Computer Organisation unit 1 basics of computer Organisation
- 1. UNIT-I BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTER,MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS AND PROGRAM
- 2. WHAT IS COMPUTER • A computer is a digital electronic machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of task
- 3. BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTER
- 4. • All types of computers follow a same basic logical structure and perform the following five basic operations for converting raw input data into information useful to their users. • Input Unit • This unit contains devices with the help of which we enter data into computer. This unit makes link between user and computer. The input devices translate the information into the form understandable by computer. • CPU (Central Processing Unit) • CPU is considered as the brain of the computer. CPU performs all types of data processing operations. It stores data, intermediate results and instructions(program). It controls the operation of all parts of computer. • CPU itself has following three components • ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit) • Memory Unit • Control Unit • Output Unit • Output unit consists of devices with the help of which we get the information from computer. This unit is a link between computer and users. Output devices translate the computer’s output into the form understandable by users.
- 5. Computer types • Classification of Computers by Size • Supercomputers • Mainframe computers • Minicomputers • Personal computers (PCs) or microcomputers
- 6. Supercomputers • a powerful computer that can process large amounts of data and do a great amount of computation very quickly. • Supercomputers are used for areas related to: • Science • Engineering • Education • Defence • Aerospace • Supercomputers are useful for applications involving very large databases or that require a great amount of computation.
- 7. • Supercomputers are used for complex tasks, such as: • Weather forecasting • Climate research • Scientific simulation • Oil and gas exploration • Quantum mechanics • Cryptanalysis
- 8. Mainframe computers • a high-performance computer used for large information processing jobs. • Mainframe computers are primarily used in : • Institutions • Research • Academics • Health care • Libraries • Large businesses • Financial institutions • Stock brokerage firms • Insurance agencies
- 9. • Mainframe computers are useful for tasks related to: • Census taking • Industry and consumer statistics • Enterprise resource planning • Transaction processing • e-business and e-commerce
- 10. Minicomputers • a mid-range computer that is intermediate in size, power, speed, storage capacity, etc., between a mainframe and a microcomputer. • Minicomputers are used by small organizations. • “Minicomputer” is a term that is no longer used much. In recent years, minicomputers are often referred to as small or midsize servers. • A server is a central computer that provides information to other computers.
- 11. Personal computers • a small computer designed for use by a single user at a time. • A PC or microcomputer uses a single chip (microprocessor) for its central processing unit (CPU). • “Microcomputer” is now primarily used to mean a PC, but it can refer to any kind of small computer, such as a desktop computer, laptop computer, tablet, smartphone, or wearable.
- 12. Types of personal computers • desktop computer • laptop computer • tablet • Smart phone 1. desktop computer: a personal computer that is designed to stay at one location and fits on or under a desk. It typically has a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and a tower (system unit).
- 13. laptop computer • A portable personal computer that is small enough to rest on the user’s lap and can be powered by a battery. It includes a flip down screen and a keyboard with a touchpad.
- 14. tablet • A wireless touchscreen PC that is slightly smaller and weighs less than the average laptop.
- 15. Smart phone • A mobile phone that performs many of the functions of a personal computer.
- 16. Functional Units of Computer • The functional units of a computer i.e. input unit, arithmetic and logic unit, memory, control unit, output unit all are connected with the interconnection network that helps them in exchanging the information as you can see in the image below. Now, let us explore each functional unit separately
- 17. Input Unit • The input to the computer is either a data or instruction, that guides the arithmetic and logic unit about what operations have to be performed and also controls the movement of data between the computer and its I/O devices. • Now, the input i.e. data or instruction are accepted with the help of input units such as a keyboard, mouse, touchpad. The most familiar device that we use to accept input is the ‘keyboard’ and ‘mouse’. All of these input devices are graphic input devices and you can see their effect on the display unit. • Whenever you strike any key on the keyboard it gets converts to the binary code and is handed over to the processor which would interpret the code and perform the appropriate action. • For audio and video input, microphones and cameras are used respectively. Now a day, the internet can also be used to issue an input to a computer from other computers or databases.
- 18. Memory Unit • A memory unit is required to store the programs that have the set of instructions that instructs Arithmetic and logic unit which operation has to be performed. It also stores the data associated with the program. The memory can further be classified into three types: • Primary Memory • primary memory is also known as the main memory or the random-access memory (RAM). It is the fastest accessible memory of the computer. If a program has to be executed it first needs to be placed in the primary memory. • The memory is organized in such a way that in one basic operation, one-word can be retrieved from the memory or one word can be stored to the memory. A word length could be 16, 32, or 64 bits. • The primary memory is expensive as well as faster. But primary memory is volatile in nature it does not retain its content when the power gets off.
- 19. Secondary Memory • Secondary memory is the hard disk of your system, it also includes flash drive, optical disks, magnetic disk. The secondary memory is slower and less expensive as compared to primary memory. • It doesn’t lose its contents even if the supply of power gets off. We require secondary memory to store a large volume of data or program permanently or the data that is less likely to be retrieved. • Cache Memory • Cache memory can be accessed much faster as compared to primary memory and it is even smaller in size. It is stored with the data that is required frequently by the processor. • As we know the program to be executed and the data associated with it is brought to the primary memory and the processor fetches the program instructions from there.
- 20. • The process also places a copy of the instructions and associated data in the cache memory. Now, the instructions that are required to be executed repeatedly such as loops are retrieved from the cache memory to improve the execution rate. • Arithmetic Logic Unit • All the arithmetic operations are performed by the arithmetic logic unit of the processors. Arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, division, multiplication, comparison between the numbers, etc. • The ALU unit performs the operations present in the instruction and stores the result into the memory. It also stores the intermediate results of the operation in the registers. • The arithmetic operation is performed on the operands. The operands are placed into the registers which store one word at a time which is sufficient for an operand.
- 21. Output Unit • A computer is a functional unit and as it has an input unit to accept the input it also has the output unit to provide the generated output by the system. The most familiar device used to output a result is a printer. • A display screen is also an output unit as it displays the generated result, but it also displays the input provided to the system. That’s why the display screen is termed as the ‘I/O unit’ because of its dual function. • Control Unit • The functions of input, ALU, memory, and output unit must be coordinated so that everything goes in sequence i.e. the processor accepts input, place it in memory, processes the stored input, and generates output. This entire sequence is coordinate by the control unit. • In this way, the functional units of computers cooperate to generate useful output. We have discussed each of the functional units of the computer in brief and understood their functional behaviour.
- 22. • What is an operation? • An operation in computer science is the completion of a task achieved through a series of actions carried out by the computer. There are a total of five basic operations of a computer: • Input – This means giving an input to the computer by an action like left-clicking an icon on the computer or typing on the keyboard to search for something on Google. • Processing – processors carry out the calculations and equations needed to get the desired results. An example of a processor is an arithmetic logic unit used to carry out all the mathematical calculations on the computer. • Output – This is when the outcome derived from the processing stage is displayed as a final result for the user. Output can be of different types. For example, a user inputs a maths calculation in the device’s calculator so that the screen will show the results.
- 23. • Storage – Several software, apps, and websites keep track of the user history. The storage comes in handy for these. The storage means memory keeps a copy of all the inputs and outputs that are done on the computer as a memory. It can be as a primary memory- which means the data is stored for a short period and the data is deleted once the computer or app is closed or shut down, or secondary memory- this is usually used as a long term storage device like a hard disk drive or Pendrive that can store vast amounts of data in a small space and is portable. • Control – The central processing unit comes into action at this point; during the process of computer operation, all the input, information processing, and displaying an output can become challenging to manage for the computer, making it slow . The CPU prevents glitches in the program’s running by controlling all these actions and executing everything in order.
- 24. What is the concept of basic computer organization? • The instructions that a computer follows to produce the output are stored in the memory of the computer • The devices store their instructions in memory devices, also known as registers • Function registers are situated in a microprocessor. They control the smooth running of the microprocessors • Functional registers are divided into three parts: • (PC) Program counters – The location of instructions on the memory device is stored here so that it can be used when required. • 2. (IR) Instruction registers – the instructions that will be used are located here. They are encoded, so they will be decoded before the IR executes it. • 3. (MAR) Memory address registers – Data locations from start to finish/ end of the operation are stored here. • MAR and MDR are two registers used to handle the transfers of data between the processor and the device’s main memory. • (MDR) Memory data register – The data that is transferred is stored here.
- 25. Bus Structure in Computer Architecture • A system bus has typically from fifty to hundreds of distinct lines where each line is meant for a certain function. These lines can be categories into three functional groups i.e., data lines, address lines, and control lines. Let us discuss them one by one each.
- 26. 1. Data Lines • Data lines coordinate in transferring the data among the system components. The data lines are collectively called data bus. A data bus may have 32 lines, 64 lines, 128 lines, or even more lines. The number of lines present in the data bus defines the width of the data bus. • Each data line is able to transfer only one bit at a time. So the number of data lines in a data bus determines how many bits it can transfer at a time. The performance of the system also depends on the width of the data bus.
- 27. 2.Address Lines • The content of the address lines of the bus determines the source or destination of the data present on the data bus. The number of address lines together is referred to as address bus. The number of address lines in the address bus determines its width. • The width of the address bus determines the memory capacity of the system. The content of address lines is also used for addressing I/O ports. The higher- order bits determine the bus module and the lower ordered bits determine the address of memory locations or I/O ports. • Whenever the processor has to read a word from the memory it simply places the address of the corresponding word on the address line.
- 28. 3. Control Lines • The address lines and data lines are shared by all the components of the system so there must some means to control the use and access of data and address lines. The control signals placed on the control lines control the use and access to address and data lines of the bus. The control signal consists of the command and timing information. Here the command in the control signal specify the operation that has to be performed. And the timing information over the control signals specify till when the data and address information is valid .
- 29. Software • Software is a set of programs, which is designed to perform a well-defined function. A program is a sequence of instructions written to solve a particular problem. • There are two types of software − • System Software • Application Software
- 30. System Software • The system software is a collection of programs designed to operate, control, and extend the processing capabilities of the computer itself. System software is generally prepared by the computer manufacturers. • These software products comprise of programs written in low-level languages, which interact with the hardware at a very basic level. System software serves as the interface between the hardware and the end users. Some examples of system software are Operating System, Compilers, Interpreter, Assemblers, etc.
- 31. • Here is a list of some of the most prominent features of a system software − • Close to the system • Fast in speed • Difficult to design • Difficult to understand • Less interactive • Smaller in size • Difficult to manipulate • Generally written in low-level language
- 32. Performance • The most important measure of the performance of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs. The speed with which a computer executes programs is affected by the design of its hardware and its machine language instructions. • Because programs are usually written in a high-level language, performance is also affected by the compiler that translates programs into machine language. • For best performance, it is necessary to design the compiler, the machine instruction set, and the hardware in a coordinated way. • The operating system overlaps processing, disk transfers, and printing for several programs to make the best possible use of the resources available. The total time required to execute the program is called elapsed time in operating system. • This elapsed time is a measure of the performance of the entire computer system. It is affected by the speed of the processor, the disk, and the printer.
- 33. Multiprocessor and Multicomputer • Multiprocessor:- • A Multiprocessor is a computer system with two or more central processing units (CPUs) share full access to a common RAM. • The main objective of using a multiprocessor is to boost the system’s execution speed, with other objectives being fault tolerance and application matching. • There are two types of multiprocessors, one is called shared memory multiprocessor and another is distributed memory multiprocessor. • In shared memory multiprocessors, all the CPUs shares the common memory but in a distributed memory multiprocessor, every CPU has its own private memory.
- 36. • Benefits of using a Multiprocessor – • Enhanced performance. • Multiple applications. • Multi-tasking inside an application. • High throughput and responsiveness. • Hardware sharing among CPUs.
- 37. Multicomputer • A multicomputer system is a computer system with multiple processors that are connected together to solve a problem. • Each processor has its own memory and it is accessible by that particular processor and those processors can communicate with each other via an interconnection network. • As the multicomputer is capable of messages passing between the processors, it is possible to divide the task between the processors to complete the task. • Hence, a multicomputer can be used for distributed computing. It is cost effective and easier to build a multicomputer than a multiprocessor.
- 39. Multiprocessor •It consists of multiple processors within a single computer. •It is a singly shared memory that is attached to the elements being processed. •It is necessary for the processing elements to communicate with each other. •It is a dynamic network. •Example of multiprocessor is a sequent symmetry S-81. Multicomputer •It is an interlinked multiple autonomous computer. •The memory attached to the processing elements are distributed in multiples. •It is not required for elements being processed to communicate. •It is a type of static network. •Example of a multicomputer is a message passing multicomputer.
- 40. MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS AND PROGRAMS • NUMBERS: • Number systems are the technique to represent numbers in the computer system architecture, every value that you are saving or getting into/from computer memory has a defined number system. • Computer architecture supports following number systems. • Binary number system • Octal number system • Decimal number system • Hexadecimal (hex) number system
- 41. • 1) Binary Number System • A Binary number system has only two digits that are 0 and 1. Every number (value) represents with 0 and 1 in this number system. The base of binary number system is 2, because it has only two digits. • 2) Octal number system • Octal number system has only eight (8) digits from 0 to 7. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7 in this number system. The base of octal number system is 8, because it has only 8 digits. • 3) Decimal number system • Decimal number system has only ten (10) digits from 0 to 9. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, 7,8 and 9 in this number system. The base of decimal number system is 10, because it has only 10 digits. • 4) Hexadecimal number system • A Hexadecimal number system has sixteen (16) alphanumeric values from 0 to 9 and A to F. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, 7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E and F in this number system. The base of hexadecimal number system is 16, because it has 16 alphanumeric values. Here A is 10, B is 11, C is 12, D is 13, E is 14 and F is 15.
- 42. INSTRUCTIONS AND INSTRUCTION SEQUENCING • Four types of operations • 1. Data transfer between memory and processor registers. • 2. Arithmetic & logic operations on data • 3. Program sequencing & control • 4. I/O transfers. • 1) Register transfer notations(RTN) • R3<–[R1]+[R2] • Right hand side of RTN-denotes a value. • Left hand side of RTN-name of a location. • 2) Assembly language notations(ALN) • Add R1, R2, R3 • Adding contents of R1, R2 & place sum in R3.
- 43. • 3) Basic instruction types-4 types • Three address instructions– Add A,B,C • A, B-source operands • C-destination operands • Two address instructions-Add A,B • B <–[A] + [B] • One address instructions –Add A • Add contents of A to accumulator & store sum back to accumulator. • Zero address instructions • Instruction store operands in a structure called push down stack.
- 44. • 4) Instruction execution & straight line sequencing • The processor control circuits use information in PC to fetch & execute instructions one at a time in order of increasing address. • This is called straight line sequencing. • Executing an instruction-2 phase procedures. • 1st phase–“instruction fetch”-instruction is fetched from memory location whose address is in PC. • This instruction is placed in instruction register in processor • 2nd phase-“instruction execute”-instruction in IR is examined to determine which operation to be performed. • 5) Branching • Branch-type of instruction loads a new value into program counter. • So processor fetches & executes instruction at this new address called “branch target” • Conditional branch-causes a branch if a specified condition is satisfied. • E.g. Branch>0 LOOP –conditional branch instruction .it executes only if it satisfies condition.
- 45. • 6) Condition codes • Recording required information in individual bits called “condition code flags”. • These flags are grouped together in a special processor register called “condition code register” or “status register” • Individual condition code flags-1 or 0. • 4 commonly used flags. • 1) N (negative)-set to 1 if result is –ve or else 0. • 2) Z (zero)-set to 1 if result is 0, or else 0 . • 3) V (overflow)-set to 1if arithmetic overflow occurs or else 0. • 4) C(carry)-set to 1 if carry out results from operation or else 0
- 46. Addressing Modes • The operation field of an instruction specifies the operation to be performed. This operation will be executed on some data which is stored in computer registers or the main memory. The way any operand is selected during the program execution is dependent on the addressing mode of the instruction. • Types of Addressing Modes • Immediate Mode • In this mode, the operand is specified in the instruction itself. An immediate mode instruction has an operand field rather than the address field. • For EXAMPLE:ADD 7,which says Add 7 to contents of accumulator. 7 is the operand here.
- 49. • Auto Increment/Decrement Mode • In this the register is incremented or decremented after or before its value is used. • Direct Addressing Mode • In this mode, effective address of operand is present in instruction itself. • Single memory reference to access data. • No additional calculations to find the effective address of the operand.
- 52. Relative Addressing Mode • It is a version of Displacement addressing mode. • In this the contents of PC(Program Counter) is added to address part of instruction to obtain the effective address. • EA=A+(PC),where EA is effective address and PC is program counter. • The operand is A cells away from the current cell(the one pointed to by PC) •Base Register Addressing Mode • It is again a version of Displacement addressing mode. This can be defined as • where • EA=A+(R) ,where A is displacement and R holds pointer to base address.
- 53. • Stack Addressing Mode • In this mode, operand is at the top of the stack. • FOR EXAMPLE:ADD, this instruction will POP top two items from the stack, add them, and will then PUSH the result to the top of the stack.
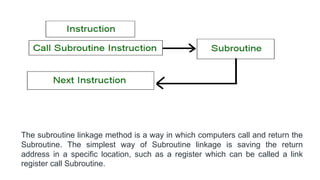
- 62. subroutines • A set of instructions that are used repeatedly in a program can be referred to as Subroutine. Only one copy of this Instruction is stored in the memory. When a Subroutine is required it can be called many times during the Execution of a particular program. A call Subroutine Instruction calls the Subroutine. Care Should be taken while returning a Subroutine as Subroutine can be called from a different place from the memory. • The content of the PC must be Saved by the call Subroutine Instruction to make a correct return to the calling program.
- 63. The subroutine linkage method is a way in which computers call and return the Subroutine. The simplest way of Subroutine linkage is saving the return address in a specific location, such as a register which can be called a link register call Subroutine.








































![INSTRUCTIONS AND INSTRUCTION SEQUENCING
• Four types of operations
• 1. Data transfer between memory and processor registers.
• 2. Arithmetic & logic operations on data
• 3. Program sequencing & control
• 4. I/O transfers.
• 1) Register transfer notations(RTN)
• R3<–[R1]+[R2]
• Right hand side of RTN-denotes a value.
• Left hand side of RTN-name of a location.
• 2) Assembly language notations(ALN)
• Add R1, R2, R3
• Adding contents of R1, R2 & place sum in R3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/counit-1-240411050802-f4212b8c/85/Computer-Organisation-unit-1-basics-of-computer-Organisation-42-320.jpg)
![• 3) Basic instruction types-4 types
• Three address instructions– Add A,B,C
• A, B-source operands
• C-destination operands
• Two address instructions-Add A,B
• B <–[A] + [B]
• One address instructions –Add A
• Add contents of A to accumulator & store sum back to accumulator.
• Zero address instructions
• Instruction store operands in a structure called push down stack.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/counit-1-240411050802-f4212b8c/85/Computer-Organisation-unit-1-basics-of-computer-Organisation-43-320.jpg)














































![Computer fundamental basic comuter organization [www.studysharebd.com]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/computerfundamentalbasiccomuterorganizationwww-200124111133-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)











![Ise iv-computer organization [10 cs46]-notes new](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ise-iv-computerorganization10cs46-notesnew-140624013827-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
















![[2025] Qualtric XM-EX-EXPERT Study Plan | Practice Questions + Exam Details](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/2025qualtricxm-ex-expertstudyplanpracticequestionsexamdetails-250527093747-448c8922-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)















