C-Language Unit-2
- 1. Modularizing and Reusing of code through Functions Calculation of area of Circle is separated into a separate module from Calculation of area of Ring and the same module can be reused for multiple times. /* program to find area of a ring /* program to find area of a ring */ */ #include<stdio.h> #include<stdio.h> float area(); Function Declaration int main() Repeated & Reusable int main() { blocks of code { float a1,a2,a,r1,r2; float a1,a2,a; a1 = area(); Function Calls printf("Enter the radius : "); a2 = area(); scanf("%f",&r1); a = a1- a2; a1 = 3.14*r1*r1; printf("Area of Ring : %.3fn", a); printf("Enter the radius : "); } scanf("%f",&r2); float area() Function Definition a2 = 3.14*r2*r2; { a = a1- a2; float r; printf("Area of Ring : %.3fn", printf("Enter the radius : "); scanf("%f", &r); a); return (3.14*r*r); } }
- 2. A Function is an independent, reusable module of statements, that specified by a name. This module (sub program) can be called by it’s name to do a specific task. We can call the function, for any number of times and from anywhere in the program. The purpose of a function is to receive zero or more pieces of data, operate on them, and return at most one piece of data. A Called Function receives control from a Calling Function. When the called function completes its task, it returns control to the calling function. It may or may not return a value to the caller. The function main() is called by the operating system; main() calls other functions. When main() is complete, control returns to the operating system. value of ‘p’ is copied to loan’ value of ‘n’ is copied to terms’ int main() { value of ‘r’ is copied to ‘iRate’ int n; float p, r, si; printf(“Enter Details of Loan1:“); float calcInterest(float loan , int terms , float iRate ) { scanf( “%f %d %f”, &p, &n, &r); float interest; The block is si =calcInterest( p, n , r ); interest = ( loan * terms * iRate )/100; executed printf(“Interest : Rs. %f”, si); return ( interest ); printf(“Enter Details of Loan2:“); } } Called Function value of ‘interest’ is assigned to ‘si ’ Calling Function Process of Execution for a Function Call
- 3. int main() { int n1, n2; printf("Enter a number : "); scanf("%d",&n1); printOctal(n1); readPrintHexa(); printf("Enter a number : "); scanf("%d",&n2); 1 2 printOctal(n2); printf(“n”); } 3 7 Flow of 8 void printOctal(int n) { Control printf("Number in octal form : %o n", n); in } Multi-Function 6 void readPrintHexa() Program { int num; printf("Enter a number : "); scanf("%d",&num); printHexa(num); printf(“n”); } 4 void printHexa(int n) 5 { printf("Number in Hexa-Decimal form : %x n",n); }
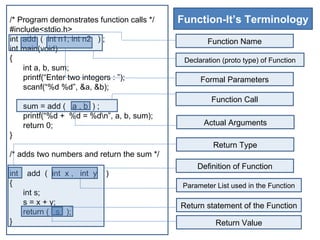
- 4. /* Program demonstrates function calls */ Function-It’s Terminology #include<stdio.h> int add ( int n1, int n2 ) ; Function Name int main(void) { Declaration (proto type) of Function int a, b, sum; printf(“Enter two integers : ”); Formal Parameters scanf(“%d %d”, &a, &b); Function Call sum = add ( a , b ) ; printf(“%d + %d = %dn”, a, b, sum); return 0; Actual Arguments } Return Type /* adds two numbers and return the sum */ Definition of Function int add ( int x , int y ) { Parameter List used in the Function int s; s = x + y; Return statement of the Function return ( s ); } Return Value
- 5. Categories of Functions /* using different functions */ void printMyLine() Function with No parameters int main() { and No return value int i; { for(i=1; i<=35;i++) printf(“%c”, ‘-’); float radius, area; printf(“n”); printMyLine(); } printf(“ntUsage of functionsn”); printYourLine(‘-’,35); void printYourLine(char ch, int n) radius = readRadius(); { Function with parameters area = calcArea ( radius ); and No return value printf(“Area of Circle = %f”, int i; for(i=1; i<=n ;i++) printf(“%c”, ch); area); printf(“n”); } } float calcArea(float r) float readRadius() Function with return { Function with return { value & No parameters float r; float a; value and parameters printf(“Enter the radius : “); a = 3.14 * r * r ; scanf(“%f”, &r); return ( a ) ; return ( r ); } } Note: ‘void’ means “Containing nothing”
- 6. Static Local Variables #include<stdio.h> void area() Visible with in the function, float length, breadth; { created only once when int main() static int num = 0; function is called at first { time and exists between printf("Enter length, breadth : "); float a; function calls. scanf("%f %f",&length,&breadth); num++; area(); a = (length * breadth); perimeter(); printf(“nArea of Rectangle %d : %.2f", num, a); printf(“nEnter length, breadth: "); } scanf("%f %f",&length,&breadth); area(); void perimeter() perimeter(); { } int no = 0; float p; no++; External Global Variables p = 2 *(length + breadth); Scope: Visible across multiple printf(“Perimeter of Rectangle %d: %.2f",no,p); functions Lifetime: exists till the end } of the program. Automatic Local Variables Enter length, breadth : 6 4 Scope : visible with in the function. Area of Rectangle 1 : 24.00 Lifetime: re-created for every function call and Perimeter of Rectangle 1 : 20.00 destroyed automatically when function is exited. Enter length, breadth : 8 5 Area of Rectangle 2 : 40.00 Perimeter of Rectangle 1 : 26.00 Storage Classes – Scope & Lifetime
- 7. File1.c File2.c #include<stdio.h> extern float length, breadth ; float length, breadth; /* extern base , height ; --- error */ float rectanglePerimeter() static float base, height; { int main() float p; { p = 2 *(length + breadth); float peri; return ( p ); printf("Enter length, breadth : "); } scanf("%f %f",&length,&breadth); rectangleArea(); peri = rectanglePerimeter(); External Global Variables printf(“Perimeter of Rectangle : %f“, peri); Scope: Visible to all functions across all printf(“nEnter base , height: "); files in the project. scanf("%f %f",&base,&height); Lifetime: exists till the end of the triangleArea(); program. } void rectangleArea() { float a; Static Global Variables a = length * breadth; Scope: Visible to all functions with in printf(“nArea of Rectangle : %.2f", a); the file only. } Lifetime: exists till the end of the void triangleArea() { program. float a; a = 0.5 * base * height ; printf(“nArea of Triangle : %.2f", a); Storage Classes – Scope & Lifetime }
- 8. #include<stdio.h> Preprocessor Directives void showSquares(int n) A function { calling itself #define - Define a macro substitution if(n == 0) #undef - Undefines a macro is #ifdef - Test for a macro definition return; Recursion #ifndef - Tests whether a macro is not else defined showSquares(n-1); #include - Specifies the files to be included printf(“%d “, (n*n)); #if - Test a compile-time condition } #else - Specifies alternatives when #if int main() test fails { #elif - Provides alternative test facility showSquares(5); #endif - Specifies the end of #if } #pragma - Specifies certain instructions #error - Stops compilation when an error occurs Output : 1 4 9 16 25 # - Stringizing operator addition showSquares(1) execution ## - Token-pasting operator of showSquares(2) of function function calls showSquares(3) calls Preprocessor is a program that to showSquares(4) in processes the source code before it call- reverse passes through the compiler. stack showSquares(5) main() call-stack