Configuring-Cisco-CME and its details.ppt
- 1. 1 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Configuring Cisco CallManager Express (CME) Cisco Networking Academy Program
- 2. 2 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Overview of Cisco CME
- 3. 3 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony What is Cisco CallManager Express? Cisco CME Trunks WAN • Call processing for small to medium sized deployments • VoIP integrated solution • Up to 120 IP phones • IOS based solution PSTN
- 4. 4 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony What is Cisco CallManager Express? (Cont.) • Select IOS based platform • Multiservice access routers 2600XM 3700 1700
- 5. 5 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony How Does Cisco CallManager Express Work? Connection(s) to PSTN • Analog • Digital PSTN
- 6. 6 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony WAN How Does Cisco CallManager Express/Cisco Unity Express Work? (Cont.) H.323 between Cisco CME systems H.323 H.323 H.323 PSTN Gateway and IP to IP Gateway functionality PSTN WAN SIP PSTN PSTN
- 7. 7 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Differences between Traditional Telephony and VoIP
- 8. 8 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Basic Components of a Telephony Network
- 9. 9 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Central Office Switches
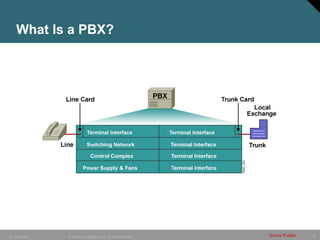
- 10. 10 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony What Is a PBX?
- 11. 11 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony What Is a Key System?
- 12. 12 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Basic Call Setup
- 13. 13 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Digitizing Analog Signals 1. Sample the analog signal regularly 2. Quantize the sample 3. Encode the value into a binary expression 4. Compress the samples to reduce bandwidth (multiplexing), optional step
- 14. 14 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Nyquist Theorem
- 15. 15 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Quantization
- 16. 16 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Quantization Techniques • Linear Uniform quantization • Logarithmic quantization Compands the signal Provides a more uniform signal-to-noise ratio • Two methods α-law (most countries) μ-law (Canada, U.S., and Japan)
- 17. 17 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Voice-Compression Techniques • Waveform algorithms PCM ADPCM • Source algorithms LDCELP CS-ACELP
- 18. 18 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Example: Waveform Compression • PCM Waveform coding scheme • ADPCM Waveform coding scheme Adaptive: automatic companding Differential: encode changes between samples only • ITU standards: G.711 rate: 64 kbps = (2 x 4 kHz) x 8 bits/sample G.726 rate: 32 kbps = (2 x 4 kHz) x 4 bits/sample G.726 rate: 24 kbps = (2 x 4 kHz) x 3 bits/sample G.726 rate: 16 kbps = (2 x 4 kHz) x 2 bits/sample
- 19. 19 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Example: Source Compression • CELP Hybrid coding scheme • High-quality voice at low bit rates, processor intensive • G.728: LDCELP—16 kbps • G.729: CS-ACELP—8 kbps G.729A variant—8 kbps, less processor intensive, allows more voice channels encoded per DSP Annex-B variant –VAD and CNG
- 20. 20 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony G.729 and G.729A Comparison • Both are ITU standards • Both are 8 kbps CS-ACELP • G.729 more complex and processor intensive • G.729 slightly higher quality than G.729A • Compression delay the same (10 to 20 ms) • Annex-B variant may be applied to either
- 21. 21 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Real-Time Transport Protocol • Provides end-to-end network functions and delivery services for delay-sensitive, real-time data, such as voice and video • Works with queuing to prioritize voice traffic over other traffic • Services include: Payload type identification Sequence numbering Timestamping Delivery monitoring
- 22. 22 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Real-Time Transport Control Protocol • Monitors the quality of the data distribution and provides control information • Provides feedback on current network conditions • Allows hosts involved in an RTP session to exchange information about monitoring and controlling the session • Provides a separate flow from RTP for UDP transport use
- 23. 23 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony RTP Header Compression • RTP header compression saves bandwidth by compressing packet headers across WAN links
- 24. 24 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony When to Use RTP Header Compression • Narrowband links • Slow links (less than 2 Mbps) • Need to conserve bandwidth on a WAN interface
- 25. 25 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Challenges and Solutions in VoIP
- 26. 26 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Reliability and Availability • Traditional telephony networks claim 99.999% uptime • Data networks must consider reliability and availability requirements when incorporating voice • Methods to improve reliability and availability include: Redundant hardware Redundant links UPS Proactive network management
- 27. 27 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Bandwidth Implications of Codec
- 28. 28 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Impact of Voice Samples
- 29. 29 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Data Link Overhead • Ethernet: 18 bytes overhead • MLP: 6 bytes overhead • Frame Relay: 6 bytes overhead
- 30. 30 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Total Bandwidth Required
- 31. 31 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Effect of VAD
- 32. 32 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CME Features and Functionality
- 33. 33 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) Analog Phones V V ATA Skinny Skinny Analog V V H.323 FAX ATA
- 34. 34 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) • Cisco proprietary • Call Control protocol • Lightweight protocol • Low memory requirements • Low complexity • Low CPU requirements
- 35. 35 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) Skinny Protocol Caveats • QoS, bandwidth and CAC support are not built into the Skinny protocol • Complex connection paths can cause QoS problems • Remote registration of IP phones and ATAs is not supported
- 36. 36 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) • Cisco CME does not support remotely registered phones Remote Phones Local Phones PSTN WAN CME X X
- 37. 37 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) H.323 Protocol • Supports Voice, Video, and Data • Industry Standard • Complex protocol • Higher complexity than Skinny protocol • CAC functionality is part of the protocol • Authentication is part of the protocol
- 38. 38 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) H.323 Connections PSTN WAN CME CME Vmail CallManager Cluster H.323 H.323 H.323 V V H.323 Recommended
- 39. 39 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) Gatekeeper WAN Register Extension number and/or E.164 number Register H.323 Register Extension number and/or E.164 number 1000 2095551000 2000 3095552000 Register Cisco CME can register to a H.323 gatekeeper thereby ensuring the WAN is not oversubscribed
- 40. 40 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) SIP Protocol • Emerging standard • Vendor specific in most cases • Higher complexity than Skinny protocol • Authentication is part of the protocol • Based on other well known protocols
- 41. 41 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Supported Protocols and Integration Options (Cont.) SIP Connections PSTN WAN CME CME Vmail CallManager Cluster SIP SIP SIP V V H.323 H.323 is recommended today
- 42. 42 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Requirements • Feature license • Seat license • IOS platform 12.3(7)T or greater is recommended IP Voice • Cisco CME software and files GUI files Firmware
- 43. 43 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Restrictions Cisco CME 3.1 caveats • TAPI v2.1 • Cisco JTAPI • Cisco IP Softphone • Remote SCCP phones across a WAN • G.729 conferences • MGCP
- 44. 44 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Restrictions (Cont.) • TAPI Lite Functionality • Supported: Operation of multiple independent clients (e.g. one client per phone line) Windows phone dialer Outlook contact dialer Third party applications • Not Supported: TAPI based softphone Multiple-user or multiple-call handling (Required for ACD) Direct media- and voice-handling JTAPI
- 45. 45 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CME Network Parameters
- 46. 46 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Auxiliary VLANs • Prevent unnecessary IP address renumbering • Simplifies Quality of Service (QoS) configurations • Separates Voice and Data traffic • Requires two Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) one for Data and one for Voice • Requires only one drop down Ethernet for the CallManager Express IP phone and the PC plugged into the phone
- 47. 47 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Auxiliary VLANs (Cont.) IP Addressing Deployment Options 171.68.249.101 171.68.249.100 IP Phone + PC on separate switch ports Public IP addresses 171.68.249.100 171.68.249.101 Public IP addresses IP Phone + PC on same switch ports 10.1.1.1 171.68.249.100 IP Phone uses private Network IP Phone + PC on same switch ports IP Phone uses private network IP Phone + PC on separate switch ports 10.1.1.1 171.68.249.100 Recommended
- 48. 48 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Configuring Auxiliary VLANs Tagged 802.1q (Voice VLAN) Untagged 802.3 (Native VLAN) • An access port able to handle 2 VLANs • Native VLAN (PVID) and Auxiliary VLAN (VVID) • Hardware set to dot1q trunk
- 49. 49 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Configuring Auxiliary VLANs - Switching Review • Address learning • Forward/filter decision • Loop avoidance
- 50. 50 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Configuring Auxiliary VLANs (Cont.) Console(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 Console(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Console(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 1 Console)config-if)#switchport access vlan 12 Console(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Console(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 112 Console(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast Example 3550 switch or EtherSwitch Network Module • 802.1q trunking is enabled on the port • The access VLAN is used for the PC plugged into the IP phone • The voice VLAN is used for voice and signaling that originates and terminates on the IP phone • Spanning tree portfast enables the port to initialize quickly
- 51. 51 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Configuring Auxiliary VLANs (Cont.) Switch# show interface fa0/17 switchport Name: Fa0/17 Switchport: Enabled Administrative mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: Disabled Access Mode VLAN: 0 ((Inactive)) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 12 (VLAN0012) Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Trunking VLANs Active: 1-3,5,10,12 Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001 Priority for untagged frames: 0 Override vlan tag priority: FALSE Voice VLAN: 112 Appliance trust: none
- 52. 52 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Configuring Auxiliary VLANs - Router Configuration 802.1q trunk interface fastethernet 1/0.1 encapsulation dot1q 10 ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.255.0 interface fastethernet 1/0.2 encapsulation dot1q 20 ip address 10.20.0.1 255.255.255.0 ... VLAN 10 VLAN 20 Trunk on a router
- 53. 53 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony DHCP Service Setup • Assigns an IP addresses and subnet masks for one or more subnets • Optionally can assign a default gateway • Optionally can assign DNS servers • Optionally can assign other commonly used servers • The DHCP scope can be customized to assign a TFTP server to IP phones • Best practice is to configure a DHCP scope for the IP phones Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- 54. 54 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony DHCP Service Setup (Cont.) • Single DHCP IP Address Pool • Separate DHCP IP Address Pool for Each Cisco IP Phone • DHCP Relay Server DHCP Service Options
- 55. 55 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony DHCP Service Setup (Cont.): Phone Bootup • Range of available IP addresses • The subnet mask • A default gateway • The address of the TFTP server • DNS server(s) On the Cisco CME router a DHCP Scope can be configured. The scope should define the following: The IP phone powers on The phone performs a Power on Self Test (POST) Through CDP the IP phone learns what the auxiliary VLAN is The phone initializes the IP stack The phone boots up Continued next slide…
- 56. 56 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony DHCP Service Setup (Cont.): Phone Bootup (Cont.) IP phone send DHCP Discover broadcast requesting an IP address DHCP server selects a free IP address from the pool and sends along with the other scope parameters as a DHCP Offer The IP phone initializes applies the IP configuration to the IP stack The IP phone requests it configuration file from the TFTP server
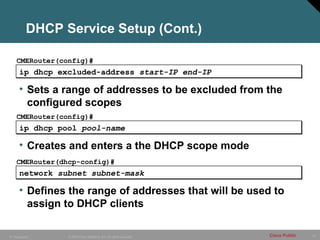
- 57. 57 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony ip dhcp excluded-address start-IP end-IP CMERouter(config)# • Sets a range of addresses to be excluded from the configured scopes ip dhcp pool pool-name CMERouter(config)# • Creates and enters a the DHCP scope mode DHCP Service Setup (Cont.) network subnet subnet-mask CMERouter(dhcp-config)# • Defines the range of addresses that will be used to assign to DHCP clients
- 58. 58 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony default-router IP-address CMERouter(dhcp-config)# • Sets the default gateway that will handed out to the DCHP clients dns-server primary-IP [secondary IP] CMERouter(dhcp-config)# • Sets the DNS server(s) that will assigned to the DHCP clients DHCP Service Setup (Cont.) option option-number ip IP-address CMERouter(dhcp-config)# • Defines a custom option and its value
- 59. 59 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony DHCP Service Setup (Cont.) Configuring DHCP on an IOS router • Option 150 sets the TFTP server on the IP phone • The TFTP server contains the configuration files and firmware for the IP phone CMERouter(config)#ip dhcp exluded-address 10.90.0.1 10.90.0.10 CMERouter(config)#ip dhcp pool mypool CMERouter(dhcp-config)#network 10.90.0.0 255.255.255.0 CMERouter(dhcp-config)#option 150 ip 10.90.0.1 CMERouter(dhcp-config)#default-router 10.90.0.1 CMERouter(dhcp-config)#dns-server 10.100.0.1 10.100.0.2 CMERouter(dhcp-config)#exit
- 60. 60 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony IP Phone Registration
- 61. 61 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Files • Firmware • SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml • XmlDefault.cnf.xml • SCCP-dictionary.xml • Phonemodel-dictionary.xml • Phonemodel-tones.xml Files critical to the IP phone TFTP Server 7960 Firmware XML SEP XML SEP XML SEP XML SEP 7940 Firmware 7920 Firmware 7912 Firmware 7905 Firmware 7902 Firmware 7910 Firmware XML SEP
- 62. 62 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Files (Cont.): Firmware • Firmware is installed in flash RAM with the Cisco CME software or individually as needed • Served up by the TFTP server on the Cisco CME router • The command tftp-server flash:firmware-file-name CMERouter1#show flash -#- --length-- -----date/time------ path 1 399514 Mar 1 2002 12:56:28 P00305000301.sbn 2 22649180 Mar 1 2002 12:38:00 c3725-ipvoice-mz.123-7.T.bin 3 321939 Mar 1 2002 12:55:58 CP7902010200SCCP031023A.sbin 4 317171 Mar 1 2002 12:56:06 CP7905010200SCCP031023A.sbin 5 317968 Mar 1 2002 12:56:10 CP7912010200SCCP031023A.sbin 6 700651 Mar 1 2002 12:56:18 CiscoIOSTSP.zip 7 369950 Mar 1 2002 12:56:22 P00303020214.bin 8 333822 Mar 1 2002 12:56:30 P00403020214.bin 9 47904 Mar 1 2002 12:56:54 S00103020002.bin 10 301298 Mar 1 2002 12:56:56 ata18x-v2-16-ms-030327b.zup 11 496521 Mar 1 2002 12:57:22 music-on-hold.au 12 1908762 Mar 1 2002 12:56:54 P00503010100.bin 13 21 Mar 1 2002 12:56:18 OS7920.txt 14 839984 Mar 1 2002 12:57:18 cmterm_7920.3.3-01-06.bin … … 33 307067 Mar 1 2002 12:56:02 CP79050101SCCP030530B31.zup 34 710144 Mar 1 2002 12:57:06 cme-gui-3.1.1.tar 7905 Firmware 7940 Firmware 7960 Firmware
- 63. 63 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Files (Cont.): Device Configuration XML File <device> <devicePool> <callManagerGroup> <members> <member priority="0"> <callManager> <ports> <ethernetPhonePort>2000</ethernetPhonePort> </ports> <processNodeName>10.15.0.1</processNodeName> </callManager> </member> </members> </callManagerGroup> </devicePool> <versionStamp>{Jan 01 2002 00:00:00}</versionStamp> <loadInformation>P00303020214</loadInformation> - <userLocale> <name>English_United_States</name> <langCode>en</langCode> </userLocale> <networkLocale>United_States</networkLocale> <idleTimeout>0</idleTimeout> <authenticationURL /> <directoryURL>http://10.15.0.1/localdirectory</directoryURL> <idleURL /> <informationURL /> <messagesURL /> <proxyServerURL /> <servicesURL /> </device> SEPXXXXXXXXXXXX.cnf.xml * XXXXXXXXXXX = to the MAC address XML SEP
- 64. 64 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Files (Cont.): Default XML File <Default> <callManagerGroup> <members> <member priority="0"> <callManager> <ports> <ethernetPhonePort>2000</ethernetPhonePort> </ports> <processNodeName>10.15.0.1</processNodeName> </callManager> </member> </members> </callManagerGroup> <loadInformation6 model="IP Phone 7910">P00403020214</loadInformation6> <loadInformation124 model="Addon 7914"></loadInformation124> <loadInformation9 model="IP Phone 7935"></loadInformation9> <loadInformation8 model="IP Phone 7940">P00303020214</loadInformation8> <loadInformation7 model="IP Phone 7960">P00303020214</loadInformation7> <loadInformation20000 model="IP Phone 7905"></loadInformation20000> <loadInformation30008 model="IP Phone 7902"></loadInformation30008> <loadInformation30002 model="IP Phone 7920"></loadInformation30002> <loadInformation30019 model="IP Phone 7936"></loadInformation30019> <loadInformation30007 model="IP Phone 7912"></loadInformation30007> </Default> XMLDefault.cnf.xml * Notice there is no ATA or 7914 XML Default
- 65. 65 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Files (Cont.): Language Specific XML Files <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?> <phrases> <phrase i="173" t="Login"/> <phrase i="172" t="Flash"/> <phrase i="171" t="Acct"/> <phrase i="170" t="Incompatible device type"/> <phrase i="169" t="Another Barge exists"/> <phrase i="168" t="Failed to setup Barge"/> <phrase i="167" t="Barge" /> <phrase i="166" t="Network congestion,rerouting" /> <phrase i="165" t="CallBack" /> <phrase i="164" t="SAC" /> <phrase i="163" t="DND" /> <phrase i="162" t="TrnsfVM" /> <phrase i="161" t="SetWtch" /> <phrase i="160" t="Intrcpt" /> <phrase i="159" t="ImmDiv" /> <phrase i="158" t="Voicemail"/> <phrase i="157" t="RmLstC"/> <phrase i="156" t="Unknown Number"/> <phrase i="155" t="Not Enough Bandwidth"/> <phrase i="154" t="Private"/> <phrase i="153" t="Park Number"/> <phrase i="152" t="Conference"/> <phrase i="151" t="Error Mismatch"/> <phrase i="150" t="Error Unknown"/> <phrase i="149" t="Error Pass Limit"/> … 7960-dictionary.xml SCCP-dictionary.xml Contents will vary based upon language selected with the user-locale command XML Language
- 66. 66 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Files (Cont.): Call Progress XML File <tones> <tone c1="30831" i1="-2032" c2="30467" i2="-1104" d="2" t="ringing"> <part m="on" t="2000"/> <part m="off" t="4000"/> <repeat c="65535"/> </tone> <tone c1="30467" i1="-1104" c2="28959" i2="-1404" d="2" t="reorder"> <part m="on" t="250"/> <part m="off" t="250"/> <repeat c="65535"/> </tone> <tone c1="30467" i1="-1104" c2="28959" i2="-1404" d="2" t="busy"> <part m="on" t="500"/> <part m="off" t="500"/> <repeat c="65535"/> </tone> <tone c1="30743" i1="-1384" c2="29780" i2="-1252" d="2" t="odial"> <part m="on" t="65535"/> <repeat c="65535"/> </tone> <tone c1="30831" i1="-2032" c2="31538" i2="-814" d="2" t="idial"> <part m="on" t="65535"/> <repeat c="65535"/> </tone> </tones> 7960-tones.xml Contents will vary based upon call progress tones selected with the network- locale command XML Call Progress
- 67. 67 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony IP Phone Information • The 7914 expansion module cannot auto register • Require the use of the “type” command entered by the administrator • All other valid devices can be recognized automatically by the Cisco CME system <loadInformation6 model="IP Phone 7910">P00403020214</loadInformation6> <loadInformation124 model="Addon 7914"></loadInformation124> <loadInformation9 model="IP Phone 7935"></loadInformation9> <loadInformation8 model="IP Phone 7940">P00303020214</loadInformation8> <loadInformation7 model="IP Phone 7960">P00303020214</loadInformation7> <loadInformation20000 model="IP Phone 7905"></loadInformation20000> <loadInformation30008 model="IP Phone 7902"></loadInformation30008> <loadInformation30002 model="IP Phone 7920"></loadInformation30002> <loadInformation30019 model="IP Phone 7936"></loadInformation30019> <loadInformation30007 model="IP Phone 7912"></loadInformation30007> No 7914 in the XMLDefault.cnf.xml XML Default
- 68. 68 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Download and Registration Power over Ethernet Step 1 - Switch sends a Fast Link Pulse (FLP) Step 3 - Power is applied FLP FLP Step 4 - Link is detected on switchport Step 6 - The amount of power really needed is passed through CDP from the IP phone to the switch CDP Step 5 - The IP phone boots up Power needed Step 2 - The phone returns the FLP to the switch due to a completed circuit
- 69. 69 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Download and Registration (Cont.) DHCP Step 7 - CDP is used to send the auxiliary VLAN information from the switch to the IP phone Step 8 - The IP phone initializes the IP stack and sends a DHCPDiscover broadcast message Step 9 - The DHCP server hears the DHCPDiscover message and selects an IP address from the scope and sends a DHCPOffer CDP DHCPDiscover DHCPOffer IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and TFTP server (option 150) Broadcast Voice VLAN DHCP Server DHCP Relay or
- 70. 70 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Download and Registration (Cont.) Existing IP Phone Step 10 - Phone applies addressing information obtained through DHCP to the IP stack Step 11 - Using the address of the TFTP server learned from the option 150 in the DHCPOffer the phone looks for and downloads the file named SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml (where AAAABBBBCCCC is the MAC address), if the file is found the phone will register Cisco CME is the TFTP Server SEP000F2470AA32.cnf.xml file TFTP request for the SEP000F2470AA32.cnf.xml file MAC 000F.2470.AA32 If no SEP XML file is found go to Step 14 XML SEP
- 71. 71 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Download and Registration (Cont.) Unknown IP Address Step 12 - If the firmware version currently on the phone is different than the version specified in the SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml file then the firmware is downloaded from the TFTP server Cisco CME is the TFTP Server TFTP request for firmware if needed Step 13 - IP phone will reboot if the firmware was updated MAC 000F.2470.AA32 Firmware file 7960 Firmware
- 72. 72 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Download and Registration (Cont.) Unknown IP Phone Step 15 - The phone will register to CallManager Express but without any assigned extension. No calls will be able to be placed or received and a SEP file will be created on the CallManager Express router Step 14 - If no SEP XML file was found then download from the TFTP server the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file CallManager Express is the TFTP Server XMLDefault.cnf.xml file TFTP request for the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file Unknown IP address with MAC 000F.2470.AA32 Step 16 - If auto assign is enabled or the phone has been configured then the new IP phone will register to the CallManager Express and given an extension number or XML Default
- 73. 73 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone-dn and Ephone
- 74. 74 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone-dn DN1 DN1 A DN and Extension number are equivalent Line and voice port are equivalent Has a unique tag or sequence number assigned when the ephone-dn is created Can have one or more telephone numbers associated with it Can have one voice channel or two voice channels Creates one or more telephony system pots dial peers when the ephone-dn is initially configured DN1 and DN2 Primary/Secondary extensions configured on a single line ephone-dn where the primary is an internal extension number and the secondary is an E.164 number One phone extension on a dual line ephone-dn for ephone-dns that need call waiting, consultative transfer and conferencing DN1 Primary extension number on a single line ephone-dn that can make or receive one call at a time ephone-dn ephone-dn ephone-dn
- 75. 75 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony ephone-dn dn-tag [dual-line] router(config)# • This command is used to create an extension (ephone-dn) for a Cisco IP phone line, an intercom line, a paging line, a voice-mail port, or a message- waiting indicator (MWI). number dn-number secondary dn-number [no-reg [both | primary]] router(config-ephone-dn)# • This command is used to associate a DN number with the ephone-dn instance Ephone-dn (Cont.)
- 76. 76 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone MAC 000F.2470.F92A MAC 000F.2470.F92E MAC 000F.2470.F92B 7960 7912 ATA 188 Button 1 Analog 1 Analog 2 Button 1 Button 2 Button 3 Button 4 Button 5 Button 6 DN DN DN DN DN DN DN DN DN MAC 000F.2470.F92D • Software configuration of a physical phone • Has a unique tag or sequence number assigned when the ephone is created • Can be an IP phone, analog phone attached to an ATA • The MAC of the IP phone or ATA is used to tie the software configuration to the hardware • The hardware is auto detected for all supported models except the ATA and 7914 expansion module • Can have one or more ephone- dn(s) associated with the ephone • Number of line buttons will vary based on the hardware
- 77. 77 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony ephone phone-tag router(config)# • Creates an ephone instance and enters ephone configuration mode mac-address mac-address router(config-ephone)# • Assigns the physical IP phone by MAC address with this instance of an ephone Ephone (Cont.)
- 78. 78 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone (Cont.) button button-number {separator} dn-tag [[button-number {separator} dn-tag]…] router(config-ephone)# • Associates the ephone-dn(s) with a specific button(s) on the IP phone type {7940 | 7960} addon 1 7914 [2 7914] router(config-ephone)# • Defines the device as a 7914 module(s)
- 79. 79 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone (Cont.): Basic Example CMERouter(Config)#ephone-dn 7 CMERouter(Config-ephone-dn)#number 1001 CMERouter(config)#ephone 1 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.F8F8 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:7 MAC 000F.2470.F8F8 1001 ephone 1 Button 1 ephone-dn 7: one virtual port 000F.2470.F8F8
- 80. 80 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone (Cont.): Example Multiple Ephones • Four physical phones • Four ephones defined • Four ephone-dns defined ATA-186/188 V V 1004 1005 1006 1007 1004 1004 1005 1005 1006 1006 1007 1007
- 81. 81 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone (Cont.): Example Multiple Ephones Configuration CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 10 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1004 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 11 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1005 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 12dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1006 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 13 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1007 CMERouter(config)#ephone 1 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.F8F1 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:10 CMERouter(config)#ephone 2 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.A302 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:11 CMERouter(config)#ephone 3 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.66F6 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:12 CMERouter(config)#ephone 4 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.7B54 CMERouter(config-ephone)#type ata CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:13 Configuration example
- 82. 82 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone (Cont.): Multiple Ephone-dns • Two physical phones • Four dual line ephone-dns defined • Two ephones defined 1008 on line 1 1009 on line 2 1008 1008 1009 1009 1010 1010 1011 1011 1010 on line 1 1011 on line 6 Button 1 Button 2 Button 1 Button 6
- 83. 83 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone (Cont.): Multiple Ephone-dns Configuration Example CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 14 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1008 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 15 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1009 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 16 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1010 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 17 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1011 CMERouter(config)#ephone 5 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.FAA1 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:14 2:15 CMERouter(config)#ephone 6 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.A7E2 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:16 6:17 Multiple line ephone configuration example
- 84. 84 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Type of Ephone-dns: Overview 1002 1002 1001 1004 and 1005 1006 1006 1007 Single line Dual line Primary and secondary extension on a single or dual line ephone-dn Shared single or dual line ephone-dn Overlay ephone- dns on an ephone 1003 1003 Multiple single or dual line ephone- dns on one or more ephones 1003 1003 Six types of ephone-dns • Single-line ephone-dn • Dual-line ephone-dn • Primary and secondary extension on ephone-dn • Shared ephone-dn • Multiple ephone-dns • Overlay ephone-dn
- 85. 85 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Single Line Ephone-dn • The ephone-dn creates one virtual voice port • One call to or from this ephone-dn at any one time CMERouter(Config)#ephone-dn 1 CMERouter(Config-ephone-dn)#number 1001 1001 One channels One virtual voice port
- 86. 86 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Dual Line Ephone-dn • The ephone-dn creates one virtual voice port • The “dual-line” keyword indicates two voice channels for calls to terminate on an ephone-dn extension • Use on ephone-dns that need call waiting, consultative transfer, or conferencing on one button • Cannot be used on ephone-dns used for intercoms, paging, MWI or MoH feeds CMERouter(Config)#ephone-dn 2 dual-line CMERouter(Config-ephone-dn)#number 1002 1002 1002 Two channels One virtual voice port
- 87. 87 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Primary and Secondary Extension Number on Ephone-dn • The ephone-dn creates one virtual voice port • Two different directory numbers can be dialed to reach this ephone-dn • One call connection allowed if configured as a single-line ephone-dn • Two call connections allowed if configured as a dual-line ephone-dn • Allows two numbers to be configured without using an extra ephone-dn • The secondary number will be registered to the H.323 gatekeeper CMERouter(Config)#ephone-dn 6 CMERouter(Config-ephone-dn)#number 1005 secondary 2065559005 no-reg primary 1005 and 2065559005 One channels One virtual voice port
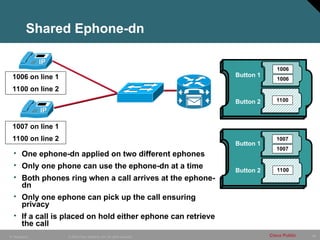
- 88. 88 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Shared Ephone-dn • One ephone-dn applied on two different ephones • Only one phone can use the ephone-dn at a time • Both phones ring when a call arrives at the ephone- dn • Only one ephone can pick up the call ensuring privacy • If a call is placed on hold either ephone can retrieve the call 1006 on line 1 1100 on line 2 1006 1006 1007 1007 1007 on line 1 1100 on line 2 Button 1 Button 2 Button 1 Button 2 1100 1100
- 89. 89 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Shared Ephone-dn Configuration Example CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 7 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1006 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 8 dual-line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1007 CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 9 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1100 CMERouter(config)#ephone 7 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.FAA1 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:7 2:9 CMERouter(config)#ephone 8 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.A7E2 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:8 2:9 Shared line appearance configuration example
- 90. 90 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Two Ephone-dns with one extension number 1003 1003 Button 1 Button 2 preference 0 no huntstop preference 1 huntstop Ephone 3 1003 1003 1004 Button 2 preference 0 no huntstop 1004 Button 2 preference 1 huntstop Ephone 4 Ephone 5 Multiple ephone-dns 1004 1004 • On the same ephone Used when more than two calls to the same extension are needed • On different ephones Used when two different ephones need the same number Not a shared line Only one ephone will ring at a time A call on hold can be retrieved only by the ephone that put the call on hold
- 91. 91 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony preference {0-10} router(config-ephone-dn)# • Sets the dial-peer preference order huntstop [channel] router(config-ephone-dn)# • Discontinues the call hunting behavior for an extension (ephone-dn) or an extension line (dual-line) Preference and Huntstop Commands
- 92. 92 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Huntstop Ephone-dn 10 Channel 1 Channel 2 Ephone-dn 11 Channel 1 Channel 2 Ephone-dn 12 Channel 1 Channel 2 no huntstop no huntstop Ephone-dn 13 Channel 1 Channel 2 huntstop no huntstop channel no huntstop channel no huntstop channel * Ring no answer timeout of 10 seconds set globally X Busy Busy Busy Busy Busy Call arrives at first ephone-dn Preference 0 Preference 1 Preference 2 Preference 3 1020 DN 1020 DN 1020 DN 1020 DN * Same DN on the ephone-dns
- 93. 93 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Huntstop Channel Ephone-dn 10 Channel 1 Channel 2 Ephone-dn 11 Channel 1 Channel 2 Ephone-dn 12 Channel 1 Channel 2 no huntstop no huntstop Ephone-dn 13 Channel 1 Channel 2 huntstop huntstop channel huntstop channel no huntstop channel * Ring no answer timeout of 10 seconds set globally X Busy Busy Busy Call arrives at first ephone-dn Preference 0 Preference 1 Preference 2 Preference 3 1020 DN 1020 DN 1020 DN 1020 DN
- 94. 94 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Two Ephone-dns/One Number/Same Ephone • If either of the two voice channels are available, the ephone-dn assigned to line button 1 will be used when an incoming call is setup • When the two voice channels on the ephone-dn are being used on line button 1, an incoming call will roll to the ephone-dn assigned to line button 2 • A fifth call will receive busy treatment when both voice channels on both ephone-dns are being used on line button 1 and 2 • The preference of 0 is more preferred than a preference of 1. The default is 0 • The “no huntstop” on the line button 1 ephone-dn allows the call to hunt to the second ephone-dn when the first ephone-dn is busy • The “huntstop” on the line button 2 ephone-dn stops the hunting behavior and applies the busy treatment 1003 on line button 1 1003 on line button 2 1003 1003 Button 1 Button 2 preference 0 no huntstop preference 1 huntstop Ephone 3 1003 1003
- 95. 95 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Two Ephone-dns/One Number/Same Ephone CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 3 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1003 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#preference 0 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#no huntstop CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 4 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1003 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#preference 1 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#huntstop CMERouter(config)#ephone 3 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.FAA1 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 1:3 2:4 Two ephone-dns with one number on the same ephone configuration example
- 96. 96 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Two Ephone-dns/One Number/Diff Ephones • Ephone 4 will be used first if available • When the first ephone-dn is being used on ephone 4, an incoming call will use the ephone-dn assigned to ephone 5 • A third call will receive busy treatment when both ephone-dns are being used on line ephone 4 and 5 • The preference of 0 is more preferred than a preference of 1; the default is 0 • The “no huntstop” on the ephone-dn on ephone 4 allows the call to hunt to the second ephone-dn on ephone 5 when the first ephone-dn is busy • The “huntstop” on the ephone-dn on ephone 5 stops the hunting behavior and applies the busy treatment for the third call • Unlike a share line appearance, if a call is placed on hold, only the original phone will be able to retrieve the call 1004 on line button 2 1004 Button 2 preference 0 no huntstop 1004 on line button 2 1004 Button 2 preference 1 huntstop Ephone 4 Ephone 5
- 97. 97 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Two Ephone-dns/One Number/Diff Ephones Two ephone-dns with one number on different ephones configuration example CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 5 dual line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1004 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#preference 0 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#no huntstop CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 6 dual line CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1004 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#preference 1 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#huntstop CMERouter(config)#ephone 4 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.F131 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 2:5 CMERouter(config)#ephone 5 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.FA5B CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 2:6
- 98. 98 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Overlay Ephone-dn • Two or more ephone-dns applied to the same ephone line button • Up to ten ephone-dns per line button on the phone 1101 on line 4 1101 on line 4 1101 1101 1101 1101 1101 on line 4 1101 on line 4 Button 4 Button 4 Button 4 Button 4 Preference 0 no huntstop Preference 1 huntstop Preference 0 no huntstop Preference 1 huntstop • All ephone-dns in the overlay set must be either single-line or all must be dual-line • The ephone-dns are usually applied on more than one phone • Allows up to ten calls (depending on the number of ephone-dns) to the same phone number that resides on multiple ephones • Call waiting and call pickup not supported • A call placed on hold can be retrieved by only the phone that placed the call on hold
- 99. 99 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Type of Ephone-dns (Cont.) Overlay Configuration Example CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 10 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1101 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#no huntstop CMERouter(config)#ephone-dn 11 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#number 1101 CMERouter(config-ephone-dn)#preference 1 CMERouter(config)#ephone 9 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.FA31 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 4o10,11 CMERouter(config)#ephone 10 CMERouter(config-ephone)#mac-address 000F.2470.A2E2 CMERouter(config-ephone)#button 4o10,11 Overlay configuration example
- 100. 100 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony max-dn max-dn router(config-telephone)# • Sets the maximum definable number of ephone-dns that may be configured in the system Number of Ephone-dns max-dn Command • The maximum number of ephone-dns supported is a function of the license and hardware platform • The default is zero
- 101. 101 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Number of Ephone-dns (Cont.) DN DN DN DN DN DN DN DN DN DN CMERouter(config-telephony)#max-dn 10 Attempting to create an 11th ephone-dn will fail
- 102. 102 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Ephone-dn (Cont.): Basic Configuration CMERouter(Config)#ephone-dn 7 CMERouter(Config-ephone-dn)#number 1001 One virtual voice port • Assigns a primary extension number to an ephone-dn 1001 One Line or channel
- 103. 103 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CME Files
- 104. 104 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files TFTP or FTP server GUI files firmware Music on Hold IOS copy ftp flash copy tftp flash or • Load firmware for IP phones and devices • Used to upgrade Cisco CME • Load music on hold files FLASH
- 105. 105 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) Bundled Files Bundled Cisco CME File
- 106. 106 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) Bundled Files cme-3.1.1.tar or cme-3.1.1.zip extracted yields • GUI Files cme-gui-3.1.1.zip • Cisco TAPI file CiscoIOSTSP.zip • Firmware files ATA 7902 7905 7912 7914 7914 Expansion Module 7920 7935 7936 7940 7960 • Music on Hold music-on-hold.au
- 107. 107 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) Individual Files Individual Cisco CME Files • Firmware files • Basic Cisco CME tar • GUI tar
- 108. 108 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) GUI Files GUI Files
- 109. 109 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) GUI Files cme-gui-3.1.1.tar extracted yields • XMLTemplate xml.template • GUI files admin_user.html admin_user.js CiscoLogo.gif Delete.gif dom.js downarrow.gif ephone_admin.html logohome.gif normal_user.html normal_user.js Plus.gif sxiconad.gif Tab.gif telephony_service.html uparrow.gif xml-test.html
- 110. 110 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) TAPI Integration Cisco CME - TAPI Integration
- 111. 111 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) TAPI Integration CiscoIOSTSP1.2.zip
- 112. 112 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Cisco CallManager Express Files (Cont.) Additional Files music-on-hold.au • Use the music-on-hold.au audio file to provide music for external callers on hold when you are not using a live feed xml.template • Use the xml.template file to allow or restrict the GUI functions that are available to an optional customer administrator
- 113. 113 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Initial Phone Setup
- 114. 114 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Phones Setup in Cisco CallManager Express System Three ways to setup phones: • Manual Numerous commands from the CLI Requires knowledge of Cisco CME commands Phones entered manually • Partially automated Numerous commands from the CLI Requires knowledge of Cisco CME commands Simplifies deployment of many IP phones • Automated Few commands needed from the CLI Requires little knowledge of Cisco CME commands Simplifies deployments
- 115. 115 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Automated Setup: Overview Automated Setup • Simple to configure • Question and answer interface • Good for inexperienced administrators • Created IOS commands in the background • Deployment and configuration are automated • Must be no existing telephony service configuration
- 116. 116 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Automated Setup (Cont.) • Configure NTP prior to running the setup utility • Load the firmware files into flash RAM prior to running the setup utility • Enter the automated setup mode by entering the command “telephony-service setup” • A question and answer session will start asking for basic parameters • CTRL + c keystroke can be used at any time to break out of the setup mode • No changes are committed until the end CMERouter1(config)#telephony-service setup --- Cisco IOS Telephony Services Setup --- Do you want to setup DHCP service for your IP Phones? [yes/no]: y Configuring DHCP Pool for Cisco IOS Telephony Services : IP network for telephony-service DHCP Pool:10.90.0.0 Subnet mask for DHCP network :255.255.255.0 TFTP Server IP address (Option 150) :10.90.0.1 Default Router for DHCP Pool :10.90.0.1 Do you want to start telephony-service setup? [yes/no]: y Configuring Cisco IOS Telephony Services : Enter the IP source address for Cisco IOS Telephony Services :10.90.0.1 Enter the Skinny Port for Cisco IOS Telephony Services : [2000]:2000 How many IP phones do you want to configure : [0]: 10 Do you want dual-line extensions assigned to phones? [yes/no]: y What Language do you want on IP phones : 0 English 6 Dutch 1 French 7 Norwegian 2 German 8 Portuguese 3 Russian 9 Danish 4 Spanish 10 Swedish 5 Italian [0]: 0
- 117. 117 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Automated Setup (Cont.) • When configuration is committed the settings show up in the running-config Which Call Progress tone set do you want on IP phones : 0 United States 1 France 2 Germany 3 Russia 4 Spain 5 Italy 6 Netherlands 7 Norway 8 Portugal 9 UK 10 Denmark 11 Switzerland 12 Sweden 13 Austria 14 Canada [0]: 0 What is the first extension number you want to configure : [0]: 9000 Do you have Direct-Inward-Dial service for all your phones? [yes/no]: y Enter the full E.164 number for the first phone :2095559000 Do you want to forward calls to a voice message service? [yes/no]: y Enter extension or pilot number of the voice message service:9999 Call forward No Answer Timeout : [18]: 10 Do you wish to change any of the above information? [yes/no]: n ---- Setup completed config ---
- 118. 118 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Automated Setup (Cont.): Results DHCP pool created Firmware available to TFTP server Flash is searched and if firmware is found it will be loaded Telephony-service configuration results DID configuration Firmware is searched and if MoH is found this entry is made The selected number of ephone- dns are configured Creates SEP XML files at boot up and load to RAM ip dhcp pool ITS network 10.90.0.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 10.90.0.1 option 150 ip 10.90.0.1 tftp-server flash:P00303020214.bin tftp-server flash:P00403020214.bin telephony-service load 7910 P00403020214 load 7960-7940 P00303020214 create cnf-files max-ephones 10 max-dn 10 ip source-address 10.10.0.1 port 2000 voicemail 9999 auto assign 1 to 10 dialplan-pattern 1 2095559... extension-length 4 extension- pattern 1... moh music-on-hold.au ephone-dn 1 dual-line number 401 call-forward busy 9999 call-forward noans 9999 timeout 10
- 119. 119 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Partially Automated Setup: Overview • Partially Automated Setup • Is the same as a manual setup except for deploying phones • Deployment of IP phones is automated • Uses the “auto assign” command • All ephone-dns must be the same type (single-line or dual-line)
- 120. 120 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony auto assign start-dn to stop-dn [type model] [cfw number timeout seconds] CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Automatically assigns the ephone-dns configured to new ephones Partially Automated Setup (Cont.) Auto Assign Command Auto assign usage guidelines • Can take up to 5 minutes for phones to register • Wait for all phones to register before saving the configuration • cfw setting defines the call forward busy number and timeout value for phones that register
- 121. 121 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Phones Setup in Cisco CallManager Express System • The lowest unassigned ephone-dn in matching statement range will be used • If all ephone-dns in a range have been assigned, some phones may not receive an ephone-dn or may overflow to the general auto assign without a type • If the new IP phone does not match any auto assign with a type, then the auto assign without a type will be used New phone plugs in telephony-service auto assign 1 to 10 type 7920 auto assign 11 to 20 type 7940 auto assign 21 to 40 type 7960 auto assign 41 to 50 ... ephone-dn 1 dual-line number 1000 ... • When an new IP phone registers with the Cisco CME system, this creates a new ephone with the MAC address of the IP phone • A pre-existing ephone-dn is assigned to the new ephone; this is selected from the range defined for the type of phone
- 122. 122 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Manual Setup: Overview • All commands can be entered from the CLI • Good for experienced administrators • Leverages IOS knowledge • Full functionality through IOS commands • Deployment of IP phones can be batched or scripted through a text file
- 123. 123 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Manual Setup (Cont.): Commands Overview • tftp-server flash:filename • telephony-service • max-ephones max-ephones • max-dn max-directory-numbers • load phone-type firmware-file • ip source-address ip-address [port port] • create cnf-files • keepalive seconds • dialplan-pattern tag pattern extension-length length extension-pattern pattern Commands needed to configure a basic telephony service
- 124. 124 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony 7940/60 Firmware tftp-server flash:filename CMERouter(config)# • Allows a file in flash to be downloadable with TFTP Manual Setup (Cont.): tftp-server Command tftp-server flash:P00303020214.bin tftp-server flash:cmterm_7920.3.3-01-06.bin tftp-server flash:P00403020214.bin Available through TFTP 7920 Firmware 7910 Firmware
- 125. 125 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony telephony-service CMERouter(config)# • Enters telephony service mode max-ephone maximum-ephones CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets the maximum number of ephones that may be defined in the system (default is 0) max-dn maximum-directory-numbers CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets the maximum number of ephone-dn that may be defined in the system (default is 0) Manual Setup (Cont.): Telephony Service Commands
- 126. 126 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony load model firmware-file CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Associates a firmware file with the model of IP phone Manual Setup (Cont.): Firmware Association 7940/7960 7920 7910 telephony-service load 7960-7940 P00303020214 load 7920 cmterm_7920.3.3-01-06.bin load 7910 P00403020214 Filenames are case-sensitive 7940/60 Firmware 7920 Firmware 7910 Firmware
- 127. 127 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony ip source-address ip-address [port port] CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Identifies the address and port through which IP phones communicate with Cisco CME Manual Setup (Cont.): Source IP and Port telephony-service ip source-address 10.90.0.1 port 2000 10.90.0.1 XML Default
- 128. 128 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony create cnf-files CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Builds the specific XML files necessary for the IP phones Manual Setup (Cont.): Create XML Files telephony-service create cnf-files 10.90.0.1 000F.2473.AB14 SEP000F2473AB14.cnf.xml XML SEP
- 129. 129 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony keepalive seconds CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets the length of the time interval between keepalive message from the IP phones to Cisco CME Manual Setup (Cont.): Keepalive • Default is 30 seconds, range is 10 – 65535 seconds • If 3 keepalives are missed in a row, the device will have to register again telephony-service keepalive 10 Keepalive Keepalive
- 130. 130 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony dialplan-pattern tag pattern extension-length length extension-pattern pattern [no-reg] CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets a dial plan pattern which can expand extension numbers to E.164 numbers that can be used for DIDs Manual Setup (Cont.): DID Configuration Commands PSTN ISDN PRI DN 1000 DN 1099 DN 10XX DIDs assigned 2015559000 thru 2015559099 … telephony-service dialplay-pattern 1 20155590.. extension-length 4 extension pattern 10..
- 131. 131 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Manual Setup (Cont.): Example tftp-server flash:P00303020214.bin tftp-server flash:P00403020214.bin telephony-service load 7910 P00403020214 load 7960-7940 P00303020214 create cnf-files max-ephones 10 max-dn 10 ip source-address 10.10.0.1 port 2000 dialplan-pattern 1 2095559... extension-length 4 extension-pattern 1... ephone-dn 1 dual-line number 401 call-forward busy 1999 call-forward noans 1999 timeout 10 ephone 1 mac-address 000F.2745.2AD8 button 1:1 Manual Setup of the Cisco CME Manually configured see module 3 lesson 3
- 132. 132 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Setup Troubleshooting: Verify IP Addressing Verify the IP addressing on the IP phone • Use the Settings button and select “Network Configuration” • Verify IP and subnet mask are correct • Verify the TFTP server is the Cisco CME router • Verify the default gateway is correct
- 133. 133 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Setup Tips (Cont.): Verify the Correct Files in Flash Show flash CMERouter#show flash -#- --length-- -----date/time------ path 1 399514 Mar 1 2002 12:56:28 P00305000301.sbn 2 22649180 Mar 1 2002 12:38:00 c3725-ipvoice-mz.123-7.T.bin 3 321939 Mar 1 2002 12:55:58 CP7902010200SCCP031023A.sbin 4 317171 Mar 1 2002 12:56:06 CP7905010200SCCP031023A.sbin 5 317968 Mar 1 2002 12:56:10 CP7912010200SCCP031023A.sbin 6 369950 Mar 1 2002 12:56:22 P00303020214.bin 7 333822 Mar 1 2002 12:56:30 P00403020214.bin 8 47904 Mar 1 2002 12:56:54 S00103020002.bin 9 301298 Mar 1 2002 12:56:56 ata18x-v2-16-ms-030327b.zup 10 496521 Mar 1 2002 12:57:22 music-on-hold.au 11 1908762 Mar 1 2002 12:56:54 P00503010100.bin 12 21 Mar 1 2002 12:56:18 OS7920.txt 13 839984 Mar 1 2002 12:57:18 cmterm_7920.3.3-01-06.bin 14 307067 Mar 1 2002 12:56:02 CP79050101SCCP030530B31.zup ...
- 134. 134 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Optional Parameters: Locale Parameters Allow changes to: • Language of phone display • Locale for call progress tones and cadences Danish Dutch French German Swedish Spanish Portuguese Norwegian Italian Russian Federation English
- 135. 135 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony user-locale language-code CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Specifies the language for display on an IP phone network-locale language-code CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Specifies the set of call progress tones and cadence on the IP phone Optional Parameters: Locale Parameters
- 136. 136 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony date-format {mm-dd-yy | dd-mm-yy | yy-dd-mm | yy-mm-dd} CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets the date format for IP phone displays time-format {12 | 24} CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Specifies the set of call progress tones and cadence on the IP phone Optional Parameters: Date and Time
- 137. 137 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Rebooting Cisco CallManager Express Phones Reset Command • Hard reboot • Phone firmware changes • User locales changes • Network locales changes • URL parameters changes • DHCP and TFTP invoked • Takes longer than restart Restart Command • Soft reboot • Phone buttons changes • Phone lines changes • Speed-dial number changes • No DHCP or TFTP invoked • System message changes
- 138. 138 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony reset {all [time-interval] | cancel | mac-address | sequence-all} CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets the date format for IP phone displays reset CMERouter(config-ephone)# • Resets a specific ephone Router Configuration: Two Commands (Cont.)
- 139. 139 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony restart {all [time-interval] | mac-address} CMERouter(config-telephony-service)# • Sets the date format for IP phone displays restart CMERouter(config-ephone)# • Restarts the ephone Router Configuration: Two Commands (Cont.)
- 140. 140 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Setup Troubleshooting Troubleshooting setup overview • Verify that a correct IP address and scope options are received on the IP phone • Verify the correct files are in flash • Debug the tftp server • Verify phone firmware install • Verify locale is correct • Verify phone setup • Review configuration
- 141. 141 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Verifying Cisco CallManager Express Phone Configuration Verify ephone-dn Configurations show running-config telephony-service load 7910 P00403020214 load 7960-7940 P00303020214 max-ephones 10 max-dn 10 ip source-address 10.90.0.1 port 2000 auto assign 1 to 10 create cnf-files dialplan-pattern 1 2015559... extension-length 4 extension-pattern 1... voicemail 9999 max-conferences 8 ! ephone-dn 1 dual-line number 9000 ! ephone 1 mac-address 000F.2470.F8F8 button 1:1
- 142. 142 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Setup Tips (Cont.): Debug tftp events command Debug tftp events command CMERouter#debug tftp events Mar 2 19:32:59.333: TFTP: Looking for OS79XX.TXT Mar 2 19:32:59.337: TFTP: Looking for SEP000F2470F8F8.cnf.xml Mar 2 19:32:59.681: TFTP: Opened system:/its/XMLDefault7960.cnf.xml, fd 0, size 784 for process 131 Mar 2 19:32:59.685: TFTP: Finished system:/its/XMLDefault7960.cnf.xml, time 00:00:00 for process 131 Mar 2 19:33:02.713: TFTP: Looking for SEP000F2470F8F8.cnf.xml Mar 2 19:33:02.713: TFTP: Opened system:/its/XMLDefault7960.cnf.xml, fd 0, size 784 for process 131 Mar 2 19:33:02.745: TFTP: Finished system:/its/XMLDefault7960.cnf.xml, time 00:00:00 for process 131 • Can verify if the SEP file for the phone is found • Can verify the downloading of the correct firmware
- 143. 143 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Verifying Cisco CallManager Express Phone Configuration (Cont.) Verify Phone Firmware Installation debug ephone register Mar 2 15:16:57.582: New Skinny socket accepted [1] (2 active) Mar 2 15:16:57.582: sin_family 2, sin_port 49692, in_addr 10.90.0.11 Mar 2 15:16:57.582: skinny_add_socket 1 10.90.0.11 49692 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: %IPPHONE-6-REG_ALARM: 20: Name=SEP000F2470F8F8 Load=3.2(2.14) Last=Phone-Keypad Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Skinny StationAlarmMessage on socket [1] 10.90.0.11 SEP000F2470F8F8 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: severityInformational p1=2368 [0x940] p2=184551946 [0xB000A0A] Mar 2 15:16:57.766: 20: Name=SEP000F2470F8F8 Load=3.2(2.14) Last=Phone-Keypad Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-(1)[1] StationRegisterMessage (1/2/2) from 10.90.0.11 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-(1)[1] Register StationIdentifier DeviceName SEP000F2470F8F8 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-(1)[1] StationIdentifier Instance 1 deviceType 7 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[-1]:stationIpAddr 10.90.0.11 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[1]:phone SEP000F2470F8F8 re-associate OK on socket [1] Mar 2 15:16:57.766: %IPPHONE-6-REGISTER: ephone-1:SEP000F2470F8F8 IP:10.90.0.11 has registered. Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Phone 0 socket 1 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Skinny Local IP address = 10.95.0.1 on port 2000 ... Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Skinny Phone IP address = 10.90.0.11 49692 Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[1]:Date Format M/D/Y Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[1][SEP000F2470F8F8]:RegisterAck sent to ephone 1: keepalive period 30
- 144. 144 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Verifying Cisco CallManager Express Phone Configuration (Cont.) Verify Locale-Specific Files CMERouter1#show telephony-service tftp-bindings tftp-server system:/its/SEPDEFAULT.cnf tftp-server system:/its/SEPDEFAULT.cnf alias SEPDefault.cnf tftp-server system:/its/XMLDefault.cnf.xml alias XMLDefault.cnf.xml tftp-server system:/its/ATADefault.cnf.xml tftp-server system:/its/united_states/7960-tones.xml alias United_States/7960-tones.xml tftp-server system:/its/united_states/7960-font.xml alias English_United_States/7960-font.xml tftp-server system:/its/united_states/7960-dictionary.xml alias English_United_States/7960- dictionary.xml tftp-server system:/its/united_states/7960-kate.xml alias English_United_States/7960-kate.xml tftp-server system:/its/united_states/SCCP-dictionary.xml alias English_United_States/SCCP- dictionary.xml tftp-server system:/its/XMLDefault7960.cnf.xml alias SEP000F2470F8F8.cnf.xml tftp-server system:/its/XMLDefault7960.cnf.xml alias SEP000F23FC9CF0.cnf.xml
- 145. 145 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony Verifying Cisco CallManager Express Phone Configuration (Cont.) Verify Cisco IP Phone Setup CMERouter1#show ephone ephone-1 Mac:000F.2470.F8F8 TCP socket:[1] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:1 IP:10.10.0.11 49692 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 29 max_line 6 button 1: dn 1 number 1000 CH1 IDLE CH2 IDLE ephone-2 Mac:000F.23FC.9CF0 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:1 IP:10.10.0.13 52633 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 135 max_line 6 button 1: dn 2 number 1001 CH1 IDLE CH2 IDLE
- 146. 146 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public IP Telephony
Editor's Notes
- #2: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #7: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #25: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #32: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #45: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #60: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #73: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #103: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.
- #113: Thanks for joining us today to attend the Cisco Brand and Corporate Identity Workshop. In the first half of the workshop I am going to cover Brand Matters and talk in detail about the Cisco brand, and in the second half my colleague Gary McCavvit is going to take you through our updated visual identity system. At the end of the workshop we’re going to leave some time for a fun quiz as well as some Q&A.























































![58
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
default-router IP-address
CMERouter(dhcp-config)#
• Sets the default gateway that will handed out to the
DCHP clients
dns-server primary-IP [secondary IP]
CMERouter(dhcp-config)#
• Sets the DNS server(s) that will assigned to the DHCP
clients
DHCP Service Setup (Cont.)
option option-number ip IP-address
CMERouter(dhcp-config)#
• Defines a custom option and its value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-58-320.jpg)
















![75
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
ephone-dn dn-tag [dual-line]
router(config)#
• This command is used to create an extension
(ephone-dn) for a Cisco IP phone line, an intercom
line, a paging line, a voice-mail port, or a message-
waiting indicator (MWI).
number dn-number secondary dn-number [no-reg [both |
primary]]
router(config-ephone-dn)#
• This command is used to associate a DN number with
the ephone-dn instance
Ephone-dn (Cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-75-320.jpg)


![78
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
Ephone (Cont.)
button button-number {separator} dn-tag [[button-number
{separator} dn-tag]…]
router(config-ephone)#
• Associates the ephone-dn(s) with a specific button(s)
on the IP phone
type {7940 | 7960} addon 1 7914 [2 7914]
router(config-ephone)#
• Defines the device as a 7914 module(s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-78-320.jpg)











![91
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
preference {0-10}
router(config-ephone-dn)#
• Sets the dial-peer preference order
huntstop [channel]
router(config-ephone-dn)#
• Discontinues the call hunting behavior for an
extension (ephone-dn) or an extension line (dual-line)
Preference and Huntstop Commands](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-91-320.jpg)
























![116
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
Automated Setup (Cont.)
• Configure NTP prior to
running the setup utility
• Load the firmware files
into flash RAM prior to
running the setup utility
• Enter the automated
setup mode by entering
the command
“telephony-service
setup”
• A question and answer
session will start asking
for basic parameters
• CTRL + c keystroke can
be used at any time to
break out of the setup
mode
• No changes are
committed until the end
CMERouter1(config)#telephony-service setup
--- Cisco IOS Telephony Services Setup ---
Do you want to setup DHCP service for your IP Phones? [yes/no]: y
Configuring DHCP Pool for Cisco IOS Telephony Services :
IP network for telephony-service DHCP Pool:10.90.0.0
Subnet mask for DHCP network :255.255.255.0
TFTP Server IP address (Option 150) :10.90.0.1
Default Router for DHCP Pool :10.90.0.1
Do you want to start telephony-service setup? [yes/no]: y
Configuring Cisco IOS Telephony Services :
Enter the IP source address for Cisco IOS Telephony Services :10.90.0.1
Enter the Skinny Port for Cisco IOS Telephony Services : [2000]:2000
How many IP phones do you want to configure : [0]: 10
Do you want dual-line extensions assigned to phones? [yes/no]: y
What Language do you want on IP phones :
0 English 6 Dutch
1 French 7 Norwegian
2 German 8 Portuguese
3 Russian 9 Danish
4 Spanish 10 Swedish
5 Italian
[0]: 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-116-320.jpg)
![117
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
Automated Setup (Cont.)
• When configuration
is committed the
settings show up in
the running-config
Which Call Progress tone set do you want on IP phones :
0 United States
1 France
2 Germany
3 Russia
4 Spain
5 Italy
6 Netherlands
7 Norway
8 Portugal
9 UK
10 Denmark
11 Switzerland
12 Sweden
13 Austria
14 Canada
[0]: 0
What is the first extension number you want to configure : [0]: 9000
Do you have Direct-Inward-Dial service for all your phones? [yes/no]: y
Enter the full E.164 number for the first phone :2095559000
Do you want to forward calls to a voice message service? [yes/no]: y
Enter extension or pilot number of the voice message service:9999
Call forward No Answer Timeout : [18]: 10
Do you wish to change any of the above information? [yes/no]: n
---- Setup completed config ---](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-117-320.jpg)


![120
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
auto assign start-dn to stop-dn [type model] [cfw number
timeout seconds]
CMERouter(config-telephony-service)#
• Automatically assigns the ephone-dns configured to
new ephones
Partially Automated Setup (Cont.)
Auto Assign Command
Auto assign usage guidelines
• Can take up to 5 minutes for phones to register
• Wait for all phones to register before saving the
configuration
• cfw setting defines the call forward busy number
and timeout value for phones that register](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-120-320.jpg)


![123
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
Manual Setup (Cont.): Commands Overview
• tftp-server flash:filename
• telephony-service
• max-ephones max-ephones
• max-dn max-directory-numbers
• load phone-type firmware-file
• ip source-address ip-address [port port]
• create cnf-files
• keepalive seconds
• dialplan-pattern tag pattern extension-length length
extension-pattern pattern
Commands needed to configure a basic
telephony service](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-123-320.jpg)



![127
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
ip source-address ip-address [port port]
CMERouter(config-telephony-service)#
• Identifies the address and port through which IP
phones communicate with Cisco CME
Manual Setup (Cont.): Source IP and Port
telephony-service
ip source-address 10.90.0.1 port 2000
10.90.0.1
XML
Default](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-127-320.jpg)


![130
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
dialplan-pattern tag pattern extension-length length
extension-pattern pattern [no-reg]
CMERouter(config-telephony-service)#
• Sets a dial plan pattern which can expand extension
numbers to E.164 numbers that can be used for DIDs
Manual Setup (Cont.): DID Configuration
Commands
PSTN ISDN PRI
DN 1000
DN 1099
DN 10XX
DIDs assigned
2015559000
thru
2015559099
…
telephony-service
dialplay-pattern 1 20155590.. extension-length 4 extension pattern 10..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-130-320.jpg)







![138
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
reset {all [time-interval] | cancel | mac-address |
sequence-all}
CMERouter(config-telephony-service)#
• Sets the date format for IP phone displays
reset
CMERouter(config-ephone)#
• Resets a specific ephone
Router Configuration: Two Commands
(Cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-138-320.jpg)
![139
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
restart {all [time-interval] | mac-address}
CMERouter(config-telephony-service)#
• Sets the date format for IP phone displays
restart
CMERouter(config-ephone)#
• Restarts the ephone
Router Configuration: Two Commands
(Cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-139-320.jpg)



![143
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
Verifying Cisco CallManager Express
Phone Configuration (Cont.)
Verify Phone Firmware Installation
debug ephone register
Mar 2 15:16:57.582: New Skinny socket accepted [1] (2 active)
Mar 2 15:16:57.582: sin_family 2, sin_port 49692, in_addr 10.90.0.11
Mar 2 15:16:57.582: skinny_add_socket 1 10.90.0.11 49692
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: %IPPHONE-6-REG_ALARM: 20: Name=SEP000F2470F8F8 Load=3.2(2.14) Last=Phone-Keypad
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Skinny StationAlarmMessage on socket [1] 10.90.0.11 SEP000F2470F8F8
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: severityInformational p1=2368 [0x940] p2=184551946 [0xB000A0A]
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: 20: Name=SEP000F2470F8F8 Load=3.2(2.14) Last=Phone-Keypad
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-(1)[1] StationRegisterMessage (1/2/2) from 10.90.0.11
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-(1)[1] Register StationIdentifier DeviceName SEP000F2470F8F8
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-(1)[1] StationIdentifier Instance 1 deviceType 7
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[-1]:stationIpAddr 10.90.0.11
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[1]:phone SEP000F2470F8F8 re-associate OK on socket [1]
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: %IPPHONE-6-REGISTER: ephone-1:SEP000F2470F8F8 IP:10.90.0.11 has registered.
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Phone 0 socket 1
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Skinny Local IP address = 10.95.0.1 on port 2000
...
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: Skinny Phone IP address = 10.90.0.11 49692
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[1]:Date Format M/D/Y
Mar 2 15:16:57.766: ephone-1[1][SEP000F2470F8F8]:RegisterAck sent to ephone 1: keepalive period 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-143-320.jpg)

![145
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
IP Telephony
Verifying Cisco CallManager Express
Phone Configuration (Cont.)
Verify Cisco IP Phone Setup
CMERouter1#show ephone
ephone-1 Mac:000F.2470.F8F8 TCP socket:[1] activeLine:0 REGISTERED
mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:1
IP:10.10.0.11 49692 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 29 max_line 6
button 1: dn 1 number 1000 CH1 IDLE CH2 IDLE
ephone-2 Mac:000F.23FC.9CF0 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTERED
mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:1
IP:10.10.0.13 52633 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 135 max_line 6
button 1: dn 2 number 1001 CH1 IDLE CH2 IDLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250415100354-89809706/85/Configuring-Cisco-CME-and-its-details-ppt-145-320.jpg)
