Ad
CDI Best Practices with Real-Life Examples - TUT3287
- 1. CDI Best Practices with Real-Life Examples Ahmad Gohar Software Architect & Technical Team Lead IBM Experienced IT-Specialist Client Innovation Center (CIC), IBM TUT3287
- 3. Gohar , Ahmad Nabil • Software Architect & Technical Team Lead (9Y.) | CIC, IBM. • IBM/Open Group Certified Experienced IT Specialist. • M.Sc. in Information System, FCI, Egypt. • MIBA in Global Management, ESLSCA, France. • OCEJPA | OCPWCD | OCPJP | OCP PL/SQL | MCP(s). • JAVA Community Process (JCP) Member. • Blogger Author and Academic Researcher.
- 6. Introduction to CDI JSR 299: Contexts and Dependency Injection for the Java EE platform
- 7. Q : What is the old name of the CDI ?
- 8. What is CDI (JSR 299)? • Java Specification Requests • JSR is a document of a proposed specification used in the Java Community Process (JCP). • Classes specify what their dependencies • NOT how to obtain them (container responsibility)
- 9. What is CDI (JSR 299)? • Provides a unifying Dependency Injection and contextual life-cycle model for Java EE • Unified existing Dependency Injection schemes – Spring, Guice, Seam • A completely new, richer dependency management model • Type-safe dependency injection • Designed for use with stateful objects (scoped objects)
- 10. What is CDI (JSR 299)? • Makes it much easier to build applications using JSF and EJB together • Let you use EJBs directly as JSF managed beans
- 11. Q : What is Weld ?
- 12. What is Weld? • The CDI Reference Implementation (RI) • Service Provider Interfaces (SPI) • Weld provides a complete SPI allowing Java EE containers to use CDI implementation • Weld also runs in servlet engines, or even in a plain Java SE environment
- 13. Common Dependency Injection Frameworks • Spring • Guice • Seam • EJB 3.X • CDI
- 14. CDI is more than a framework • It’s a whole, rich programming model • The theme of CDI is loosecoupling with strong typing. • A bean specifies only the type and semantics of other beans it depends upon • It need not be aware of the actual lifecycle, concrete implementation, threading model or other clients of any bean it interacts with • Even better, the concrete implementation, lifecycle and threading model of a bean may vary according to the deployment scenario, without affecting any client • This loose-coupling makes your code easier to maintain
- 15. CDI theme – Loose coupling with Strong typing • Events, interceptors and decorators enhance the loose-coupling inherent in this model: • Event notifications • Decouple event producers from event consumers • Interceptors • Decouple technical concerns from business logic • Decorators • Allow business concerns to be compartmentalized
- 16. CDI theme – Loose coupling • Decouple Server (dependency) and client (dependency user) • Using well-defiend types and qualifiers • Allows server implementations to vary • Decouple lifecycle of collaboration components (dependencies) from application (dependency user) • Automatic contextual life-cycle management by the CDI runtime • Decouple orthogonal concerns (AOP) from business logic • Interceptors & Decorators • Decouple message producer from consumer • Events
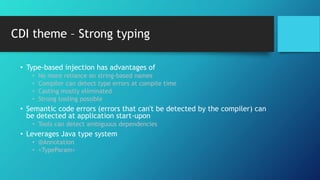
- 17. CDI theme – Strong typing • Type-based injection has advantages of • No more reliance on string-based names • Compiler can detect type errors at compile time • Casting mostly eliminated • Strong tooling possible • Semantic code errors (errors that can't be detected by the compiler) can be detected at application start-upon • Tools can detect ambiguous dependencies • Leverages Java type system • @Annotation • <TypeParam>
- 18. Getting our feet wet CDI First Example
- 19. • http://ansgohar.blogspot.com/2016/09/create-first-cdi-application.html
- 20. • http://ansgohar.blogspot.com/2016/09/create-first-cdi-application.html
- 21. Automatic Bean Discovery • • How can container scan bean? • By detecting the presence of “beans.xml” in application archive • For WAR file, the “beans.xml” is under WEB-INF directory • For JAR file, the “beans.xml” is under META-INF directory • • “beans.xml” • It is not for declaring beans (like in Spring) • It can be empty • Used for some other purposes (like declaring an alternative)
- 22. Getting our feet wet EJB Simple Example
- 24. Getting our feet wet Injecting EJB using CDI
- 26. CDI Beans & Injection Point CDI Beans
- 27. What is a Bean anyway? • Many forms of a “bean” already exist. So which bean arewe talking about? • JSF bean • EJB bean • Spring bean • Seam bean • Guice bean • CDI bean • Java EE needs a unified bean definition • Managed Bean 1.0 specification in Java EE 6 provides it
- 28. What about Managed, EJB, REST, CDI Bean? • Managed Beans are container-managed POJOs • Lightweight component model • Instances are managed by the container • You could see everything as a Managed Bean with extra services • • An EJB is a Managed Bean with • Transaction support • Security • Thread safety • Persistence • • A REST service is a Managed Bean with • HTTP support • • A CDI bean is a Managed Bean with • CDI services (explained in the next slide)
- 29. CDI is more than a framework • Auto-discovered • by the container • Set of qualifiers • solves ambiguity • Scope • context of a bean • Bean EL name • support non-type based invocation • Set of interceptor bindings • Alternative • replace bean at deployment time
- 30. CDI Beans & Injection Point Injection Point
- 31. Managed Bean CDI Bean
- 32. Q : How to Inject CDI Beans (Injection Point) ?
- 33. CDI Injection Point • Use @Inject <Java-Type> <variable> for field injection • <Java-Type> can be Java interface • Bean can be injected at “Injection points” • Field • Method parameter • Method can be • Constructor (useful for created immutable object) • Initializer • Setter method • Producer • Observer
- 37. Qualifiers, Alternatives, Programmatically Lookup Qualifiers
- 38. Q : What is the result of injecting CDI beans that :- 1- have single Implementation ? 2- have no Implementation ? 3- have multiple Implementation ?
- 39. What is a Qualifier? • For a given bean type (class or interface), there may be multiple beans which implement the type (in the classpath) • For an interface, there could be multiple implementations • For a class, there could be multiple child types • Ambiguity error will result • A qualifier is an annotation that lets a client choose one between multiple candidates of a certain type • Make type more specific • Assigns semantic meaning • Injected type is identified by • Qualifier(s) + Java type
- 43. Qualifier and Type Safety (Strong Typing) • Qualifier + Java type makes a composite type (extended type) • Again, think of a Qualifier as a type • Qualifiers make type safe injection possible • Qualifiers replace “look-up via string-based names” • Qualifier and Type Safety (Strong Typing)
- 44. Qualifiers, Alternatives, Programmatically Lookup Alternatives
- 45. What is Alternative Bean? • Any bean with @Alternative is not considered for injection • Lets you package multiple beans that match injection type without ambiguity errors • In order to be considered for injection, it has to be activated in “beans.xml” • Provide a replacement implementation during deployment • You can apply the @Alternative annotation to two or more beans, then, based on your deployment, specify the bean you want to use in the “beans.xml” configuration file • Useful for providing mock objects for testing – mock objects are annotated with @Alternative
- 47. Qualifiers, Alternatives, Programmatically Lookup Programmatically Lookup
- 49. Scope, & Context CDI Beans Scope
- 50. Q : What the allowed scopes in CDI ?
- 51. Request – @RequestScoped • This scope describes a user’s interaction with a web application in a single HTTP request. • The instance of the @RequestScoped annotated bean has an HTTP request lifecycle.
- 52. Session – @SessionScoped • This scope describes a user’s interaction with a web application across multiple HTTP requests.
- 53. Application – @ApplicationScoped • In this case the state is shared across all users’ interactions with a web application. • The container provides the same instance of the @ApplicationScoped annotated bean to all client requests.
- 54. Dependent – @Dependent pseudo-scope • This pseudo-scope means that an object exists to serve exactly one client (bean) and has the same lifecycle as that client (bean). • This is the default scope for a bean which does not explicitly declare a scope type. • An instance of a dependent bean is never shared between different clients or different injection points. • It is strictly a dependent object of some other object. • It is instantiated when the object it belongs to is created, and destroyed when the object it belongs to is destroyed.
- 57. View – @ ViewScoped • @ViewScoped belongs to JSF specification • Retains the scope lifespan for current page view • If the controller navigates away to a different page view the bean is de-scoped • Therefore view-scope is great for form validation and rich AJAX request and response sequences!
- 58. Conversation – @ConversationScoped • A lifespan sits between a Http Request scope and Http Session scope • Maintains state for the unique interaction • Works for individual tab in web browsers • Better than @ViewScoped bean controllers • Application defined lifespan
- 60. Session & Conversation Scoped Bean • A thing to notice is that beans must be serializable. • This is because the container passivates the HTTP session from time to time, so when the session is activated again the beans’ state must be retrieved.
- 61. Singleton – @Singleton pseudo-scope • This is a pseudo-scope. • It defines that a bean is once instantiated. • When a CDI managed bean is injected into another bean, the CDI container makes use of a proxy. • The proxy is the one to handle calls to the bean. • Though, @Singleton annotated beans don’t have a proxy object. • Clients hold a direct reference to the singleton instance.
- 62. Singleton – @Singleton pseudo-scope • So, what happens when a client is serialized ? • We must ensure that the singleton bean remains a singleton. • To do so there are a fiew ways, such as, have the singleton bean implement writeResolve() and readReplace() (as defined by the Java serialization specification), make sure the client keeps only a transient reference to the singleton bean, or give the client a reference of type Instance<X> where X is the bean type of the singleton bean.
- 63. Contextual scope • All predefined scopes except @Dependent are contextual scopes. • CDI places beans of contextual scope in the context whose lifecycle is defined by the Java EE specifications. • For example, a session context and its beans exist during the lifetime of an HTTP session. • Injected references to the beans are contextually aware. • The references always apply to the bean that is associated with the context for the thread that is making the reference. The CDI container ensures that the objects are created and injected at the correct time as determined by the scope that is specified for these objects.
- 66. Interceptors • Interceptor functionality is defined in the Java Interceptors specification. • The Interceptors specification defines three kinds of interception points: • Business method interception, • Lifecycle callback interception, and • Timeout method interception (EJB only). • A business method interceptor applies to invocations of methods of the bean by clients of the bean • By default, all interceptors are disabled
- 67. Business Method Interceptor • A business method interceptor applies to invocations of methods of the bean by clients of the bean
- 68. Lifecycle Callback Interceptor • A lifecycle callback interceptor applies to invocations of lifecycle callbacks by the container • An interceptor class may intercept both lifecycle callbacks and business methods
- 69. Timeout Method Interceptor • A timeout method interceptor applies to invocations of EJB timeout methods by the container
- 72. Q : What is the deference between Interceptor and Decorators in CDI ?
- 73. What is a Decorator? • Decorators implement the Decorator design pattern • Allows implementation of an additional business logic for a bean • A Decorator decorates interfaces they implement • @Delegate is used to inject the original object • Original object business logic can be be invoked within the decorator • Decorators must be activated through “beans.xml”
- 76. Interceptors VS Decorators • Interceptors and Decorators both geared towards cross-cutting logic. • Bypass traditional complexity associated with AOP by avoiding point-cuts. • Interceptors are designed for system-level crosscutting concerns very decoupled from business logic. • Decorators intended for concerns that should be compartmentalized but are still very close to business logic.
- 77. Events Events
- 78. Q : What is Events ?
- 79. CDI Event Observer Pattern • Completely decouple action (event producer) and reactions • (event consumers) • Qualifiers tune which event notifications are received • Define Event Class • Event producer fires an event • Event consumer observes event through @Observes
- 80. Event • Event Producers • An event is fired by an injected javax.enterprise.event.Event object • Event Consumer (Event Observer) • The only thing event consumer has to do is to use @Observes <Event-class> annotation
- 82. CDI and EJB When you still need EJB?
- 83. Q : When you still need EJB ?
- 84. When you still need EJB ? … not yet aligned! • Security • @RolesAllowed • @PermitAll • @DenyAll • Usable by • @Stateless • @Stateful • @Singleton
- 85. When you still need EJB ? … not yet aligned! • Startup • @Startup • Eagerly creates the instance upon startup • Usable by • @Singleton
- 86. When you still need EJB ? … not yet aligned! • Asynchronous • @Asynchronsous • Allows method calls to be asynchronous and return Future objects • Usable by • @Stateless • @Stateful • @Singleton
- 87. When you still need EJB ? … not yet aligned! • Schedule • @Schedule • Effectively Cron -- schedule invocations by minute or date, etc. • Usable by • @Stateless • @Singleton • Not @Stateful
- 88. When you still need EJB ? … not yet aligned! • Locking • @Lock(READ • @Lock(WRITE) • @AccessTimeout • Allows for synchronization of methods without complex code • Usable by • @Singleton • Not @Stateless • Not @Stateful
- 89. When you still need EJB ? … not yet aligned! • MDBs • @MessageDriven • Connector-Driven Beans • Usable by • Not @Singleton • Not @Stateless • Not @Stateful
- 90. CDI Takeover • EJB adopts CDI (Java EE 6) • JSF adopts CDI (Java EE 7) • MVC adopts CDI (Java EE 8) • JAX-RS considers CDI (Java EE 8) • CDI moves to SE (Java EE 8)
- 91. Common Mistakes you will make • Not putting a beans.xml in your app (Java EE 6) • No CDI for you! • Not understanding @Typed • Think @Local from EJB • Bites you when using @Produces • Not understanding what Dependent and NormalScope • Dependent == plain object • NormalScoped == proxied object • Bites you when creating custom scopes
- 92. Result for EJB after CDI ? • Java EE 7 • Focus on realignment: @Transactional • • Java EE 8 • First spec round with no new EJB JSR • Realignment stalled • Awkward relationship
- 93. CDI Wrap-up Who did this now ! ! !
- 94. CDI Wrap-up • Basic dependency injection • @Inject, @Qualifier, @Stereotype, @Alternative, • Instance, @All, @Any • Component naming • @Named • Context management • @Dependent, @RequestScoped, @SessionScoped, • @ConversationScoped, @ApplicationScoped, • @Scope
- 95. CDI Wrapup • Custom Object Factories • @Produces, @Disposes, InjectionPoint • Lightweight Events • Event, @Observes • Interceptors/Decorators • @Interceptor, @InterceptorBinding, @AroundInvoke, • InvocationContext • @Decorator, @Delegate
- 96. Biggest benefits of CDI • Very active and open expert group • Fully extendable • Beans can be added at runtime • Fully Open Source • Spec is open source • All implementations are open source • Compliance test (TCK) suite is open source