Constructors and destructors in C++ part 2
Download as PPT, PDF1 like617 views
Constructors and destructors are special member functions in C++ that are used to initialize and cleanup objects. Constructors are called automatically when an object is created and are used to set initial values for object attributes. Destructors are called automatically when an object is destroyed and can perform cleanup tasks. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Constructors and destructors have the same name as the class but constructors don't have a return type while destructors are preceded by a tilde (~).
1 of 42
Download to read offline





![Syntax
class CLASSNAME
{
public:
CLASSNAME([parameter list]);
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constructorsanddestructors-200625144711/85/Constructors-and-destructors-in-C-part-2-6-320.jpg)














![syntax
class CLASSNAME
{
……………….
public:
~CLASSNAME([parameter list]);
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constructorsanddestructors-200625144711/85/Constructors-and-destructors-in-C-part-2-22-320.jpg)




















Ad
Recommended
Virtual Function



Virtual FunctionLovely Professional University Virtual functions allow polymorphism by implementing a common interface in base and derived classes that can be called dynamically at runtime. They are declared with the virtual keyword in the base class and overridden with the same name and parameters in derived classes. Pure virtual functions are virtual functions without a body declared using =0, making a class abstract that cannot be instantiated until overridden in derived classes. Virtual destructors ensure the correct derived class destructor is called when deleting polymorphic objects through a base class pointer.
Object oriented concepts & programming (2620003)



Object oriented concepts & programming (2620003)nirajmandaliya This document discusses various C++ concepts related to functions including:
- Default pointers which receive addresses passed to called functions.
- Reference variables which receive the reference of an actual variable passed to a function. Changing the reference variable directly changes the actual variable.
- Inline functions which eliminate context switching when defined inside a class or declared with the inline keyword.
- Friend functions which have access to private/protected members of a class they are declared as a friend to.
Constructors destructors



Constructors destructorsPranali Chaudhari Constructors are used to initialize objects and allocate memory. A constructor has the same name as its class and is invoked when an object is created. There are different types of constructors including default, parameterized, copy, and dynamic constructors. A destructor is used to destroy objects and does not have any arguments or return values.
Constructor and destructor in oop 



Constructor and destructor in oop Samad Qazi Constructor and destructor are special types of methods in object-oriented programming. Constructors are used to initialize objects and are called when an object is created, while destructors are used to destroy objects and are called when an object is deleted or goes out of scope. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Constructors cannot be inherited or virtual. Destructors are used to clean up resources used by an object and are called automatically when an object is destroyed. The key differences between constructors and destructors are that constructors initialize objects and can have parameters, while destructors destroy objects and have no parameters.
C++ classes tutorials



C++ classes tutorialsakreyi The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts like classes, objects, encapsulation, and access modifiers. It provides examples of constructors, destructors, and copy constructors in C# and explains how they are used to initialize and cleanup class instances. It also discusses friend functions and how they allow non-member functions to access private and protected members of a class.
Constructors and destructors



Constructors and destructorsNilesh Dalvi Introduction to constructors
Default Constructor
Parameterized Constructor
Copy Constructor
Dynamic Constructor
const objects and member function
Constructor in java



Constructor in javaSIVASHANKARIRAJAN 1) A constructor in Java is a special method that is used to initialize objects and is called when an object is created. It can set initial values for object attributes.
2) There are different types of constructors including default, parameterized, and copy constructors. The default constructor takes no parameters, parameterized constructors take parameters to initialize objects with different values, and copy constructors are used to create a copy of an object.
3) Constructor overloading allows a class to have multiple constructors with the same name but different parameters, allowing objects to be initialized in different ways.
Constructors & Destructors



Constructors & DestructorsRokonuzzaman Rony Constructors are special member functions that are called automatically when objects are created. They initialize objects and are declared with the same name as the class but without a return type. Destructors are also special member functions that are called when objects are destroyed in order to perform cleanup tasks. Copy constructors are used to initialize objects as copies of other objects and are declared with a parameter of the class type passed by reference. Constructors and destructors perform important initialization and cleanup tasks but have certain limitations like not being able to return values.
Inheritance



Inheritanceabhay singh The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts of inheritance, interfaces, and abstract classes. It defines inheritance as allowing hierarchical classifications by inheriting variables, methods, properties, and indexers from a base class. It describes different types of inheritance like single, hierarchical, multi-level, hybrid, and multiple. It then explains the differences between interfaces and abstract classes, such as interfaces defining functionality without implementation and abstract classes allowing partial implementation.
Constructor & destructor



Constructor & destructorSaharsh Anand - Constructors are special member functions used to initialize objects when they are created. They are automatically called upon object creation and have the same name as the class. Constructors can be default, parameterized, or copy constructors.
- Destructors are also special member functions that perform cleanup actions when an object is destroyed, such as freeing memory. They are called automatically upon object destruction and have the same name as the class preceded by a tilde.
- Examples demonstrate default, parameterized, and copy constructors as well as destructors being defined and called for a class to properly initialize and cleanup objects.
Functors, Applicatives and Monads In Scala



Functors, Applicatives and Monads In ScalaKnoldus Inc. The document discusses functors, applicatives, and monads. It defines each concept and provides examples. Functors allow mapping a function over a wrapped value using map. Applicatives allow applying a function wrapped in a context to a value wrapped in a context using apply. Monads allow applying a function that returns a wrapped value to a wrapped value using flatMap. Examples of each include Option for functors, lists for applicatives, and futures for monads.
106da session5 c++



106da session5 c++Mukund Trivedi This document provides information about a C++ course for the second semester. It includes the course name "B Sc IT", subject name "C++", and semester "II".
Oop2011 actor presentation_stal



Oop2011 actor presentation_stalMichael Stal This is a talk on Actor-based Programming given at OOP 2011. It explains the paradigm, but also shows concrete examples
Java For Automation



Java For AutomationAbhijeet Dubey Slides have Java for automation content. It will help you learn java a tester needs to learn for automation.
2CPP04 - Objects and Classes



2CPP04 - Objects and ClassesMichael Heron This is an intermediate conversion course for C++, suitable for second year computing students who may have learned Java or another language in first year.
Qcon2011 functions rockpresentation_scala



Qcon2011 functions rockpresentation_scalaMichael Stal Scala functions provide powerful ways to decompose problems and harness the benefits of functional programming. The presentation introduces core concepts of functional programming using Scala as an example language, highlighting how Scala combines object-oriented and functional programming. It presents benefits like immutability, higher-order functions, and improved concurrency while avoiding past performance issues through modern virtual machines and libraries.
Constructors and destructors



Constructors and destructorsVineeta Garg Constructors and destructors are special member functions in C++ that are used to initialize objects and perform cleanup operations. There are different types of constructors - default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Constructors are called automatically when an object is created, while destructors are called when an object is destroyed or goes out of scope. Constructors initialize objects, while destructors perform cleanup tasks like deallocating memory. Overloading of constructors allows defining multiple constructors that differ in parameters.
16 virtual function



16 virtual functionDocent Education Virtual functions allow dynamic binding in C++ by allowing a function to be overridden in a derived class. A function is declared virtual by using the virtual keyword. At runtime, the compiler will call the version of a virtual function that is defined in the object's own class, rather than being bound at compile time like regular functions. This allows a base class pointer or reference to call a derived class implementation of a virtual function. Classes that contain virtual functions are called polymorphic classes.
9054799 dzone-refcard267-kotlin



9054799 dzone-refcard267-kotlinZoran Stanimirovic The document provides an overview of the Kotlin programming language. It discusses Kotlin's growing popularity, especially for Android development. It then covers various topics to help newcomers get started with Kotlin like recommended IDEs, basic syntax highlighting functions, variables, control flow structures, and classes. The document aims to equip readers with foundational Kotlin knowledge in a concise yet accessible manner.
Of Lambdas and LINQ



Of Lambdas and LINQBlackRabbitCoder A small presentation I developed that introduces lambda expressions and many of the common LINQ extension methods for a group of developers that were less familiar with these concepts.
DIWE - Programming with JavaScript



DIWE - Programming with JavaScriptRasan Samarasinghe Esoft Metro Campus - Diploma in Web Engineering - (Module V) Programming with JavaScript
(Template - Virtusa Corporate)
Contents:
Introduction to JavaScript
What JavaScript Can Do?
Script tag in HTML
Noscript tag in HTML
Your First JavaScript Program
JavaScript Placement in HTML File
JavaScript Syntax
JavaScript Data Types
JavaScript Variables
JavaScript Identifiers
Arithmetic Operators
String Concatenation Operators
Assignment Operators
Comparison Operators
Logical Operators
Bitwise Operators
If Statement
If… Else Statement
If… Else if… Else Statement
Switch Statement
The ? Operator
While Loop
Do While Loop
For Loop
For…in Loop
break Statement
continue Statement
Arrays
Functions
JavaScript Objects
JavaScript Scope
Strings
Regular Expressions
JavaScript Numbers
Math Object
Date and Time
JavaScript Events
Dialog Boxes
Error Handling in JavaScript
JavaScript Forms Validation
JavaScript HTML DOM
JavaScript BOM
Object-Oriented Programming Using C++



Object-Oriented Programming Using C++Salahaddin University-Erbil This is also from Mr Karim Zebari for OOP programming. Its better to start with simple principals of C++ programming before starting this one.
Constructors and Destructors



Constructors and DestructorsDr Sukhpal Singh Gill Constructors, Destructors, call in parameterized Constructor, Multiple constructor in a class, Explicit/implicit call, Copy constructor, Dynamic Constructors and call in parameterized Constructor
Oop2010 Scala Presentation Stal



Oop2010 Scala Presentation StalMichael Stal This presentation offers a tutorial for introducing Scala. Readers should be familiar with C++, C# or Java
Constructor and destructor in c++



Constructor and destructor in c++Learn By Watch This document discusses constructors and destructors in C++. It explains that constructors are special functions called when an object is created that have the same name as the class, cannot return a value, and are used to initialize objects. Destructors are also special functions with the same name as the class but with a ~ sign that cannot return a value and are called when an object is destroyed to cleanup resources. The document aims to help readers understand when and how constructors and destructors are used.
pointers,virtual functions and polymorphism



pointers,virtual functions and polymorphismrattaj my first presentation pointers,virtual functions and polymorphism,
most basic and simple and short presentation
its just parial overview.
C++



C++vrushali shivsharan Constructors and destructors play an important role in object-oriented programming. Constructors are special member functions that are called when objects are created. There are different types of constructors including parameterized, default, copy, conversion, and move constructors. Destructors are the inverse of constructors and are called when objects are destroyed. Destructors follow the same name convention as the class but with a tilde. Constructors and destructors are useful in real-time applications such as real-time locating systems and data transmission where they help properly allocate and release resources during an object's lifetime.
Virtual function complete By Abdul Wahab (moon sheikh)



Virtual function complete By Abdul Wahab (moon sheikh)MoonSheikh1 this presentation topic is might be taught in 2nd semester of BS-IT
in these slides you can find the working concepts of virtual function in c++ programming language
Constructors in C++.pptx



Constructors in C++.pptxRassjb Constructor and Destructor in C++ are special member functions that are automatically called by the compiler.
Constructors initialize a newly created object and are called when the object is created. Destructors destroy objects and release memory and are called when the object goes out of scope. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, and copy constructors that allow initializing objects in different ways. Destructors do not have arguments or return values and are declared with a tilde symbol preceding the class name.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Inheritance



Inheritanceabhay singh The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts of inheritance, interfaces, and abstract classes. It defines inheritance as allowing hierarchical classifications by inheriting variables, methods, properties, and indexers from a base class. It describes different types of inheritance like single, hierarchical, multi-level, hybrid, and multiple. It then explains the differences between interfaces and abstract classes, such as interfaces defining functionality without implementation and abstract classes allowing partial implementation.
Constructor & destructor



Constructor & destructorSaharsh Anand - Constructors are special member functions used to initialize objects when they are created. They are automatically called upon object creation and have the same name as the class. Constructors can be default, parameterized, or copy constructors.
- Destructors are also special member functions that perform cleanup actions when an object is destroyed, such as freeing memory. They are called automatically upon object destruction and have the same name as the class preceded by a tilde.
- Examples demonstrate default, parameterized, and copy constructors as well as destructors being defined and called for a class to properly initialize and cleanup objects.
Functors, Applicatives and Monads In Scala



Functors, Applicatives and Monads In ScalaKnoldus Inc. The document discusses functors, applicatives, and monads. It defines each concept and provides examples. Functors allow mapping a function over a wrapped value using map. Applicatives allow applying a function wrapped in a context to a value wrapped in a context using apply. Monads allow applying a function that returns a wrapped value to a wrapped value using flatMap. Examples of each include Option for functors, lists for applicatives, and futures for monads.
106da session5 c++



106da session5 c++Mukund Trivedi This document provides information about a C++ course for the second semester. It includes the course name "B Sc IT", subject name "C++", and semester "II".
Oop2011 actor presentation_stal



Oop2011 actor presentation_stalMichael Stal This is a talk on Actor-based Programming given at OOP 2011. It explains the paradigm, but also shows concrete examples
Java For Automation



Java For AutomationAbhijeet Dubey Slides have Java for automation content. It will help you learn java a tester needs to learn for automation.
2CPP04 - Objects and Classes



2CPP04 - Objects and ClassesMichael Heron This is an intermediate conversion course for C++, suitable for second year computing students who may have learned Java or another language in first year.
Qcon2011 functions rockpresentation_scala



Qcon2011 functions rockpresentation_scalaMichael Stal Scala functions provide powerful ways to decompose problems and harness the benefits of functional programming. The presentation introduces core concepts of functional programming using Scala as an example language, highlighting how Scala combines object-oriented and functional programming. It presents benefits like immutability, higher-order functions, and improved concurrency while avoiding past performance issues through modern virtual machines and libraries.
Constructors and destructors



Constructors and destructorsVineeta Garg Constructors and destructors are special member functions in C++ that are used to initialize objects and perform cleanup operations. There are different types of constructors - default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Constructors are called automatically when an object is created, while destructors are called when an object is destroyed or goes out of scope. Constructors initialize objects, while destructors perform cleanup tasks like deallocating memory. Overloading of constructors allows defining multiple constructors that differ in parameters.
16 virtual function



16 virtual functionDocent Education Virtual functions allow dynamic binding in C++ by allowing a function to be overridden in a derived class. A function is declared virtual by using the virtual keyword. At runtime, the compiler will call the version of a virtual function that is defined in the object's own class, rather than being bound at compile time like regular functions. This allows a base class pointer or reference to call a derived class implementation of a virtual function. Classes that contain virtual functions are called polymorphic classes.
9054799 dzone-refcard267-kotlin



9054799 dzone-refcard267-kotlinZoran Stanimirovic The document provides an overview of the Kotlin programming language. It discusses Kotlin's growing popularity, especially for Android development. It then covers various topics to help newcomers get started with Kotlin like recommended IDEs, basic syntax highlighting functions, variables, control flow structures, and classes. The document aims to equip readers with foundational Kotlin knowledge in a concise yet accessible manner.
Of Lambdas and LINQ



Of Lambdas and LINQBlackRabbitCoder A small presentation I developed that introduces lambda expressions and many of the common LINQ extension methods for a group of developers that were less familiar with these concepts.
DIWE - Programming with JavaScript



DIWE - Programming with JavaScriptRasan Samarasinghe Esoft Metro Campus - Diploma in Web Engineering - (Module V) Programming with JavaScript
(Template - Virtusa Corporate)
Contents:
Introduction to JavaScript
What JavaScript Can Do?
Script tag in HTML
Noscript tag in HTML
Your First JavaScript Program
JavaScript Placement in HTML File
JavaScript Syntax
JavaScript Data Types
JavaScript Variables
JavaScript Identifiers
Arithmetic Operators
String Concatenation Operators
Assignment Operators
Comparison Operators
Logical Operators
Bitwise Operators
If Statement
If… Else Statement
If… Else if… Else Statement
Switch Statement
The ? Operator
While Loop
Do While Loop
For Loop
For…in Loop
break Statement
continue Statement
Arrays
Functions
JavaScript Objects
JavaScript Scope
Strings
Regular Expressions
JavaScript Numbers
Math Object
Date and Time
JavaScript Events
Dialog Boxes
Error Handling in JavaScript
JavaScript Forms Validation
JavaScript HTML DOM
JavaScript BOM
Object-Oriented Programming Using C++



Object-Oriented Programming Using C++Salahaddin University-Erbil This is also from Mr Karim Zebari for OOP programming. Its better to start with simple principals of C++ programming before starting this one.
Constructors and Destructors



Constructors and DestructorsDr Sukhpal Singh Gill Constructors, Destructors, call in parameterized Constructor, Multiple constructor in a class, Explicit/implicit call, Copy constructor, Dynamic Constructors and call in parameterized Constructor
Oop2010 Scala Presentation Stal



Oop2010 Scala Presentation StalMichael Stal This presentation offers a tutorial for introducing Scala. Readers should be familiar with C++, C# or Java
Constructor and destructor in c++



Constructor and destructor in c++Learn By Watch This document discusses constructors and destructors in C++. It explains that constructors are special functions called when an object is created that have the same name as the class, cannot return a value, and are used to initialize objects. Destructors are also special functions with the same name as the class but with a ~ sign that cannot return a value and are called when an object is destroyed to cleanup resources. The document aims to help readers understand when and how constructors and destructors are used.
pointers,virtual functions and polymorphism



pointers,virtual functions and polymorphismrattaj my first presentation pointers,virtual functions and polymorphism,
most basic and simple and short presentation
its just parial overview.
C++



C++vrushali shivsharan Constructors and destructors play an important role in object-oriented programming. Constructors are special member functions that are called when objects are created. There are different types of constructors including parameterized, default, copy, conversion, and move constructors. Destructors are the inverse of constructors and are called when objects are destroyed. Destructors follow the same name convention as the class but with a tilde. Constructors and destructors are useful in real-time applications such as real-time locating systems and data transmission where they help properly allocate and release resources during an object's lifetime.
Virtual function complete By Abdul Wahab (moon sheikh)



Virtual function complete By Abdul Wahab (moon sheikh)MoonSheikh1 this presentation topic is might be taught in 2nd semester of BS-IT
in these slides you can find the working concepts of virtual function in c++ programming language
Similar to Constructors and destructors in C++ part 2 (20)
Constructors in C++.pptx



Constructors in C++.pptxRassjb Constructor and Destructor in C++ are special member functions that are automatically called by the compiler.
Constructors initialize a newly created object and are called when the object is created. Destructors destroy objects and release memory and are called when the object goes out of scope. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, and copy constructors that allow initializing objects in different ways. Destructors do not have arguments or return values and are declared with a tilde symbol preceding the class name.
Constructors and Destructor in C++

Constructors and Destructor in C++International Institute of Information Technology (I²IT) Constructors are special class functions which performs initialization of every object. The Compiler calls the Constructor whenever an object is created. Destructor on the other hand is used to destroy the class object.
CONSTRUCTORS IN C++ +2 COMPUTER SCIENCE



CONSTRUCTORS IN C++ +2 COMPUTER SCIENCEVenugopalavarma Raja - Constructors are special member functions that are used to initialize objects of a class. They are automatically called when an object is created.
- There are different types of constructors including default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Default constructors take no parameters while parameterized constructors allow passing initial values.
- Constructors can be explicitly or implicitly called. Implicit calls are made when an object is declared while explicit calls directly call the constructor. Constructors ensure objects are properly initialized.
constructor in object oriented program.pptx



constructor in object oriented program.pptxurvashipundir04 Constructors are special member functions that are used to initialize objects. There are three main types of constructors: default constructors that take no arguments, parameterized constructors that allow passing arguments, and copy constructors that are used to initialize one object from another of the same type. Destructors are special member functions that are automatically called to destroy objects when they go out of scope or the program terminates. Constructors and destructors are important concepts in object-oriented programming with C++.
Constructor and Destructor in c++



Constructor and Destructor in c++aleenaguen What are the constructor and destructors in c++? Constructor and Destructor in c++ with example|| example of constructor and destructor in c++
Constructor and destructor



Constructor and destructorrajshreemuthiah This document discusses various C++ constructor and destructor concepts including:
- Constructors are special methods that initialize object data members when created and can be parameterized to initialize with different values.
- Classes can contain multiple constructors and constructors with default arguments.
- Copy constructors initialize objects using another object of the same class.
- Const objects can only access const member functions and attempts to modify will generate errors.
- Destructors are used to destroy objects and release memory, and their name matches the class name preceded by a tilde. They do not take arguments or return values.
Constructor and Destructor



Constructor and DestructorSunipa Bera Slide 2:
What are the Constructor & destructor ?
Slide 3:
Characteristics of Constructor
Slide 4:
Special CHaracteristics of Destructor
Slide 5:
Similarities
Slide 6:
Dissimilarities
Slides 7:
Default Constructor with example
Slide 8:
Parameterized Constructor
Slide 9:
Copy Constructor with example
Slide 10:
Destructor
Slide 11:
Bibliography
Learning C++ - Class 4



Learning C++ - Class 4Ali Aminian This document provides an introduction to classes in C++, including constructors, destructors, class members, inheritance, and errors. It defines a class called MyCoordinate with members like x, y, and an array. It discusses using constructors to initialize members and destructors to clean up memory. The document also covers defining classes with public and private members and inheriting from parent classes.
Oops



OopsGayathri Ganesh The document discusses inheritance in C# through an example program. The Child class inherits from the Parent class and overrides the print() method. When an instance of the Child class is created, it first calls the Parent class constructor through the base keyword, then the Child constructor is called. When print() is called on the Child instance, it first calls the base print() method from the Parent class, then calls the Child's print() method.
Constructors & Destructors [Compatibility Mode].pdf![Constructors & Destructors [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/9constructorsdestructorscompatibilitymode-220826110509-edd9be6a-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Constructors & Destructors [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/9constructorsdestructorscompatibilitymode-220826110509-edd9be6a-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Constructors & Destructors [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/9constructorsdestructorscompatibilitymode-220826110509-edd9be6a-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Constructors & Destructors [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/9constructorsdestructorscompatibilitymode-220826110509-edd9be6a-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Constructors & Destructors [Compatibility Mode].pdfLadallaRajKumar The document discusses constructors and destructors in C++. It states that constructors and destructors are special member functions that control how objects are created, initialized, copied, and destroyed. Constructors have the same name as the class and are executed when an object is declared, while destructors are preceded by a tilde symbol and are executed when objects go out of scope. The document provides examples of defining different types of constructors, such as default, parameterized, copy constructors, and multiple constructors. It also demonstrates how arrays of objects can be initialized using constructors and how constructors and destructors are automatically called by the compiler.
Constructors and destructors in C++



Constructors and destructors in C++RAJ KUMAR The constructor constructs objects and initializes member variables when an object is created. The destructor destroys objects when they are no longer needed. Constructors and destructors have the same name as the class and are automatically called by the compiler. Constructors can be overloaded and can have default arguments to initialize objects differently. Copy constructors allow objects to be initialized by passing references of other objects. Destructors destroy objects before they go out of scope.
Constructors and destructors



Constructors and destructorsProf. Dr. K. Adisesha Constructors and destructors are special member functions in C++ that are used for initializing objects and cleaning up resources. Constructors are called automatically when an object is created and are used to initialize member variables. Destructors are called when an object is destroyed in order to clean up resources. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Constructors can be invoked implicitly, explicitly, or through initialization. Destructors have the same name as the class preceded by a tilde and are used to de-allocate memory allocated by the constructor.
C++ Unit-III Lecture-3a-C++ Programming Concepts



C++ Unit-III Lecture-3a-C++ Programming Conceptsdharawagh9999 This document discusses constructors and destructors in C++. It defines a constructor as a special member function that initializes an object when it is created, and has the same name as the class. A destructor destroys an object and is preceded by a tilde (~). An example class is given with a constructor that initializes data members to 0, and a destructor that prints a message. Key characteristics of constructors and destructors are listed, such as constructors being automatically called during object creation and destructors being called upon program exit. The document concludes that constructors initialize objects while destructors destroy objects created by constructors.
Bca 2nd sem u-2 classes & objects



Bca 2nd sem u-2 classes & objectsRai University The document discusses various object-oriented programming concepts in C++ like classes, objects, member functions, data members, constructors, destructors, friend functions, and namespaces. It provides examples of defining classes with data members and member functions, declaring objects of a class, and using constructors and destructors. It also explains concepts like overloaded constructors, copy constructors, nested classes, dynamic initialization of objects, and friend functions.
Constructors and Destructors in C++.pptx



Constructors and Destructors in C++.pptxshivanigarg18041 These slides give an overview of constructors and destructors in C++
Constructor



Constructorabhay singh The document discusses classes, objects, constructors, and other object-oriented programming concepts in C#:
1) A class defines the data and behavior of a type using variables, methods, and events. Objects are instances of classes that have identity, data, and behaviors defined by the class.
2) Constructors initialize objects and are called using the new keyword. Constructors can be overloaded, parameterized, static, or chained to call another constructor.
3) Classes support concepts like inheritance, hiding, overriding, and polymorphism to extend and customize behavior in derived classes. References and values can be passed into methods.
Mca 2nd sem u-2 classes & objects



Mca 2nd sem u-2 classes & objectsRai University This document discusses various concepts related to classes and objects in C++, including member functions, data members, constructors, destructors, friend functions, and nested classes. It provides examples of defining member functions inside and outside the class, different access specifiers for data members, examples of friend functions and classes, returning objects from functions, arrays of objects, and nested classes. It also discusses constructors in more detail, including overloaded constructors, copy constructors, dynamic initialization of objects, constructors for primitive types, and constructors with default arguments.
Constructor,destructors cpp



Constructor,destructors cppरमन सनौरिया This document discusses various types of constructors in C++ including default, parameterized, copy constructors, and destructors. It also covers initialization lists, static class members, constant objects, and summarizes their key purposes and behaviors. Default constructors initialize objects without parameters, parameterized constructors allow passing initialization values, and copy constructors copy data from one object to another. Destructors clean up object resources. Initialization lists assign member values, static members have a single instance shared among objects, and constant objects cannot be modified.
Ad
More from Lovely Professional University (20)
Constructor and destructor in C++



Constructor and destructor in C++Lovely Professional University Constructors and destructors are special member functions in C++ that are used to initialize and cleanup objects. Constructors are called automatically when an object is created and are used to set initial values for object attributes. Destructors are called automatically when an object is destroyed and can perform cleanup tasks. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Destructors do not have parameters and are used to deallocate memory when objects are destroyed.
Classes and objects



Classes and objectsLovely Professional University A class defines the structure and behavior of an object. It groups together data members and member functions that operate on those data members. An object is an instance of a class created by declaring a variable of that class type. Classes in C++ use access specifiers like public and private to control access to members. A class declaration defines the structure while objects are instantiated from the class. Member functions allow manipulating and accessing private data members from outside the class.
Cin and cout



Cin and coutLovely Professional University The document discusses different types of conditional statements in C++ including if, if/else, nested if/else, and else if statements. It provides the syntax for each statement, examples of code using them, and flowcharts illustrating how they work. The key conditional statements covered are:
- if statement which executes code if a test expression is true
- if/else statement which executes one code block if the test is true and another if it's false
- nested if/else statements which allow multiple levels of conditional logic
- else if ladder which chains multiple conditions together
Major project synopsis format



Major project synopsis formatLovely Professional University This document provides guidelines for submitting a major project synopsis, including formatting requirements and content sections. The synopsis should be 5 pages or less and include: 1) a problem profile, 2) the proposed idea, 3) project requirements, 4) modules to be implemented with diagrams, 5) a data flow diagram, 6) 2-3 applications, and 7) a bibliography. The content should be typed in Times New Roman 12 pt font with 1.5 line spacing and figures/tables can be inserted or appended. Headings should be bold 14 pt font.
Docslide.net soyabean milk-project-class-12



Docslide.net soyabean milk-project-class-12Lovely Professional University This document is a student's chemistry project report on comparing soya bean milk to natural milk. It includes an acknowledgements section, aim, introduction, materials, procedure, observations, results, bibliography, and contents pages. The key points are:
1. The student prepared soya bean milk and compared its curd formation, taste, and temperature effects to natural milk.
2. Observations found that natural milk forms good curd at 40-50°C while soya milk forms good curd at 15-20°C, and natural milk tastes sweeter while soya milk tastes sour.
3. The results showed that curd formation increases with rising temperature in both milks, but
Physics first page



Physics first pageLovely Professional University This document is from St. Xaviers School in Bhitirawat, Sahjanwa, Gorakhpur for the 2017-18 session. It discusses a physics project to design an appropriate logic gate for a given truth table that was created by Shraddha Mishra, a class 12 student with roll number, under the guidance of Mr. Ankur Tripathi.
Uses of transformer



Uses of transformerLovely Professional University Transformers are used in a variety of electronic devices to change alternating current (AC) voltages for different purposes. They allow AC to be transmitted over long distances and are used in devices like televisions, refrigerators, computers, and air conditioners to regulate voltage. Transformers also enable applications like welding, X-Rays, neon signs, and induction furnaces by stepping voltages up or down as needed.
Theory and working



Theory and workingLovely Professional University 1) When an alternating current is passed through the primary coil of a transformer, it produces an alternating magnetic flux that induces voltages in both the primary and secondary coils.
2) The induced voltages are directly proportional to the number of turns in each coil. Specifically, the ratio of the secondary voltage to the primary voltage equals the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary coil to the number of turns in the primary coil.
3) A step-up transformer has a secondary coil with more turns than the primary, producing a higher secondary voltage than primary voltage. A step-down transformer has fewer turns in the secondary than primary, producing a lower secondary voltage. The current is inversely related, so a step-up
Main page vishnu



Main page vishnuLovely Professional University This document is an investigatory project report on the principle and working of transformers submitted for a CBSE Physics practical exam in the 2017-18 session. It was projected by a student in Gorakhpur, Kazakpur for their practical exam requirements.
Main page v physics



Main page v physicsLovely Professional University This document describes a student project on the principle and working of transformers. It was created by a student in Gorakhpur, India for their 2017-2018 CBSE physics practical exam. The project investigates and explains how transformers function.
Main page saurabh



Main page saurabhLovely Professional University This document appears to be a student project on the principle and working of transformers. It was created by a student in Bhitirawat, Sahjanwa, Gorakhpur for their 2017-2018 CBSE physics practical exam. The project explores and explains the basic principle and functioning of electrical transformers.
Introduction



IntroductionLovely Professional University The transformer is a static electrical device that transfers energy through inductive coupling between its winding circuits. It converts alternating voltages from low to high levels or vice versa. Transformers range greatly in size and are used in applications from microphones to power stations. They operate on basic principles to transfer electrical energy between circuits without moving parts. Transformers that increase voltage are called step-up transformers, while those that decrease voltage are step-down transformers.
Efficiency and energy losses



Efficiency and energy lossesLovely Professional University The efficiency of an ideal transformer is 100% because there are no power losses, but actual transformers have efficiencies less than 100% due to various power loss mechanisms. These power losses include: 1) magnetic flux not being perfectly coupled between coils, 2) eddy currents induced in the iron core causing heat loss, 3) heat loss from resistance in the coil windings, 4) energy loss from hysteresis in the iron core during alternating magnetization, and 5) possible vibration and sound from the magnetic field that represents lost energy.
Contents



ContentsLovely Professional University This document provides an overview of the key topics covered in a guide about transformers, including sections on the apparatus, principle and construction, theory and working, efficiency and energy losses, and uses of transformers. It also includes an introduction, bibliography, and index.
Certificate



CertificateLovely Professional University This certificate certifies that Vishwajeet Singh from St. Xavier's School completed a project titled "Transformer" for his 2017-2018 Physics practical examination under the guidance of Mr. Ankur Tripathi. The teacher in charge confirms that Vishwajeet completed the project with his own effort and guidance from the teacher, and it is being submitted to the Central Board of Secondary Education for evaluation.
Bibliography



BibliographyLovely Professional University This document is a bibliography listing 5 sources used for a physics practical or text book. It includes a comprehensive physics practical manual for class 12, an NCERT physics textbook, the online encyclopedia Wikipedia, the digital library Scribd, and the presentation sharing website Slideshare.
Acknowledgement



AcknowledgementLovely Professional University The student thanks his teacher, Mr. Ankur Tripathi, and school management for guiding and advising him to complete his project on the principles and workings of transformers, which taught him new things. He also thanks God for blessings that helped him finish. Finally, he thanks his parents and friends for their help, encouragement, and support in completing the project within the limited time frame.
Principle construction



Principle constructionLovely Professional University A transformer works on the principle of mutual induction where a varying current in one circuit induces an electromotive force (emf) in a neighboring circuit. It consists of two coils wound on a rectangular iron core, with the primary coil connected to an alternating current source and the secondary coil connected to a load through a switch. The varying magnetic flux produced by the primary current induces an emf in the secondary coil to power the load.
Theory and procedure



Theory and procedureLovely Professional University Foods naturally deteriorate over time due to temperature, enzymes, and microbes which can be inhibited by potassium bisulfite. The effectiveness of potassium bisulfite as a preservative depends on its concentration under different conditions. Potassium bisulfite is a white powdered food additive that prevents bacterial, mold, and yeast growth and food discoloration by being dissolved in water. An experiment was described to make fruit jam and study the effects of sugar concentration, potassium bisulfite concentration, temperature, and time on food preservation.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Data Structures_Introduction to algorithms.pptx



Data Structures_Introduction to algorithms.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 Concept of Problem Solving, Introduction to Algorithms, Characteristics of Algorithms, Introduction to Data Structure, Data Structure Classification (Linear and Non-linear, Static and Dynamic, Persistent and Ephemeral data structures), Time complexity and Space complexity, Asymptotic Notation - The Big-O, Omega and Theta notation, Algorithmic upper bounds, lower bounds, Best, Worst and Average case analysis of an Algorithm, Abstract Data Types (ADT)
Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...



Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering In tube drawing process, a tube is pulled out through a die and a plug to reduce its diameter and thickness as per the requirement. Dimensional accuracy of cold drawn tubes plays a vital role in the further quality of end products and controlling rejection in manufacturing processes of these end products. Springback phenomenon is the elastic strain recovery after removal of forming loads, causes geometrical inaccuracies in drawn tubes. Further, this leads to difficulty in achieving close dimensional tolerances. In the present work springback of EN 8 D tube material is studied for various cold drawing parameters. The process parameters in this work include die semi-angle, land width and drawing speed. The experimentation is done using Taguchi’s L36 orthogonal array, and then optimization is done in data analysis software Minitab 17. The results of ANOVA shows that 15 degrees die semi-angle,5 mm land width and 6 m/min drawing speed yields least springback. Furthermore, optimization algorithms named Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Simulated Annealing (SA) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) are applied which shows that 15 degrees die semi-angle, 10 mm land width and 8 m/min drawing speed results in minimal springback with almost 10.5 % improvement. Finally, the results of experimentation are validated with Finite Element Analysis technique using ANSYS.
Value Stream Mapping Worskshops for Intelligent Continuous Security



Value Stream Mapping Worskshops for Intelligent Continuous SecurityMarc Hornbeek This presentation provides detailed guidance and tools for conducting Current State and Future State Value Stream Mapping workshops for Intelligent Continuous Security.
Fort night presentation new0903 pdf.pdf.



Fort night presentation new0903 pdf.pdf.anuragmk56 This is the document of fortnight review progress meeting
RICS Membership-(The Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors).pdf



RICS Membership-(The Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors).pdfMohamedAbdelkader115 Glad to be one of only 14 members inside Kuwait to hold this credential.
Please check the members inside kuwait from this link:
https://www.rics.org/networking/find-a-member.html?firstname=&lastname=&town=&country=Kuwait&member_grade=(AssocRICS)&expert_witness=&accrediation=&page=1
AI-assisted Software Testing (3-hours tutorial)



AI-assisted Software Testing (3-hours tutorial)Vəhid Gəruslu Invited tutorial at the Istanbul Software Testing Conference (ISTC) 2025 https://iststc.com/
fluke dealers in bangalore..............



fluke dealers in bangalore..............Haresh Vaswani The Fluke 925 is a vane anemometer, a handheld device designed to measure wind speed, air flow (volume), and temperature. It features a separate sensor and display unit, allowing greater flexibility and ease of use in tight or hard-to-reach spaces. The Fluke 925 is particularly suitable for HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) maintenance in both residential and commercial buildings, offering a durable and cost-effective solution for routine airflow diagnostics.
some basics electrical and electronics knowledge



some basics electrical and electronics knowledgenguyentrungdo88 This chapter discribe about common electrical divices such as passive component, the internaltional system unit and international system prefixes.
Avnet Silica's PCIM 2025 Highlights Flyer



Avnet Silica's PCIM 2025 Highlights FlyerWillDavies22 See what you can expect to find on Avnet Silica's stand at PCIM 2025.
π0.5: a Vision-Language-Action Model with Open-World Generalization



π0.5: a Vision-Language-Action Model with Open-World GeneralizationNABLAS株式会社 今回の資料「Transfusion / π0 / π0.5」は、画像・言語・アクションを統合するロボット基盤モデルについて紹介しています。
拡散×自己回帰を融合したTransformerをベースに、π0.5ではオープンワールドでの推論・計画も可能に。
This presentation introduces robot foundation models that integrate vision, language, and action.
Built on a Transformer combining diffusion and autoregression, π0.5 enables reasoning and planning in open-world settings.
Lidar for Autonomous Driving, LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars.pptx



Lidar for Autonomous Driving, LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars.pptxRishavKumar530754 LiDAR-Based System for Autonomous Cars
Autonomous Driving with LiDAR Tech
LiDAR Integration in Self-Driving Cars
Self-Driving Vehicles Using LiDAR
LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars
railway wheels, descaling after reheating and before forging



railway wheels, descaling after reheating and before forgingJavad Kadkhodapour railway wheels, descaling after reheating and before forging
IntroSlides-April-BuildWithAI-VertexAI.pdf



IntroSlides-April-BuildWithAI-VertexAI.pdfLuiz Carneiro ☁️ GDG Cloud Munich: Build With AI Workshop - Introduction to Vertex AI! ☁️
Join us for an exciting #BuildWithAi workshop on the 28th of April, 2025 at the Google Office in Munich!
Dive into the world of AI with our "Introduction to Vertex AI" session, presented by Google Cloud expert Randy Gupta.
Introduction to FLUID MECHANICS & KINEMATICS



Introduction to FLUID MECHANICS & KINEMATICSnarayanaswamygdas Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. Originally applied to water (hydromechanics), it found applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical, and biomedical engineering, as well as geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology.
It can be divided into fluid statics, the study of various fluids at rest, and fluid dynamics.
Fluid statics, also known as hydrostatics, is the study of fluids at rest, specifically when there's no relative motion between fluid particles. It focuses on the conditions under which fluids are in stable equilibrium and doesn't involve fluid motion.
Fluid kinematics is the branch of fluid mechanics that focuses on describing and analyzing the motion of fluids, such as liquids and gases, without considering the forces that cause the motion. It deals with the geometrical and temporal aspects of fluid flow, including velocity and acceleration. Fluid dynamics, on the other hand, considers the forces acting on the fluid.
Fluid dynamics is the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion. It is a branch of continuum mechanics, a subject which models matter without using the information that it is made out of atoms; that is, it models matter from a macroscopic viewpoint rather than from microscopic.
Fluid mechanics, especially fluid dynamics, is an active field of research, typically mathematically complex. Many problems are partly or wholly unsolved and are best addressed by numerical methods, typically using computers. A modern discipline, called computational fluid dynamics (CFD), is devoted to this approach. Particle image velocimetry, an experimental method for visualizing and analyzing fluid flow, also takes advantage of the highly visual nature of fluid flow.
Fundamentally, every fluid mechanical system is assumed to obey the basic laws :
Conservation of mass
Conservation of energy
Conservation of momentum
The continuum assumption
For example, the assumption that mass is conserved means that for any fixed control volume (for example, a spherical volume)—enclosed by a control surface—the rate of change of the mass contained in that volume is equal to the rate at which mass is passing through the surface from outside to inside, minus the rate at which mass is passing from inside to outside. This can be expressed as an equation in integral form over the control volume.
The continuum assumption is an idealization of continuum mechanics under which fluids can be treated as continuous, even though, on a microscopic scale, they are composed of molecules. Under the continuum assumption, macroscopic (observed/measurable) properties such as density, pressure, temperature, and bulk velocity are taken to be well-defined at "infinitesimal" volume elements—small in comparison to the characteristic length scale of the system, but large in comparison to molecular length scale
Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...



Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering
Constructors and destructors in C++ part 2
- 2. Constructors A special member function having same name as that of its class which is used to initialize some valid values to the member variables.
- 3. Key points while defining constructor A constructor has same name as that of the class to which it belongs. A constructor is executed automatically whenever the object is created A constructor doesn`t have a return type, not even void We can declare more than one constructor in a class. These constructor differ in there parameter list. If you don’t provide a constructor of your own then the compiler generates a default constructor (expects no parameters and has an empty body). A constructor can preferably be used for initialization and not for inputoutput operations.
- 4. • They can’t be inherited; through a derived class, can call the base class constructor. • Like other C++ functions, they can have default arguments. • Constructors can’t be virtual. • Constructors can be inside the class definition or outside the class definition. • Constructor can’t be friend function. • They can’t be used in union.
- 5. Contd.. • Constructor should be declared in the public section of the class. If it is not declared in public section of the class then the whole class become private . By doing this the object of the class created from outside cannot invoke the constructor which is the first member function to be executed automatically.
- 7. Example #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class Rectangle { private: int length,breadth; public: Rectangle() { length=5,breadth=6; } void area() { int a=(length*breadth); cout<<"area is"<<a; } }; void main() { clrscr(); Rectangle r1; r1.area(); getch(); }
- 8. TYPES OF CONSTRUCTOR • 1.Default Constructor • 2.Parameterized Constructor • 3.Copy Constructor
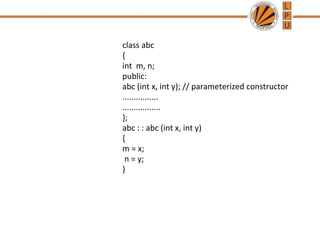
- 9. Parameterized Constructor In order to initialize various data elements of different objects with different values when they are created. C++ permits us to achieve this objects by passing argument to the constructor function when the object are created . The constructor that can take arguments are called parameterized constructors
- 10. class abc { int m, n; public: abc (int x, int y); // parameterized constructor ................ ................. }; abc : : abc (int x, int y) { m = x; n = y; }
- 11. Parameterized constructor #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class Rectangle { private: int length,breadth; public: Rectangle(int a,int b) { length=a; breadth=b; } void area() { int a=(length*breadth); cout<<"area is="<<a; } }; void main() { Rectangle r1(5,6); Rectangle r2(7,8); clrscr(); r1.area();cout<<endl; r2.area(); getch(); }
- 12. Copy constructor • A constructor is a constructor that creates a new object using an existing object of the same class • and initializes each data member of newly created object with corresponding data member of existing object passed as argumnt. • since it creates a copy of an existing object so it is called copy constructor.
- 13. Example class counter { Int c; public: Counter(int a) //single parameter constructor { c=a; } counter(counter &ob) //copy constructor { cout<<“copy constructor invoked”; c=ob.c; } }
- 14. void show() { cout<<c; } }; void main() { clrscr(); counter C1(10); counter C2(C1);// call copy constructor C1.show(); C2.show(); getch(); }
- 15. Another example of copy constructor #include<iostream> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; class Point { private: int x, y; public: Point(int x1, int y1) { x = x1; y = y1; }
- 16. // Copy constructor Point(const Point &p2) { x = p2.x; y = p2.y; } int getX() { return x; } int getY() { return y; } };
- 17. int main() { Point p1(10, 15); // Normal constructor is called here Point p2 = p1; // Copy constructor is called here // Let us access values assigned by constructors cout << "p1.x = " << p1.getX() << ", p1.y = " << p1.getY(); cout << "np2.x = " << p2.getX() << ", p2.y = " << p2.getY(); return 0; }
- 18. class code { int id; public: code() { } code(int a) { id = a; } code (code & x) { id = x. id; } void display() { cout<<id; } }; int main() { code A(100); code B(A); code C = A; code D; D = A; A.display(); B.display(); C.display(); D.display(); getch(); return 0; }
- 19. Destructors Is a member function having same name as that of constructor but it is preceded by a tilde(~) symbol and is executed automatically when object of a class is destroyed
- 20. Key points while defining destructor • A destructor has same name as that of the class to which it belongs preceded by tilde(~)sign. • A destructor is executed automatically whenever the object is destroyed. • A destructor doesn`t have a return type, not even void and no arguments • There is only one destructor in class . • If you don’t provide a destructor of your own then the compiler generates a default destructor • A destructor can be used to deallocate memory for an object and declared in the public section.
- 21. Need for Destructors • To de-initialize the objects when they are destroyed • To clear memory space occupied by a data member.
- 23. Note • Execute the program in Turbo c++. • To see the output, press Alt+F5
- 24. Program on destructor Class sample { Public: Sample { Cout<<“object born”<<endl; }
- 26. int main() { sample s; Cout<<“main terminated”<<endl; getch(); return 0; }
- 27. Example #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class counter { int id; public: counter(int i) { id=i; cout<<“contructor of object with id=”<<id;
- 28. ~counter() { cout<<“destructor with id=”<<id; } }; void main() { counter c1(1); counter c2(2); counter c3(3); cout<<“n end of main”; getch(); }
- 29. • Output constructor of object with id=1 constructor of object with id=2 constructor of object with id=3 End of main destructor with id=3 destructor with id=2 destructor with id=1 Note ::Destructor Always deallocate memory in reverse order.
- 30. 1 Statically allocated object for class A in C++ is A *obj = new A(); A obj; A obj = new A(); None
- 31. When you create an object of a class A like A obj ; then which one will be called automatically A Constructor B Destructor C Copy constructor D Assignment operator
- 32. 3 Data members and member functions of a class in C++ program are by default protected public private None
- 33. 4 Which operator is used to allocate an object dynamically of a class in C++? Scope resolution operator Conditional operator New operator Membership access
- 34. The static member functions __________________ a) Have access to all the members of a class b) Have access to only constant members of a class c.) Have access to only the static members of a class d) Have direct access to all other class members also
- 35. The static member functions ____________________ a.) Can be called using class name b) Can be called using program name c) Can be called directly d) Can’t be called outside the function
- 36. Which among the following is true? a) Static member functions can be overloaded b.) Static member functions can’t be overloaded c) Static member functions can be overloaded using derived classes d) Static member functions are implicitly overloaded
- 37. Which keyword should be used to declare the static member functions? a.) static b) stat c) const d) common
- 38. Assume class TEST. Which of the following statements is/are responsible to invoke copy constructor? a. TEST T2(T1) b. TEST T4 = T1 c. T2 = T1 D). both a and b
- 39. Which of the following statements are not true about destructor? 1. It is invoked when object goes out of the scope 2. Like constructor, it can also have parameters 3. It can be virtual 4. It can be declared in private section 5. It bears same name as that of the class and precedes Lambda sign. a. Only 2, 3, 5 b. Only 2, 3, 4 c). Only 2, 4, 5 d. Only 3, 4, 5
- 40. A Constructor that does not have any parameters is called____________ Constructor. a. Custom b. Dynamic c. Static d). Default
- 41. Which of the followings are true about constructors? 1. A class can have more than one constructor. 2. They can be inherited. 3. Their address can be referred. 4. Constructors cannot be declared in protected section of the class. 5. Constructors cannot return values. a. Only 1,2,4 b. 1,2,4,5 c. 1,3,5 d.) 1,4,5
- 42. In a program, If there exists a function template with two parameters and normal function say void add(int , int), so add(3,4) will _____________________ . a. Invoke function template body as it is generic one b.) Invokes normal function as it exactly matches with its prototype c. Not be called and Compiler issues warning d. Not be called and Compiler issues ambiguity in calling add()









