Computer network & communication answer
- 1. Computer network & communication Computer network is a system of interconnected computers & peripheral devices. eg: it may connect computer, printer, scanners and cameras. Communications is about the transfer of information from a sender, across a distance, to a receiver.
- 2. Physical medium Cable wire Atmosphere Information can be transmitted: text Voice/ sound Image/ graphic video
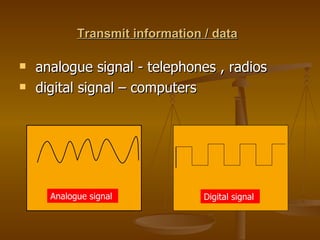
- 3. Transmit information / data analogue signal - telephones , radios digital signal – computers Analogue signal Digital signal
- 4. Signal translator – MODEM Modem – short form of Modulator or Demodulator Functions: converts digital signal into analogue and back again into digital signal for information to move across the telephone line. Connections for networking a physical medium Protocols System application
- 5. Failure of communications physical medium is cut off. protocol between interconnected is not same. Protocol : is a set of rules or standard designed so that computers can exchange information with a minimal errors.
- 6. Advantages of networking can shared data can shared resources can exchange information can sharing devices or software can communicate with each others.
- 7. Components of communications hardware software -computers - hub -switch -router - NIC -wired -wireless -operating System - applications “ google, yahoo, msn”
- 8. Types Network communication channels twisted pair wire coaxial cable fibre-optic cable satellite systems wireless systems (namely using radio waves, microwaves, and infrared)
- 9. Network Interface Card (NIC) NIC provides connection between the computer & the network communication media. to move data from the PC’s system to the network medium. able the networking devices work properly.
- 10. Importance of Network & Communications E-business To conduct business transactions on The internet. Including online Shopping, selling and renting. Online Education Students at any location around the World can participate in an online Classroom, download tutorial Questions & submit their assignments. E-banking It handles all types of banking transactions such as account Management, fund transfer, Payments Bills, check account balance…. Long Distance Communication Cheaper, faster and more effective (video conference meeting)
- 11. Types of networks Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) KL City Local Area Network (LAN) SMK KL Wide Area Network (WAN) Between KL & London
- 12. Local Area Network (LAN) smallest network. single building, home, school. simplest form of LAN is to connect two computers together. less than 500 interconnected devices. inexpensive hardware: twisted pair, coaxial cable, fiber optic or wireless. faster than MAN and WAN.
- 13. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Cities: Kuala Lumpur, Manila, Singapore, Tokyo, London and New York. Large physical area : city Example: bank MAN used fiber optic. High speed network (not fast as LAN).
- 14. Wide Area Network (WAN) Largest network in the world Cover large distances such as states, countries or continents. WAN is group of MANs and LANs Use Router to connect between networks. WAN use fiber optic, speed 20-2000kbps (slower than LAN and MAN).
- 15. Differences between types of network Criteria LAN MAN WAN Cost Low High Higher Network size Small Larger Largest Speed Fasters Slower Slowest Transmission media type Twisted pair Twisted pair & fiber optic cable Fiber optic, satellite, radio wave No. of computers. Smallest Large Largest
- 16. Types of Network Architecture Network architecture is the overall design of computer network that describes how a computer network configured and what strategies are being used. Client- Server Network Peer to Peer Network
- 17. Def: Is a network in which the shared files and application are stored in the server but network users (clients) can still store files on their individual PCs. Server : Sometimes called host computer . Server is a computer that provides services to other computers called clients. Functions Server: i) Control access to the hardware, software and other resources on the network. ii) Centralized storage area for programs, data and information. Dedicated Server: Perform specific tasks, eg: file server, printer server, database server and network server. Client- Server Network
- 18. Peer 2 Peer Network (P2P) Is a network with all the nodes acting as both server and clients. Have equal responsibilities and capabilities to use the resources available on the network. No server is needed, each computer in the network is called a peer.
- 19. Differences between client-server and peer to peer Client –server Peer to peer Server control ability while client don’t All computers have equal ability High cost Cheaper cost Use small and large network Small networks Easy to manage Hard to manage
- 20. 3 types of network toplogies
- 21. Bus Topology Consists of single central cable (Backbone). All nodes are share the backbone to communicate with each other on the network. No or 1 server is needed on the network. Advantages: i) easy implementation ii) failure of the node doesn’t affect the entire LAN. Disadvantages: i) If the backbone fails, the entire bus network will be affected. ii) Network speed decreases when no. of nodes increases. iii) Troubleshooting is difficult.
- 22. Ring Topology All computer & devices are connect in a loop. Can be found in the LAN. Have Server. Advantages: i) troubleshooting is easy Disadvantages: i) If one node fail to function, the network will fail to function. ii) Implementation is difficult. iii) speed decreases when the no. of nodes increases.
- 23. Star topology All computers are connected to a centralized mainframe computer. Consists of central host and all nodes are connect to a host. The host as a server, hub or router. The host will control the flow of communication in the network. Advantages: i) easy implement ii) failure of a node doesn’t affect the entire LAN. Disadvantages: i) If the host fails, the entire LAN will be affected. ii) troubleshooting is difficult.
- 24. Differences of network topologies Bus topology Ring topology Star topology Structure Single central cable (backbone) Connected in the loop (circle) Central host Host existence Depends on the network Depend on the network Yes Connection between nodes No connection Yes No connection Host failure Network still can run Network will fail Network will fail. Node failure Network still can run Network will fail Network will fail
- 25. Common Network Standards 802.3 (Ethernet LAN) 802.7 (Broadband LAN) 802.8 (Fibre-optic LAN and MAN) 802.11 (Wireless LAN) Protocols Protocols provide the rules on how computers communicate. They define how devices intercommunicate in a network environment. Some types of protocols: i) Hypertext Transfer Protocols (HTTP) ii) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) iii) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) iv) Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- 26. 3 Types of network communication technology Internet largest computer network usages of internet: Information, research & exchange Commerce Real time communication banking Shopping Entertainment education Gaming Intranet internal network within an organization, 2 buildings, cities, states.. Usages of intranet: Telephone directories event calendars employee handbook job posting staff information Extranet private network that Uses Internet technology and public Telecommunication System to securely Share relevant information With authorized parties.
- 27. Intranet Internet Internal network Global information Within an organization Various Organizations Internet Extranet Uses internet technology Uses intranet technology Serves everybody Serves enterprise (customer & suppliers) With/ without firewall With firewall Low security Tight security
- 28. Communication devices Network Interface Card Wireless Network Interface Card allow the computers to communicate over a computer network. connects to a radio-based computer network. uses an antenna to communicate through microwaves. Operates in 2 modes: i) Infrastructure Mode ii) Hoc Mode
- 29. Communication devices Hub/ switch enables a computer to transmit data over telephone or cable lines. to connect segments of LAN Hub contains multiple ports. Modem
- 30. Communication devices Wireless Access Point Device that forwards data packets across a network toward their destinations, through a process known as routing. connect wireless communication devices together to form a wireless Network. Router
- 31. 2 types of transmission medium A) Physical transmission media (guided medium) - Twisted pair, Coaxial cable, Fiber optic cable. - eg: connect a PC to a printer B) Wireless transmission media (unguided medium) - without using cables or cords. - using radio frequency or infrared waves. - transmission divided into 3 categorized: i) Short range (Bluetooth or infrared) ii) Medium range (WiFi / wirelass LAN) iii) Long range (3G) - Listen to the radio - Talk over the telephone.
- 32. Physical Transmission Media A) Twisted Pair Cable – 2 insulated copper wires that are twisted around each other. B) Coaxial Cable – consisting of a conducting outer metal tube that encloses and is insulated from a central conducting core, used primarily for the transmission of high- frequency signals. C) Fibre Optic Cable – glass fibre used for laser transmission of video, audio and data.
- 33. Wireless Transmission Media Mediums used are air, vacuum and water. Wireless transmission: i) Radio waves ( 1 and 300 GHz) ii) Microwaves (2 types of antenna – parabolic antenna & horn antenna) iii) Infrared (300 GHz – 400 THz)- cannot penetrate walls.
- 34. Server Software Examples of network operating system: Window NT Window 2000 server Window Server 2003 Red Hat Linux Client Software Web browsers
- 35. Wireless Technology Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM) General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE) Universal Mobile telecommunications System (UMTS) Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) i-MODE
- 36. Types of wireless Fixed wireless Mobile wireless Portable wireless IR wireless Mobile computing Mobile computing is about the new strategies of computing that utilise portable or mobile devices and wireless communication networks. There are various types of mobile computing devices such as notebook computer, tablet PC, handheld computer, PDA and smartphone.
- 37. Common service for mobile computing Email capabilities Print stations Tracking and navigation system Instant mobile massaging Mobile security services