code snippets to test different scenarios and the expected output. Complete solutions and explanations are given for each question at the end.
Recently uploaded (20)
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 817 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 97 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 817 (As of 05/3/2025)
• Texas: 688 (+20)(62% of these cases are in Gaines County).
• New Mexico: 67 (+1 )(92.4% of the cases are from Eddy County)
• Oklahoma: 16 (+1)
• Kansas: 46 (32% of the cases are from Gray County)
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 97 (+2)
• Texas: 89 (+2) - This is 13.02% of all TX cases.
• New Mexico: 7 - This is 10.6% of all NM cases.
• Kansas: 1 - This is 2.7% of all KS cases.
DEATHS: 3
• Texas: 2 – This is 0.31% of all cases
• New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.54% of all cases
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 967 (Confirmed and suspected):
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD (As of 4/2/2025)
• Mexico – 865 (+58)
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 844 (+58) cases, 3 hospitalizations, 1 fatality
• Canada: 1531 (+270) (This reflects Ontario's Outbreak, which began 11/24)
‒Ontario, Canada – 1243 (+223) cases, 84 hospitalizations.
• Europe: 6,814
Introduction to Vibe Coding and Vibe Engineering



Introduction to Vibe Coding and Vibe EngineeringDamian T. Gordon Introduction to Vibe Coding and Vibe Engineering
To study the nervous system of insect.pptx



To study the nervous system of insect.pptxArshad Shaikh The *nervous system of insects* is a complex network of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells that process and transmit information. Here's an overview:
Structure
1. *Brain*: The insect brain is a complex structure that processes sensory information, controls behavior, and integrates information.
2. *Ventral nerve cord*: A chain of ganglia (nerve clusters) that runs along the insect's body, controlling movement and sensory processing.
3. *Peripheral nervous system*: Nerves that connect the central nervous system to sensory organs and muscles.
Functions
1. *Sensory processing*: Insects can detect and respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
2. *Motor control*: The nervous system controls movement, including walking, flying, and feeding.
3. *Behavioral responThe *nervous system of insects* is a complex network of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells that process and transmit information. Here's an overview:
Structure
1. *Brain*: The insect brain is a complex structure that processes sensory information, controls behavior, and integrates information.
2. *Ventral nerve cord*: A chain of ganglia (nerve clusters) that runs along the insect's body, controlling movement and sensory processing.
3. *Peripheral nervous system*: Nerves that connect the central nervous system to sensory organs and muscles.
Functions
1. *Sensory processing*: Insects can detect and respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
2. *Motor control*: The nervous system controls movement, including walking, flying, and feeding.
3. *Behavioral responses*: Insects can exhibit complex behaviors, such as mating, foraging, and social interactions.
Characteristics
1. *Decentralized*: Insect nervous systems have some autonomy in different body parts.
2. *Specialized*: Different parts of the nervous system are specialized for specific functions.
3. *Efficient*: Insect nervous systems are highly efficient, allowing for rapid processing and response to stimuli.
The insect nervous system is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation, enabling insects to thrive in diverse environments.
The insect nervous system is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation, enabling insects to thrive
The ever evoilving world of science /7th class science curiosity /samyans aca...



The ever evoilving world of science /7th class science curiosity /samyans aca...Sandeep Swamy The Ever-Evolving World of
Science
Welcome to Grade 7 Science4not just a textbook with facts, but an invitation to
question, experiment, and explore the beautiful world we live in. From tiny cells
inside a leaf to the movement of celestial bodies, from household materials to
underground water flows, this journey will challenge your thinking and expand
your knowledge.
Notice something special about this book? The page numbers follow the playful
flight of a butterfly and a soaring paper plane! Just as these objects take flight,
learning soars when curiosity leads the way. Simple observations, like paper
planes, have inspired scientific explorations throughout history.
Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdf



Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdfSandeep Swamy Exploring Substances:
Acidic, Basic, and
Neutral
Welcome to the fascinating world of acids and bases! Join siblings Ashwin and
Keerthi as they explore the colorful world of substances at their school's
National Science Day fair. Their adventure begins with a mysterious white paper
that reveals hidden messages when sprayed with a special liquid.
In this presentation, we'll discover how different substances can be classified as
acidic, basic, or neutral. We'll explore natural indicators like litmus, red rose
extract, and turmeric that help us identify these substances through color
changes. We'll also learn about neutralization reactions and their applications in
our daily lives.
by sandeep swamy
Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...



Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...Library Association of Ireland
pulse ppt.pptx Types of pulse , characteristics of pulse , Alteration of pulse



pulse ppt.pptx Types of pulse , characteristics of pulse , Alteration of pulsesushreesangita003 what is pulse ?
Purpose
physiology and Regulation of pulse
Characteristics of pulse
factors affecting pulse
Sites of pulse
Alteration of pulse
for BSC Nursing 1st semester
for Gnm Nursing 1st year
Students .
vitalsign
Quality Contril Analysis of Containers.pdf



Quality Contril Analysis of Containers.pdfDr. Bindiya Chauhan Quality control test for containers, rubber closures and secondary packing materials.
Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s Guide



Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s GuideGS Virdi Dive into the fundamentals of P–N junctions, the heart of every diode and semiconductor device. In this concise presentation, Dr. G.S. Virdi (Former Chief Scientist, CSIR-CEERI Pilani) covers:
What Is a P–N Junction? Learn how P-type and N-type materials join to create a diode.
Depletion Region & Biasing: See how forward and reverse bias shape the voltage–current behavior.
V–I Characteristics: Understand the curve that defines diode operation.
Real-World Uses: Discover common applications in rectifiers, signal clipping, and more.
Ideal for electronics students, hobbyists, and engineers seeking a clear, practical introduction to P–N junction semiconductors.
LDMMIA Reiki Master Spring 2025 Mini Updates



LDMMIA Reiki Master Spring 2025 Mini UpdatesLDM Mia eStudios As of Mid to April Ending, I am building a new Reiki-Yoga Series. No worries, they are free workshops. So far, I have 3 presentations so its a gradual process. If interested visit: https://www.slideshare.net/YogaPrincess
https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
Blessings and Happy Spring. We are hitting Mid Season.
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan. This chapter provides an in-depth overview of the viscosity of macromolecules, an essential concept in biophysics and medical sciences, especially in understanding fluid behavior like blood flow in the human body.
Key concepts covered include:
✅ Definition and Types of Viscosity: Dynamic vs. Kinematic viscosity, cohesion, and adhesion.
⚙️ Methods of Measuring Viscosity:
Rotary Viscometer
Vibrational Viscometer
Falling Object Method
Capillary Viscometer
🌡️ Factors Affecting Viscosity: Temperature, composition, flow rate.
🩺 Clinical Relevance: Impact of blood viscosity in cardiovascular health.
🌊 Fluid Dynamics: Laminar vs. turbulent flow, Reynolds number.
🔬 Extension Techniques:
Chromatography (adsorption, partition, TLC, etc.)
Electrophoresis (protein/DNA separation)
Sedimentation and Centrifugation methods.
Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...



Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...Library Association of Ireland Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services Clare Doyle - Cork City Libraries
CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - Worksheet



CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - WorksheetSritoma Majumder Introduction
All the materials around us are made up of elements. These elements can be broadly divided into two major groups:
Metals
Non-Metals
Each group has its own unique physical and chemical properties. Let's understand them one by one.
Physical Properties
1. Appearance
Metals: Shiny (lustrous). Example: gold, silver, copper.
Non-metals: Dull appearance (except iodine, which is shiny).
2. Hardness
Metals: Generally hard. Example: iron.
Non-metals: Usually soft (except diamond, a form of carbon, which is very hard).
3. State
Metals: Mostly solids at room temperature (except mercury, which is a liquid).
Non-metals: Can be solids, liquids, or gases. Example: oxygen (gas), bromine (liquid), sulphur (solid).
4. Malleability
Metals: Can be hammered into thin sheets (malleable).
Non-metals: Not malleable. They break when hammered (brittle).
5. Ductility
Metals: Can be drawn into wires (ductile).
Non-metals: Not ductile.
6. Conductivity
Metals: Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Non-metals: Poor conductors (except graphite, which is a good conductor).
7. Sonorous Nature
Metals: Produce a ringing sound when struck.
Non-metals: Do not produce sound.
Chemical Properties
1. Reaction with Oxygen
Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides.
These metal oxides are usually basic.
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides.
These oxides are usually acidic.
2. Reaction with Water
Metals:
Some react vigorously (e.g., sodium).
Some react slowly (e.g., iron).
Some do not react at all (e.g., gold, silver).
Non-metals: Generally do not react with water.
3. Reaction with Acids
Metals react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
Non-metals: Do not react with acids.
4. Reaction with Bases
Some non-metals react with bases to form salts, but this is rare.
Metals generally do not react with bases directly (except amphoteric metals like aluminum and zinc).
Displacement Reaction
More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their salt solutions.
Uses of Metals
Iron: Making machines, tools, and buildings.
Aluminum: Used in aircraft, utensils.
Copper: Electrical wires.
Gold and Silver: Jewelry.
Zinc: Coating iron to prevent rusting (galvanization).
Uses of Non-Metals
Oxygen: Breathing.
Nitrogen: Fertilizers.
Chlorine: Water purification.
Carbon: Fuel (coal), steel-making (coke).
Iodine: Medicines.
Alloys
An alloy is a mixture of metals or a metal with a non-metal.
Alloys have improved properties like strength, resistance to rusting.
K12 Tableau Tuesday - Algebra Equity and Access in Atlanta Public Schools



K12 Tableau Tuesday - Algebra Equity and Access in Atlanta Public Schoolsdogden2 Algebra 1 is often described as a “gateway” class, a pivotal moment that can shape the rest of a student’s K–12 education. Early access is key: successfully completing Algebra 1 in middle school allows students to complete advanced math and science coursework in high school, which research shows lead to higher wages and lower rates of unemployment in adulthood.
Learn how The Atlanta Public Schools is using their data to create a more equitable enrollment in middle school Algebra classes.
Multi-currency in odoo accounting and Update exchange rates automatically in ...



Multi-currency in odoo accounting and Update exchange rates automatically in ...Celine George Most business transactions use the currencies of several countries for financial operations. For global transactions, multi-currency management is essential for enabling international trade.
Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptx



Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptxArya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. The Pala kings were people-protectors. In fact, Gopal was elected to the throne only to end Matsya Nyaya. Bhagalpur Abhiledh states that Dharmapala imposed only fair taxes on the people. Rampala abolished the unjust taxes imposed by Bhima. The Pala rulers were lovers of learning. Vikramshila University was established by Dharmapala. He opened 50 other learning centers. A famous Buddhist scholar named Haribhadra was to be present in his court. Devpala appointed another Buddhist scholar named Veerdeva as the vice president of Nalanda Vihar. Among other scholars of this period, Sandhyakar Nandi, Chakrapani Dutta and Vajradatta are especially famous. Sandhyakar Nandi wrote the famous poem of this period 'Ramcharit'.
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...



Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...Library Association of Ireland
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan.
Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...



Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...Library Association of Ireland
Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptx



Political History of Pala dynasty Pala Rulers NEP.pptxArya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
C programming session5
- 1. C_Programming Part 5 ENG. KEROLES SHENOUDA 1
- 2. Functions 2
- 3. 3 The call a = calcm(5,6) works as follows: 1. Copies the values 5 and 6 to the variables x and y 2. Performs the internal calculations to calculate m 3. When executing the line (return m), the computer copies the value inside m and return it to the line (a = calcm(5,6)) 4. Copies the return value to (a) variable
- 4. Function Definition 4 Function Name: like variable, must have no spaces and no special characters and must starts with letters Input Parameters: supplied parameters types and names. You can define any number of inputs; also you can define zero number of inputs. Return Type: the data type of the function output, if the function has no output use (void) keyword. Function Body: performs specific function operation. Return Statement: this statement tells the computer that the function execution is completed and the required function output is ready for the caller. The computer takes the returned value and supplies it to the caller.
- 5. 5 Prototype
- 6. 6
- 7. C functions aspects syntax function definition Return_type function_name (arguments list) { Body of function; } function call function_name (arguments list); function declaration return_type function_name (argument list); 7
- 8. 8 The compiler gives an error at the line printWelcome(); in the main function, the error state that “the function printWelcome is undefined”. Which means that the compiler cannot locate the function before the main, even if it is located after the main?
- 9. 9
- 10. Calculate the Factorial Write a program uses a function to calculate the factorial of any positive number 10
- 11. 11
- 12. Lab:Calculate the Minimum Value of any Given Array int calcMin(int values[], int n) ; 12 Important: calcMin function takes two parameters an array and (int) value containing the array size. Know that function could not expect the given array size, you must supply it by yourself.
- 13. 13
- 14. Finding a Name in a Set of Names int findName(char names[][14], int n, char name[]); 14 void main() { char name[14]; char names[5][14] = {"Alaa", "Osama", "Mamdouh", "Samy", "Hossain"}; puts("Enter your first name:"); gets(name); if(findName(names, 5, name)==1) puts("Welcome"); else puts("Goodby"); }
- 15. Difference between Passing Single Values and Arrays 15 This method copies the actual value of an argument into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to the parameter inside the function have no effect on the argument. This method copies the address of an argument into the formal parameter. Inside the function, the address is used to access the actual argument used in the call. This means that changes made to the parameter affect the argument.
- 16. 16
- 17. 17
- 18. 18
- 19. 19
- 20. 20
- 21. 21
- 22. 22
- 23. Write a program that produces the following output: 23
- 24. What is memory layout of C-program ? when you run any C-program, its executable image is loaded into RAM This memory layout is organized in following fashion: Text segment Data segment Heap segment Stack segment Unmapped or reserved 24
- 25. Text segment Text segment contain executable instructions of your C program, its also called code segment. This is the machine language representation of the program steps to be carried out, including all functions making up the program, both user defined and system 25
- 26. Data segment There are two sub section of this segment called initialized & uninitialized data segment Initialized data:- It contains both static and global data that are initialized with non-zero values. This segment can be further classified into read-only area and read-write area. For example : The global string defined by char string[ ] = “hello world” and a statement like int count=1 outside the main (i.e. global) would be stored in initialized read-write area. And a global statement like const int A=3 makes the variable ‘A’ read-only and to be stored in initialized read-only area. Uninitialized data (bss segment):- Uninitialized data segment is also called BSS segment. BSS stands for ‘Block Started by Symbol’ named after an ancient assembler operator. Uninitialized data segment contains all global and static variables that are initialized to zero or do not have explicit initialization in source code. For example : The global variable declared as int A would be stored in uninitialized data segment. A statement like static int X=0 will also stored in this segment cause it initialized with zero. 26
- 27. Heap segment The heap segment is area where dynamically allocated memory (allocated by malloc(), calloc(), realloc() and new for C++) resides. When we allocate memory through dynamic allocation techniques(in simple word, run time memory allocation), program acquire space from system and process address space grows that’s why we saw upward arrow indication in figure for Heap. 27
- 28. Stack segment The stack segment is area where local variables are stored. By saying local variable means that all those variables which are declared in every function including main( ) in your C program. When we call any function, stack frame is created and when function returns, stack frame is destroyed including all local variables of that particular function. Stack frame contain some data like return address, arguments passed to it, local variables, and any other information needed by the invoked function. A “stack pointer (SP)” keeps track of stack by each push & pop operation onto it, by adjusted stack pointer to next or previous address. 28
- 29. Local Variables 29 Above program have three functions each with different scopes; each scope holds different local variables. The variable a, b and c of main function are inaccessible through myAdd or myMull functions. The variables x, y and z of myMull function are inaccessible through myAdd or main functions, even if myAdd function has the same variables names
- 30. Global Variables In the following program the variable name is defined as a global variable, all program function can access this variable. 30
- 31. Static Variables Static variables are defined by the modifier static. Static variables are initialized once in the program life. For example if the variable (x) is defined inside a function, the variable is initialized only at first function call, further function calls do not perform the initialization step, this means that if the variable is modified by any call the modification result remains for the next call. Following example illustrate this idea 31
- 34. Recursion Recursion is a situation happens when a function calls itself directly or indirectly. 34
- 35. Recursion Is recursion useful? Recursion is an alternative way to repeat the function execution with the same or variant parameters values. In another way recursion is an indirect way to make a loop; simply you can convert any recursion to a normal loop 35 Infinite Printing Loop
- 36. Recursion Is recursion useful? Recursion is an alternative way to repeat the function execution with the same or variant parameters values. In another way recursion is an indirect way to make a loop; simply you can convert any recursion to a normal loop 36 Finite Printing Loop
- 37. Follow Chapter 4/5: Controlling Program Flow C PROGRAMMING FOR ENGINEERS, DR. MOHAMED SOBH 37The next Part we will talk about Variables Scope
- 38. References 38 The Case for Learning C as Your First Programming Language A Tutorial on Data Representation std::printf, std::fprintf, std::sprintf, std::snprintf….. C Programming for Engineers, Dr. Mohamed Sobh C programming expert. fresh2refresh.com/c-programming Memory Layout of C Program





