COMPUTER NETWORK With it's Types and Layer
- 1. COMPUTER NETWORKS INTRODUCTION COMPONENTS OF NETWORK TYPES OF COMPUTER NETWORKS NETWORK TOPOLOGIES Prof.Reena Comp.Dept
- 2. Introduction:- An arrangement of two or more inter connected computers is called a computer network. It is a logical extension of a data communications system. Two or more computers or processors are linked together with data communication devices and transmission media in a computer network. Definition :- Two or more computers connected logically with the help of data communication devices and transmission media referred to as computer Network. Networks allow for the efficient exchange of data, enabling various applications such as email, file sharing, and internet browsing.
- 3. Basic Terminologies / components of Computer Networks • 1. Media It is the medium through which the data travels like Twisted pair cable, Coaxial cable, Fibre optics, Microwave satellite, Cellular Radio. • 2. Processor Processor is the hardware which helps to transfer the data from source to destination like Modems, Multiplexer , Routers, Bridges, Gateway , Front end processor, • 3. Software To transfer the data from source to destination we require software. Various software are : Communication Software, Network Operating system software, SMTP, MSN internet explorer, Navigator • 4. Channels Various channels used in data communication are Analog/digital, switched/non switched, Circuit/Message/Packet switching Simplex/Duplex, Synchronous/Asynchronous. • 5. Topology It is way through which the data travels. The various topologies are: Star, Ring, Mesh, Bus, Tree, etc. • 6. Architecture The various Architecture available for computer networks are OSI, IEEE, ISDN, PSTN.
- 4. • 7.Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted over a network. Examples of protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP. • 8.Nodes: Nodes are devices that are connected to a network. These can include computers, Servers, Printers, Routers, Switches, and other devices. • 9.Network: A network is a collection of computers and devices that are connected together to enable communication and data exchange. • 10.IP Address: An IP address is a unique numerical identifier that is assigned to every device on a network. IP addresses are used to identify devices and enable communication between them. • 11 DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that is used to translate human-readable domain names (such as www.google.com) into IP addresses that computers can understand. • 12. Firewall: A firewall is a security device that is used to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls are used to protect networks from unauthorized access and other security threats.
- 5. Types of Computer Networks:- 1.Personal Area Network (PAN) 2. Local area network (LAN) 3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) 4.Wide Area Network (WAN)
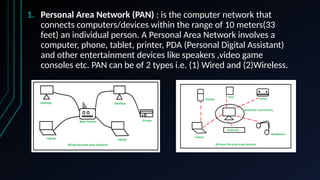
- 6. 1. Personal Area Network (PAN) : is the computer network that connects computers/devices within the range of 10 meters(33 feet) an individual person. A Personal Area Network involves a computer, phone, tablet, printer, PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) and other entertainment devices like speakers ,video game consoles etc. PAN can be of 2 types i.e. (1) Wired and (2)Wireless.
- 7. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF PAN – • APPLICATIONS OF PAN – • Home and Offices • Organizations and the Business sector • Medical and Hospital • School and College Education • Military and Defense Advantages of PAN : 1. PAN is relatively flexible and provides high efficiency for short network ranges. 2. It needs easy setup and relatively low cost. 3. It does not require frequent installations and maintenance 4. It is easy and portable. 5. Needs fewer technical skills to use. Disadvantages of PAN : 6. Low network coverage area/range. 7. Limited to relatively low data rates. 8. Devices are not compatible with each other. 9. Inbuilt WPAN devices are a little bit costly.
- 8. 2. Local Area Network (LAN): • When two or more computers are connected in a small area and more than a few kilometers then such a network is known as local area network. The data rate in LAN is of the order of Mbps(Mega bits per second). A LAN is a network that is used to link devices in a single office, building or campus of up to a short distance. In LAN networks internet speed is from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps . The most common topologies used in LAN networks are bus, ring, and star. • Types of LAN client-server Peer to peer Wired Wireless
- 9. Advantages of a LAN Privacy: LAN is a private network, thus no outside regulatory body controls it, giving it a privacy. High Speed: LAN offers a much higher speed (around 100 mbps ) Supports different transmission mediums: LAN support a variety of communications transmission medium such as an Ethernet cable (thin cable, thick cable, and twisted pair), fiber and wireless transmission. Inexpensive and Simple: A LAN usually has low cost, installation, expansion and maintenance and LAN installation is relatively easy to use, good scalability. Disadvantages of LAN The initial setup costs of installing Local Area Networks is high because there is special software required to make a server. Communication devices like an ethernet cable, switches, hubs, routers, cables are costly. LAN administrator can see and check personal data files as well as Internet history of each and every LAN user. Hence, the privacy of the users are violated LANs are restricted in size and cover only a limited area Since all the data is stored in a single server computer, if it can be accessed by an unauthorized user, can cause a serious data security threat.
- 10. 3.METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK (MAN) A MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. This is the type of computer network that connects computers over a geographical distance through a shared communication path over a city, town, or metropolitan area. This network mainly uses CDDI and ATM as the technology with a range from 5km to 50km. It is difficult to maintain and it comes with a high cost. Examples of MAN are networking in towns, cities, a single large city, a large area within multiple buildings, etc.
- 11. ADVANTAGES OF MAN • MAN offers high-speed connectivity in which the speed ranges from 10-100 Mbps. • The security level in MAN is high and strict as compared to WAN. • It support to transmit data in both directions concurrently because of dual bus architecture. • MAN can serve multiple users at a time with the same high-speed internet to all the users. • MAN allows for centralized management and control of the network, making it easier to monitor and manage network resources and security. DISADVANTAGES OF MAN • The architecture of MAN is quite complicated hence, it is hard to design and maintain. • This network is highly expensive because it required the high cost to set up fiber optics. • It provides less fault tolerance. • The Data transfer rate in MAN is low when compare to LANs.
- 12. 4.Wide Area Network (WAN) • A WAN (Wide Area Network) is to connect multiple smaller Local Area Networks (LANs). It is a computer network designed. WANs can help in communication, the sharing of information, and much more between systems or devices from around the world through a WAN provider. • WAN is a type of computer network that connects computers over a large geographical distance through a shared communication path. It is not restrained to a single location but extends over many locations. WAN can also be defined as a group of local area networks that communicate with each other with a range above 50km. Here we use Leased-Line & Dial-up technology. Its transmission speed is very low and it comes with very high maintenance and very high cost. The most common example of WAN is the Internet.
- 13. ADVANTAGES OF WAN • It covers large geographical area which enhances the reach of organisation to transmit data quickly and cheaply. • The data can be stored in centralised manner because of remote access to data provided by WAN. • The travel charges that are needed to cover the geographical area of work can be minimised. • WAN enables a user or organisation to connect with the world very easily and allows to exchange data and do business at global level. DISADVANTAGES OF WAN • Traffic congestion in Wide Area Network is very high. • The fault tolerance ability of WAN is very less. • Noise and error are present in large amount due to multiple connection point. • The data transfer rate is slow in comparison to LAN because of large distances and high number of connected system within the network.
- 14. Comparison between Different Computer Networks Parameters PAN LAN MAN WAN Full Name Personal Area Network Local Area Network Metropolitan Area Network Wide Area Network Technology Bluetooth, IrDA,Zigbee Ethernet & Wifi FDDI, CDDi. ATM Leased Line, Dial-Up Range 1-100 m Upto 2km 5-50 km Above 50 km Transmission Speed Very High Very High Average Low Ownership Private Private Private or Public Private or Public Maintenance Very Easy Easy Difficult Very Difficult Cost Very Low Low High Very High
- 15. Types of Network Topology Define:- Network topology refers to the arrangement of different elements like nodes, links, or devices in a computer network. It defines how these components are connected and interact with each other. The arrangement of a network that comprises nodes and connecting lines via sender and receiver is referred to as Network Topology . The various network topologies are: 1. P2P Topology 2. Mesh Topology 3. Star Topology 4. Ring Topology 5. Tree Topology 6. Bus Topology 7. Hybrid Topology
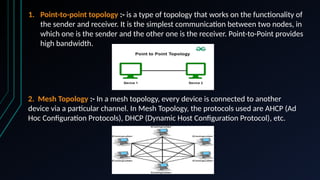
- 16. 1. Point-to-point topology :- is a type of topology that works on the functionality of the sender and receiver. It is the simplest communication between two nodes, in which one is the sender and the other one is the receiver. Point-to-Point provides high bandwidth. 2. Mesh Topology :- In a mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via a particular channel. In Mesh Topology, the protocols used are AHCP (Ad Hoc Configuration Protocols), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), etc.
- 17. ADVANTAGES OF MESH TOPOLOGY • Communication is very fast between the nodes. • Mesh Topology is robust. • The fault is diagnosed easily. Data is reliable because data is transferred among the devices through dedicated channels or links. • Provides security and privacy. DISADVANTAGES OF MESH TOPOLOGY • Installation and configuration are difficult. • The cost of cables is high as bulk wiring is required, hence suitable for less number of devices. • The cost of maintenance is high
- 18. 3.Star Topology :- In Star Topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node. This central node is known as Server and other computers connected to server are known as Clients or Work Station . Active hubs have repeaters in them. Coaxial cables or RJ-45 cables are used to connect the computers. A common example of star topology is a local area network (LAN) in an office where all computers are connected to a central hub. This topology is also used in wireless networks where all devices are connected to a wireless access point.
- 19. ADVANTAGES OF STAR TOPOLOGY • If N devices are connected to each other in a star topology, then the number of cables required to connect them is N. So, it is easy to set up. • Each device requires only 1 port i.e. to connect to the hub, therefore the total number of ports required is N. • It is Robust. If one link fails only that link will affect and not other than that. • Easy to fault identification and fault isolation. • Star topology is cost-effective as it uses inexpensive coaxial cable. DISADVANTAGES OF STAR TOPOLOGY • The entire network depends on central computer (hub) on which the whole topology work so if the servers relies fails, the whole system will crash down. • The cost of installation is high. • Performance is based on the single concentrator i.e. hub. • The distributed processing capability is limited.
- 20. 4. Ring Topology :- In a Ring Topology, it forms a ring connecting devices with exactly two neighboring devices. A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with a large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network. The data flows in one direction, i.e. it is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology. In-Ring Topology, the Token Ring Passing protocol is used by the workstations to transmit the data.