Ad
Cloud Security: What you need to know about IBM SmartCloud Security
- 1. © 2012 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems SmartCloud Security Overview Gretchen Marx, Program Manager, Portfolio Strategy IBM Security Division
- 2. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 2 Agenda § Cloud security landscape § IBM SmartCloud Security offerings § SmartCloud Security demo
- 3. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 3 Cloud computing is hot and growing fast Rest of IT Rest of IT WW IT Spend ($B) Source: IBM Market Insights Cloud Phase 2 assessment, Feb 2011 What organizations like about cloud computing: § Elastic capacity – Resource can be elastically provisioned to quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in § Fast provisioning – Automated provisioning / deprovisioning of resources as needed § Self-service requests – User request services via a web portal § Low cost, pay-as-you-go – Users pay for what they use Cloud Non-Cloud Traditional IT 3% CAGR 25% CAGR
- 4. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 4 The Cloud security market is growing PrivatePublic Cloud Security is estimated to be 10.6% of total security spending in 2013, growing to 13.9% in 2015 2013 – 2016 Worldwide Cloud Security Opportunity ($B) Worldwide Public and Private Cloud Security Product Share by Subcategory, 2011 19% 24% Source: IDC, December 2012
- 5. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 5 Cloud environments present new challenges
- 6. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 6 Security remains #1 inhibitor to broad scale cloud adoption Source: 2012 Cloud Computing – Key Trends and Future Effects – IDG
- 7. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 7 Self-Service Highly Virtualized Location Independence Workload Automation Rapid Elasticity Standardization Cloud computing tests the limits of security operations and infrastructure People and Identity Application and Process Network, Server and Endpoint Data and Information Physical Infrastructure Governance, Risk and Compliance Security and Privacy Domains Multiple logins, onboarding issues Multi-tenancy, data separation Audit silos, compliance controls Provider controlled, lack of visibility Virtualization, network isolation External facing, quick provisioning To the Cloud In a cloud environment, access expands, responsibilities change, control shifts, and the speed of provisioning resources and applications increases - greatly affecting all aspects of IT security
- 8. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 8 Cloud computing changes the way we think about security . Private cloud Public cloudHybrid IT • High multi-tenancy and data separation • Image management and compliance • Security of the virtual / hypervisor layer • Virtual network visibility • Need for Service level agreements (SLAs) • Provider responsibility for infrastructure • Customization of security controls • Visibility into day-to-day operations • Access to logs and policies • Applications and data are publically exposed Changes in Security and Privacy While security concerns are often shared across the different cloud models, the responsibility changes from consumer to provider which can present unique challenges
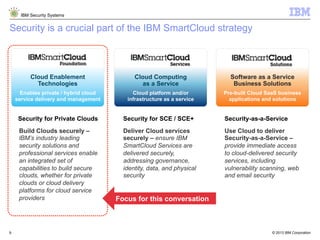
- 9. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 9 Security is a crucial part of the IBM SmartCloud strategy Build Clouds securely – lBM’s industry leading security solutions and professional services enable an integrated set of capabilities to build secure clouds, whether for private clouds or cloud delivery platforms for cloud service providers Deliver Cloud services securely – ensure IBM SmartCloud Services are delivered securely, addressing governance, identity, data, and physical security Use Cloud to deliver Security-as-a-Service – provide immediate access to cloud-delivered security services, including vulnerability scanning, web and email security Security for Private Clouds Security for SCE / SCE+ Security-as-a-Service Cloud Enablement Technologies Enables private / hybrid cloud service delivery and management Cloud Computing as a Service Cloud platform and/or infrastructure as a service Software as a Service Business Solutions Pre-built Cloud SaaS business applications and solutions Focus for this conversation
- 10. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 10 1. Manage the registration and control the access of thousands or even millions of Cloud users in a cost- effective way 2. Ensure the safety and privacy of critical enterprise data in Cloud environments without disrupting operations 3. Provide secure access to applications in the Cloud 4. Manage patch requirements for virtualized systems 5. Provide protection against network threat and vulnerabilities in the Cloud 6. Protect virtual machines 7. Achieve visibility and transparency in Cloud environments to find advanced threats and meet regulatory and compliance requirements Key customer Cloud security concerns
- 11. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 11 IBM Security Systems IBM Security: Delivering intelligence, integration and expertise across a comprehensive framework § IBM Security Framework built on the foundation of COBIT and ISO standards § End-to-end coverage of the security domains § Managed and Professional Services to help clients secure the enterprise
- 12. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 12 SmartCloud Security Capabilities Administer, secure, and extend identity and access to and from the cloud Secure enterprise databases Build, test and maintain secure cloud applications Prevent advanced threats with layered protection and analytics § IBM Security Identity and Access Management Suite § IBM Security Federated Identity Manager - Business Gateway § IBM Security Privileged Identity Manager § IBM InfoSphere Guardium § IBM Security AppScan Suite § IBM AppScan OnDemand (hosted) § IBM Security Key Life Cycle Manager § IBM SmartCloud Patch § IBM Security Network IPS and Virtual IPS § IBM Security Virtual Server Protection for VMware IBM SmartCloud Security Intelligence IBM Security QRadar SIEM and VFlow Collectors IBM SmartCloud Security Identity Protection IBM SmartCloud Security Data and Application Protection IBM SmartCloud Security Threat Protection 13-04-02
- 13. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 13 Cost-effective and standards-based registration and access control of Cloud users External users need identity and access controls Internal users need easy and secure access to Cloud applications Compliance and audit controls need to cover all the users and services External users Internal users Application Application Internal Applications External Applications When millions of users need access to cloud- based resources, user provisioning (and de- provisioning) must be simple, efficient and scalable Need to protect against threats that can lead to data loss and web fraud Organizations need the ability to tie cloud-based applications together with internal applications and enable users to access them easily with single sign-on 1 Identity Enterprise Single Sign On Federated Identity Management Custodians of the Cloud
- 14. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 14 Security Event and Log Mgt. Vulnerability Mgt. Service Cost-effective user registration and access control of Cloud users Addressing compliance requirements, reducing operational costs, enhancing security posture and developing operational efficiencies Requirement Capability Full life-cycle identity management (“cradle-to- grave”) for cloud-based users § Federated single sign-on to multiple web-based and cloud applications with a single ID and password for employees, customers, BPs, vendors § User self-service for identity creation and password reset § Securely provision, manage, automate and track privileged access to critical enterprise resources Access, authorization control, and fraud prevention for applications and data in the cloud § Automated management and risk-based enforcement of access control policies across every application, data source, operating system and even company boundaries § Role-based identity and access management aligns users’ roles to their access capabilities, simplifies management and compliance Ability to track and log user activities, report violations, and prove compliance § Security incident and event management for compliance reporting and auditing of users and their activities—in both cloud and traditional environments § The ability to monitor, control, and report on privileged identities (e.g., systems and database administrators) for cloud-based administrators 1 Identity
- 15. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 15 Know who can access the cloud Single access method for users into workload aware Cloud Getting started on ramp for the Cloud with Federated SSO Federated Access / Identity Management 15 Identity Federation enables web single sign on across applications • Access controls on cloud applications • Provide users with the ability to single sign on to multiple Web-based cloud applications with disparate user IDs/passwords • Self service identity registration, validation and processing user credentials IBM Security Access Manager for Cloud and Mobile IBM Security Identity Manager 1 Identity
- 16. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 16 Beyond the basics: Next steps in IAM for Cloud security Summary: Improve visibility and securely connect users to the workload aware Cloud; enforce auditable access and enable secure collaboration Cloud Use Case: Federated SSO to SaaS / Cloud; self-service identity provisioning, validation and processing user credentials Deployment Scenario: Hosted, managed and deployed as a Cloud Computing Infrastructure SystemsStorage Network Service Requestor 3rd Party Cloud Service Provider Service Management IAA Add Identity and Access Assurance to manage identities, entitlements, access control and auditing Add full Identity and Access Assurance solutions • Build on access and authorization control • Full life-cycle user / identity management • Role-based identity and access management • Privileged identity management • Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) IBM Security Identity and Access Assurance Know who can access the cloud Single access method for users into workload aware Cloud FIM Systems & Image Management 1 Identity
- 17. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 17 Use Case: Prevent fraudulent access to Cloud applications and services using risk-based access policy and strong authentication User attempts high- value transaction Transaction completes Strong authentication challenge IBM Security Access Manager for Cloud and Mobile Transactions < $100 Allowed with no additional authentication Attempt to transfer >= $100 Requires strong authentication 1 Identity
- 18. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 18 Privileged Identity Management: Centralized management of privileged and shared identities IBM security solution IBM Security Privileged Identity Management Track and audit activities of privileged users (e.g., root, financial app administrators) for effective governance Business challenge Addressing insider threat with privileged users access management Key solution highlights New Privileged Identity Management (PIM) solution providing complete identity management and enterprise single sign-on capabilities for privileged users DatabasesID Check in / check out using secure credential vault Control shared access to sensitive user IDs Request, approve and re- validate privileged access Reduce risk, enhance compliance Track usage of shared identities Provide increased accountability and audit trail Automated password management Automated checkout of IDs, hide password from requesting employee, automate password reset to eliminate password theft 1 Identity
- 19. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 19 SmartCloud Security Capabilities Administer, secure, and extend identity and access to and from the cloud Secure enterprise databases Build, test and maintain secure cloud applications Prevent advanced threats with layered protection and analytics § IBM Security Identity and Access Management Suite § IBM Security Federated Identity Manager - Business Gateway § IBM Security Privileged Identity Manager § IBM InfoSphere Guardium § IBM Security AppScan Suite § IBM AppScan OnDemand (hosted) § IBM Security Key Life Cycle Manager § IBM SmartCloud Patch § IBM Security Network IPS and Virtual IPS § IBM Security Virtual Server Protection for VMware IBM SmartCloud Security Intelligence IBM Security QRadar SIEM and VFlow Collectors IBM SmartCloud Security Identity Protection IBM SmartCloud Security Data and Application Protection IBM SmartCloud Security Threat Protection 13-04-02
- 20. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 20 Old approaches to data protection are not efficient for Cloud and virtualization § Multi-tenancy raises security concerns in Cloud environments § Lack of visibility over DB access in Cloud environments § Security alerts not real time § No separation of duties as required by auditors § Inconsistent policies enterprise-wide § Native logging causes high performance impact on DBMS 2 Data “A data security strategy should include database auditing and monitoring, patch management, data masking, access control, discovery / classification, and change management.” -- Why Enterprise Database Security Strategy Has Become Critical, Forrester Research, Inc, July 13, 2011
- 21. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 21 Assess database vulnerabilities De-identify confidential data in non-production environments Define policies & metrics Audit and report for compliance Protect enterprise data from authorized & unauthorized access Four steps to data security in the Cloud Define policies & metrics De-identify confidential data in non-production environments Assess database vulnerabilities Classify & define data types Fully redacted unstructured data Monitor and enforce review of policy exceptions Protect enterprise data from authorized & unauthorized access A data security strategy should include database auditing and monitoring, patch management, data masking, access control, discovery/classification, and change management. -- Why Enterprise Database Security Strategy Has Become Critical, Forrester Research, Inc., July 13, 2011 Define policies & metrics Classify & define data types Define policies & metrics Classify & define data types Protect enterprise data from authorized & unauthorized access Define policies & metrics Classify & define data types Fully redacted unstructured data Protect enterprise data from authorized & unauthorized access Define policies & metrics Classify & define data types De-identify confidential data in non-production environments Fully redacted unstructured data Protect enterprise data from authorized & unauthorized access Define policies & metrics Classify & define data types Assess database vulnerabilities De-identify confidential data in non-production environments Fully redacted unstructured data Define policies and metrics Classify & define data types Monitor and enforce review of policy exceptions Fully redact unstructured data Classify and define data types Audit and report for compliance Protect enterprise data from authorized and unauthorized access Discover where sensitive data resides Discover where sensitive data resides Discover where sensitive data resides Discover where sensitive data resides Discover where sensitive data resides Discover where sensitive data resides Discover where sensitive data resides “ ” Monitor and Audit 3 Secure and Protect 2 Understand and Define 1 Enterprise Security intelligence4
- 22. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 22 Key Themes Reduced Total Cost of Ownership Expanded support for databases and unstructured data, automation, handling and analysis of large volumes of audit records, and new preventive capabilities Enhanced Compliance Management Enhanced Database Vulnerability Assessment (VA) and Database Protection Subscription Service (DPS) with improved update frequency, labels for specific regulations, and product integrations Dynamic Data Protection Data masking capabilities for databases (row level, role level) and for applications (pattern based, form based) to safeguard sensitive and confidential data Data security for the Cloud Across Multiple Deployment Models QRadar Integration 2 Data
- 23. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 23 Application security challenge: manage risk § 76% of CEOs feel reducing security flaws within business-critical applications is the most important aspect of their data protection programs § 79% of compromised records used Web Apps as the attack pathway § 81% of breached organizations subject to PCI were found to be non- compliant 3 Applications Web Application Vulnerabilities As a Percentage of All Disclosures in 2012 Web Applications: 43 percent Others: 57 percent Source: IBM X-Force® 2012 Full-Year Trend and Risk Report Web application vulnerabilities up 14% in 2012
- 24. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 24 Scan applications Analyze (identify issues) Automate Application Security Testing Report (detailed and actionable) Finding and fixing application vulnerabilities § During coding § During production § Web vulnerabilities § PII use and security § Remediation steps § Compliance 3 Applications
- 25. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 25 Key Themes Coverage for Cloud and mobile apps & new threats Identify and reduce risk by expanding scanning capabilities to new platforms such as Cloud and mobile using next generation dynamic analysis scanning and glass box testing Simplified interface and accelerated ROI Improve time to value and consumability with out-of-the-box scanning, static analysis templates and ease of use features Security Intelligence integration Automatically adjust threat levels based on knowledge of application vulnerabilities by integrating and analyzing scan results with SiteProtector and the QRadar Security Intelligence Platform AppScan security for Cloud environments
- 26. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 26 SmartCloud Security Capabilities Administer, secure, and extend identity and access to and from the cloud Secure enterprise databases Build, test and maintain secure cloud applications Prevent advanced threats with layered protection and analytics § IBM Security Identity and Access Management Suite § IBM Security Federated Identity Manager - Business Gateway § IBM Security Privileged Identity Manager § IBM InfoSphere Guardium § IBM Security AppScan Suite § IBM AppScan OnDemand (hosted) § IBM Security Key Life Cycle Manager § IBM SmartCloud Patch § IBM Security Network IPS and Virtual IPS § IBM Security Virtual Server Protection for VMware IBM SmartCloud Security Intelligence IBM Security QRadar SIEM and VFlow Collectors IBM SmartCloud Security Identity Protection IBM SmartCloud Security Data and Application Protection IBM SmartCloud Security Threat Protection 13-04-02
- 27. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 27 Optimizing the patch cycle and help ensure the security of both traditional and Cloud computing assets Customer Pain Points § Time required to patch all enterprise physical, virtual, distributed, and cloud assets § Lack of control over deployed and dormant virtual systems OS patch levels and related security configurations Distributed Endpoints Web App DB Virtual ServersPhysical Servers + + 4 Patch Management Capability § Automatically manage patches for multiple OSs and applications across physical and virtual servers § Reduce security and compliance risk by slashing remediation cycles from weeks to hours § Patch running / offline / dormant VMs § Continuously monitor and enforce endpoint configuration
- 28. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 28 § Patch as fast as you can provision with rapid patching, configuration and policy deployment across thousands of endpoints regardless of location, connection type or status § Reduce security risk by slashing remediation cycles from weeks to days or hours § Gain greater visibility into patch compliance with flexible, real-time monitoring and reporting from a single management console § Efficiently deploy patches, even over low- bandwidth or globally distributed networks reducing labor requirements by over 75% § Patch endpoints on or off the network-- including roaming devices using Internet connections providing over 98.5% first pass patch compliance Enforce Evaluate PublishReport Enhanced Security and Patch Management with SmartCloud Patch Stay in Control and Prove it SmartCloud Patch
- 29. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 29 The challenging state of network security Social media sites present productivity, privacy and security risks including new threat vectors SOCIAL NETWORKING Limited visibility into traffic patterns or types of traffic traversing the network LIMITED NETWORK VISIBILITY Point solutions are siloed with minimal integration or data sharing POINT SOLUTIONSURL Filtering • IDS / IPS IM / P2P • Web App Protection Vulnerability Management Increasingly sophisticated attacks are using multiple attack vectors and increasing risk exposure SOPHISTICATED ATTACKS Stealth Bots • Targeted Attacks Worms • Trojans • Designer Malware 5 Network Protection
- 30. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 30 Network intrusion protection is a primary building block in Cloud security Firewall Datacenter Network Intrusion Prevention § Protect both applications and network from being exploited § Control protocols and applications § Monitor traffic for anomalous traffic patterns § Protect users from being attacked (e.g., through malicious documents) § Prove compliance with regulation requirements (e.g., PCI) § Enforce corporate policy with employees and 3rd parties (e.g., consultants) § Monitor network traffic for sensitive information leaving the company § Prevent data from being stolen from databases via web applications 5 Network Protection
- 31. © 2012 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 31 IBM Internal and Business Partner Use Only IBM Security Network Protection XGS 5000 IBM XGS 5000: Extensible, 0-Day protection powered by X-Force® • Vulnerability modeling and algorithms • Stateful packet inspection • Port variability • Port assignment • Port following • Protocol tunneling • Shellcode heuristics • Application layer pre- processing • Context field analysis • RFC compliance • Statistical analysis • TCP reassembly and flow reassembly • Host response analysis • Port probe detection • Pattern matching • Custom signatures • Injection logic engine • IPv6 tunnel analysis • SIT tunnel analysis – 15 years+ of vulnerability research and development – Trusted by the world’s largest enterprises and government agencies – True protocol-aware intrusion prevention, not reliant on signatures – Backed by X-Force ® – Specialized engines • Exploit Payload Detection • Web Application Protection • Content and File Inspection “When we see these attacks coming in, it will shut them down automatically.” – Melbourne IT § Next Generation IPS powered by X-Force® Research protects weeks or even months “ahead of the threat” § Full protocol, content and application aware protection goes beyond signatures § Expandable protection modules defend against emerging threats such as malicious file attachments and Web application attacks [The IBM Threat Protection Engine] “defended an attack against a critical government network another protocol aware IPS missed” – Government Agency IBM Security Threat Protection Ability to protect against the threats of today and tomorrow
- 32. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 32 Why virtualization security? 6 Protect VMs
- 33. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 33 Summary of virtualization system security challenges § Migration of VMs for load balancing can make them more difficult to secure § Ease of addition of VMs increases likelihood that insecure systems will go online § Malicious insiders can inflict massive damage very quickly Increased flexibility can increase security risk § Virtual endpoints have same security challenges as their physical counterparts § Virtualization management systems provide new attack vector § Hypervisor itself is an attack vector Larger attack surface § 259 new virtualization vulnerabilities over the last 5 years § New attack types (e.g., Hyperjacking, hypervisor escape, VM attacks) New vulnerabilities1 2 3 6 Protect VMs
- 34. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 3434 Virtual Server Protection increases ROI of the virtual infrastructure, while reducing risk § Automated protection as each VM comes online – Automatic discovery – Automated vulnerability assessment – Simplified patch management § Non-intrusive – No reconfiguration of the virtual network – No presence in the guest OS ü Improved stability ü More CPU / memory available for workloads ü Reduced attack surface § Protection for any guest OS – Reduction in security agents for multiple OSs 6 Protect VMs VMware vCloud
- 35. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 35 SmartCloud Security Capabilities Administer, secure, and extend identity and access to and from the cloud Secure enterprise databases Build, test and maintain secure cloud applications Prevent advanced threats with layered protection and analytics § IBM Security Identity and Access Management Suite § IBM Security Federated Identity Manager - Business Gateway § IBM Security Privileged Identity Manager § IBM InfoSphere Guardium § IBM Security AppScan Suite § IBM AppScan OnDemand (hosted) § IBM Security Key Life Cycle Manager § IBM SmartCloud Patch § IBM Security Network IPS and Virtual IPS § IBM Security Virtual Server Protection for VMware
- 36. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 36 Security Intelligence: Integrating across IT silos 7 Security Intelligence
- 37. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 37 Supplemented with Security-as-a-Service offerings
- 38. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 38 Cloud Auditing Data Federation (CADF) WG ISO JTC 1/SC 27: IT Security Techniques IETF OAuth 2.0 Driving client-focused open standards and interoperability Customer security standards guidance Open source cloud computing infrastructure (IaaS focus)
- 39. © 2013 IBM Corporation IBM Security Systems 3939 Thank you






























![© 2012 IBM Corporation
IBM Security Systems
31 IBM Internal and Business Partner Use Only
IBM Security Network Protection XGS 5000
IBM XGS 5000: Extensible, 0-Day protection powered by X-Force®
• Vulnerability modeling and
algorithms
• Stateful packet inspection
• Port variability
• Port assignment
• Port following
• Protocol tunneling
• Shellcode heuristics
• Application layer pre-
processing
• Context field analysis
• RFC compliance
• Statistical analysis
• TCP reassembly and flow
reassembly
• Host response analysis
• Port probe detection
• Pattern matching
• Custom signatures
• Injection logic engine
• IPv6 tunnel analysis
• SIT tunnel analysis
– 15 years+ of vulnerability research and
development
– Trusted by the world’s largest enterprises
and government agencies
– True protocol-aware intrusion prevention,
not reliant on signatures
– Backed by X-Force ®
– Specialized engines
• Exploit Payload Detection
• Web Application Protection
• Content and File Inspection
“When we see these attacks coming
in, it will shut them down
automatically.”
– Melbourne IT
§ Next Generation IPS powered
by X-Force® Research
protects weeks or even months
“ahead of the threat”
§ Full protocol, content and
application aware protection
goes beyond signatures
§ Expandable protection
modules defend against
emerging threats such as
malicious file attachments and
Web application attacks
[The IBM Threat Protection Engine]
“defended an attack against a
critical government network another
protocol aware IPS missed”
– Government Agency
IBM Security Threat Protection
Ability to protect against the threats of today and tomorrow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudsecurity-whatyouneedtoknowaboutibmsmartcloudsecurity-130618125951-phpapp01/85/Cloud-Security-What-you-need-to-know-about-IBM-SmartCloud-Security-31-320.jpg)






























































































