Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer / Function and Interconection
Download as PPT, PDF9 likes9,217 views
The document discusses computer system buses and their role in connecting different components of a computer system. It describes the functions of different types of buses including data, address, and control buses. It also explains bus arbitration techniques and timing protocols for synchronous and asynchronous buses. Specific bus architectures like PCI are discussed with details on their components, commands, and arbitration process.
1 of 47
Downloaded 378 times














































Ad
Recommended
Computer performance



Computer performanceAmit Kumar Rathi Computer performance is characterized by the amount of useful work accomplished by a system over the resources and time used. It can be measured through metrics like response time, throughput, and utilization. Several factors influence performance, including hardware, software, memory, and I/O. Benchmarks are used to evaluate performance by measuring how systems perform standard tasks. Maintaining high performance requires optimizing these various components through techniques like CPU enhancement, memory improvement, and I/O optimization.
Chapter 01 - Introduction



Chapter 01 - IntroductionCésar de Souza The document discusses the differences between computer architecture and organization. Architecture refers to attributes visible to programmers like instruction sets, while organization refers to how features are implemented internally. It also discusses the functional view of a computer in terms of data movement, control, storage, and processing. Finally, it outlines the chapters of the book which will cover topics like CPU structure, instruction sets, and computer evolution.
Lecture 4: Classification of system 



Lecture 4: Classification of system Jawaher Abdulwahab Fadhil 1. The document discusses different types of systems based on their properties, including static vs dynamic, time-variant vs time-invariant, linear vs non-linear, causal vs non-causal, and stable vs unstable.
2. A system is defined as a physical device or algorithm that performs operations on a discrete-time signal. Static systems have outputs that depend only on the present input, while dynamic systems have outputs that depend on present and past/future inputs.
3. Time-invariant systems have characteristics that do not change over time, while time-variant systems have characteristics that do change. Linear systems follow the superposition principle, while causal systems have outputs dependent only on present and past inputs.
Multicore computers



Multicore computersSyed Zaid Irshad A multi-core processor is a single computing component with two or more independent actual processing units (called "cores"), which are units that read and execute program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such as add, move data, and branch), but the multiple cores can run multiple instructions at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs amenable to parallel computing. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die (known as a chip multiprocessor or CMP), or onto multiple dies in a single chip package.
Cyber attack



Cyber attackManjushree Mashal CYBER ATTACK INTRODUCTION,TYPES OF CYBER ATTACK,DOS ATTACK,MAJOR CYBER ATTACK IN INDIA,PREVENTION TIPS
Linear & Non-Linear Systems |Solved problems|



Linear & Non-Linear Systems |Solved problems|National Engineering College This document discusses linear and nonlinear systems. It defines a linear system as one that satisfies the principles of superposition and homogeneity or scaling. The principles of homogeneity and superposition for a linear system are defined. Homogeneity means that scaling the input scales the output by the same factor. Superposition means that the output for the sum of two inputs is the sum of the outputs for each input individually. A linear system thus satisfies the property of linearity, where the output of scaled and summed inputs is the scaled and summed outputs. Nonlinear systems do not satisfy these properties.
Chapter 2 - Computer Evolution and Performance



Chapter 2 - Computer Evolution and PerformanceCésar de Souza The document discusses the evolution of computer hardware from the 1940s onwards. It describes early computers like ENIAC which used vacuum tubes and was programmed manually via switches. The stored program concept developed by von Neumann separated the program and data into memory. Transistors replaced vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, cheaper and more reliable. Integrated circuits led to generations of computers with increasing numbers of components on a single chip due to Moore's Law. Memory speed could not keep up with rising CPU speeds, leading to cache memory and other performance improvements.
Types Of Buses



Types Of BusesAkhil Ahuja The document discusses several computer bus architectures used to connect components internally in a computer system, including ISA, EISA, VESA Local Bus (VLB), PCI, PCI-X, PCI Express, and RS-232. The ISA bus was introduced in 1981 as a 16-bit standard but has been replaced by newer standards capable of higher data transfer speeds such as 32-bit EISA, VLB, and PCI, as well as serial standards PCI Express and USB. Each new standard aimed to offer improvements in speed, functionality and compatibility over older designs.
04 cache memory.ppt 1



04 cache memory.ppt 1Anwal Mirza This document discusses cache memory organization and characteristics. It begins by describing cache location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, and physical characteristics. It then covers the different mapping techniques used in caches, including direct mapping, set associative mapping, and fully associative mapping. The document also discusses cache performance factors like hit ratio, replacement algorithms, write policies, block size, and multilevel cache hierarchies. It provides examples of specific processor cache designs like those used in Intel Pentium processors.
Computer Systems Organization



Computer Systems OrganizationLiEdo The document discusses the organization and operation of computer systems at both the hardware and software level. It covers topics such as the central processing unit, instruction execution, pipelining, parallelism, memory hierarchies, storage devices, input/output, networking, and encoding of digital data. The document contains detailed diagrams and explanations of how different components of computer systems work individually and interact together.
02 Computer Evolution And Performance



02 Computer Evolution And PerformanceJeanie Delos Arcos The document discusses the evolution of computers from early machines like ENIAC to modern microprocessors. It describes key developments such as the stored-program concept pioneered by von Neumann, the transition to transistors which made computers smaller and more reliable, the development of integrated circuits and Moore's Law. It also summarizes improvements in processor design including pipelining, caching, superscalar execution and the use of multiple processor cores.
Ch 4 95



Ch 4 95Jecka Cortez This document summarizes key characteristics of internal memory, including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, performance, physical type, organization, and hierarchy. It discusses the following memory types: registers, cache, main memory, external memory, backing store. Specific topics covered include memory access times, cycle times, transfer rates, physical implementations (semiconductor, magnetic, optical), organization, error correction, cache design principles, mapping functions, and write policies. Newer RAM technologies like SDRAM that improve performance are also overviewed.
03 top level view of computer function and interconnection.ppt.enc



03 top level view of computer function and interconnection.ppt.encAnwal Mirza The document summarizes key topics from Chapter 3 of William Stallings' Computer Organization and Architecture textbook, including:
1) It describes the basic components of a computer including the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, main memory, and input/output.
2) It explains the fetch-execute instruction cycle and how interrupts can alter the normal flow of instruction processing.
3) It discusses different types of computer buses that connect the central processing unit to main memory and input/output devices, such as data, address, and control buses, and how bus arbitration works.
System bus



System busAmanLodhi3 The system bus is a pathway composed of cables and connectors used to carry data between a computer microprocessor and the main memory. The bus provides a communication path for the data and control signals moving between the major components of the computer system
top level view of computer function and interconnection



top level view of computer function and interconnectionSajid Marwat The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of William Stallings' Computer Organization and Architecture textbook. It describes the top-level view of computer function and interconnection, including:
- The components of a computer system and how they interconnect via buses
- Common bus types like data, address, and control buses
- Bus arbitration and timing, whether synchronous or asynchronous
- Specific bus architectures like ISA and PCI buses
It provides instruction on computer organization concepts like instruction cycles, interrupts, and program flow control at a high level.
Computer organization & architecture chapter-1



Computer organization & architecture chapter-1Shah Rukh Rayaz The document provides an introduction to computer organization and architecture. It discusses the structure and function of computers, including data processing, storage, and movement functions. It also explains why this course is studied. The document then outlines the topics that will be covered in subsequent chapters, including computer evolution and performance, basic computer components and functions, and interconnection structures. It provides an overview of cache memory principles and the memory hierarchy in general.
Computer system architecture



Computer system architectureKumar The document discusses the evolution of computer systems from the first generation to the sixth generation. It describes the key technologies that defined each generation as well as representative computer systems. It also covers Moore's Law and defines it as the observation that the number of transistors on integrated circuits doubles every 18 months. The document then provides an overview of computer components including the CPU, memory, storage, input/output ports and devices. It discusses the internal components of the CPU like the ALU, registers, control unit and buses. Finally, it briefly introduces the Von Neumann architecture.
Cache memory



Cache memoryShailesh Tanwar Cache memory is a small, fast memory located close to the CPU that stores frequently accessed instructions and data. It aims to bridge the gap between the fast CPU and slower main memory. Cache memory is organized into blocks that each contain a tag field identifying the memory address, a data field containing the cached data, and status bits. There are different mapping techniques like direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping to determine how blocks are stored in cache. When cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU, FIFO, LFU, and random are used to determine which existing block to replace with the new block.
Intel processor family



Intel processor familySuhas Javalgikar This document discusses the evolution and key specifications of Intel microprocessors. It begins with an overview of microprocessors in general and Intel's role in their development. Key Intel processors are then outlined chronologically from the 4004 in 1971 to the present day Core i7. Each new generation introduced improvements like increased processing power, additional features, and reduced transistor size. The document provides concise details on the characteristics of important processors in Intel's history and how they advanced computing capabilities over time.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnsari Maviya About Cache Memory
working of cache memory
levels of cache memory
mapping techniques for cache memory
1. direct mapping techniques
2. Fully associative mapping techniques
3. set associative mapping techniques
Cache memroy organization
cache coherency
every thing in detail
PCI express



PCI expresssarangaprabod PCI Express is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that was created to replace older standards like PCI, PCI-X, and AGP. It provides dedicated bandwidth to devices through the use of lanes and is commonly used as the interface for graphics cards, hard drives, and other peripherals. PCIe has gone through several generations that have increased its maximum bandwidth. It uses a layered protocol architecture and is designed for compatibility while providing scalable bandwidth and other advantages over older standards.
Bus interconnection



Bus interconnectionMuhammad Ishaq The document discusses bus interconnection in computers. It describes how a bus is a shared communication pathway that connects major components like the CPU, memory and I/O devices. The key parts of a bus are the data lines that transfer information, address lines that specify locations, and control lines that manage access and transfers. Buses can be designed in different ways like dedicated vs multiplexed and vary in aspects such as width, timing, and arbitration method. Common transfer types on a bus include reads, writes, and block transfers.
0 introduction to computer architecture



0 introduction to computer architectureaamc1100 The document provides information about a computer architecture course taught by Mohamed ELARBI including:
- Contact information for the instructor
- Recommended textbooks and other resources
- A list of topics to be covered each week throughout the course including parallel processing, CPU design, pipelining, and memory hierarchy
- Definitions of key terms related to computer architecture and organization such as the difference between architecture and organization
- An overview of the von Neumann model and system bus model of computer system organization
cache memory



cache memoryArmy Public School and College -Faisal This document discusses the key characteristics of computer memory, including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, performance, physical type, physical characteristics, and organization. It covers different types of memory like CPU registers, main memory, cache, disk, and tape. The different access methods like sequential, direct, random, and associative access are explained. The memory hierarchy and performance aspects like access time, memory cycle time, and transfer rate are defined. Factors like cache size, mapping function, replacement algorithm, write policy, block size that impact cache performance are also summarized.
BASIC COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE 



BASIC COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Himanshu Sharma This presentation discusses various computer input, output, and storage devices. It covers common input devices like keyboards, mice, microphones, and cameras. Output devices discussed include monitors, printers, and speakers. The central processing unit and memory are also summarized, including the CPU components like the ALU and control unit. Registers in the CPU and different types of computer memory are defined.
CISC & RISC Architecture 



CISC & RISC Architecture Suvendu Kumar Dash This document discusses the history and characteristics of CISC and RISC architectures. It describes how CISC architectures were developed in the 1950s-1970s to address hardware limitations at the time by allowing instructions to perform multiple operations. RISC architectures emerged in the late 1970s-1980s as hardware improved, focusing on simpler instructions that could be executed faster through pipelining. Common RISC and CISC processors used commercially are also outlined.
07 Input Output



07 Input OutputJeanie Delos Arcos The document discusses various techniques for input/output (I/O) in computer systems, including programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). It describes how I/O modules interface with CPUs and peripherals to handle data transfer between devices that operate at different speeds. Common I/O bus standards like ISA, PCI, FireWire, and InfiniBand are also overviewed in terms of their architecture, protocols, and applications.
Cache memory



Cache memorychauhankapil This document discusses cache memory and techniques to improve cache performance. It defines cache memory as a small, fast type of volatile memory that stores frequently accessed instructions and data to increase performance. The memory hierarchy is described, with cache memory sitting between the CPU and main memory. Factors that influence cache performance like cache hits, misses, and replacement policies for direct mapped caches are also outlined. Finally, methods for reducing cache miss rates and penalties are presented, such as using compiler optimizations, increasing cache size and associativity, adding multiple cache levels, and reducing cache hit times.
Coa presentation2



Coa presentation2rickypatel151 This document provides information about various digital circuits including half adder, full adder, encoder, decoder, multiplexer, demultiplexer, seven segment display circuit, clock, flip flop, integrated circuit and more. It defines combinational and sequential circuits. It describes half adder, full adder, encoder, decoder, multiplexer, demultiplexer and seven segment display circuits. It also explains clock, flip flops including SR, D, JK flip flops, integrated circuits and definitions.
ADDRESSING MODE



ADDRESSING MODEAnika Shahabuddin This document discusses different types of addressing modes used in computers. It defines addressing mode as the way operands are chosen during program execution based on the addressing technique specified in an instruction. There are several addressing modes described, including implied, immediate, register, register indirect, auto-increment/decrement, direct, indirect, relative, indexed, and base register modes. Examples and a numerical example are provided to illustrate the different addressing modes.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
04 cache memory.ppt 1



04 cache memory.ppt 1Anwal Mirza This document discusses cache memory organization and characteristics. It begins by describing cache location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, and physical characteristics. It then covers the different mapping techniques used in caches, including direct mapping, set associative mapping, and fully associative mapping. The document also discusses cache performance factors like hit ratio, replacement algorithms, write policies, block size, and multilevel cache hierarchies. It provides examples of specific processor cache designs like those used in Intel Pentium processors.
Computer Systems Organization



Computer Systems OrganizationLiEdo The document discusses the organization and operation of computer systems at both the hardware and software level. It covers topics such as the central processing unit, instruction execution, pipelining, parallelism, memory hierarchies, storage devices, input/output, networking, and encoding of digital data. The document contains detailed diagrams and explanations of how different components of computer systems work individually and interact together.
02 Computer Evolution And Performance



02 Computer Evolution And PerformanceJeanie Delos Arcos The document discusses the evolution of computers from early machines like ENIAC to modern microprocessors. It describes key developments such as the stored-program concept pioneered by von Neumann, the transition to transistors which made computers smaller and more reliable, the development of integrated circuits and Moore's Law. It also summarizes improvements in processor design including pipelining, caching, superscalar execution and the use of multiple processor cores.
Ch 4 95



Ch 4 95Jecka Cortez This document summarizes key characteristics of internal memory, including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, performance, physical type, organization, and hierarchy. It discusses the following memory types: registers, cache, main memory, external memory, backing store. Specific topics covered include memory access times, cycle times, transfer rates, physical implementations (semiconductor, magnetic, optical), organization, error correction, cache design principles, mapping functions, and write policies. Newer RAM technologies like SDRAM that improve performance are also overviewed.
03 top level view of computer function and interconnection.ppt.enc



03 top level view of computer function and interconnection.ppt.encAnwal Mirza The document summarizes key topics from Chapter 3 of William Stallings' Computer Organization and Architecture textbook, including:
1) It describes the basic components of a computer including the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, main memory, and input/output.
2) It explains the fetch-execute instruction cycle and how interrupts can alter the normal flow of instruction processing.
3) It discusses different types of computer buses that connect the central processing unit to main memory and input/output devices, such as data, address, and control buses, and how bus arbitration works.
System bus



System busAmanLodhi3 The system bus is a pathway composed of cables and connectors used to carry data between a computer microprocessor and the main memory. The bus provides a communication path for the data and control signals moving between the major components of the computer system
top level view of computer function and interconnection



top level view of computer function and interconnectionSajid Marwat The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of William Stallings' Computer Organization and Architecture textbook. It describes the top-level view of computer function and interconnection, including:
- The components of a computer system and how they interconnect via buses
- Common bus types like data, address, and control buses
- Bus arbitration and timing, whether synchronous or asynchronous
- Specific bus architectures like ISA and PCI buses
It provides instruction on computer organization concepts like instruction cycles, interrupts, and program flow control at a high level.
Computer organization & architecture chapter-1



Computer organization & architecture chapter-1Shah Rukh Rayaz The document provides an introduction to computer organization and architecture. It discusses the structure and function of computers, including data processing, storage, and movement functions. It also explains why this course is studied. The document then outlines the topics that will be covered in subsequent chapters, including computer evolution and performance, basic computer components and functions, and interconnection structures. It provides an overview of cache memory principles and the memory hierarchy in general.
Computer system architecture



Computer system architectureKumar The document discusses the evolution of computer systems from the first generation to the sixth generation. It describes the key technologies that defined each generation as well as representative computer systems. It also covers Moore's Law and defines it as the observation that the number of transistors on integrated circuits doubles every 18 months. The document then provides an overview of computer components including the CPU, memory, storage, input/output ports and devices. It discusses the internal components of the CPU like the ALU, registers, control unit and buses. Finally, it briefly introduces the Von Neumann architecture.
Cache memory



Cache memoryShailesh Tanwar Cache memory is a small, fast memory located close to the CPU that stores frequently accessed instructions and data. It aims to bridge the gap between the fast CPU and slower main memory. Cache memory is organized into blocks that each contain a tag field identifying the memory address, a data field containing the cached data, and status bits. There are different mapping techniques like direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping to determine how blocks are stored in cache. When cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU, FIFO, LFU, and random are used to determine which existing block to replace with the new block.
Intel processor family



Intel processor familySuhas Javalgikar This document discusses the evolution and key specifications of Intel microprocessors. It begins with an overview of microprocessors in general and Intel's role in their development. Key Intel processors are then outlined chronologically from the 4004 in 1971 to the present day Core i7. Each new generation introduced improvements like increased processing power, additional features, and reduced transistor size. The document provides concise details on the characteristics of important processors in Intel's history and how they advanced computing capabilities over time.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnsari Maviya About Cache Memory
working of cache memory
levels of cache memory
mapping techniques for cache memory
1. direct mapping techniques
2. Fully associative mapping techniques
3. set associative mapping techniques
Cache memroy organization
cache coherency
every thing in detail
PCI express



PCI expresssarangaprabod PCI Express is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that was created to replace older standards like PCI, PCI-X, and AGP. It provides dedicated bandwidth to devices through the use of lanes and is commonly used as the interface for graphics cards, hard drives, and other peripherals. PCIe has gone through several generations that have increased its maximum bandwidth. It uses a layered protocol architecture and is designed for compatibility while providing scalable bandwidth and other advantages over older standards.
Bus interconnection



Bus interconnectionMuhammad Ishaq The document discusses bus interconnection in computers. It describes how a bus is a shared communication pathway that connects major components like the CPU, memory and I/O devices. The key parts of a bus are the data lines that transfer information, address lines that specify locations, and control lines that manage access and transfers. Buses can be designed in different ways like dedicated vs multiplexed and vary in aspects such as width, timing, and arbitration method. Common transfer types on a bus include reads, writes, and block transfers.
0 introduction to computer architecture



0 introduction to computer architectureaamc1100 The document provides information about a computer architecture course taught by Mohamed ELARBI including:
- Contact information for the instructor
- Recommended textbooks and other resources
- A list of topics to be covered each week throughout the course including parallel processing, CPU design, pipelining, and memory hierarchy
- Definitions of key terms related to computer architecture and organization such as the difference between architecture and organization
- An overview of the von Neumann model and system bus model of computer system organization
cache memory



cache memoryArmy Public School and College -Faisal This document discusses the key characteristics of computer memory, including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, performance, physical type, physical characteristics, and organization. It covers different types of memory like CPU registers, main memory, cache, disk, and tape. The different access methods like sequential, direct, random, and associative access are explained. The memory hierarchy and performance aspects like access time, memory cycle time, and transfer rate are defined. Factors like cache size, mapping function, replacement algorithm, write policy, block size that impact cache performance are also summarized.
BASIC COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE 



BASIC COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Himanshu Sharma This presentation discusses various computer input, output, and storage devices. It covers common input devices like keyboards, mice, microphones, and cameras. Output devices discussed include monitors, printers, and speakers. The central processing unit and memory are also summarized, including the CPU components like the ALU and control unit. Registers in the CPU and different types of computer memory are defined.
CISC & RISC Architecture 



CISC & RISC Architecture Suvendu Kumar Dash This document discusses the history and characteristics of CISC and RISC architectures. It describes how CISC architectures were developed in the 1950s-1970s to address hardware limitations at the time by allowing instructions to perform multiple operations. RISC architectures emerged in the late 1970s-1980s as hardware improved, focusing on simpler instructions that could be executed faster through pipelining. Common RISC and CISC processors used commercially are also outlined.
07 Input Output



07 Input OutputJeanie Delos Arcos The document discusses various techniques for input/output (I/O) in computer systems, including programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). It describes how I/O modules interface with CPUs and peripherals to handle data transfer between devices that operate at different speeds. Common I/O bus standards like ISA, PCI, FireWire, and InfiniBand are also overviewed in terms of their architecture, protocols, and applications.
Cache memory



Cache memorychauhankapil This document discusses cache memory and techniques to improve cache performance. It defines cache memory as a small, fast type of volatile memory that stores frequently accessed instructions and data to increase performance. The memory hierarchy is described, with cache memory sitting between the CPU and main memory. Factors that influence cache performance like cache hits, misses, and replacement policies for direct mapped caches are also outlined. Finally, methods for reducing cache miss rates and penalties are presented, such as using compiler optimizations, increasing cache size and associativity, adding multiple cache levels, and reducing cache hit times.
Viewers also liked (16)
Coa presentation2



Coa presentation2rickypatel151 This document provides information about various digital circuits including half adder, full adder, encoder, decoder, multiplexer, demultiplexer, seven segment display circuit, clock, flip flop, integrated circuit and more. It defines combinational and sequential circuits. It describes half adder, full adder, encoder, decoder, multiplexer, demultiplexer and seven segment display circuits. It also explains clock, flip flops including SR, D, JK flip flops, integrated circuits and definitions.
ADDRESSING MODE



ADDRESSING MODEAnika Shahabuddin This document discusses different types of addressing modes used in computers. It defines addressing mode as the way operands are chosen during program execution based on the addressing technique specified in an instruction. There are several addressing modes described, including implied, immediate, register, register indirect, auto-increment/decrement, direct, indirect, relative, indexed, and base register modes. Examples and a numerical example are provided to illustrate the different addressing modes.
Addressing modes



Addressing modesMahesh Kumar Attri The document discusses different addressing modes used in computer instructions. It explains that the addressing mode specifies how the operands are chosen during program execution. Some key addressing modes are direct, indirect, register, register indirect, and relative addressing. The addressing mode determines the effective address, which is the actual memory location of the operand.
8086 microprocessor instruction set by Er. Swapnil Kaware



8086 microprocessor instruction set by Er. Swapnil KawareProf. Swapnil V. Kaware The document describes the instruction set of the 8086 microprocessor. It discusses the different types of instructions including data transfer instructions like MOV, PUSH, POP, XCHG, IN, OUT, and XLAT. It also covers addressing modes, instruction formats, and the various registers used by the 8086 microprocessor like the stack pointer and flag register. In total there are 14 different data transfer instructions described that are used to move data between registers, memory, ports, and the flag and stack pointers.
8085 Paper Presentation slides,ppt,microprocessor 8085 ,guide, instruction set



8085 Paper Presentation slides,ppt,microprocessor 8085 ,guide, instruction setSaumitra Rukmangad The document provides information about the 8085 microprocessor. It describes the 8085 as an 8-bit processor with 40 pins that can access 64KB of memory and 256 I/O ports. It has 5 hardware interrupts, 8 general purpose registers including the program counter and stack pointer, and provides 74 instructions across 5 addressing modes.
1327 Addressing Modes Of 8086



1327 Addressing Modes Of 8086techbed The document discusses the different addressing modes of the 8086 processor. It describes 6 main addressing modes - register, immediate, memory, port, relative, and implied. The memory addressing mode has several sub-types including direct, register indirect, based, indexed, based indexed, and string addressing modes which specify how the effective address of the memory operand is calculated using segment registers and offsets.
Basic Computer Organization and Design



Basic Computer Organization and DesignKamal Acharya This slide provide the introduction to the computer , instruction formats and their execution, Common Bus System , Instruction Cycle, Hardwired Control Unit and I/O operation and handling of interrupt
Fms



Fmshydeumb The document provides an overview of Pace University's new Financial Management System chart of accounts structure. It describes the basic elements of the chart of accounts like fund, organization, account, program, and location. It also discusses how the index code relates all the elements except account, and how this structure will provide flexibility for reporting, budgeting, and interfacing with other systems.
Instruction cycle



Instruction cycleshweta-sharma99 The instruction cycle describes the process a computer follows to execute each machine language instruction. It involves 4 phases: 1) Fetch - the instruction is fetched from memory and placed in the instruction register. 2) Decode - the instruction is analyzed and decoded. 3) Execute - the processor executes the instruction by performing the specified operation. 4) The program counter is then incremented to point to the next instruction, and the cycle repeats. Each phase involves transferring data between the program counter, instruction register, memory, and other components via a common bus under the control of a timing unit. The instruction specifies the operation to be performed, such as a memory reference, register operation, or I/O access.
11 instruction sets addressing modes 



11 instruction sets addressing modes Sher Shah Merkhel This chapter discusses instruction sets and addressing modes. It covers common addressing modes like immediate, direct, indirect, register, register indirect, displacement, and stack addressing. It provides examples and diagrams to illustrate each addressing mode. The chapter also discusses instruction formats for different architectures like PDP-8, PDP-10, PDP-11, VAX, x86, and ARM. It covers ARM's load/store multiple addressing and thumb instruction set. The chapter concludes with an overview of assemblers and a simple example program.
Instruction cycle



Instruction cycleKumar The document describes the phases of the instruction cycle in a CPU. It discusses the following phases: 1) Fetch - the next instruction is fetched from memory and stored in the instruction register using the program counter; 2) Decode - the instruction inside the register is decoded; 3) Execute - the control unit passes signals to function units like the ALU to perform the required actions like arithmetic or logic operations. It also describes common circuits used in a CPU like the program counter, memory address register, and instruction register.
Types of Addressing modes- COA



Types of Addressing modes- COARuchi Maurya Addressing mode is the way of addressing a memory location in instruction. Microcontroller needs data or operands on which the operation is to be performed. The method of specifying source of operand and output of result in an instruction is known as addressing mode.
There are various methods of giving source and destination address in instruction, thus there are various types of Addressing Modes. Here you will find the different types of Addressing Modes that are supported in Micro Controller 8051. Types of Addressing Modes are explained below:
1.Register Addressing Mode
2.Direct Addressing Mode
3.Register Indirect Addressing Mode
4.Immediate Addressing Mode
5.Index Addressing Mode
Explanation:
Register Addressing Mode: In this addressing mode, the source of data or destination of result is Register. In this type of addressing mode the name of the register is given in the instruction where the data to be read or result is to be stored.
Example: ADD A, R5 ( The instruction will do the addition of data in Accumulator with data in register R5)
Direct Addressing Mode: In this type of Addressing Mode, the address of data to be read is directly given in the instruction. In case, for storing result the address given in instruction is used to store the result.
Example: MOV A, 46H ( This instruction will move the contents of memory location 46H to Accumulator)
Register Indirect Addressing Mode: In Register Indirect Addressing Mode, as its name suggests the data is read or stored in register indirectly. That is, we provide the register in the instruction, in which the address of the other register is stored or which points to other register where data is stored or to be stored.
Example: MOV A, @R0 ( This instruction will move the data to accumulator from the register whose address is stored in register R0 ).
Also Read: Architecture Of 8051
Immediate Addressing Mode : In Immediate Addressing Mode , the data immediately follows the instruction. This means that data to be used is already given in the instruction itself.
Example: MOV A, #25H ( This instruction will move the data 25H to Accumulator. The # sign shows that preceding term is data, not the address.)
Index Addressing Mode: Offset is added to the base index register to form the effective address if the memory location.This Addressing Mode is used for reading lookup tables in Program Memory. The Address of the exact location of the table is formed by adding the Accumulator Data to the base pointer.
Example: MOVC, @A+DPTR ( This instruction will move the data from the memory to Accumulator; the address is made by adding the contents of Accumulator and Data Pointer.
Unit II arm 7 Instruction Set



Unit II arm 7 Instruction SetDr. Pankaj Zope The document discusses various aspects of the ARM-7 architecture including its addressing modes, instruction set, and data processing instructions. It describes 9 different addressing modes including immediate, absolute, indirect, register, register indirect, base plus offset, base plus index, base plus scaled index, and stack addressing. It also provides details about the ARM instruction set, Thumb instruction set, and I/O system. Examples are given to illustrate different instructions such as MOV, SUB, ORR, CMP, MUL, branch instructions, LDR, STR, and SWI.
Input and Output Devices.



Input and Output Devices.abena This document discusses various input and output devices used with computers. It describes common input devices like the mouse, keyboard, joystick, scanner, and barcode reader which are used to enter data and instructions into a computer. It then explains key output devices such as computer monitors, printers in different types like dot matrix, inkjet and laser, plotters which produce drawings, and microfilm/microfiche which store large amounts of data on film.
Unit 3



Unit 3Assistant Professor Mobile IP allows mobile nodes to change their point of attachment to the internet while maintaining ongoing communications. It includes the following key entities:
- Mobile nodes can move between home and foreign networks while keeping their IP address.
- Foreign agents provide services to visiting mobile nodes and advertise care-of addresses for tunneling packets to mobile nodes' current locations.
- The home agent maintains a location registry with mobile nodes' care-of addresses and tunnels packets to their current points of attachment when away from home.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) can be used by mobile nodes to obtain temporary IP addresses at foreign networks to use as their care-of addresses.
LinkedIn SlideShare: Knowledge, Well-Presented



LinkedIn SlideShare: Knowledge, Well-PresentedSlideShare 70 million professionals use LinkedIn SlideShare to learn about any topic quickly and stand out.
Ad
Similar to Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer / Function and Interconection (20)
03 Buses



03 BusesJeanie Delos Arcos The document discusses computer system buses and their role in connecting central processing units to memory and input/output devices. Buses transfer data, addresses, and control signals between components. Common bus types include data buses to transfer data, address buses to specify memory locations, and control buses that coordinate timing. Interrupt signals can suspend normal processing to handle higher priority events. Modern buses like PCI use arbitration to allow shared access among devices.
Counit2 2



Counit2 2Himanshu Dua The document discusses the basic components and operation of computers. It describes how a central processing unit (CPU) works with memory and input/output devices using control signals and buses to execute instructions. The CPU fetches and executes instructions in cycles, and can be interrupted by external events using interrupt signals. Buses connect the different components and allow for communication between the CPU, memory, and input/output devices.
Computer function-and-interconnection 3



Computer function-and-interconnection 3Mujaheed Sulantingan The document provides a top-level overview of the basic components and functions of a computer system. It describes how a central processing unit (CPU) works with memory and input/output devices via buses to execute instructions. Interrupts allow efficient processing by suspending the current program to handle higher priority tasks or events before resuming the original program.
Computer function-and-interconnection 3



Computer function-and-interconnection 3Mujaheed Sulantingan The document provides a top-level overview of the function and interconnection of computer components. It describes how a program is executed through an instruction cycle of fetching and executing instructions. It explains the role of the control unit and how different computer components like the CPU, memory, and I/O devices are interconnected through buses to allow the transfer of data and instructions. Interrupts provide a way to improve processing efficiency and allow different tasks to be interleaved.
Ch 3 System Buses



Ch 3 System BusesNestleJuco The document discusses computer system buses. It describes how buses connect different components like the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. It explains that buses transfer data, addresses, and control signals. Common bus types include data buses to transfer data, address buses to identify memory locations, and control buses for timing and control signals. The document outlines bus arbitration when multiple devices need bus access and synchronous/asynchronous timing of signal transfers over the bus. It provides examples of the ISA and PCI bus standards.
Chapter 6



Chapter 6Qiyo Jung The document discusses various methods for input/output (I/O) in computer systems, including programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). It describes I/O modules that interface peripherals with the CPU and memory. Common I/O techniques include programmed I/O where the CPU directly controls I/O, interrupt-driven I/O where devices interrupt the CPU, and DMA where an I/O controller handles data transfers without CPU involvement. Specific I/O interfaces like SCSI and FireWire are also overviewed.
Chapter 2



Chapter 2Er. Nawaraj Bhandari The Control Unit and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit constitute the Central Processing Unit
Data and instructions need to get into the system and results out
Input/output
Temporary storage of code and results is needed
Main memory
03 top level view of computer function and interconnection



03 top level view of computer function and interconnectionSher Shah Merkhel The document summarizes key topics from Chapter 3 of William Stallings' Computer Organization and Architecture textbook, including:
- The components of a computer including the control unit, ALU, main memory, and I/O.
- How programs are executed through an instruction cycle of fetching and executing instructions.
- Mechanisms for flow control including interrupts, program counters, and jumps.
- How the different computer components are interconnected through buses for data, addresses, and control signals.
- Common bus architectures and how arbitration works to allow shared access to buses.
Chapter 3 caal (1)



Chapter 3 caal (1)talhashahid40 The document discusses the von Neumann architecture and basic components of a computer system. It describes how the CPU, memory, and I/O devices are interconnected via buses. The key buses are the data bus, address bus, and control bus. It explains synchronous and asynchronous timing of bus operations, with synchronous relying on a shared clock and asynchronous using handshaking signals between devices. Interrupts allow I/O devices to signal the CPU to pause normal instruction execution.
03_Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection.ppt



03_Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection.pptMalkhaz Nikolashvili Computer Organization
and Architecture 3
Chapter 4



Chapter 4Er. Nawaraj Bhandari The document discusses input/output (I/O) problems in computer systems and solutions to those problems. Some key issues addressed are the variety of peripheral devices with different data rates and formats, and the mismatch between peripheral and processor speeds. The document describes I/O modules that interface between the CPU/memory and peripherals. I/O modules handle control, buffering, error detection and allow different I/O techniques like programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O and direct memory access (DMA) to transfer data efficiently.
03 buses



03 busesdilip kumar The document discusses computer system buses and how they connect different components. It describes how buses carry data, addresses, and control signals between the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. It explains that buses can be synchronous or asynchronous and include address buses, data buses, and control buses. Common bus types like PCI are also covered.
Report in SAD



Report in SADjesseledm The document provides an overview of computer function and interconnection. It discusses the basic components of a computer system including the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. It describes the Von Neumann architecture with a single memory to store both instructions and data. It then explains the fetch-execute cycle of instruction processing and how interrupts can alter the normal flow of a program. Finally, it discusses common interconnection structures like bus architectures and the elements involved in bus design.
COMPUTER BASIC AND FUNDAMENTAL AND ITS ORGANISATION.pptx



COMPUTER BASIC AND FUNDAMENTAL AND ITS ORGANISATION.pptxPannaBushratul The bus system allows communication between computer components through address lines, data lines, and control lines. It transfers data and control signals using a shared transmission pathway. The operating system acts as an interface between the user and computer hardware by managing processes, memory, files, devices, networking, and security. Key functions include process scheduling, virtual memory, file systems, device drivers, user interfaces, and protection mechanisms.
IS 139 Lecture 5



IS 139 Lecture 5wajanga The document provides an overview of the components and architecture of the MARIE computer system, which was designed to illustrate basic computer concepts. It describes the CPU, registers, memory, bus, instruction set, and fetch-decode-execute cycle. The MARIE CPU has 7 registers, including the accumulator, program counter, and instruction register. It uses a 16-bit instruction format. Example load and add instructions are shown in register transfer language to demonstrate how instructions are executed as a series of microoperations. Interrupts can alter the execution cycle by adding an additional "process interrupt" step.
Itc lec 3 Ip cycle , system unit, interface



Itc lec 3 Ip cycle , system unit, interfaceAnzaDar3 Information processing life cycle
input
Output
Processing
Storage
Components of System Unit
Interface (user communication with computer)
Presentation
BEST OF LUCK
Chap2 comp architecture



Chap2 comp architectureraksharao This document provides an overview of the central processing unit (CPU). It discusses that the CPU is referred to as the brain of the computer and contains an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU). The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations, while the CU directs other parts of the system. The CPU also includes registers for temporary storage. Communication between the CPU and other components like memory and I/O devices occurs via buses that transfer data, addresses, and control signals. Caches provide faster access to frequently used data and instructions.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Presentation of the MIPLM subject matter expert Erdem Kaya



Presentation of the MIPLM subject matter expert Erdem KayaMIPLM Presentation of the MIPLM subject matter expert Erdem Kaya
To study the nervous system of insect.pptx



To study the nervous system of insect.pptxArshad Shaikh The *nervous system of insects* is a complex network of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells that process and transmit information. Here's an overview:
Structure
1. *Brain*: The insect brain is a complex structure that processes sensory information, controls behavior, and integrates information.
2. *Ventral nerve cord*: A chain of ganglia (nerve clusters) that runs along the insect's body, controlling movement and sensory processing.
3. *Peripheral nervous system*: Nerves that connect the central nervous system to sensory organs and muscles.
Functions
1. *Sensory processing*: Insects can detect and respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
2. *Motor control*: The nervous system controls movement, including walking, flying, and feeding.
3. *Behavioral responThe *nervous system of insects* is a complex network of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells that process and transmit information. Here's an overview:
Structure
1. *Brain*: The insect brain is a complex structure that processes sensory information, controls behavior, and integrates information.
2. *Ventral nerve cord*: A chain of ganglia (nerve clusters) that runs along the insect's body, controlling movement and sensory processing.
3. *Peripheral nervous system*: Nerves that connect the central nervous system to sensory organs and muscles.
Functions
1. *Sensory processing*: Insects can detect and respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
2. *Motor control*: The nervous system controls movement, including walking, flying, and feeding.
3. *Behavioral responses*: Insects can exhibit complex behaviors, such as mating, foraging, and social interactions.
Characteristics
1. *Decentralized*: Insect nervous systems have some autonomy in different body parts.
2. *Specialized*: Different parts of the nervous system are specialized for specific functions.
3. *Efficient*: Insect nervous systems are highly efficient, allowing for rapid processing and response to stimuli.
The insect nervous system is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation, enabling insects to thrive in diverse environments.
The insect nervous system is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation, enabling insects to thrive
How to Set warnings for invoicing specific customers in odoo



How to Set warnings for invoicing specific customers in odooCeline George Odoo 16 offers a powerful platform for managing sales documents and invoicing efficiently. One of its standout features is the ability to set warnings and block messages for specific customers during the invoicing process.
K12 Tableau Tuesday - Algebra Equity and Access in Atlanta Public Schools



K12 Tableau Tuesday - Algebra Equity and Access in Atlanta Public Schoolsdogden2 Algebra 1 is often described as a “gateway” class, a pivotal moment that can shape the rest of a student’s K–12 education. Early access is key: successfully completing Algebra 1 in middle school allows students to complete advanced math and science coursework in high school, which research shows lead to higher wages and lower rates of unemployment in adulthood.
Learn how The Atlanta Public Schools is using their data to create a more equitable enrollment in middle school Algebra classes.
Link your Lead Opportunities into Spreadsheet using odoo CRM



Link your Lead Opportunities into Spreadsheet using odoo CRMCeline George In Odoo 17 CRM, linking leads and opportunities to a spreadsheet can be done by exporting data or using Odoo’s built-in spreadsheet integration. To export, navigate to the CRM app, filter and select the relevant records, and then export the data in formats like CSV or XLSX, which can be opened in external spreadsheet tools such as Excel or Google Sheets.
Kenan Fellows Participants, Projects 2025-26 Cohort



Kenan Fellows Participants, Projects 2025-26 CohortEducationNC These are the educators participating in the Kenan Fellows Program for Teacher Leadership at NC State University.
APM Midlands Region April 2025 Sacha Hind Circulated.pdf



APM Midlands Region April 2025 Sacha Hind Circulated.pdfAssociation for Project Management APM event hosted by the Midlands Network on 30 April 2025.
Speaker: Sacha Hind, Senior Programme Manager, Network Rail
With fierce competition in today’s job market, candidates need a lot more than a good CV and interview skills to stand out from the crowd.
Based on her own experience of progressing to a senior project role and leading a team of 35 project professionals, Sacha shared not just how to land that dream role, but how to be successful in it and most importantly, how to enjoy it!
Sacha included her top tips for aspiring leaders – the things you really need to know but people rarely tell you!
We also celebrated our Midlands Regional Network Awards 2025, and presenting the award for Midlands Student of the Year 2025.
This session provided the opportunity for personal reflection on areas attendees are currently focussing on in order to be successful versus what really makes a difference.
Sacha answered some common questions about what it takes to thrive at a senior level in a fast-paced project environment: Do I need a degree? How do I balance work with family and life outside of work? How do I get leadership experience before I become a line manager?
The session was full of practical takeaways and the audience also had the opportunity to get their questions answered on the evening with a live Q&A session.
Attendees hopefully came away feeling more confident, motivated and empowered to progress their careers
CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - Worksheet



CBSE - Grade 8 - Science - Chemistry - Metals and Non Metals - WorksheetSritoma Majumder Introduction
All the materials around us are made up of elements. These elements can be broadly divided into two major groups:
Metals
Non-Metals
Each group has its own unique physical and chemical properties. Let's understand them one by one.
Physical Properties
1. Appearance
Metals: Shiny (lustrous). Example: gold, silver, copper.
Non-metals: Dull appearance (except iodine, which is shiny).
2. Hardness
Metals: Generally hard. Example: iron.
Non-metals: Usually soft (except diamond, a form of carbon, which is very hard).
3. State
Metals: Mostly solids at room temperature (except mercury, which is a liquid).
Non-metals: Can be solids, liquids, or gases. Example: oxygen (gas), bromine (liquid), sulphur (solid).
4. Malleability
Metals: Can be hammered into thin sheets (malleable).
Non-metals: Not malleable. They break when hammered (brittle).
5. Ductility
Metals: Can be drawn into wires (ductile).
Non-metals: Not ductile.
6. Conductivity
Metals: Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Non-metals: Poor conductors (except graphite, which is a good conductor).
7. Sonorous Nature
Metals: Produce a ringing sound when struck.
Non-metals: Do not produce sound.
Chemical Properties
1. Reaction with Oxygen
Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides.
These metal oxides are usually basic.
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides.
These oxides are usually acidic.
2. Reaction with Water
Metals:
Some react vigorously (e.g., sodium).
Some react slowly (e.g., iron).
Some do not react at all (e.g., gold, silver).
Non-metals: Generally do not react with water.
3. Reaction with Acids
Metals react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
Non-metals: Do not react with acids.
4. Reaction with Bases
Some non-metals react with bases to form salts, but this is rare.
Metals generally do not react with bases directly (except amphoteric metals like aluminum and zinc).
Displacement Reaction
More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their salt solutions.
Uses of Metals
Iron: Making machines, tools, and buildings.
Aluminum: Used in aircraft, utensils.
Copper: Electrical wires.
Gold and Silver: Jewelry.
Zinc: Coating iron to prevent rusting (galvanization).
Uses of Non-Metals
Oxygen: Breathing.
Nitrogen: Fertilizers.
Chlorine: Water purification.
Carbon: Fuel (coal), steel-making (coke).
Iodine: Medicines.
Alloys
An alloy is a mixture of metals or a metal with a non-metal.
Alloys have improved properties like strength, resistance to rusting.
How to Manage Opening & Closing Controls in Odoo 17 POS



How to Manage Opening & Closing Controls in Odoo 17 POSCeline George In Odoo 17 Point of Sale, the opening and closing controls are key for cash management. At the start of a shift, cashiers log in and enter the starting cash amount, marking the beginning of financial tracking. Throughout the shift, every transaction is recorded, creating an audit trail.
World war-1(Causes & impacts at a glance) PPT by Simanchala Sarab(BABed,sem-4...



World war-1(Causes & impacts at a glance) PPT by Simanchala Sarab(BABed,sem-4...larencebapu132 This is short and accurate description of World war-1 (1914-18)
It can give you the perfect factual conceptual clarity on the great war
Regards Simanchala Sarab
Student of BABed(ITEP, Secondary stage)in History at Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar Punjab 🙏🙏
Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdf



Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdfArab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport This version of the lectures is provided free of charge to graduate students studying the Operations Management course at the MBA level.
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan. This chapter provides an in-depth overview of the viscosity of macromolecules, an essential concept in biophysics and medical sciences, especially in understanding fluid behavior like blood flow in the human body.
Key concepts covered include:
✅ Definition and Types of Viscosity: Dynamic vs. Kinematic viscosity, cohesion, and adhesion.
⚙️ Methods of Measuring Viscosity:
Rotary Viscometer
Vibrational Viscometer
Falling Object Method
Capillary Viscometer
🌡️ Factors Affecting Viscosity: Temperature, composition, flow rate.
🩺 Clinical Relevance: Impact of blood viscosity in cardiovascular health.
🌊 Fluid Dynamics: Laminar vs. turbulent flow, Reynolds number.
🔬 Extension Techniques:
Chromatography (adsorption, partition, TLC, etc.)
Electrophoresis (protein/DNA separation)
Sedimentation and Centrifugation methods.
pulse ppt.pptx Types of pulse , characteristics of pulse , Alteration of pulse



pulse ppt.pptx Types of pulse , characteristics of pulse , Alteration of pulsesushreesangita003 what is pulse ?
Purpose
physiology and Regulation of pulse
Characteristics of pulse
factors affecting pulse
Sites of pulse
Alteration of pulse
for BSC Nursing 1st semester
for Gnm Nursing 1st year
Students .
vitalsign
SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptx



SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptxRonisha Das SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS - XTASY 2025
Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)



Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)Sritoma Majumder Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)
Introduction-to-Communication-and-Media-Studies-1736283331.pdf



Introduction-to-Communication-and-Media-Studies-1736283331.pdfjames5028 Introduction-to-Communication and media studies
Engage Donors Through Powerful Storytelling.pdf



Engage Donors Through Powerful Storytelling.pdfTechSoup In this webinars, members learn how to craft impactful messages that connect with donors to create donor engagement.
How to Customize Your Financial Reports & Tax Reports With Odoo 17 Accounting



How to Customize Your Financial Reports & Tax Reports With Odoo 17 AccountingCeline George The Accounting module in Odoo 17 is a complete tool designed to manage all financial aspects of a business. Odoo offers a comprehensive set of tools for generating financial and tax reports, which are crucial for managing a company's finances and ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s Guide



Understanding P–N Junction Semiconductors: A Beginner’s GuideGS Virdi Dive into the fundamentals of P–N junctions, the heart of every diode and semiconductor device. In this concise presentation, Dr. G.S. Virdi (Former Chief Scientist, CSIR-CEERI Pilani) covers:
What Is a P–N Junction? Learn how P-type and N-type materials join to create a diode.
Depletion Region & Biasing: See how forward and reverse bias shape the voltage–current behavior.
V–I Characteristics: Understand the curve that defines diode operation.
Real-World Uses: Discover common applications in rectifiers, signal clipping, and more.
Ideal for electronics students, hobbyists, and engineers seeking a clear, practical introduction to P–N junction semiconductors.
Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdf



Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdfArab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan.
Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer / Function and Interconection
- 1. William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 3 System Buses
- 2. Program Concept Hardwired systems are inflexible General purpose hardware can do different tasks, given correct control signals Instead of re-wiring, supply a new set of control signals
- 3. What is a program? A sequence of steps For each step, an arithmetic or logical operation is done For each operation, a different set of control signals is needed
- 4. Function of Control Unit For each operation a unique code is provided e.g. ADD, MOVE A hardware segment accepts the code and issues the control signals We have a computer!
- 5. Components The Control Unit and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit constitute the Central Processing Unit Data and instructions need to get into the system and results out Input/output Temporary storage of code and results is needed Main memory
- 6. Computer Components: Top Level View
- 7. Instruction Cycle Two steps: Fetch Execute
- 8. Fetch Cycle Program Counter (PC) holds address of next instruction to fetch Processor fetches instruction from memory location pointed to by PC Increment PC Unless told otherwise Instruction loaded into Instruction Register (IR) Processor interprets instruction and performs required actions
- 9. Execute Cycle Processor-memory data transfer between CPU and main memory Processor I/O Data transfer between CPU and I/O module Data processing Some arithmetic or logical operation on data Control Alteration of sequence of operations e.g. jump Combination of above
- 10. Example of Program Execution
- 11. Instruction Cycle - State Diagram
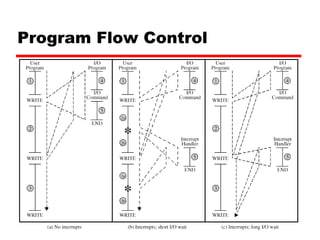
- 12. Interrupts Mechanism by which other modules (e.g. I/O) may interrupt normal sequence of processing Program e.g. overflow, division by zero Timer Generated by internal processor timer Used in pre-emptive multi-tasking I/O from I/O controller Hardware failure e.g. memory parity error
- 14. Interrupt Cycle Added to instruction cycle Processor checks for interrupt Indicated by an interrupt signal If no interrupt, fetch next instruction If interrupt pending: Suspend execution of current program Save context Set PC to start address of interrupt handler routine Process interrupt Restore context and continue interrupted program
- 15. Instruction Cycle (with Interrupts) - State Diagram
- 16. Multiple Interrupts Disable interrupts Processor will ignore further interrupts whilst processing one interrupt Interrupts remain pending and are checked after first interrupt has been processed Interrupts handled in sequence as they occur Define priorities Low priority interrupts can be interrupted by higher priority interrupts When higher priority interrupt has been processed, processor returns to previous interrupt
- 17. Multiple Interrupts - Sequential
- 18. Multiple Interrupts - Nested
- 19. Connecting All the units must be connected Different type of connection for different type of unit Memory Input/Output CPU
- 20. Memory Connection Receives and sends data Receives addresses (of locations) Receives control signals Read Write Timing
- 21. Input/Output Connection(1) Similar to memory from computer’s viewpoint Output Receive data from computer Send data to peripheral Input Receive data from peripheral Send data to computer
- 22. Input/Output Connection(2) Receive control signals from computer Send control signals to peripherals e.g. spin disk Receive addresses from computer e.g. port number to identify peripheral Send interrupt signals (control)
- 23. CPU Connection Reads instruction and data Writes out data (after processing) Sends control signals to other units Receives (& acts on) interrupts
- 24. Buses There are a number of possible interconnection systems Single and multiple BUS structures are most common e.g. Control/Address/Data bus (PC) e.g. Unibus (DEC-PDP)
- 25. What is a Bus? A communication pathway connecting two or more devices Usually broadcast Often grouped A number of channels in one bus e.g. 32 bit data bus is 32 separate single bit channels Power lines may not be shown
- 26. Data Bus Carries data Remember that there is no difference between “data” and “instruction” at this level Width is a key determinant of performance 8, 16, 32, 64 bit
- 27. Address bus Identify the source or destination of data e.g. CPU needs to read an instruction (data) from a given location in memory Bus width determines maximum memory capacity of system e.g. 8080 has 16 bit address bus giving 64k address space
- 28. Control Bus Control and timing information Memory read/write signal Interrupt request Clock signals
- 30. Big and Yellow? What do buses look like? Parallel lines on circuit boards Ribbon cables Strip connectors on mother boards e.g. PCI Sets of wires
- 31. Single Bus Problems Lots of devices on one bus leads to: Propagation delays Long data paths mean that co-ordination of bus use can adversely affect performance If aggregate data transfer approaches bus capacity Most systems use multiple buses to overcome these problems
- 32. Traditional (ISA) (with cache)
- 34. Bus Types Dedicated Separate data & address lines Multiplexed Shared lines Address valid or data valid control line Advantage - fewer lines Disadvantages More complex control Ultimate performance
- 35. Bus Arbitration More than one module controlling the bus e.g. CPU and DMA controller Only one module may control bus at one time Arbitration may be centralised or distributed
- 36. Centralised Arbitration Single hardware device controlling bus access Bus Controller Arbiter May be part of CPU or separate
- 37. Distributed Arbitration Each module may claim the bus Control logic on all modules
- 38. Timing Co-ordination of events on bus Synchronous Events determined by clock signals Control Bus includes clock line A single 1-0 is a bus cycle All devices can read clock line Usually sync on leading edge Usually a single cycle for an event
- 41. PCI Bus Peripheral Component Interconnection Intel released to public domain 32 or 64 bit 50 lines
- 42. PCI Bus Lines (required) Systems lines Including clock and reset Address & Data 32 time mux lines for address/data Interrupt & validate lines Interface Control Arbitration Not shared Direct connection to PCI bus arbiter Error lines
- 43. PCI Bus Lines (Optional) Interrupt lines Not shared Cache support 64-bit Bus Extension Additional 32 lines Time multiplexed 2 lines to enable devices to agree to use 64-bit transfer JTAG/Boundary Scan For testing procedures
- 44. PCI Commands Transaction between initiator (master) and target Master claims bus Determine type of transaction e.g. I/O read/write Address phase One or more data phases
- 45. PCI Read Timing Diagram
- 47. Foreground Reading Stallings, chapter 3 (all of it) www.pcguide.com/ref/mbsys/buses/ In fact, read the whole site! www.pcguide.com/




