Cassandra Summit 2014: A Train of Thoughts About Growing and Scalability — Bumping up Startup Business with Apache
- 1. Movile is the industry leader for development of mobile content and commerce platforms in Latin America. With products for mobile phones, smartphones and tablets. Games, on-line education, entertainment apps for adults and kids and many options for buying with confidence and comfort. All of that comes to you through Movile. For companies, Movile delivers complete products, integrating transactions in M-Payments and content distribution, fast and with quality.
- 3. Subscription and Billing Platform a.k.a SBS • It is a service API • responsible to manage users subscriptions • charge users in carriers • renew subscriptions • “can not” stop anyway • should be as performatic as possible
- 4. Some platform numbers Renewal Engine: ~ 52,1 million of billing tries a day • about 603 request/s • 1,5 billion billing tries per month 50 million subscriptions ~ 50 request/s Operations: ★ subscribe ★ cancel ★ profile
- 5. Data Distribution Subscriptions by Country 1% 2% 4% 25% 68% Others Colombia Argentina Mexico Brazil
- 6. Platform Architecture “There isn’t just one way to state a system’s architecture; rather, there are multiple architectures in a system, and the view of what is architecturally significant is one that can change over a system’s lifetime.” - Patterns of Enterprise Application Architecture Martin Fowler
- 8. • scalabe • high availability • high performance
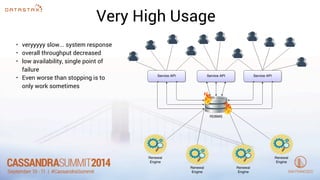
- 9. Very High Usage • veryyyyy slow... system response • overall throughput decreased • low availability, single point of failure • Even worse than stopping is to only work sometimes
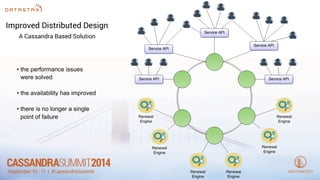
- 10. Improved Distributed Design A Cassandra Based Solution • the operations are distributed across the nodes • we achieved linear scalability
- 11. Improved Distributed Design A Cassandra Based Solution • the performance issues were solved • the availability has improved • there is no longer a single point of failure
- 12. C* Data Modeling • Dernormalization: Writes are cheap, reads are expensive, so insert data in every arrangement that you need to read • Don't be afraid of denormalization • There are different ways to model your solution, there is no right or wrong way • plan your queries and how you need to get the information before modeling. Use it as driver for modeling decisions
- 13. Data Model V1 CREATE TABLE subscription ( subscription-id text PRIMARY KEY, phone-number text, config-id int, … enabled boolean, creation-date timestamp ); CREATE TABLE user_subscriptions ( phone-number text, subscription-id text, PRIMARY KEY (phone-number, subscription-id) );
- 14. Data Model V1 user_subscriptions phone-number subscription-id 551900001212 subs-093123 551911114567 subs-002202 551911114567 subs-002203 551911114567 subs-002204 subscriptions subscription-id phone-number config-id . . . enabled creation-date subs-093123 551900001212 342 . . . true 2013-08-01 subs-002202 551911114567 567 . . . false 2014-06-27 subs-002203 551911114567 678 . . . true 2014-07-05 subs-002204 551911114567 654 . . . true 2014-08-07
- 15. Data Model V1 – Quering Profile user_subscriptions phone-number subscription-id 551900001212 subs-093123 551911114567 subs-002202 551911114567 subs-002203 551911114567 subs-002204 #cql> _ 1st step • check the index table to get the ids of subscriptions for a given user
- 16. Data Model V1 – Quering Profile #cql> SELECT * FROM user_subscriptions WHERE phone-‐number = 551911114567; user_subscriptions phone-number subscription-id 551900001212 subs-093123 551911114567 subs-002202 551911114567 subs-002203 551911114567 subs-002204 551911114567 subs-002202 551911114567 subs-002203 551911114567 subs-002204
- 17. Data Model V1 – Quering Profile #cql> _ 2nd step • query all the user’s subscriptions by its id 551911114567 subs-002202 551911114567 subs-002203 551911114567 subs-002204
- 18. Data Model V1 – Quering Profile #cql> SELECT * FROM subscriptions WHERE subscription-‐id = ‘subs-‐002204’; #cql> SELECT * FROM subscriptions WHERE subscription-‐id = ‘subs-‐002203’; #cql> SELECT * FROM subscriptions WHERE subscription-‐id = ‘subs-‐002202’; subscriptions subscription-id phone-number config-id . . . enabled creation-date subs-093123 551900001212 342 . . . true 2013-08-01 subs-002202 551911114567 567 . . . false 2014-06-27 subs-002203 551911114567 678 . . . true 2014-07-05 subs-002204 551911114567 654 . . . true 2014-08-07
- 19. Data Model V2 CREATE TABLE subscription ( phone-number text, subscription-id text, serialized blob, PRIMARY KEY(phone-number, subscription-id) );
- 20. Data Model V2 subscriptions phone-number subscription-id serialized-data 551900001212 subs-093123 array [1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002202 array [0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002203 array [0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002203 array [1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1] 542154231121 subs-320012 array [1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,1]
- 21. Data Model V2 – Quering Profile #cql> SELECT * FROM subscriptions WHERE phone-‐number = ‘551911114567’; 551911114567 subs-002202 array [0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002203 array [0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002204 array [1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1] subscriptions phone-number subscription-id serialized-data 551900001212 subs-093123 array [1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002202 array [0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002203 array [0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0] 551911114567 subs-002204 array [1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1] 542154231121 subs-320012 array [1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,1]
- 22. Storage Strategy • we tried some various ways to store information • it optimizes network traffic as well 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 Object Representation 1 Object size in bytes Types of object representation XML Java Byte Array JSON protobuff
- 23. Database volume • the database size, decreases considerably • less data to handle, more performance XML Java Byte Array JSON protobuff 0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00 Data Size in GB Storage Strategy Subscription Data Volume
- 24. C* New Data Model • performance increased significantly • reduced complexity: from 2 tables to 1, simpler, lighter • reduced number of remote calls • V1 • 1 query to the index table • X queries (one per index returned) • V2 • 1 query brings all data • data volume reduced
- 25. Cassandra Cluster Configuration • Geographically distributed • 2 data centers in São Paulo Brazil
- 26. Ring Topology nodetool status Datacenter: DC1 =============== Status=Up/Down |/ State=Normal/Leaving/Joining/Moving -‐-‐ Address Load Tokens Owns (effective) Host ID Rack UN 200.xxx.xxx.73 29.58 GB 256 76,7% b9f890b6-‐6137-‐4359-‐90c2-‐74f87ce1676d RAC1 UN 200.xxx.xxx.72 29.8 GB 256 74,5% ec7fa873-‐edd9-‐4cb9-‐938d-‐60f1c9b8f742 RAC1 UN 200.xxx.xxx.71 30.76 GB 256 76,1% 1091799e-‐0617-‐42dd-‐a396-‐363f10c03295 RAC1 UN 200.xxx.xxx.74 26.68 GB 256 72,7% 984b848b-‐0ecb-‐4db3-‐a1fe-‐c9b088c295f6 RAC1 Datacenter: DC2 =============== Status=Up/Down |/ State=Normal/Leaving/Joining/Moving -‐-‐ Address Load Tokens Owns (effective) Host ID Rack UN 200.xxx.xxx.72 28.99 GB 256 100,0% f9b820d6-‐111f-‐4a3a-‐af6c-‐39d0e8e88084 RAC1 UN 200.xxx.xxx.71 30.36 GB 256 100,0% 120939bd-‐a6b4-‐4d88-‐b2cf-‐dbf79d93181c RAC1 UN 200.xxx.xxx.74 27.93 GB 256 100,0% c821b8f7-‐2224-‐4512-‐8a0e-‐0371460d900e RAC1
- 27. Hardware Infrastructure v1.0 4 Servers • Centos 5.9 • 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5606 @ 2.13GHz (4 cores) • 24GB / 32GB RAM • 1x SATA 500gb (OS) • 1x SSD CSSD-F120GB2 (data and commit logs) • Apache Cassandra v1.0.6
- 28. Hardware Infrastructure v2.0 6 Servers • 2 Intel (R) Xeon (R) CPU @3.1GHz • 128 GB of total RAM Memory per Server 6 Virtual Machines (one per physical server) • Running Cent OS 6.5 • 32 GB of RAM per VM • 1 Intel (R) Xeon (R) CPU @3.1GHz • 2 SSD Disks Model : CSSD-F120GBGT • Configured as RAID0 • Apache Cassandra 1.2.13 VMs
- 29. Keyspace Keyspace: SBSPlatform: Replication Strategy: org.apache.cassandra.locator.NetworkTopologyStrategy Options: [DC2:3, DC1:3] cassandra-cli : describe Column Families: ColumnFamily: subscription ColumnFamily: delivery_ticket ColumnFamily: hard_limit_control ColumnFamily: hard_limit_rules ColumnFamily: idx_config_subsc ColumnFamily: user_directives
- 30. Column Family Status Column Family: subscription ./nodetool cfstats SBSPlatform Space used (total): 13499012297 Number of Keys (estimate): 46.369.536 Read Count: 5599788263 / Read Latency: 0,497 ms. Write Count: 5212858995 / Write Latency: 0,017 ms. Compacted row mean size: 576 Column Family: hard_limit_control Space used (total): 7812531598 Number of Keys (estimate): 44.785.024 Read Count: 3987345295 / Read Latency: 0,509 ms. Write Count: 11646786043 / Write Latency: 0,021 ms. Compacted row mean size: 188
- 31. Overall cluster response time Node 1 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.71 load_avg: 0.39 write_latency(us): 900.8 read_latency(us): 553.6 Node 2 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.72 load_avg: 0.51 write_latency(us): 874.1 read_latency(us): 620.5 Node 3 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.74 load_avg: 0.35 write_latency(us): 834.87 read_latency(us): 515.6 Node 4 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.73 load_avg: 0.35 write_latency(us): 900.87 read_latency(us): 700.6 Node 1 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.71 load_avg: 0.63 write_latency(us): 806.3 read_latency(us): 882.3 Node 2 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.72 load_avg: 0.37 write_latency(us): 802.8 read_latency(us): 969.0 Node 3 -‐ : 200.xxx.xxx.74 load_avg: 0.62 write_latency(us): 965.7 read_latency(us): 887.43 Now: 2014-‐08-‐30 14:49:15 Total Reads/second: 13262 Total Writes/second: 9529 DATACENTER 2 DATACENTER 1
- 32. O.S. and Software Customizations According to the Cassandra Docs the Recommended Settings for Production • Java 1.7 + JNA • Disable Swap • NTP server in all servers
- 33. O.S. - limits.conf # number of open files root soft nofile 100000 root hard nofile 100000 * soft nofile 100000 * hard nofile 100000 # allocated memory root soft memlock unlimited root hard memlock unlimited * soft memlock unlimited * hard memlock unlimited # addressing (virtual memory) root soft as unlimited root hard as unlimited * soft as unlimited * hard as unlimited # number of open processes root soft nproc unlimited root hard nproc unlimited * soft nproc unlimited * hard nproc unlimited
- 34. Daily Cluster Operations Total Reads Total Writes > 1 billion
- 35. Conclusion: Why Cassandra? • Good performance for Reads • Excellent performance for Writes • Read and Write throughput highly scalable (linear) • Supports GEO distributed information • Fault Tolerant • Tunable consistency per client • FOSS (Free and Open Source Software) + Support
- 36. Thank You! Questions? [email protected] eitikimura facebook.com/eiti.kimura


















![Data Model V2
subscriptions
phone-number subscription-id serialized-data
551900001212 subs-093123 array [1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002202 array [0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002203 array [0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002203 array [1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1]
542154231121 subs-320012 array [1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eitikimura-cassandrasummit20142-140929173408-phpapp01/85/Cassandra-Summit-2014-A-Train-of-Thoughts-About-Growing-and-Scalability-Bumping-up-Startup-Business-with-Apache-20-320.jpg)
![Data Model V2 – Quering Profile
#cql>
SELECT
*
FROM
subscriptions
WHERE
phone-‐number
=
‘551911114567’;
551911114567 subs-002202 array [0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002203 array [0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002204 array [1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1]
subscriptions
phone-number subscription-id serialized-data
551900001212 subs-093123 array [1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002202 array [0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002203 array [0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]
551911114567 subs-002204 array [1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1]
542154231121 subs-320012 array [1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,10,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eitikimura-cassandrasummit20142-140929173408-phpapp01/85/Cassandra-Summit-2014-A-Train-of-Thoughts-About-Growing-and-Scalability-Bumping-up-Startup-Business-with-Apache-21-320.jpg)







![Keyspace
Keyspace:
SBSPlatform:
Replication
Strategy:
org.apache.cassandra.locator.NetworkTopologyStrategy
Options:
[DC2:3,
DC1:3]
cassandra-cli : describe
Column
Families:
ColumnFamily:
subscription
ColumnFamily:
delivery_ticket
ColumnFamily:
hard_limit_control
ColumnFamily:
hard_limit_rules
ColumnFamily:
idx_config_subsc
ColumnFamily:
user_directives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eitikimura-cassandrasummit20142-140929173408-phpapp01/85/Cassandra-Summit-2014-A-Train-of-Thoughts-About-Growing-and-Scalability-Bumping-up-Startup-Business-with-Apache-29-320.jpg)







