Ad
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources
- 1. Outline Roles and Boundaries Cloud Characteristics Cloud Delivery Models Cloud Deployment Models
- 2. Roles and Boundaries Cloud Provider Cloud Consumer Cloud Service Owner Cloud Resource Administrator Additional roles: • Cloud Auditor • Cloud Broker • Cloud Carrier
- 3. Cloud Provider •The organization that provides cloud-based IT resources responsible for making cloud services available to cloud consumers, as per agreed upon SLA guarantees. •Cloud providers normally own the IT resources that are made available for lease by cloud consumers, however, some cloud providers also “resell” IT resources leased from other cloud providers.
- 4. Cloud Consumer A cloud consumer is an organization (or a human) that has a formal contract or arrangement with a cloud provider to use IT resources made available by the cloud provider. Specifically, the cloud consumer uses a cloud service consumer to access a cloud service .
- 5. Figure 4.1 A cloud consumer (Organization A) interacts with a cloud service from a cloud provider (that owns Cloud A). Within Organization A, the cloud service consumer is being used to access the cloud service.
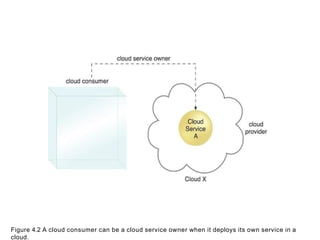
- 6. Cloud Service Owner •The person or organization that legally owns a cloud service . •The cloud service owner can be the cloud consumer, or the cloud provider that owns the cloud within which the cloud service resides. •For example, either the cloud consumer of Cloud X or the cloud provider of Cloud X could own Cloud Service A .
- 7. Figure 4.2 A cloud consumer can be a cloud service owner when it deploys its own service in a cloud.
- 8. Figure 4.3 A cloud provider becomes a cloud service owner if it deploys its own cloud service, typically for other cloud consumers to use.
- 9. Cloud Resource Administrator •the person or organization responsible for administering a cloud-based IT resource (including cloud services). •can be (or belong to) the cloud consumer or cloud provider of the cloud within which the cloud service resides. •it can be (or belong to) a third-party organization contracted to administer the cloud-based IT resource.
- 10. Figure 4.4 A cloud resource administrator can be with a cloud consumer organization and administer remotely accessible IT resources that belong to the cloud consumer.
- 11. Figure 4.5 A cloud resource administrator can be with a cloud provider organization for which it can administer the cloud providerʼs internally and externally available IT resources.
- 12. Cloud Auditor •A third-party (often accredited) that conducts independent assessments of cloud environments . •Responsible for the evaluation of security controls, privacy impacts, and performance. •provide an unbiased assessment (and possible endorsement) of a cloud environment to help strengthen the trust relationship between cloud consumers and cloud providers.
- 13. Cloud Broker •a party that assumes the responsibility of managing and negotiating the usage of cloud services between cloud consumers and cloud providers.
- 14. Cloud Carrier The party responsible for providing the wire- level connectivity between cloud consumers and cloud providers . This role is often assumed by network and telecommunication providers.
- 15. Organizational Boundary represents the physical perimeter that surrounds a set of IT resources that are owned and governed by an organization. does not represent the boundary of an actual organization, only an organizational set of IT assets and IT resources. Similarly, clouds have an organizational boundary.
- 16. Organizational Boundary Figure 4.6 Organizational boundaries of a cloud consumer (left), and a cloud provider (right), represented by a broken line notation.
- 17. Trust Boundary a logical perimeter that typically spans beyond physical boundaries to represent the extent to which IT resources are trusted . An organizational boundary represents the physical scope of IT resources owned and governed by an organization. A trust boundary is the logical perimeter that encompasses the IT resources trusted by an organization.
- 18. Trust Boundary Figure 4.7 An extended trust boundary encompasses the organizational boundaries of the cloud provider and the cloud consumer.
- 19. 4.2. Cloud Characteristics •on-demand usage: A cloud consumer can unilaterally access cloud-based IT resources giving the cloud consumer the freedom to self-provision these IT resources. •ubiquitous access: represents the ability for a cloud service to be widely accessible. •multitenancy (and resource pooling): A cloud provider pools its IT resources to serve multiple cloud service consumers by using multitenancy models that frequently rely on the use of virtualization technologies.
- 20. 4.2. Cloud Characteristics •Elasticity: the automated ability of a cloud to transparently scale IT resources, as required in response to runtime conditions or as pre-determined by the cloud consumer or cloud provider. •measured usage: represents the ability of a cloud platform to keep track of the usage of its IT resources, primarily by cloud consumers.
- 21. 4.3. Cloud Delivery Models represents a specific, pre-packaged combination of IT resources offered by a cloud provider. • Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) • Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) • Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
- 22. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) represents a self-contained IT environment comprised of infrastructure-centric IT resources that can be accessed and managed via cloud service-based interfaces and tools. Include hardware, network, connectivity, operating systems, and other “raw” IT resources.
- 23. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) This model is therefore used by cloud consumers that require a high level of control over the cloud-based environment they intend to create. A central and primary IT resource within a typical IaaS environment is the virtual server. Virtual servers are leased by specifying server hardware requirements, such as processor capacity, memory, and local storage space
- 24. Figure 4.11 A cloud consumer is using a virtual server within an IaaS environment. Cloud consumers are provided with a range of contractual guarantees by the cloud provider, pertaining to characteristics such as capacity, performance, and availability.
- 25. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) •represents a pre-defined “ready-to-use” environment typically comprised of already deployed and configured IT resources. •PaaS relies on (and is primarily defined by) the usage of a ready- made environment that establishes a set of pre-packaged products and tools used to support the entire delivery lifecycle of custom applications.
- 26. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) •the cloud consumer is granted a lower level of control over the underlying IT resources that host and provision the platform •PaaS products are available with different development stacks. For example, Google App Engine offers a Java and Python-based environment.
- 27. Figure 4.12 A cloud consumer is accessing a ready-made PaaS environment. The question mark indicates that the cloud consumer is intentionally shielded from the implementation details of the platform.
- 28. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) A software program positioned as a shared cloud service and made available as a “product” or generic utility. The SaaS delivery model is typically used to make a reusable cloud service widely available (often commercially) to a range of cloud consumers. A cloud consumer is generally granted very limited administrative control over a SaaS implementation.
- 29. Figure 4.13 The cloud service consumer is given access the cloud service contract, but not to any underlying IT resources or implementation details.
- 30. Comparing Cloud Delivery Models
- 31. Comparing Cloud Delivery Models
- 32. IaaS + PaaS Figure 4.14 A PaaS environment based on the IT resources provided by an underlying IaaS environment.
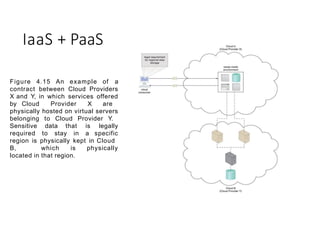
- 33. IaaS + PaaS Figure 4.15 An example of a contract between Cloud Providers X and Y, in which services offered by Cloud Provider X are physically hosted on virtual servers belonging to Cloud Provider Y. Sensitive data that is legally required to stay in a specific region is physically kept in Cloud B, which is physically located in that region.
- 34. IaaS + PaaS + SaaS Figure 4.16 A simple l a y e re d v i e w o f a n architecture comprised of I a a S a n d environments P a a S hosting three SaaS cloud service implementations.
- 35. 4.4. Cloud Deployment Models There are four common cloud deployment models: 1. Public Cloud 2. Community Cloud 3. Private Cloud 4. Hybrid Cloud
- 36. Public Clouds A public cloud is a publicly accessible cloud environment owned by a third-party cloud provider. The IT resources on public clouds are usually provisioned via the previously described cloud delivery models and are generally offered to cloud consumers at a cost or are commercialized via other avenues (such as advertisement).
- 37. Figure 4.17 Organizations act as cloud consumers when accessing cloud services and IT resources made available by different cloud providers.
- 38. Community Clouds •A community cloud is similar to a public cloud except that its access is limited to a specific community of cloud consumers. •The community cloud may be jointly owned by the community members or by a third-party cloud provider that provisions a public cloud with limited access. •Membership in the community does not necessarily guarantee access to or control of all the cloud’s IT resources. •Parties outside the community are generally not granted access unless allowed by the community.
- 39. Figure 4.18 An example of a “community” of organizations accessing IT resources from a community clou
- 40. Private Clouds A private cloud is owned by a single organization Private clouds enable an organization to use cloud computing technology as a means of centralizing access to IT resources by different parts, locations, or departments of the organization. The actual administration of a private cloud environment may be carried out by internal or outsourced staff. the same organization is technically both the cloud consumer and cloud provider.
- 41. Figure 4.19 A cloud service consumer in the organizationʼs on-premise environment accesses a cloud service hosted on the same organizationʼs private cloud via a virtual private network.
- 42. Hybrid Clouds •A hybrid cloud is a cloud environment comprised of two or more different cloud deployment models. •For example, a cloud consumer may choose to deploy cloud services processing sensitive data to a private cloud and other, less sensitive cloud services to a public cloud.
- 43. Figure 4.20 An organization using a hybrid cloud architecture that utilizes both a private and public cloud.