Computer architecture memory system
Download as pptx, pdf7 likes8,371 views
Computer architecture memory system seminar Mustansiriya University Department of Education Computer Science
1 of 30
Downloaded 146 times





























Recommended
Memory organization (Computer architecture)



Memory organization (Computer architecture)Sandesh Jonchhe Memory is organized in a hierarchy with different levels providing trade-offs between speed and cost.
- Cache memory sits between the CPU and main memory for fastest access.
- Main memory (RAM) is where active programs and data reside and is faster than auxiliary memory but more expensive.
- Auxiliary memory (disks, tapes) provides backup storage and is slower than main memory but larger and cheaper.
Virtual memory manages this hierarchy through address translation techniques like paging that map virtual addresses to physical locations, allowing programs to access more memory than physically available. When data is needed from auxiliary memory a page fault occurs and page replacement algorithms determine what data to remove from main memory.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnuj Modi Cache memory is a small, fast memory located between the CPU and main memory. It stores copies of frequently used instructions and data to accelerate access and improve performance. There are different mapping techniques for cache including direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping. When the cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU and FIFO are used to determine which content to remove. The cache can write to main memory using either a write-through or write-back policy.
Computer Organisation & Architecture (chapter 1) 



Computer Organisation & Architecture (chapter 1) Subhasis Dash This document discusses the basic organization and design of computers. It covers topics such as architecture versus organization, functional units like the arithmetic logic unit and control unit, instruction formats, processor registers, stored program concepts, basic operational concepts like loading and storing data, memory access, and factors that impact performance such as pipelining and instruction set design. The document provides an overview of fundamental computer hardware components and operations.
Java package



Java packageCS_GDRCST This presentation introduces Java packages, including system packages that are part of the Java API and user-defined packages. It discusses how packages organize related classes and interfaces, the structure of package names and directories, and how to create and access packages. Packages provide advantages like grouping related code, preventing name collisions, and improving reusability.
CPU (Central Processing Units)



CPU (Central Processing Units)Prabin Maharjan The document discusses the central processing unit (CPU). It describes the CPU as the multipurpose, programmable component of a computer that interprets instructions and performs logical and arithmetic operations. The CPU is composed of an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs calculations, a control unit (CU) that directs signals between memory and the ALU, and register arrays that temporarily store processed data. Factors like clock rate, memory size, and instruction set complexity can impact a CPU's processing speed. The CPU executes a cycle of fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, executing operations, and storing results.
Cyber Security



Cyber SecurityBhandari Hìmáñßhü The document discusses an introduction to cyber security presented by Himansh Bhandari. It defines cyber security as the body of technologies, processes, and practices designed to protect networks, devices, programs, and data from attack, damage, or unauthorized access. It discusses the history and evolution of the internet. It also covers types of malware like viruses, worms, Trojan horses and spyware. It discusses types of hackers like white hat, grey hat and black hat hackers. It provides information on implementing cyber security for mobile phones, banking and in India. It highlights major cyber security problems like viruses, hackers, malware and password cracking and discusses solutions to prevent them.
Instruction pipeline: Computer Architecture



Instruction pipeline: Computer ArchitectureInteX Research Lab Pipelining is an speed up technique where multiple instructions are overlapped in execution on a processor.
It is an important topic in Computer Architecture.
This slide try to relate the problem with real life scenario for easily understanding the concept and show the major inner mechanism.
3-phase circuit



3-phase circuitLong Thang Pham Engineering review on AC circuit steady state analysis.
Presentation lecture for energy engineering class.
Course: MS in Renewable Energy Engineering, Oregon institute of technology
Computer organization memory



Computer organization memoryDeepak John The document discusses the memory system in computers including main memory, cache memory, and different types of memory chips. It provides details on the following key points in 3 sentences:
The document discusses the different levels of memory hierarchy including main memory, cache memory, and auxiliary memory. It describes the basic concepts of memory including addressing schemes, memory access time, and memory cycle time. Examples of different types of memory chips are discussed such as SRAM, DRAM, ROM, and cache memory organization and mapping techniques.
Virtual memory



Virtual memoryAnuj Modi The document discusses the concept of virtual memory. Virtual memory allows a program to access more memory than what is physically available in RAM by storing unused portions of the program on disk. When a program requests data that is not currently in RAM, it triggers a page fault that causes the needed page to be swapped from disk into RAM. This allows the illusion of more memory than physically available through swapping pages between RAM and disk as needed by the program during execution.
Direct memory access



Direct memory accessshubham kuwar This document discusses different types of data transfer modes between I/O devices and memory, including programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). It explains that DMA allows I/O devices to access memory directly without CPU intervention by using a DMA controller. The basic operations of DMA include the DMA controller gaining control of the system bus, transferring data directly between memory and I/O devices by updating address and count registers, and then relinquishing control back to the CPU. Different DMA transfer techniques like byte stealing, burst, and continuous modes are also covered.
Direct memory access



Direct memory accessRoshan kumar sahu This document discusses Direct Memory Access (DMA). It defines DMA as allowing hardware subsystems like disk drives, graphics cards, and network cards to access system memory independently of the CPU. It describes the principles of DMA in offloading data transfers from the CPU. It also outlines the different DMA operation modes of single transfer, block transfer, and burst block transfer. Uses of DMA include providing high performance I/O and zero copy implementations, while limitations include unpredictable behavior if writing to flash without setting flags.
Coa module1



Coa module1cs19club The document provides an overview of computer organization and architecture. It discusses the basic structure of computers including functional units like the CPU, memory, I/O devices, and buses. It covers topics like data and instruction representation, memory operations, interrupts, and bus structures. The document also provides a brief history of computer development from mechanical calculators to modern integrated circuit computers. It defines key concepts like software, system software, and discusses the role of the control unit in coordinating functional units.
Types of Addressing modes- COA



Types of Addressing modes- COARuchi Maurya Addressing mode is the way of addressing a memory location in instruction. Microcontroller needs data or operands on which the operation is to be performed. The method of specifying source of operand and output of result in an instruction is known as addressing mode.
There are various methods of giving source and destination address in instruction, thus there are various types of Addressing Modes. Here you will find the different types of Addressing Modes that are supported in Micro Controller 8051. Types of Addressing Modes are explained below:
1.Register Addressing Mode
2.Direct Addressing Mode
3.Register Indirect Addressing Mode
4.Immediate Addressing Mode
5.Index Addressing Mode
Explanation:
Register Addressing Mode: In this addressing mode, the source of data or destination of result is Register. In this type of addressing mode the name of the register is given in the instruction where the data to be read or result is to be stored.
Example: ADD A, R5 ( The instruction will do the addition of data in Accumulator with data in register R5)
Direct Addressing Mode: In this type of Addressing Mode, the address of data to be read is directly given in the instruction. In case, for storing result the address given in instruction is used to store the result.
Example: MOV A, 46H ( This instruction will move the contents of memory location 46H to Accumulator)
Register Indirect Addressing Mode: In Register Indirect Addressing Mode, as its name suggests the data is read or stored in register indirectly. That is, we provide the register in the instruction, in which the address of the other register is stored or which points to other register where data is stored or to be stored.
Example: MOV A, @R0 ( This instruction will move the data to accumulator from the register whose address is stored in register R0 ).
Also Read: Architecture Of 8051
Immediate Addressing Mode : In Immediate Addressing Mode , the data immediately follows the instruction. This means that data to be used is already given in the instruction itself.
Example: MOV A, #25H ( This instruction will move the data 25H to Accumulator. The # sign shows that preceding term is data, not the address.)
Index Addressing Mode: Offset is added to the base index register to form the effective address if the memory location.This Addressing Mode is used for reading lookup tables in Program Memory. The Address of the exact location of the table is formed by adding the Accumulator Data to the base pointer.
Example: MOVC, @A+DPTR ( This instruction will move the data from the memory to Accumulator; the address is made by adding the contents of Accumulator and Data Pointer.
Cache Memory



Cache MemorySubid Biswas The document discusses cache memory and provides information on various aspects of cache memory including:
- Introduction to cache memory including its purpose and levels.
- Cache structure and organization including cache row entries, cache blocks, and mapping techniques.
- Performance of cache memory including factors like cycle count and hit ratio.
- Cache coherence in multiprocessor systems and coherence protocols.
- Synchronization mechanisms used in multiprocessor systems for cache coherence.
- Paging techniques used in cache memory including address translation using page tables and TLBs.
- Replacement algorithms used to determine which cache blocks to replace when the cache is full.
Input Output Organization



Input Output OrganizationKamal Acharya The document discusses various methods for input/output (IO) in computer systems, including IO interfaces, programmed IO, interrupt-initiated IO, direct memory access (DMA), and input-output processors (IOPs). It describes how each method facilitates the transfer of data between the CPU, memory, and external IO devices.
Memory Hierarchy



Memory Hierarchychauhankapil The document discusses the memory hierarchy in computers. It describes the different levels of memory from fastest to slowest as register memory, cache memory, main memory (RAM and ROM), and auxiliary memory (magnetic tapes, hard disks, etc.). The main memory directly communicates with the CPU while the auxiliary memory provides backup storage and needs to transfer data to main memory to be accessed by the CPU. A cache memory is also used to increase processing speed.
Storage Structure in OS



Storage Structure in OSUniSoftCorner Pvt Ltd India. This document discusses different types of computer memory structures. It introduces registers and cache memory as the fastest types of volatile memory closest to the CPU. Registers are very small memory locations inside the CPU used to store instructions and data during processing. Cache memory is faster than main memory and stores frequently used data and instructions from main memory. Volatile memory loses its data when power is removed, while non-volatile memory retains data permanently in storage devices like hard drives, USB drives, and optical discs.
Dma transfer



Dma transfergmnithya The document describes the process of DMA transfer in a computer system. It explains that the DMA controller requests a transfer using the DMA request line and requests control of the buses from the CPU using the bus request signal. The CPU then grants control of the buses to the DMA controller using the bus grant signal, allowing the DMA controller to directly access memory and transfer data using the address bus, data bus, read/write lines, and device/register select lines. When the transfer is complete, the DMA controller interrupts the CPU.
Computer organization and architecture



Computer organization and architectureSubesh Kumar Yadav This document discusses computer instruction and addressing modes. It covers basic instruction types like data transfers, arithmetic/logical operations, program control, and I/O transfers. It also describes common addressing modes like register, immediate, indirect, indexed, relative, auto-increment and auto-decrement that allow flexible access to operands in memory and registers. Instruction execution involves fetching and executing instructions sequentially based on the program counter until a branch instruction redirects execution.
Memory hierarchy



Memory hierarchyMahesh Kumar Attri The document discusses the memory hierarchy in computers. It explains that main memory communicates directly with the CPU, while auxiliary memory devices like magnetic tapes and disks provide backup storage. The total memory is organized in a hierarchy from slow but high-capacity auxiliary devices to faster main memory to an even smaller and faster cache memory. The goal is to maximize access speed while minimizing costs. Cache memory helps speed access to frequently used data and programs.
Thrashing allocation frames.43



Thrashing allocation frames.43myrajendra This document discusses thrashing and allocation of frames in an operating system. It defines thrashing as when a processor spends most of its time swapping pieces of processes in and out rather than executing user instructions. This leads to low CPU utilization. It also discusses how to allocate a minimum number of frames to each process to prevent thrashing and ensure efficient paging.
Memory mapping



Memory mappingSnehalataAgasti Cache memory is located between the processor and main memory. It is smaller and faster than main memory. There are two types of cache memory policies - write-back and write-through. Mapping is a technique that maps CPU-generated memory addresses to cache lines. There are three types of mapping - direct, associative, and set associative. Direct mapping maps each main memory block to a single cache line using the formula: cache line number = main memory block number % number of cache lines. This can cause conflict misses.
Instruction codes



Instruction codespradeepa velmurugan An instruction code consists of an operation code and operand(s) that specify the operation to perform and data to use. Operation codes are binary codes that define operations like addition, subtraction, etc. Early computers stored programs and data in separate memory sections and used a single accumulator register. Modern computers have multiple registers for temporary storage and performing operations faster than using only memory. Computer instructions encode an operation code and operand fields to specify the basic operations to perform on data stored in registers or memory.
Auxiliary memory



Auxiliary memoryYuvrajVyas2 This is the PPT for Diploma Engineering Student 4th sem subject Computer Organization And Architecture.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnsari Maviya About Cache Memory
working of cache memory
levels of cache memory
mapping techniques for cache memory
1. direct mapping techniques
2. Fully associative mapping techniques
3. set associative mapping techniques
Cache memroy organization
cache coherency
every thing in detail
Operating system memory management



Operating system memory managementrprajat007 Operating System
Topic Memory Management
for Btech/Bsc (C.S)/BCA...
Memory management is the functionality of an operating system which handles or manages primary memory. Memory management keeps track of each and every memory location either it is allocated to some process or it is free. It checks how much memory is to be allocated to processes. It decides which process will get memory at what time. It tracks whenever some memory gets freed or unallocated and correspondingly it updates the status.
04 Cache Memory



04 Cache MemoryJeanie Delos Arcos The document summarizes key characteristics of cache memory including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, performance, physical types, organization, and hierarchy. It discusses cache memory in terms of where it is located (internal or external to the CPU), its typical sizes (word, block), access techniques (sequential, random, associative), performance metrics (access time, transfer rate), common physical implementations (SRAM, disk), and organizational aspects like mapping functions, replacement algorithms, and write policies. A cache sits between the CPU and main memory, using fast but small memory to speed up access to frequently used data from larger but slower main memory.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Computer organization memory



Computer organization memoryDeepak John The document discusses the memory system in computers including main memory, cache memory, and different types of memory chips. It provides details on the following key points in 3 sentences:
The document discusses the different levels of memory hierarchy including main memory, cache memory, and auxiliary memory. It describes the basic concepts of memory including addressing schemes, memory access time, and memory cycle time. Examples of different types of memory chips are discussed such as SRAM, DRAM, ROM, and cache memory organization and mapping techniques.
Virtual memory



Virtual memoryAnuj Modi The document discusses the concept of virtual memory. Virtual memory allows a program to access more memory than what is physically available in RAM by storing unused portions of the program on disk. When a program requests data that is not currently in RAM, it triggers a page fault that causes the needed page to be swapped from disk into RAM. This allows the illusion of more memory than physically available through swapping pages between RAM and disk as needed by the program during execution.
Direct memory access



Direct memory accessshubham kuwar This document discusses different types of data transfer modes between I/O devices and memory, including programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). It explains that DMA allows I/O devices to access memory directly without CPU intervention by using a DMA controller. The basic operations of DMA include the DMA controller gaining control of the system bus, transferring data directly between memory and I/O devices by updating address and count registers, and then relinquishing control back to the CPU. Different DMA transfer techniques like byte stealing, burst, and continuous modes are also covered.
Direct memory access



Direct memory accessRoshan kumar sahu This document discusses Direct Memory Access (DMA). It defines DMA as allowing hardware subsystems like disk drives, graphics cards, and network cards to access system memory independently of the CPU. It describes the principles of DMA in offloading data transfers from the CPU. It also outlines the different DMA operation modes of single transfer, block transfer, and burst block transfer. Uses of DMA include providing high performance I/O and zero copy implementations, while limitations include unpredictable behavior if writing to flash without setting flags.
Coa module1



Coa module1cs19club The document provides an overview of computer organization and architecture. It discusses the basic structure of computers including functional units like the CPU, memory, I/O devices, and buses. It covers topics like data and instruction representation, memory operations, interrupts, and bus structures. The document also provides a brief history of computer development from mechanical calculators to modern integrated circuit computers. It defines key concepts like software, system software, and discusses the role of the control unit in coordinating functional units.
Types of Addressing modes- COA



Types of Addressing modes- COARuchi Maurya Addressing mode is the way of addressing a memory location in instruction. Microcontroller needs data or operands on which the operation is to be performed. The method of specifying source of operand and output of result in an instruction is known as addressing mode.
There are various methods of giving source and destination address in instruction, thus there are various types of Addressing Modes. Here you will find the different types of Addressing Modes that are supported in Micro Controller 8051. Types of Addressing Modes are explained below:
1.Register Addressing Mode
2.Direct Addressing Mode
3.Register Indirect Addressing Mode
4.Immediate Addressing Mode
5.Index Addressing Mode
Explanation:
Register Addressing Mode: In this addressing mode, the source of data or destination of result is Register. In this type of addressing mode the name of the register is given in the instruction where the data to be read or result is to be stored.
Example: ADD A, R5 ( The instruction will do the addition of data in Accumulator with data in register R5)
Direct Addressing Mode: In this type of Addressing Mode, the address of data to be read is directly given in the instruction. In case, for storing result the address given in instruction is used to store the result.
Example: MOV A, 46H ( This instruction will move the contents of memory location 46H to Accumulator)
Register Indirect Addressing Mode: In Register Indirect Addressing Mode, as its name suggests the data is read or stored in register indirectly. That is, we provide the register in the instruction, in which the address of the other register is stored or which points to other register where data is stored or to be stored.
Example: MOV A, @R0 ( This instruction will move the data to accumulator from the register whose address is stored in register R0 ).
Also Read: Architecture Of 8051
Immediate Addressing Mode : In Immediate Addressing Mode , the data immediately follows the instruction. This means that data to be used is already given in the instruction itself.
Example: MOV A, #25H ( This instruction will move the data 25H to Accumulator. The # sign shows that preceding term is data, not the address.)
Index Addressing Mode: Offset is added to the base index register to form the effective address if the memory location.This Addressing Mode is used for reading lookup tables in Program Memory. The Address of the exact location of the table is formed by adding the Accumulator Data to the base pointer.
Example: MOVC, @A+DPTR ( This instruction will move the data from the memory to Accumulator; the address is made by adding the contents of Accumulator and Data Pointer.
Cache Memory



Cache MemorySubid Biswas The document discusses cache memory and provides information on various aspects of cache memory including:
- Introduction to cache memory including its purpose and levels.
- Cache structure and organization including cache row entries, cache blocks, and mapping techniques.
- Performance of cache memory including factors like cycle count and hit ratio.
- Cache coherence in multiprocessor systems and coherence protocols.
- Synchronization mechanisms used in multiprocessor systems for cache coherence.
- Paging techniques used in cache memory including address translation using page tables and TLBs.
- Replacement algorithms used to determine which cache blocks to replace when the cache is full.
Input Output Organization



Input Output OrganizationKamal Acharya The document discusses various methods for input/output (IO) in computer systems, including IO interfaces, programmed IO, interrupt-initiated IO, direct memory access (DMA), and input-output processors (IOPs). It describes how each method facilitates the transfer of data between the CPU, memory, and external IO devices.
Memory Hierarchy



Memory Hierarchychauhankapil The document discusses the memory hierarchy in computers. It describes the different levels of memory from fastest to slowest as register memory, cache memory, main memory (RAM and ROM), and auxiliary memory (magnetic tapes, hard disks, etc.). The main memory directly communicates with the CPU while the auxiliary memory provides backup storage and needs to transfer data to main memory to be accessed by the CPU. A cache memory is also used to increase processing speed.
Storage Structure in OS



Storage Structure in OSUniSoftCorner Pvt Ltd India. This document discusses different types of computer memory structures. It introduces registers and cache memory as the fastest types of volatile memory closest to the CPU. Registers are very small memory locations inside the CPU used to store instructions and data during processing. Cache memory is faster than main memory and stores frequently used data and instructions from main memory. Volatile memory loses its data when power is removed, while non-volatile memory retains data permanently in storage devices like hard drives, USB drives, and optical discs.
Dma transfer



Dma transfergmnithya The document describes the process of DMA transfer in a computer system. It explains that the DMA controller requests a transfer using the DMA request line and requests control of the buses from the CPU using the bus request signal. The CPU then grants control of the buses to the DMA controller using the bus grant signal, allowing the DMA controller to directly access memory and transfer data using the address bus, data bus, read/write lines, and device/register select lines. When the transfer is complete, the DMA controller interrupts the CPU.
Computer organization and architecture



Computer organization and architectureSubesh Kumar Yadav This document discusses computer instruction and addressing modes. It covers basic instruction types like data transfers, arithmetic/logical operations, program control, and I/O transfers. It also describes common addressing modes like register, immediate, indirect, indexed, relative, auto-increment and auto-decrement that allow flexible access to operands in memory and registers. Instruction execution involves fetching and executing instructions sequentially based on the program counter until a branch instruction redirects execution.
Memory hierarchy



Memory hierarchyMahesh Kumar Attri The document discusses the memory hierarchy in computers. It explains that main memory communicates directly with the CPU, while auxiliary memory devices like magnetic tapes and disks provide backup storage. The total memory is organized in a hierarchy from slow but high-capacity auxiliary devices to faster main memory to an even smaller and faster cache memory. The goal is to maximize access speed while minimizing costs. Cache memory helps speed access to frequently used data and programs.
Thrashing allocation frames.43



Thrashing allocation frames.43myrajendra This document discusses thrashing and allocation of frames in an operating system. It defines thrashing as when a processor spends most of its time swapping pieces of processes in and out rather than executing user instructions. This leads to low CPU utilization. It also discusses how to allocate a minimum number of frames to each process to prevent thrashing and ensure efficient paging.
Memory mapping



Memory mappingSnehalataAgasti Cache memory is located between the processor and main memory. It is smaller and faster than main memory. There are two types of cache memory policies - write-back and write-through. Mapping is a technique that maps CPU-generated memory addresses to cache lines. There are three types of mapping - direct, associative, and set associative. Direct mapping maps each main memory block to a single cache line using the formula: cache line number = main memory block number % number of cache lines. This can cause conflict misses.
Instruction codes



Instruction codespradeepa velmurugan An instruction code consists of an operation code and operand(s) that specify the operation to perform and data to use. Operation codes are binary codes that define operations like addition, subtraction, etc. Early computers stored programs and data in separate memory sections and used a single accumulator register. Modern computers have multiple registers for temporary storage and performing operations faster than using only memory. Computer instructions encode an operation code and operand fields to specify the basic operations to perform on data stored in registers or memory.
Auxiliary memory



Auxiliary memoryYuvrajVyas2 This is the PPT for Diploma Engineering Student 4th sem subject Computer Organization And Architecture.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnsari Maviya About Cache Memory
working of cache memory
levels of cache memory
mapping techniques for cache memory
1. direct mapping techniques
2. Fully associative mapping techniques
3. set associative mapping techniques
Cache memroy organization
cache coherency
every thing in detail
Operating system memory management



Operating system memory managementrprajat007 Operating System
Topic Memory Management
for Btech/Bsc (C.S)/BCA...
Memory management is the functionality of an operating system which handles or manages primary memory. Memory management keeps track of each and every memory location either it is allocated to some process or it is free. It checks how much memory is to be allocated to processes. It decides which process will get memory at what time. It tracks whenever some memory gets freed or unallocated and correspondingly it updates the status.
04 Cache Memory



04 Cache MemoryJeanie Delos Arcos The document summarizes key characteristics of cache memory including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, performance, physical types, organization, and hierarchy. It discusses cache memory in terms of where it is located (internal or external to the CPU), its typical sizes (word, block), access techniques (sequential, random, associative), performance metrics (access time, transfer rate), common physical implementations (SRAM, disk), and organizational aspects like mapping functions, replacement algorithms, and write policies. A cache sits between the CPU and main memory, using fast but small memory to speed up access to frequently used data from larger but slower main memory.
Similar to Computer architecture memory system (20)
Chapter 8 computer memory system overview



Chapter 8 computer memory system overviewAhlamAli20 The document discusses various aspects of computer memory systems including:
- Memory can be internal (e.g. main memory, cache) or external (e.g. disks, tapes). Internal memory is faster but has lower capacity, while external memory is slower but can store more data.
- Memory is characterized by its access method (e.g. random, sequential), capacity, units of transfer (e.g. words, blocks), and performance parameters like access time and transfer rate.
- Common semiconductor memory types include RAM (random access, volatile), ROM (read-only, non-volatile), and flash memory. RAM can be static or dynamic.
MEMORY & I/O SYSTEMS 



MEMORY & I/O SYSTEMS Amirthavalli Senthil Memory Hierarchy – memory technologies – Cache Memory – Performance Considerations, Virtual Memory, TLB’s – Accessing I/O devices – Interrupts – Direct Memory Access – Bus Structure – Bus operation.
COA notes



COA notesShrutiKushwaha29 The document discusses computer memory systems and cache memory principles. It provides an overview of:
- The memory hierarchy, which uses different memory technologies arranged in order of decreasing cost per bit, increasing capacity, and increasing access time. This hierarchy satisfies the conflicting demands of large capacity, fast speed, and low cost.
- Cache memory, which sits between the processor and main memory in the hierarchy. Cache memory exploits locality of reference to improve average memory access time.
- Characteristics of different levels of memory, including location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, physical types, volatility, and erasability. Faster but smaller and more expensive memories are higher in the hierarchy to satisfy performance needs.
ch-5 COA\szdghfjgkvjbmyughbhjtngfbvc.pptx



ch-5 COA\szdghfjgkvjbmyughbhjtngfbvc.pptxFiraolGadissa Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that organizes software design around data, or objects, rather than functions and logic. It is widely used for developing complex, scalable, and maintainable software systems. The core principles of OOP include encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, and polymorphism.
Key Concepts of OOP
Encapsulation: This involves bundling data and methods that operate on that data within a single unit, called an object. It helps protect the internal state of an object from external interference23.
Abstraction: This principle focuses on exposing only necessary information while hiding complex details. It allows users to interact with objects without knowing their internal workings23.
Inheritance: This feature enables a new class (subclass) to inherit properties and behaviors from an existing class (superclass), promoting code reuse and hierarchical organization23.
Polymorphism: This allows objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common superclass. It enables multiple behaviors to be implemented through a common interface23.
Object Technology and Programming Environment
Object Technology: This refers to the use of objects to model real-world entities in software development. It includes classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation7.
Programming Environment: OOP is typically supported in class-based languages like Java, Python, and C++. These environments provide tools for designing, developing, and testing object-oriented software
Topic-10 Memory Basics and Different Storages.pptx



Topic-10 Memory Basics and Different Storages.pptxMuhammadMustafaShaki3 It describes what is a memory, what are different categories, and how do they differ
CH04-COA10e.pptx



CH04-COA10e.pptxRahmadaniPutri The document discusses cache memory and memory systems. It provides details on:
- The memory hierarchy including registers, cache, main memory, and external storage. Faster but smaller memory levels exist closer to the CPU.
- Characteristics of memory systems such as location, capacity, unit of transfer, access methods, and performance parameters.
- Cache addressing methods including direct mapping, set associative mapping, and fully associative mapping. Caches use mapping to determine where to store memory blocks.
cache cache memory memory cache memory.pptx



cache cache memory memory cache memory.pptxsaimawarsi This document discusses cache memory and memory systems. It begins by defining key characteristics of computer memory like location, capacity, unit of transfer, and access methods. It then covers cache memory in more detail, including cache organization, read operations, and different mapping functions like direct, associative, and set associative mapping. Examples are provided to illustrate these mapping techniques. The document also discusses memory hierarchy and how faster cache memory is used to improve performance of slower main memory.
Memory hierarchy.pdf



Memory hierarchy.pdfISHAN194169 1. Memory hierarchy takes advantage of spatial and temporal locality by keeping frequently used data closer to the CPU.
2. Caches store the most recently used data from main memory and are faster but smaller than main memory.
3. If a memory request is in cache it is a "hit" and faster to access, if not in cache it is a "miss" and requires fetching from slower main memory.
internal_memory



internal_memorylimyamahgoub This document discusses memory characteristics including location, capacity, access methods, performance, and types. It covers the memory hierarchy from registers to external memory. Key points include that dynamic RAM needs refreshing to prevent data loss while static RAM maintains data without refreshing, and that memory performance is determined by access time, cycle time, and transfer rate. The document provides diagrams of DRAM and SRAM cell structures.
Csc1401 lecture05 - cache memory



Csc1401 lecture05 - cache memoryIIUM The document discusses cache memory principles and design. It begins with an overview of the memory hierarchy and how cache memory fits between the CPU and main memory. It then covers key elements of cache design, including cache addressing, size, mapping functions, and replacement algorithms. Mapping functions discussed include direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping. The document provides examples and diagrams to illustrate these cache mapping techniques.
Computer memory book notes 



Computer memory book notes Navtej Duhoon Computer memory consists of three levels in a hierarchy: internal processor memory, primary or main memory, and secondary or auxiliary memory. Internal processor memory is very fast but small and stores temporary data. Main memory is larger but slower, storing both instructions and data directly accessible by the processor. Secondary memory is much larger but slower, used for long-term storage of files and programs that are transferred to main memory for access.
CA UNIT V..pptx



CA UNIT V..pptxssuser9dbd7e The document discusses memory hierarchy and technologies. It describes the different levels of memory from fastest to slowest as processor registers, cache memory (levels 1 and 2), main memory, and secondary storage. The main memory technologies discussed are SRAM, DRAM, ROM, flash memory, and magnetic disks. Cache memory aims to speed up access time by exploiting locality of reference and uses mapping functions like direct mapping to determine cache locations.
3 computer memory



3 computer memoryarslanzafar13162 The document provides information about computer memory. It discusses different types of computer memory like registers, cache memory, RAM, ROM, and secondary storage devices. Registers provide the fastest access but have limited storage. Cache memory is faster than RAM and stores recently accessed data. RAM is used for temporary storage and ROM is used for permanent storage. Secondary storage devices like hard disks provide large storage but have slower access times than primary memory. The memory hierarchy ensures fast memory like registers are closest to the CPU while slower secondary storage is farther away.
Memory organization



Memory organizationishapadhy The document discusses the memory hierarchy in computers. It explains that memory is organized in a hierarchy with different levels providing varying degrees of speed and capacity. The levels from fastest to slowest are: registers, cache, main memory, and auxiliary memory such as magnetic disks and tapes. Cache memory sits between the CPU and main memory to bridge the speed gap. It exploits locality of reference to improve memory access speed. The document provides details on the working of each memory level and how they interact with each other.
More from Mazin Alwaaly (20)
Pattern recognition voice biometrics



Pattern recognition voice biometricsMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition voice biometrics seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition palm print authentication system



Pattern recognition palm print authentication systemMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition palm print authentication system seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition on line signature



Pattern recognition on line signatureMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition on line signature seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition multi biometrics using face and ear



Pattern recognition multi biometrics using face and earMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition multi biometrics using face and ear seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition IRIS recognition



Pattern recognition IRIS recognitionMazin Alwaaly The document discusses iris recognition as a biometric identification method that uses pattern recognition techniques to identify individuals based on the unique patterns in their irises. It provides an overview of the history and development of iris recognition, describes the components of an iris recognition system including image acquisition, segmentation, normalization, and feature encoding, and discusses applications of iris recognition including uses for border control, computer login authentication, and other security purposes.
Pattern recognition hand vascular pattern recognition



Pattern recognition hand vascular pattern recognitionMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition hand vascular pattern recognition seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition Hand Geometry



Pattern recognition Hand GeometryMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition hand geometry seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition forensic dental identification



Pattern recognition forensic dental identificationMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition forensic dental identification seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition fingerprints



Pattern recognition fingerprintsMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition fingerprints seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition facial recognition



Pattern recognition facial recognitionMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition facial recognition seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition ear as a biometric



Pattern recognition ear as a biometricMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition ear as a biometric seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Pattern recognition 3d face recognition



Pattern recognition 3d face recognitionMazin Alwaaly Pattern recognition 3d face recognition seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Multimedia multimedia over wireless and mobile networks



Multimedia multimedia over wireless and mobile networksMazin Alwaaly This document discusses multimedia over wireless and mobile networks. It begins by outlining the characteristics of wireless channels, including that they are more error-prone than wired channels. It then discusses various wireless networking technologies, including cellular networks from 1G to 4G, wireless local area networks, and Bluetooth. It concludes by discussing challenges for transmitting multimedia over wireless channels and techniques for error detection, error correction, and error concealment to address those challenges.
Multimedia network services and protocols for multimedia communications



Multimedia network services and protocols for multimedia communicationsMazin Alwaaly The document discusses various network services and protocols for multimedia communications. It covers protocol layers, local area networks and access network technologies, Internet technologies and protocols, quality of service for multimedia, and protocols for multimedia transmission and interaction. Specifically, it describes the OSI reference model layers, common LAN standards and technologies like Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, and digital subscriber line access networks. It also discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and key protocols like IP, TCP, and UDP.
Multimedia content based retrieval in digital libraries



Multimedia content based retrieval in digital librariesMazin Alwaaly This document provides an overview of content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems. It discusses early CBIR systems and provides a case study of C-BIRD, a CBIR system that uses features like color histograms, color layout, texture analysis, and object models to perform image searches. It also covers quantifying search results, key technologies in current CBIR systems such as robust image features, relevance feedback, and visual concept search, and the role of users in interactive CBIR systems.
Multimedia lossy compression algorithms



Multimedia lossy compression algorithmsMazin Alwaaly Multimedia lossy compression algorithms seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Multimedia lossless compression algorithms



Multimedia lossless compression algorithmsMazin Alwaaly This document discusses various lossless compression algorithms including run-length coding, Shannon-Fano algorithm, Huffman coding, extended Huffman coding, dictionary-based coding like LZW, and arithmetic coding. It provides details on the basic principles of run-length coding, an example of extended Huffman coding for a source with symbols A, B, and C, and outlines the structure of the document.
Multimedia basic video compression techniques



Multimedia basic video compression techniquesMazin Alwaaly Multimedia basic video compression techniques seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Multimedia image compression standards



Multimedia image compression standardsMazin Alwaaly Multimedia image compression standards seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Multimedia fundamental concepts in video



Multimedia fundamental concepts in videoMazin Alwaaly Multimedia fundamental concepts in video seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Recently uploaded (20)
Cardiorenal, Renocardiac, and Reno-CardioCardiac Syndromes: An Updated Review...



Cardiorenal, Renocardiac, and Reno-CardioCardiac Syndromes: An Updated Review...karishmayjm Background: Acute and chronic heart or kidney failure affect each other in cardiorenal syndromes (CRS). In CRS, hemodynamic and non-hemodynamic changes occur, causing acute or progressive renal and cardiac failures. CRS is classified into five types based on the first organ failure and causes failure of the other organ. We believe that the current CRS classification is not the correct one that effectively describes the underlying cause of CRS. Hence, we consider it better to be classified into three categories (cardiorenal, renocardiac, and cardio-reno-cardiac syndrome) and then subdivided into acute and chronic types or types 1 and 2 (respectively, according to the onset of the underlying type of failure (i.e., acute or chronic). Other subtypes that occur inthe heart and dysfunction occur simultaneously are acute cardio-reno-cardiac syndrome (type 5) and Chronic cardio-reno-cardiac syndrome (type 6).
Aim: In Part 1 of the review series, the pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical and therapeutic applications of all types of CRS will be narratively discussed and updated. Furthermore, we provide a comprehensive review of diagnostic biomarkers and their clinical significance in the identification, outcome prediction, and treatment of all CRS types. Method: An extensive search of PubMed, Google, EMBASE, Scopus, and Google Scholar was conducted for review articles, original articles, and commentaries published between Jan 2010 and Aug 2024 using different phrases, texts, and keywords, such as CRS, renocardiac syndrome, and CRS. The topics included secondary CRS, CRS pathogenesis, CRS therapy, SLGT inhibitor use in CRS, novel therapy in CRS types, and prevention of CRSs.
Conclusion: Renal and cardiac failure in patients with CRS seem to have different pathophysiological mechanisms. Early detection and treatment can improve the outcomes of CRS. Clinical manifestations and therapy protocols vary according to pathophysiology. Hence, new guidelines and research on universal diagnostic and treatment techniques are urgently required. Moreover, the current nomenclature for CRS is confusing; therefore, we believe that a new nomenclature system should be introduced, reducing confusion and making differentiation between CRS types easier and less confusing.
An Efficient and Reliable Method to Determine SpO2 in Rodents.pdf



An Efficient and Reliable Method to Determine SpO2 in Rodents.pdfScintica Instrumentation Accurate, non-invasive physiological monitoring is key to reproducible pre-clinical research studies. While the Rodent Surgical Monitor (RSM+) system has helped many researchers monitor the standard vital signs ECG, respiration, and core temperature in their experimental animals, oxygen saturation – a critical clinical parameter – has often been overlooked or under utilized. Now, a newly launched platform changes that. Featuring patent-pending ECG electrodes with integrated pulse oximetry sensors on the platform with redesigned electronics for cleaner, more reliable data, this next-generation system sets a new standard for precision monitoring during procedures.
Clinically, oxygen saturation or SpO2 measurements are made routinely because it directly reflects upon how effectively oxygen is being transported via the blood from the lungs to the entire body. It is a key indicator of respiratory and cardiovascular function used to monitor patients while under anesthesia, confirm and assess respiratory or cardiac conditions, etc. Accurate oxygen saturation monitoring can help prevent organ damage, improve patient outcomes, and support timely clinical interventions.
Even though used extensively clinically, oxygen saturation has not been routinely measured in preclinical studies. However, with changing perceptions to increase monitoring and reproducibility of studies, researchers have started to opt for this measurement. The Indus Instruments RSM+ system has a commercially available external thigh clip sensor for SpO2 measurement. However, clip SpO2 sensors depend on proper placement at the desired physical location on the animal (thigh, paw, tail, etc.), proper orientation to minimize respiration artifact, and the need to shave hair at the site of measurement are some of the key requirements. To mitigate and/or minimize these issues, Indus Instruments now offers a newly launched platform (RSMoX) that offers pulse oximetry sensors integrated into ECG electrodes that will detect oxygen saturation in the paw in either mice or rats, greatly reducing placement time and improving the reliability and reproducibility of SpO2 measurements.
Oxygen saturation measurements were obtained from the paw with RSMoX system were compared to and validated with the commercially available, Indus external thigh clip sensor and StarrLife (Mouse Ox) thigh clip sensor at baseline (normoxia) and during hypoxia induced using nitrogen gas. The results demonstrated no significant differences between the measurements of the ECG electrode paw sensor versus the clip sensors. The following presentation showcases/illustrates the results of this study as well as demonstrating other features/capabilities of the RSMoX system.
Learning Objectives:
Understand the importance of comprehensive, non-invasive physiological monitoring – including oxygen saturation – for reproducible animal research outcomes.
Learn about the new features of the redesigned Rodent Surgical Monitoring Platform
Insights to Narcotic Drugs by Urmila Nirmal



Insights to Narcotic Drugs by Urmila Nirmalurvi1504nirmal In this presentation get a glimpse of Narcotics and its types and investigative techniques, and examinations of Narcotics substances.
The Cornerstones of Social Research - Gary Hebrard.pptx



The Cornerstones of Social Research - Gary Hebrard.pptxgaryhebrard Investigating Ways to Enhance Society by Understanding Connections and Disconnections, and Uncovering Strategies to Deepen Our Understanding
Biological application of spectroscopy.pptx



Biological application of spectroscopy.pptxRahulRajai Spectroscopy in biological studies involves using light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation to analyze the structure, function, and interactions of biological molecules. It helps researchers understand how molecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids behave and interact within cells.
biological applications of spectroscopy:
1. Studying Biological Molecules:
Proteins:
Spectroscopy can reveal protein structure, including folding patterns and interactions with other molecules.
Nucleic Acids:
It helps analyze the structure of DNA and RNA, including their base sequences and interactions.
Lipids:
Spectroscopy can be used to study lipid interactions within cell membranes and their role in cellular processes.
Metabolic Pathways:
Spectroscopy can monitor changes in metabolic processes and cellular signaling pathways, providing insights into how cells function.
International Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (IJPS)



International Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (IJPS)journalijps98 Call for Research Articles.!!!
***** FREE PUBLICATION CHARGES*****
International Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (IJPS)
Webpage URL : https://www.wireilla.com/medical/IJPS/index.html
Authors are invited to submit papers through the Journal Submission System
http://allcfps.com/wireilla/submission/index.php
Submission Deadline : June 17, 2025
Contact Us
Here's where you can reach us : [email protected] or [email protected]
chapter 2 Prepare for administration of medications.pdf



chapter 2 Prepare for administration of medications.pdfBerhe4 Prepare for administration of medications
Glymphatic system dysfunction and neurodegeneration



Glymphatic system dysfunction and neurodegenerationKanakChaudhary10 Glymphatic system dysfunction and neurodegeneration
and its other factors
Slide 1: Clearing the Brain’s Waste
Slide 2: Anatomy of the Glymphatic System
Slide 3: Role in Neurotoxic Protein Clearance
Slide 4: Glymphatic Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s
Slide 5: Link to Traumatic Brain Injury
Slide 6: Mechanisms of Glymphatic Impairment
Slide 7: Imaging Glymphatic Function
Slide 8: Therapeutic Modulation Strategies
Slide 9: Challenges in Glymphatic Research
Slide 10: Future Directions for Glymphatic Therapies
Mode Of Dispersal Of Viral Disease On Plants.pptx



Mode Of Dispersal Of Viral Disease On Plants.pptxIAAS The document titled "Mode of Transmission of Viral Disease" explains how plant viruses, which are microscopic pathogens that rely on host cells for replication, spread and cause significant agricultural losses. These viruses are transmitted through two main routes: horizontal transmission (from plant to plant within the same generation) and vertical transmission (from parent to offspring via seed or pollen). The mechanisms of transmission are broadly divided into non-insect and insect-based methods. Non-insect transmission includes mechanical or sap transmission, vegetative propagation (e.g., through tubers or grafts), seed and pollen transmission, and the role of organisms like fungi, nematodes, and parasitic plants like dodder. Insect transmission is the most significant natural mode, with vectors such as aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, and whiteflies introducing viruses directly into plant tissues through feeding. Aphids alone are responsible for transmitting about 60% of known plant viruses. Each vector has specific transmission characteristics, such as the use of stylet feeding in aphids and exosomes in leafhoppers. The document also highlights important examples like Tobacco Mosaic Virus, Cucumber Mosaic Virus, and Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. Overall, the document provides a detailed understanding of how plant viruses spread, the role of vectors, and the implications for crop health and disease management.
Basic immune response against viruses.pptx



Basic immune response against viruses.pptxnehadeshmukh4702 This presentation provides a concise overview of the human immune system's fundamental response to viral infections. It covers both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms, detailing the roles of physical barriers, interferons, natural killer (NK) cells, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), B cells, and T cells in combating viruses. Designed for students, educators, and anyone interested in immunology, this slide deck simplifies complex biological processes and highlights key steps in viral detection, immune activation, and memory formation. Ideal for classroom use or self-learning.
Growing Crops with Microbiology- Endophytes and Rhizophagy Cycle.pdf



Growing Crops with Microbiology- Endophytes and Rhizophagy Cycle.pdfkahumbusu In this slide presentation Dr. James White shows us how important Microbiology is for healthy, resilient and nutritious crop production.
Computer architecture memory system
- 2. Outline • Microcomputer Memory -characteristics of memory system -location -capacity -unit of transfer • Access method • Performance • Physical type • Memory Hierarchies • Internal and external memory • RAM-Random access memory • ROM-Read only memory • Memory latency and bandwidth • Memory interleaving • Memory management
- 3. Microcomputer Memory • Memory is an essential component of the microcomputer system. • It stores binary instructions and datum for the microcomputer. • The memory is the place where the computer holds current programs and data that are in use. • None technology is optimal in satisfying the memory requirements for a computer system. • Computer memory exhibits perhaps the widest range of type, technology, organization, performance and cost of any feature of a computer system. • The memory unit that communicates directly with the CPU is called main memory. • Devices that provide backup storage are called auxiliary memory or secondary memory
- 4. Memory Hierarchies • Some fundamental and enduring properties of hardware and software: • Fast storage technologies cost more per byte and have less capacity • Gap between CPU and main memory speed is widening • Well-written programs tend to exhibit good locality • These fundamental properties complement each other beautifully • They suggest an approach for organizing memory and storage systems known as a memory hierarchy
- 6. Characteristics of memory systems • The memory system can be characterised with their Location, Capacity, Unit of transfer, Access method, Performance, Physical type, Physical characteristics, Organisation.
- 7. Location • Processor memory: The memory like registers is included within the processor and termed as processor memory. • • Internal memory: It is often termed as main memory and resides within the CPU. • • External memory: It consists of peripheral storage devices such as disk and magnetic tape that are accessible to processor via i/o controllers Capacity • Word size: Capacity is expressed in terms of words or bytes. — The natural unit of organisation • Number of words: Common word lengths are 8, 16, 32 bits etc. — or Byte
- 8. Unit of Transfer • Internal: For internal memory, the unit of transfer is equal to the number of data lines into and out of the memory module. • External: For external memory, they are transferred in block which is larger than a word. • Addressable unit — Smallest location which can be uniquely addressed — Word internally — Cluster on Magnetic disks
- 9. Access Method • Sequential access: In this access, it must start with beginning and read through a specific linear sequence. This means access time of data unit depends on position of records (unit of data) and previous location. — e.g. tape • Direct Access: Individual blocks of records have unique address based on location. Access is accomplished by jumping (direct access) to general vicinity plus a sequential search to reach the final location. — e.g. disk • Random access: The time to access a given location is independent of the sequence of prior accesses and is constant. Thus any location can be selected out randomly and directly addressed and accessed. — e.g. RAM • Associative access: This is random access type of memory that enables one to make a comparison of desired bit locations within a word for a specified match, and to do this for all words simultaneously. • e.g. cache
- 10. Performance • Access time: For random access memory, access time is the time it takes to perform a read or write operation i.e. time taken to address a memory plus to read / write from addressed memory location. Whereas for non-random access, it is the time needed to position read / write mechanism at desired location. — Time between presenting the address and getting the valid data • Memory Cycle time: It is the total time that is required to store next memory access operation from the previous memory access operation. Memory cycle time = access time plus transient time (any additional time required before a second access can commence). — Time may be required for the memory to “recover” before next access — Cycle time is access + recovery • Transfer Rate: This is the rate at which data can be transferred in and out of a memory unit. — Rate at which data can be moved — For random access, R = 1 / cycle time — For non-random access, Tn = Ta + N / R; where Tn – average time to read or write N bits, Ta – average access time, N – number of bits, R – Transfer rate in bits per second (bps).
- 11. Physical Types • Semiconductor — RAM • Magnetic — Disk & Tape • Optical — CD & DVD • Others — Bubble — Hologram
- 12. Physical Characteristics • Decay: Information decays mean data loss. • Volatility: Information decays when electrical power is switched off. • Erasable: Erasable means permission to erase. • Power consumption: how much power consumes? Organization • Physical arrangement of bits into words • Not always obvious - e.g. interleaved
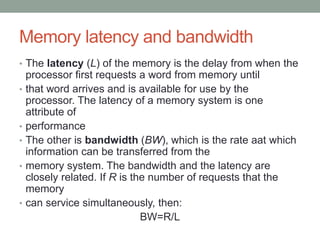
- 13. Memory latency and bandwidth • The latency (L) of the memory is the delay from when the processor first requests a word from memory until • that word arrives and is available for use by the processor. The latency of a memory system is one attribute of • performance • The other is bandwidth (BW), which is the rate aat which information can be transferred from the • memory system. The bandwidth and the latency are closely related. If R is the number of requests that the memory • can service simultaneously, then: BW=R/L
- 14. Memory latency and bandwidth • From Eq. (1) we see that a decrease in the latency will result in an increase in bandwidth, and vice versa, if R • is unchanged. We can also see that the bandwidth can be increased by increasing R, if L does not increase proportionately. • For example, we can build a memory system that takes 20 ns to service the access of a single 32-bit • word. Its latency is 20 ns per 32-bit word, and its bandwidth is : 32bits/20*10sec
- 15. Internal and External memory • Internal or Main Memory The main memory is the central unit of the computer system. It is relatively large and fast memory to store programs and data during the computer operation. These memories employ semiconductor integrated circuits. The basic element of the semiconductor memory is the memory cell. • The memory cell has three functional terminals which carries the electrical signal. • o The select terminal: It selects the cell. • o The data in terminal: It is used to input data as 0 or 1 and data out or sense terminal is used for the output of the cell's state. • o The control terminal: It controls the function i.e. it indicates read and write. • Most of the main memory in a general purpose computer is made up of RAM integrated circuits chips, but a portion of the memory may be constructed with ROM chips
- 16. External Memory Types • HDD • Magnetic Disk(s) • SDD (Solid State Disk(s)) • Optical • CD-ROM • CD-Recordable (CD-R) • CD-R/W • DVD • Magnetic Tape
- 17. Internal and External memory
- 18. RAM– Random Access memory • Memory cells can be accessed for information transfer from any desired random location. • The process of locating a word in memory is the same and requires of locating a word in memory is the same and requires an equal amount of time no matter where the cells are located physically in memory thus named 'Random access'. • Integrated RAM are available in two possible operating modes, Static and Dynamic
- 19. Types of RAM • Dynamic RAM (DRAM) – are like leaky capacitors; initially data is stored in the DRAM chip, charging its memory cells to maximum values. The charge slowly leaks out and eventually would go to low to represent valid data; before this happens, a refresh circuitry reads the contents of the DRAM and rewrites the data to its original locations, thus restoring the memory cells to their maximum charges • Static RAM (SRAM) – is more like a register; once the data has been written, it will stay valid, it doesn’t have to be refreshed. Static RAM is faster than DRAM, also more expensive. Cache memory in PCs is constructed from SRAM memory
- 20. Dynamic RAM
- 22. Static RAM • Uses flip flop to store information • Needs more space • Faster, digital device • Expensive, big in size • Don't require refreshing circuit • Used in cache memory Dynamic RAM • Uses capacitor to store information • More dense i.e. more cells can be accommodated per unit area • Slower, analog device • Less expensive, small in size • Needs refreshing circuit • Used in main memory, larger memory units
- 30. Thankyou














