Cluster Computing
0 likes149 views
Super, Mainframe computers are not cost effective Cluster technology have been developed that allow multiple low cost computers to work in coordinated fashion to process applications.
1 of 15
Download to read offline














Ad
Recommended
Cluster computing



Cluster computingShreerajKhatiwada This document provides an overview of cluster computing. It defines a cluster as multiple independent computers combined through software and networking to work together as a unified system. Clusters are used for high availability and high performance computing. There are different types of clusters, including high availability clusters designed to provide uninterrupted services if a node fails, and load balancing clusters that distribute requests across nodes. The document discusses cluster configuration, methods like passive standby and shared disks, architecture involving middleware, and compares clusters to symmetric multiprocessing systems.
Distributed computing ).ppt him



Distributed computing ).ppt himHimanshu Saini A distributed computing system is a collection of interconnected processors with local memory that communicate via message passing. There are various models including minicomputer, workstation, workstation-server, and processor pool. Distributed systems provide advantages like supporting distributed applications, sharing information and resources, extensibility, shorter response times, higher reliability, flexibility, and better price-performance ratio compared to centralized systems.
Distributed Computing



Distributed ComputingPrashant Tiwari Distributed computing deals with hardware and software systems containing more than one processing element or storage element, concurrent processes, or multiple programs, running under a loosely or tightly controlled regime. In distributed computing a program is split up into parts that run simultaneously on multiple computers communicating over a network. Distributed computing is a form of parallel computing, but parallel computing is most commonly used to describe program parts running simultaneously on multiple processors in the same computer. Both types of processing require dividing a program into parts that can run simultaneously, but distributed programs often must deal with heterogeneous environments, network links of varying latencies, and unpredictable failures in the network or the computers.
Distributed Computing



Distributed ComputingSudarsun Santhiappan The document discusses various models of parallel and distributed computing including symmetric multiprocessing (SMP), cluster computing, distributed computing, grid computing, and cloud computing. It provides definitions and examples of each model. It also covers parallel processing techniques like vector processing and pipelined processing, and differences between shared memory and distributed memory MIMD (multiple instruction multiple data) architectures.
Cloud and distributed computing, advantages



Cloud and distributed computing, advantagesknowledgeworld7 1. how to learn distributed computing 2. what is distributed computing architecture 3. what are advantages of distributed computing 4. distributing computing 5. Easy way to learn distributed computing 6. Advantages of Cloud and distributed computing 7. best ways to learning distributed computing Engineering 8. scope of distributed computing engineering in future. 9. laws of distributed computing
Distributed and clustered systems



Distributed and clustered systemsV.V.Vanniaperumal College for Women This document discusses distributed and clustered systems. It defines distributed systems as systems composed of independent computers that communicate over a network. Distributed systems can be client-server systems, where clients request resources from servers, or peer-to-peer systems, where users share resources directly. Clustered systems combine independent computers and shared storage to work together. They provide benefits like high performance, fault tolerance, and scalability.
Clusters



ClustersMuhammad Ishaq The document discusses computer clusters, which involve linking multiple computers together to work as a single logical unit. Key points include: clusters allow for cost-effective high performance and availability compared to single systems; they can be configured in shared-nothing or shared-disk models; common applications include scientific computing, databases, web services, and high availability systems; and cluster middleware helps provide a single system image and improved manageability.
Cluster computing report



Cluster computing reportSudhanshu kumar Sah This document provides a summary of cluster computing. It discusses that a cluster is a group of linked computers that work together like a single computer. It then describes different types of clusters including high availability clusters for fault tolerance, load balancing clusters for distributing work, and parallel processing clusters for computationally intensive tasks. It also outlines some key cluster components such as nodes, networking, storage and middleware. Finally it provides some examples of cluster applications including Google's search engine, petroleum reservoir simulation, and image rendering.
Design issues of dos



Design issues of dosvanamali_vanu This document provides an overview of distributed operating systems. It discusses the motivation for distributed systems including resource sharing, reliability, and computation speedup. It describes different types of distributed operating systems like network operating systems where users are aware of multiple machines, and distributed operating systems where users are not aware. It also covers network structures, topologies, communication structures, protocols, and provides an example of networking. The objectives are to provide a high-level overview of distributed systems and discuss the general structure of distributed operating systems.
Lecture 4 Cluster Computing



Lecture 4 Cluster ComputingDr. Shaikh A.Khalique This document discusses various options for building and managing computer clusters, including do-it-yourself (DIY) clusters, pre-configured solutions like OSCAR and Rocks, and Microsoft solutions. It provides overviews of the software and processes for setting up and maintaining these different types of clusters.
CLUSTER COMPUTING



CLUSTER COMPUTINGKITE www.kitecolleges.com A cluster is a type of parallel computing system made up of interconnected standalone computers that work together as a single integrated resource. Clusters provide high-performance computing at a lower cost than specialized machines. As applications requiring large processing power become more common, the need for high-performance computing via clusters is increasing. Programming clusters can be done using message passing libraries like MPI, parallel languages like HPF, or parallel math libraries. Clusters make high-level computing more accessible to groups with modest resources.
Parallel computing and its applications



Parallel computing and its applicationsBurhan Ahmed Parallel computing is a type of computing architecture in which several processors execute or process an application or computation simultaneously. Parallel computing helps in performing large computations by dividing the workload between more than one processor, all of which work through the computation at the same time. Most supercomputers employ parallel computing principles to operate. Parallel computing is also known as parallel processing.
↓↓↓↓ Read More:
Watch my videos on snack here: --> --> http://sck.io/x-B1f0Iy
@ Kindly Follow my Instagram Page to discuss about your mental health problems-
-----> https://instagram.com/mentality_streak?utm_medium=copy_link
@ Appreciate my work:
-----> behance.net/burhanahmed1
Thank-you !
Introduction to parallel processing



Introduction to parallel processingPage Maker This presentation contains flynn's classification,difference between SIMD and MIMD some applications of parallel processing
Parallel Computing



Parallel ComputingAmeya Waghmare Please contact me to download this pres.A comprehensive presentation on the field of Parallel Computing.It's applications are only growing exponentially day by days.A useful seminar covering basics,its classification and implementation thoroughly.
Visit www.ameyawaghmare.wordpress.com for more info
Parallel computing persentation



Parallel computing persentationVIKAS SINGH BHADOURIA Parallel computing is computing architecture paradigm ., in which processing required to solve a problem is done in more than one processor parallel way.
Parallel processing extra



Parallel processing extraEr Girdhari Lal Kumawat This document discusses parallel computer architectures and focuses on multiple instruction multiple data (MIMD) systems. It describes tightly coupled symmetric multiprocessors (SMPs) that share memory and loosely coupled clusters that communicate over a network. SMPs have advantages of performance, availability and scalability but clusters provide greater scalability and availability through their distributed nature. Operating systems for clusters must handle failure management, load balancing and parallelizing applications across nodes.
Distributed Systems Real Life Applications



Distributed Systems Real Life ApplicationsAman Srivastava This document discusses distributed systems applications in real life, including three key areas: distributed rendering in computer graphics, peer-to-peer networks, and massively multiplayer online gaming. It describes how distributed rendering parallelizes graphics processing across multiple computers. Peer-to-peer networks are defined as decentralized networks where nodes act as both suppliers and consumers of resources. Examples of peer-to-peer applications include file sharing and content delivery networks. The document also outlines the challenges of designing multiplayer online games using a distributed architecture rather than a traditional client-server model.
Introduction to Parallel Computing



Introduction to Parallel ComputingAkhila Prabhakaran This document provides an introduction to parallel computing. It discusses serial versus parallel computing and how parallel computing involves simultaneously using multiple compute resources to solve problems. Common parallel computer architectures involve multiple processors on a single computer or connecting multiple standalone computers together in a cluster. Parallel computers can use shared memory, distributed memory, or hybrid memory architectures. The document outlines some of the key considerations and challenges in moving from serial to parallel code such as decomposing problems, identifying dependencies, mapping tasks to resources, and handling dependencies.
Parallel processing



Parallel processingrajshreemuthiah The document provides an overview of parallel processing and multiprocessor systems. It discusses Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies computers as SISD, SIMD, MISD, or MIMD based on whether they process single or multiple instructions and data in parallel. The goals of parallel processing are to reduce wall-clock time and solve larger problems. Multiprocessor topologies include uniform memory access (UMA) and non-uniform memory access (NUMA) architectures.
parallel processing



parallel processingSudarshan Mondal Serial computing involves breaking a problem into sequential instructions executed on a single processor. Parallel computing breaks a problem into discrete parts that can be solved concurrently on multiple processors. It allows for simultaneous execution of instructions to solve large, complex problems faster than serial computing. Modern computers are inherently parallel with multiple cores and hardware threads. Parallel computing is used across science, engineering, industry and commerce to save time and money, solve larger problems, provide concurrency, and make better use of underlying parallel hardware.
message passing vs shared memory



message passing vs shared memoryHamza Zahid This document compares message passing and shared memory architectures for parallel computing. It defines message passing as processors communicating through sending and receiving messages without a global memory, while shared memory allows processors to communicate through a shared virtual address space. The key difference is that message passing uses explicit communication through messages, while shared memory uses implicit communication through memory operations. It also discusses how the programming model and hardware architecture can be separated, with message passing able to support shared memory and vice versa.
Parallel architecture



Parallel architectureMr SMAK This document discusses parallel computers and architectures. It defines parallel computers as collections of processing elements that cooperate and communicate to solve problems fast. It then examines questions about parallel computers, different types of parallelism, and opportunities for parallel computing in scientific and commercial applications. Finally, it discusses fundamental issues in parallel architectures, including naming, synchronization, latency and bandwidth, and different parallel frameworks and models like shared memory, message passing, and data parallelism.
Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computing



Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computingVajira Thambawita This gives you an introduction to parallel and distributed computing. More details: https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
Parallel computing



Parallel computingvirend111 Parallel computing is the simultaneous use of multiple compute resources to solve a computational problem faster. It allows for larger problems to be solved and provides cost savings over serial computing. There are different models of parallelism including data parallelism and task parallelism. Flynn's taxonomy categorizes computer architectures as SISD, SIMD, MISD and MIMD based on how instructions and data are handled. Shared memory and distributed memory are two common architectures that differ in scalability and communication handling. Programming models include shared memory, message passing and data parallel approaches. Design considerations for parallel programs include partitioning work, communication between processes, and synchronization.
Paralle programming 2



Paralle programming 2Anshul Sharma There are two main types of parallel computers: shared memory multiprocessors and distributed memory multicomputers. Shared memory multiprocessors have multiple processors that can access a shared memory address space, while distributed memory multicomputers consist of separate computers connected by an interconnect network that communicate by message passing. Beowulf clusters are a type of distributed memory multicomputer made from interconnected commodity computers that provide high-performance computing at low cost. Programming distributed memory systems requires using message passing libraries to explicitly specify communication between processes on different computers.
Introduction to Parallel and Distributed Computing



Introduction to Parallel and Distributed ComputingSayed Chhattan Shah Introduction
Parallel Computer Memory Architectures
Parallel Programming Models
Design Parallel Programs
Distributed Systems
Cluster computing



Cluster computingpooja khatana A computer cluster is a group of connected computers that work together closely like a single computer. Clusters allow for greater computing power than a single computer by distributing workloads across nodes. They provide improved speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness compared to single computers or mainframes. Key aspects of clusters discussed include message passing between nodes, use for parallel processing, early cluster products, the role of operating systems and networks, and applications such as web serving, databases, e-commerce, and high-performance computing. Challenges also discussed include providing a single system image across nodes and efficient communication.
network ram parallel computing



network ram parallel computingNiranjana Ambadi This document summarizes a seminar on parallel computing. It defines parallel computing as performing multiple calculations simultaneously rather than consecutively. A parallel computer is described as a large collection of processing elements that can communicate and cooperate to solve problems fast. The document then discusses parallel architectures like shared memory, distributed memory, and shared distributed memory. It compares parallel computing to distributed computing and cluster computing. Finally, it discusses challenges in parallel computing like power constraints and programmability and provides examples of parallel applications like GPU processing and remote sensing.
Cluster computing



Cluster computingRaja' Masa'deh A cluster is a type of parallel or distributed computer system, which consists of a collection of inter-connected stand-alone computers working together as a single integrated computing resource.
Cluster Computers



Cluster Computersshopnil786 This is the presentation on clusters computing which includes information from other sources too including my own research and edition. I hope this will help everyone who required to know on this topic.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Design issues of dos



Design issues of dosvanamali_vanu This document provides an overview of distributed operating systems. It discusses the motivation for distributed systems including resource sharing, reliability, and computation speedup. It describes different types of distributed operating systems like network operating systems where users are aware of multiple machines, and distributed operating systems where users are not aware. It also covers network structures, topologies, communication structures, protocols, and provides an example of networking. The objectives are to provide a high-level overview of distributed systems and discuss the general structure of distributed operating systems.
Lecture 4 Cluster Computing



Lecture 4 Cluster ComputingDr. Shaikh A.Khalique This document discusses various options for building and managing computer clusters, including do-it-yourself (DIY) clusters, pre-configured solutions like OSCAR and Rocks, and Microsoft solutions. It provides overviews of the software and processes for setting up and maintaining these different types of clusters.
CLUSTER COMPUTING



CLUSTER COMPUTINGKITE www.kitecolleges.com A cluster is a type of parallel computing system made up of interconnected standalone computers that work together as a single integrated resource. Clusters provide high-performance computing at a lower cost than specialized machines. As applications requiring large processing power become more common, the need for high-performance computing via clusters is increasing. Programming clusters can be done using message passing libraries like MPI, parallel languages like HPF, or parallel math libraries. Clusters make high-level computing more accessible to groups with modest resources.
Parallel computing and its applications



Parallel computing and its applicationsBurhan Ahmed Parallel computing is a type of computing architecture in which several processors execute or process an application or computation simultaneously. Parallel computing helps in performing large computations by dividing the workload between more than one processor, all of which work through the computation at the same time. Most supercomputers employ parallel computing principles to operate. Parallel computing is also known as parallel processing.
↓↓↓↓ Read More:
Watch my videos on snack here: --> --> http://sck.io/x-B1f0Iy
@ Kindly Follow my Instagram Page to discuss about your mental health problems-
-----> https://instagram.com/mentality_streak?utm_medium=copy_link
@ Appreciate my work:
-----> behance.net/burhanahmed1
Thank-you !
Introduction to parallel processing



Introduction to parallel processingPage Maker This presentation contains flynn's classification,difference between SIMD and MIMD some applications of parallel processing
Parallel Computing



Parallel ComputingAmeya Waghmare Please contact me to download this pres.A comprehensive presentation on the field of Parallel Computing.It's applications are only growing exponentially day by days.A useful seminar covering basics,its classification and implementation thoroughly.
Visit www.ameyawaghmare.wordpress.com for more info
Parallel computing persentation



Parallel computing persentationVIKAS SINGH BHADOURIA Parallel computing is computing architecture paradigm ., in which processing required to solve a problem is done in more than one processor parallel way.
Parallel processing extra



Parallel processing extraEr Girdhari Lal Kumawat This document discusses parallel computer architectures and focuses on multiple instruction multiple data (MIMD) systems. It describes tightly coupled symmetric multiprocessors (SMPs) that share memory and loosely coupled clusters that communicate over a network. SMPs have advantages of performance, availability and scalability but clusters provide greater scalability and availability through their distributed nature. Operating systems for clusters must handle failure management, load balancing and parallelizing applications across nodes.
Distributed Systems Real Life Applications



Distributed Systems Real Life ApplicationsAman Srivastava This document discusses distributed systems applications in real life, including three key areas: distributed rendering in computer graphics, peer-to-peer networks, and massively multiplayer online gaming. It describes how distributed rendering parallelizes graphics processing across multiple computers. Peer-to-peer networks are defined as decentralized networks where nodes act as both suppliers and consumers of resources. Examples of peer-to-peer applications include file sharing and content delivery networks. The document also outlines the challenges of designing multiplayer online games using a distributed architecture rather than a traditional client-server model.
Introduction to Parallel Computing



Introduction to Parallel ComputingAkhila Prabhakaran This document provides an introduction to parallel computing. It discusses serial versus parallel computing and how parallel computing involves simultaneously using multiple compute resources to solve problems. Common parallel computer architectures involve multiple processors on a single computer or connecting multiple standalone computers together in a cluster. Parallel computers can use shared memory, distributed memory, or hybrid memory architectures. The document outlines some of the key considerations and challenges in moving from serial to parallel code such as decomposing problems, identifying dependencies, mapping tasks to resources, and handling dependencies.
Parallel processing



Parallel processingrajshreemuthiah The document provides an overview of parallel processing and multiprocessor systems. It discusses Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies computers as SISD, SIMD, MISD, or MIMD based on whether they process single or multiple instructions and data in parallel. The goals of parallel processing are to reduce wall-clock time and solve larger problems. Multiprocessor topologies include uniform memory access (UMA) and non-uniform memory access (NUMA) architectures.
parallel processing



parallel processingSudarshan Mondal Serial computing involves breaking a problem into sequential instructions executed on a single processor. Parallel computing breaks a problem into discrete parts that can be solved concurrently on multiple processors. It allows for simultaneous execution of instructions to solve large, complex problems faster than serial computing. Modern computers are inherently parallel with multiple cores and hardware threads. Parallel computing is used across science, engineering, industry and commerce to save time and money, solve larger problems, provide concurrency, and make better use of underlying parallel hardware.
message passing vs shared memory



message passing vs shared memoryHamza Zahid This document compares message passing and shared memory architectures for parallel computing. It defines message passing as processors communicating through sending and receiving messages without a global memory, while shared memory allows processors to communicate through a shared virtual address space. The key difference is that message passing uses explicit communication through messages, while shared memory uses implicit communication through memory operations. It also discusses how the programming model and hardware architecture can be separated, with message passing able to support shared memory and vice versa.
Parallel architecture



Parallel architectureMr SMAK This document discusses parallel computers and architectures. It defines parallel computers as collections of processing elements that cooperate and communicate to solve problems fast. It then examines questions about parallel computers, different types of parallelism, and opportunities for parallel computing in scientific and commercial applications. Finally, it discusses fundamental issues in parallel architectures, including naming, synchronization, latency and bandwidth, and different parallel frameworks and models like shared memory, message passing, and data parallelism.
Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computing



Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computingVajira Thambawita This gives you an introduction to parallel and distributed computing. More details: https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
Parallel computing



Parallel computingvirend111 Parallel computing is the simultaneous use of multiple compute resources to solve a computational problem faster. It allows for larger problems to be solved and provides cost savings over serial computing. There are different models of parallelism including data parallelism and task parallelism. Flynn's taxonomy categorizes computer architectures as SISD, SIMD, MISD and MIMD based on how instructions and data are handled. Shared memory and distributed memory are two common architectures that differ in scalability and communication handling. Programming models include shared memory, message passing and data parallel approaches. Design considerations for parallel programs include partitioning work, communication between processes, and synchronization.
Paralle programming 2



Paralle programming 2Anshul Sharma There are two main types of parallel computers: shared memory multiprocessors and distributed memory multicomputers. Shared memory multiprocessors have multiple processors that can access a shared memory address space, while distributed memory multicomputers consist of separate computers connected by an interconnect network that communicate by message passing. Beowulf clusters are a type of distributed memory multicomputer made from interconnected commodity computers that provide high-performance computing at low cost. Programming distributed memory systems requires using message passing libraries to explicitly specify communication between processes on different computers.
Introduction to Parallel and Distributed Computing



Introduction to Parallel and Distributed ComputingSayed Chhattan Shah Introduction
Parallel Computer Memory Architectures
Parallel Programming Models
Design Parallel Programs
Distributed Systems
Cluster computing



Cluster computingpooja khatana A computer cluster is a group of connected computers that work together closely like a single computer. Clusters allow for greater computing power than a single computer by distributing workloads across nodes. They provide improved speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness compared to single computers or mainframes. Key aspects of clusters discussed include message passing between nodes, use for parallel processing, early cluster products, the role of operating systems and networks, and applications such as web serving, databases, e-commerce, and high-performance computing. Challenges also discussed include providing a single system image across nodes and efficient communication.
network ram parallel computing



network ram parallel computingNiranjana Ambadi This document summarizes a seminar on parallel computing. It defines parallel computing as performing multiple calculations simultaneously rather than consecutively. A parallel computer is described as a large collection of processing elements that can communicate and cooperate to solve problems fast. The document then discusses parallel architectures like shared memory, distributed memory, and shared distributed memory. It compares parallel computing to distributed computing and cluster computing. Finally, it discusses challenges in parallel computing like power constraints and programmability and provides examples of parallel applications like GPU processing and remote sensing.
Similar to Cluster Computing (20)
Cluster computing



Cluster computingRaja' Masa'deh A cluster is a type of parallel or distributed computer system, which consists of a collection of inter-connected stand-alone computers working together as a single integrated computing resource.
Cluster Computers



Cluster Computersshopnil786 This is the presentation on clusters computing which includes information from other sources too including my own research and edition. I hope this will help everyone who required to know on this topic.
paradigms cloud.pptx



paradigms cloud.pptxgunvinit931 This document discusses different types of distributed computing paradigms including distributed systems, parallel computing, collaborative computing, and peer-to-peer computing. A distributed system consists of multiple components located on different machines that communicate to appear as a single system. Distributed systems provide benefits like scalability and fault tolerance. Parallel computing involves solving problems simultaneously using multiple processing elements. Collaborative computing facilitates group work through distributed technology. Peer-to-peer networks have nodes that are equal participants sharing resources and tasks.
Symmetric multiprocessing and Microkernel



Symmetric multiprocessing and MicrokernelManoraj Pannerselum Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves connecting two or more identical processors to a single shared main memory. The processors have equal access to I/O devices and are controlled by a single operating system instance. An SMP operating system manages resources so that users see a multiprogramming uniprocessor system. Key design issues for SMP include simultaneous processes, scheduling, synchronization, memory management, and fault tolerance.
A microkernel is a small operating system core that provides modular extensions. Less essential services are built as user mode servers that communicate through the microkernel via messages. This provides advantages like uniform interfaces, extensibility, flexibility, portability, and increased security.
cluster computing



cluster computinganjalibhandari11011995 This document provides an overview of cluster computing. It defines a cluster as a group of loosely coupled computers that work together closely to function as a single computer. Clusters improve speed and reliability over a single computer and are more cost-effective. Each node has its own operating system, memory, and sometimes file system. Programs use message passing to transfer data and execution between nodes. Clusters can provide low-cost parallel processing for applications that can be distributed. The document discusses cluster architecture, components, applications, and compares clusters to grids and cloud computing.
Cloud computing



Cloud computingZeeshan Bilal This document provides an overview of cloud computing and distributed systems. It discusses large scale distributed systems, cloud computing paradigms and models, MapReduce and Hadoop. MapReduce is introduced as a programming model for distributed computing problems that handles parallelization, load balancing and fault tolerance. Hadoop is presented as an open source implementation of MapReduce and its core components are HDFS for storage and the MapReduce framework. Example use cases and running a word count job on Hadoop are also outlined.
Cluster Computing



Cluster ComputingBOSS Webtech Cluster computing involves linking multiple computers together to act as a single system. There are three main types of computer clusters: high availability clusters which maintain redundant backup nodes for reliability, load balancing clusters which distribute workloads efficiently across nodes, and high-performance clusters which exploit parallel processing across nodes. Clusters offer benefits like increased processing power, cost efficiency, expandability, and high availability.
Cluster cmputing



Cluster cmputingKajal Thakkar A computer cluster is a group of loosely coupled computers that work together closely and can be viewed as a single computer. Clusters have evolved to improve speed and support applications like e-commerce and databases. The first commodity clustering product was ARCnet in 1977, and now Microsoft, Sun, and others offer clustering packages. Clusters significantly reduce the cost of processing power, eliminate single points of failure through availability, and can grow in capacity as nodes are added. They are commonly used for web services, databases, and computationally or data-intensive tasks. Programming clusters requires messaging between nodes since memory cannot be directly accessed between nodes.
System models for distributed and cloud computing



System models for distributed and cloud computingpurplesea This document discusses different types of distributed computing systems including clusters, peer-to-peer networks, grids, and clouds. It describes key characteristics of each type such as configuration, control structure, scale, and usage. The document also covers performance metrics, scalability analysis using Amdahl's Law, system efficiency considerations, and techniques for achieving fault tolerance and high system availability in distributed environments.
Parallel and Distributed Computing chapter 1



Parallel and Distributed Computing chapter 1AbdullahMunir32 Parallel and distributed computing systems use multiple computers simultaneously to solve large computational problems faster than a single computer. Parallel computing involves breaking a problem into parts that can be solved concurrently on different processors, while distributed computing uses multiple independent computers that coordinate via message passing to appear as a single system. These approaches improve scalability, allow problems too large for one computer to be solved, and provide high throughput to handle many users concurrently.
Overview of Distributed Systems



Overview of Distributed Systemsvampugani This document provides an overview of distributed systems. It discusses tightly-coupled and loosely-coupled multiprocessor systems, with loosely-coupled systems referring to distributed systems that have independent processors, memories, and operating systems. The document outlines some key properties of distributed systems, including that they consist of independent nodes that communicate through message passing, and accessing remote resources is more expensive than local resources. It also summarizes some advantages and challenges of distributed systems.
Distributed system notes unit I



Distributed system notes unit INANDINI SHARMA Distributed computing system is a collection of interconnected computers that appear as a single system. There are two types of computer architectures for distributed systems - tightly coupled and loosely coupled. In tightly coupled systems, processors share a single memory while in loosely coupled systems, processors have their own local memory and communicate through message passing. Distributed systems provide advantages like better price-performance ratio, resource sharing, reliability, and scalability but also introduce challenges around transparency, communication, performance, heterogeneity, and fault tolerance.
Cluster computing



Cluster computingreddivarihareesh This document provides an overview of cluster computing. It defines a cluster as multiple interconnected computers that function as a single system through software and networking. Clusters are used for high availability and high performance computing applications. The key components of a cluster are the nodes, network, and job scheduler. The document discusses different types of clusters and their applications, benefits like availability and scalability, and some limitations.
Cluster computing



Cluster computingVenkat Sai Sharath Mudhigonda A computer cluster is a group of tightly coupled computers that work together like a single computer (Paragraph 1). Clusters are commonly connected through fast local area networks and have evolved to support applications ranging from e-commerce to databases (Paragraph 2). A cluster uses interconnected standalone computers that cooperate to create the illusion of a single computer with parallel processing capabilities. Clusters provide benefits like reduced costs, high availability if components fail, and scalability by allowing addition of nodes (Paragraphs 3-4). The history of clusters began in the 1970s and operating systems like Linux are now commonly used (Paragraph 5). Clusters have architectures with interconnected nodes that appear as a single system to users (Paragraph 6). Clusters are categorized based on availability
Cloud computing1



Cloud computing1ali raza A cluster is a system of two or more connected computers that work together as a single system. There are three types of clusters: high availability clusters which provide continuous service if a node fails; load-balancing clusters which distribute requests across nodes; and high performance clusters which provide faster processing through unified effort. Clusters offer cost efficiency, processing speed, flexibility, and high availability of resources compared to mainframe computers.
Cluster Computing



Cluster ComputingAAKASH SINGH Cluster computing involves connecting multiple computers together to work as a single system. The document discusses the history, architecture, types (high performance, high availability, load balancing), components, advantages and disadvantages of cluster computing. It is commonly used for applications that require high performance computing such as web serving, email services, e-commerce sites, weather forecasting and more.
Wk6a



Wk6adanielm This document provides an introduction to distributed systems, including their key features and some related concepts. It discusses how distributed systems build upon networking to allow independent machines to act as a single system transparently to users. The document also mentions client-server architectures, advantages like economies of scale and fault tolerance, challenges around naming, operating systems, shared memory, and other issues in distributed environments.
CS8603_Notes_003-1_edubuzz360.pdf



CS8603_Notes_003-1_edubuzz360.pdfKishaKiddo This document provides an introduction to distributed systems including definitions, characteristics, motivation, and models. It discusses key topics such as message passing vs shared memory, synchronous vs asynchronous execution, and challenges in distributed system design. Models of distributed computation and logical time frameworks are also introduced.
distributed-systemsfghjjjijoijioj-chap3.pptx



distributed-systemsfghjjjijoijioj-chap3.pptxlencho3d This document discusses distributed systems concepts including processes, threads, virtualization, servers, and code migration. It defines processes and threads, explaining that threads allow for parallel computation within a process and are more lightweight than processes. It describes how threads are used in distributed systems to allow for overlapping communication and processing. The document also discusses virtualization techniques including process and hypervisor virtual machines. It outlines different server architectures and considerations for server design. Finally, it examines reasons for and models of code migration in distributed systems.
types of operating system an overview of the topics.pptx



types of operating system an overview of the topics.pptxPriyadharshiniG41 types of operating system an overview of the topics.pptx
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Adobe Illustrator CC Crack Version 2025?



Adobe Illustrator CC Crack Version 2025?yousfhashmi786 ➤ ►🌍📺📱👉 Click Here to Download Link 100% Working Link
https://click4pc.com/after-verification-click-go-to-download-page/
Adobe Illustrator Crack is a professional vector graphics design software used by graphic designers, illustrators, and artists to create .
AnyDesk 5.2.1 Crack License Key Full Version 2019 {Latest}



AnyDesk 5.2.1 Crack License Key Full Version 2019 {Latest}yousfhashmi786 ➤ ►🌍📺📱👉 Click Here to Download Link 100% Working Link
https://click4pc.com/after-verification-click-go-to-download-page/
AnyDesk is a popular remote desktop software that allows you to access your computer from anywhere in the world.
linearly separable and therefore a set of weights exist that are consistent ...



linearly separable and therefore a set of weights exist that are consistent ...mebibek_hu the system work 2
Linepro - Product Profile- Capacitive Panels



Linepro - Product Profile- Capacitive PanelsPaulMalpan1 Designed, developed and manufactured by Linepro- A customized Capsense touch panel with great touch sensitivity and elegant look.
the-importance-of-learning-french-140722055824-phpapp01.ppt



the-importance-of-learning-french-140722055824-phpapp01.pptLipicaJasujaWadhwa importance of learning french
ppt untuk seminar proposal dan persiapannya



ppt untuk seminar proposal dan persiapannyaRasidinmamakidin ppt untuk seminar proposal dan persiapannya
Microsoft Office 365 Crack Latest Version 2025?



Microsoft Office 365 Crack Latest Version 2025?yousfhashmi786 COPY PASTE LInK >>
https://click4pc.com/after-verification-click-go-to-download-page/
— Microsoft 365 (Office) is a powerful application designed to centralize all of your commonly used Office and Microsoft 365 applications in one ...
Computer Hardware using mostly in daily.



Computer Hardware using mostly in daily.manshajunaid205 The complete discuss in this topic
-- Computer Hardware --
Computer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer system that you can see and touch. These components work together to perform all computing tasks. ☝️☝️
荷兰代尔夫特理工大学毕业证书文凭定制TUDelft成绩单定制



荷兰代尔夫特理工大学毕业证书文凭定制TUDelft成绩单定制Taqyea 靠谱制作荷兰毕业证代尔夫特理工大学成绩单!【q微1954292140】帮您解决在荷兰代尔夫特理工大学未毕业难题(Technische Universiteit Delft)文凭购买、毕业证购买、大学文凭购买、大学毕业证购买、买文凭、日韩文凭、英国大学文凭、美国大学文凭、澳洲大学文凭、加拿大大学文凭(q微1954292140)新加坡大学文凭、新西兰大学文凭、爱尔兰文凭、西班牙文凭、德国文凭、教育部认证,买毕业证,毕业证购买,买大学文凭,购买日韩毕业证、英国大学毕业证、美国大学毕业证、澳洲大学毕业证、加拿大大学毕业证(q微1954292140)新加坡大学毕业证、新西兰大学毕业证、爱尔兰毕业证、西班牙毕业证、德国毕业证,回国证明,留信网认证,留信认证办理,学历认证。从而完成就业。代尔夫特理工大学毕业证办理,代尔夫特理工大学文凭办理,代尔夫特理工大学成绩单办理和真实留信认证、留服认证、代尔夫特理工大学学历认证。学院文凭定制,代尔夫特理工大学原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。
特殊原因导致无法毕业,也可以联系我们帮您办理相关材料:
1:在代尔夫特理工大学挂科了,不想读了,成绩不理想怎么办???
2:打算回国了,找工作的时候,需要提供认证《TUDelft成绩单购买办理代尔夫特理工大学毕业证书范本》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Technische Universiteit Delft Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办???荷兰毕业证购买,荷兰文凭购买,
3:回国了找工作没有代尔夫特理工大学文凭怎么办?有本科却要求硕士又怎么办?
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《荷兰毕业文凭证书快速办理代尔夫特理工大学学历认证定购》【q微1954292140】《论文没过代尔夫特理工大学正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理TUDelft毕业证,改成绩单《TUDelft毕业证明办理代尔夫特理工大学学位证书电子图在线定制服务》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Technische Universiteit Delft Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,代尔夫特理工大学Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
《代尔夫特理工大学录取通知书offer在线制作荷兰毕业证书办理TUDelft学历证书申请》【q微1954292140】学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【q微1954292140】办理代尔夫特理工大学毕业证(TUDelft毕业证书)成绩单水印【q微1954292140】代尔夫特理工大学offer/学位证、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作【q微1954292140】Buy Technische Universiteit Delft Diploma购买美国毕业证,购买英国毕业证,购买澳洲毕业证,购买加拿大毕业证,以及德国毕业证,购买法国毕业证(q微1954292140)购买荷兰毕业证、购买瑞士毕业证、购买日本毕业证、购买韩国毕业证、购买新西兰毕业证、购买新加坡毕业证、购买西班牙毕业证、购买马来西亚毕业证等。包括了本科毕业证,硕士毕业证。
荷兰文凭代尔夫特理工大学成绩单,TUDelft毕业证【q微1954292140】办理荷兰代尔夫特理工大学毕业证(TUDelft毕业证书)【q微1954292140】文凭代尔夫特理工大学offer/学位证办学位证、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决代尔夫特理工大学学历学位认证难题。
荷兰文凭购买,荷兰文凭定制,荷兰文凭补办。专业在线定制荷兰大学文凭,定做荷兰本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制荷兰Technische Universiteit Delft completion letter。在线快速补办荷兰本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买荷兰学位证、代尔夫特理工大学Offer,荷兰大学文凭在线购买。高仿真还原荷兰文凭证书和外壳,定制荷兰代尔夫特理工大学成绩单和信封。修改成绩单分数电子版TUDelft毕业证【q微1954292140】办理荷兰代尔夫特理工大学毕业证(TUDelft毕业证书)【q微1954292140】毕业证成绩单信封等材料最强攻略代尔夫特理工大学offer/学位证学历认证失败怎么办、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决代尔夫特理工大学学历学位认证难题。
如果您在英、加、美、澳、欧洲等留学过程中或回国后:
1、在校期间因各种原因未能顺利毕业《TUDelft成绩单工艺详解》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】《Buy Technische Universiteit Delft Transcript快速办理代尔夫特理工大学教育部学历认证书毕业文凭证书》,拿不到官方毕业证;
2、面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
3、不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
4、回国时间很长,忘记办理;
5、回国马上就要找工作《正式成绩单代尔夫特理工大学毕业证成绩单购买》【q微1954292140】《原版高仿成绩单TUDelft挂科处理解决方案》办给用人单位看;
6、企事业单位必须要求办理的;
7、需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口、申请留学生创业基金。
Spectrophotometer instrument basics -.pptx



Spectrophotometer instrument basics -.pptxmuthulakshmitc A spectrophotometer is an essential analytical instrument widely used in various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biology, physics, environmental science, clinical diagnostics, and materials science, for the quantitative analysis of substances based on their interaction with light. At its core, a spectrophotometer measures the amount of light that a chemical substance absorbs by determining the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through the sample solution. The fundamental principle behind the spectrophotometer is the Beer-Lambert law, which relates the absorption of light to the properties of the material through which the light is traveling. According to this law, the absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species in the material and the path length that the light travels through the sample. By exploiting this principle, a spectrophotometer provides a powerful, non-destructive means of identifying and quantifying substances in both qualitative and quantitative studies.
The construction of a spectrophotometer involves several key components, each playing a vital role in the overall functioning of the instrument. The first critical component is the light source. The choice of the light source depends on the range of wavelengths needed for analysis. For ultraviolet (UV) light, typically a deuterium lamp is used, while tungsten filament lamps are commonly used for the visible light range. In some advanced spectrophotometers, xenon lamps or other broad-spectrum sources may be used to cover a wider range of wavelengths. The light emitted from the source is then directed toward a monochromator, which isolates the desired wavelength of light from the full spectrum emitted by the lamp. Monochromators generally consist of a prism or a diffraction grating, which disperses the light into its component wavelengths. By rotating the monochromator, the instrument can select and pass a narrow band of wavelengths to the sample, ensuring that only light of the desired wavelength reaches the sample compartment.
The sample is typically held in a cuvette, a small transparent container made of quartz, glass, or plastic, depending on the wavelength range of interest. Quartz cuvettes are used for UV measurements since they do not absorb UV light, while plastic or glass cuvettes are sufficient for visible light applications. The path length of the cuvette, usually 1 cm, is a critical parameter because it influences the absorbance readings according to the Beer-Lambert law. Once the monochromatic light passes through the sample, it emerges with reduced intensity due to absorption by the sample. The transmitted light is then collected by a photodetector, which converts the light signal into an electrical signal. This electrical signal is proportional to the intensity of the transmitted light and is processed by the instrument’s electronics to calculate absorbance or transmittance values. These values are then give
Wondershare Filmora Crack Free Download Latest 2025



Wondershare Filmora Crack Free Download Latest 2025yousfhashmi786 ➤ ►🌍📺📱👉 Click Here to Download Link 100% Working Link
https://click4pc.com/after-verification-click-go-to-download-page/
Wondershare Filmora is an very impressive video editing software. It allows you to edit and convert videos and share them on a variety of different hosting ...
MiniTool Partition Wizard Professional Edition 10.2.1 Crack



MiniTool Partition Wizard Professional Edition 10.2.1 Crackyousfhashmi786 ➤ ►🌍📺📱👉 Click Here to Download Link 100% Working
Link https://click4pc.com/after-verification-click-go-to-download-page/
MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro Ultimate for Windows PC, is the best professional Partition Manager for Advanced Users! With this, you can Manage .
Ad
Cluster Computing
- 1. Cluster Computing Presented by: Biswaraj Baral NCIT-ME-II
- 2. Outlines: Introduction Objective/Design requirements Cluster Configuration Design Issue Clusters Computer Architecture Implementation: Blade servers Clusters compared to SMP
- 3. Introduction: Super, Mainframe computers are not cost effective Cluster technology have been developed that allow multiple low cost computers to work in coordinated fashion to process applications. An alternative to symmetric multiprocessing as an approach to providing high performance and is attractive for server applications. Group of interconnected, whole computers working together as a unified computing resources that can create illusion of being one machine. The term whole computer means a system that can run on its own, apart from the cluster; each computer in a cluster is typically referred to as a node. Composed of many commodity computers , linked together by a high-speed dedicated network.
- 4. Objective/Design requirements: Absolute Scalability Incremental Scalability High Availability Superior Price/ Performance
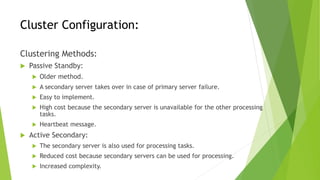
- 5. Cluster Configuration: Clustering Methods: Passive Standby: Older method. A secondary server takes over in case of primary server failure. Easy to implement. High cost because the secondary server is unavailable for the other processing tasks. Heartbeat message. Active Secondary: The secondary server is also used for processing tasks. Reduced cost because secondary servers can be used for processing. Increased complexity.
- 6. Separate Servers: No disks shared between systems. High performance as well as high availability Scheduling software needed for load balancing Data must be constantly copied among systems so that each systems has access to the current data of the other system. High availability, Communication overhead
- 7. Shared nothing and shared Memory: Reduce the communication overhead. Servers connected to common disk. Shared Nothing: common disks are partitioned into volumes, and each volume owned by a single computer. Shared Disk: Multiple computers share the same disks at the same time, so that each computer has access to all the volumes on all of the disks. Requires Locking Mechanism. (b) Shared Disk
- 8. Operating system design Issues: Failure Management: How failures are managed by a cluster depends on the clustering method used. Two approaches: Highly Available clusters: These clusters are designed to provide uninterrupted availability of data or service (typically web services) to the end user community. If a node fails, the service can be restored without affecting the availability of the services provided by the cluster, while the application will still be available, there will be a performance drop due to missing node. Failover and failback Fault tolerant clusters: Ensures that all resources are always available. This is achieved by the use of redundant shared disks and mechanisms for backing out uncommitted transactions and committing completed transactions. Load Balancing: This type of cluster distributes the incoming requests for resources or content among multiple nodes running the same program or having the same content. Every node in the cluster is able to handle requests for the same content or application. Middleware mechanisms need to recognize that services can appear on different members of cluster and may migrate from one member to another. Almost all load balancing clusters are HA clusters.
- 9. Parallelizing Computation: Parallelizing Compiler: Compiler determines which part of an application can be executed in parallel at compile time. Split off to assigned to different computers in clusters. Performance depends on the nature of the problem and how well the compiler is designed. Difficult to design such compiler. Parallelized application: The programmer writes the application from the outset to run on a cluster, and uses message passing to move data, as required, between cluster nodes. This places a high burden on the programmer but may be the best approach for exploiting clusters for some applications. Parametric computing: Can be used if the essence of the application is an program that must be executed a large number of times, each time with a different set of starting conditions or parameters. Eg-Simulation model
- 11. Individual computers are connected by some high-speed LAN or switch hardware. Each computer is capable of operating independently. Middleware layer of software is installed in each computer to enable cluster operation. The middleware provides a unified system image to the user, known as a single-system image. The middleware is responsible for providing high availability, by means of load balancing and responding to failures in individual components. Following are the desirable cluster middleware services and functions: Single entry point Single file hierarchy Single control point Single virtual networking (any node can access any other point ) Single memory space Single job-management system Single user interface Single I/O space Single process space Checkpointing (saves the process state, recovery after failure) Process migration (load balancing)
- 12. The last four items in the preceding list enhance the availability of the cluster. Others are concerned with providing a single system image. Implementation: Blade Servers Is a server architecture that houses multiple server modules (‘blades’) in a single chassis. Used in data centres. Increase server density, lowers powers and cooling costs, ease server expansion and simplifies data centre management.
- 13. Ethernet configuration for Massive Blade Server Site
- 14. Clusters Compared to SMP: Both clusters and symmetric multiprocessors provide a configuration with multiple processors to support high-demand applications. Both solutions are commercially available. SMP: the processing of programs by multiple processors that share a common OS and memory. Whereas , in clusters individual systems are tied together. The aim of SMP is time saving and of cluster computing is high availability. SMP is easier to manage and configure than cluster. SMP takes less physical space and draws less power than a comparable cluster. SMP products are well established and stable. Cluster: high performance server market. Clusters are superior to SMPs in terms of incremental and absolute scalability. Clusters are also superior in terms of availability, because all components of the system can readily be made highly redundant.
- 15. Thank you!







